Page 9 of 118

WARNING!
•Do not start or run an engine in a closed garage or
confined area. Exhaust gas contains Carbon Mon-
oxide (CO) which is odorless and colorless. Carbon
Monoxide is poisonous and can cause serious in-
jury or death when inhaled.
• Keep Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitters
away from children. Operation of the Remote Start
System, windows, door locks or other controls
could cause serious injury or death.
ENGINE BREAK-IN RECOMMENDATIONS
The diesel engine does not require a break-in period due
to its construction. Normal operation is allowed, provid-
ing the following recommendations are followed:
• Warm up the engine before placing it under load.
•
Do not operate the engine at idle for prolonged periods.
• Use the appropriate transmission gear to prevent
engine lugging.
•
Observe vehicle oil pressure and temperature indicators.
• Check the coolant and oil levels frequently.
• Vary throttle position at highway speeds when carry-
ing or towing significant weight.
NOTE: Light duty operation such as light trailer towing
or no load operation will extend the time before the
engine is at full efficiency. Reduced fuel economy and
power may be seen at this time.
The engine oil installed in the engine at the factory is a
high-quality energy conserving type lubricant. Oil changes
should be consistent with anticipated climate conditions
under which vehicle operations will occur. The recom-
mended viscosity and quality grades are shown under
“Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts”, under “Maintain-
ing Your Vehicle” in this manual. NON-DETERGENT OR
STRAIGHT MINERAL OILS MUST NEVER BE USED.
2
THINGS TO KNOW BEFORE STARTING YOUR VEHICLE 7
Page 15 of 118

the ON/RUN position before engine start. If the bulb
does not come on when turning the key from OFF to
ON/RUN, have the condition checked promptly.
Certain conditions, poor fuel quality, etc., may illuminate
the light after engine start. The vehicle should be serviced
if the light stays on through several of your typical
driving cycles. In most situations, the vehicle will drive
normally and will not require towing.
CAUTION!
Prolonged driving with the Malfunction Indicator
Light (MIL) on could cause damage to the engine
control system. It also could affect fuel economy and
driveability. If the MIL is flashing, severe catalytic
converter damage and power loss will soon occur.
Immediate service is required.
WARNING!
A malfunctioning catalytic converter, as referenced
above, can reach higher temperatures than in normal
operating conditions. This can cause a fire if you
drive slowly or park over flammable substances such
as dry plants, wood, cardboard, etc. This could result
in death or serious injury to the driver, occupants or
others.
11. Parking Brake Indicator
This light indicates the parking brake is engaged.
3
UNDERSTANDING YOUR INSTRUMENT PANEL 13
Page 16 of 118

12. Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge shows engine coolant tempera-
ture. Any reading within the normal range indicates that
the engine cooling system is operating satisfactorily.
The gauge pointer will likely indicate a higher tempera-
ture when driving in hot weather, up mountain grades,
or when towing a trailer. It should not be allowed to
exceed the upper limits of the normal operating range.
CAUTION!
Driving with a hot engine cooling system could
damage your vehicle. If the temperature gauge reads
“H” pull over and stop the vehicle. Idle the vehicle
with the air conditioner turned off until the pointer
drops back into the normal range. If the pointer
(Continued)
CAUTION!(Continued)
remains on the “H” and you hear continuous chimes,
turn the engine off immediately and call an autho-
rized dealer for service.
WARNING!
A hot engine cooling system is dangerous. You or
others could be badly burned by steam or boiling
coolant. You may want to call an authorized dealer
for service if your vehicle overheats. If you decide to
look under the hood yourself, see “Maintaining Your
Vehicle”. Follow the warnings under the Cooling
System Pressure Cap paragraph.
14 UNDERSTANDING YOUR INSTRUMENT PANEL
Page 35 of 118
STARTING AND OPERATING
CONTENTS
�STARTING PROCEDURES .................35
▫ Automatic Transmission .................36
▫ Extreme Cold Weather ...................36
▫ Normal Starting Procedure —
Keyless Enter-N-Go™ ...................37
▫ Starting Fluids ........................38
� NORMAL OPERATION ...................39
▫ Cold Weather Precautions ................39
▫ Engine Idling .........................40 ▫
Stopping The Engine ....................41
▫ Cooling System Tips —
Automatic Transmission ..................42
� ENGINE BLOCK HEATER — IF EQUIPPED ....43
� FUEL REQUIREMENTS ...................44
▫ Fuel Specifications .....................45
▫ Biodiesel Fuel Requirements ...............46
� TRAILER TOWING ......................49
▫ Common Towing Definitions ..............49
4
Page 36 of 118
▫Trailer Hitch Classification ...............52
▫ Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum Trailer
Weight Ratings) .......................53
▫ Trailer And Tongue Weight ...............54
▫ Towing Requirements ...................55
▫ Towing Tips ..........................60
� DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID .................62
▫ System Overview ......................62 �
ADDING FUEL .........................63
▫ Avoid Using Contaminated Fuel ............66
▫ Bulk Fuel Storage — Diesel Fuel ...........66
▫ Diesel Exhaust Fluid Storage ..............67
▫ Adding Diesel Exhaust Fluid ..............68
34 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 51 of 118

TRAILER TOWING
In this section you will find safety tips and information
on limits to the type of towing you can reasonably do
with your vehicle. Before towing a trailer, carefully
review this information to tow your load as efficiently
and safely as possible.
To maintain the New Vehicle Limited Warranty coverage,
follow the requirements and recommendations in this
manual concerning vehicles used for trailer towing.
Common Towing Definitions
The following trailer towing related definitions will assist
you in understanding the following information:
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
The GVWR is the total allowable weight of your vehicle.
This includes driver, passengers, cargo and tongue
weight. The total load must be limited so that you do notexceed the GVWR. Refer to “Vehicle Loading/Vehicle
Certification Label” in “Starting and Operating” for
further information.
Gross Trailer Weight (GTW)
The GTW is the weight of the trailer plus the weight of all
cargo, consumables and equipment (permanent or tem-
porary) loaded in or on the trailer in its
�loaded and
ready for operation� condition.
The recommended way to measure GTW is to put your
fully loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The entire weight
of the trailer must be supported by the scale.
WARNING!
If the gross trailer weight is 3,500 lbs (1 587 kg) or
more, it is mandatory to use a weight-distributing
hitch to ensure stable handling of your vehicle. If you
(Continued)
4
STARTING AND OPERATING 49
Page 53 of 118

Trailer Sway Control
The trailer sway control can be a mechanical telescoping
link that can be installed between the hitch receiver and
the trailer tongue that typically provides adjustable fric-
tion associated with the telescoping motion to dampen
any unwanted trailer swaying motions while traveling.
If equipped, the electronic Trailer Sway Control (TSC)
recognizes a swaying trailer and automatically applies
individual wheel brakes and/or reduces engine power to
attempt to eliminate the trailer sway.
Weight-Carrying Hitch
A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue
weight, just as if it were luggage located at a hitch ball or
some other connecting point of the vehicle. These kinds
of hitches are the most popular on the market today and
they are commonly used to tow small and medium sized
trailers.
Weight-Distributing Hitch
A weight-distributing system works by applying lever-
age through spring (load) bars. They are typically used
for heavier loads to distribute trailer tongue weight to the
tow vehicle’s front axle and the trailer axle(s). When used
in accordance with the manufacturer’s directions, it pro-
vides for a more level ride, offering more consistent
steering and brake control thereby enhancing towing
safety. The addition of a friction/hydraulic sway control
also dampens sway caused by traffic and crosswinds and
contributes positively to tow vehicle and trailer stability.
Trailer sway control and a weight distributing (load
equalizing) hitch are recommended for heavier Tongue
Weights (TW) and may be required depending on vehicle
and trailer configuration/loading to comply with Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) requirements.
4
STARTING AND OPERATING 51
Page 54 of 118
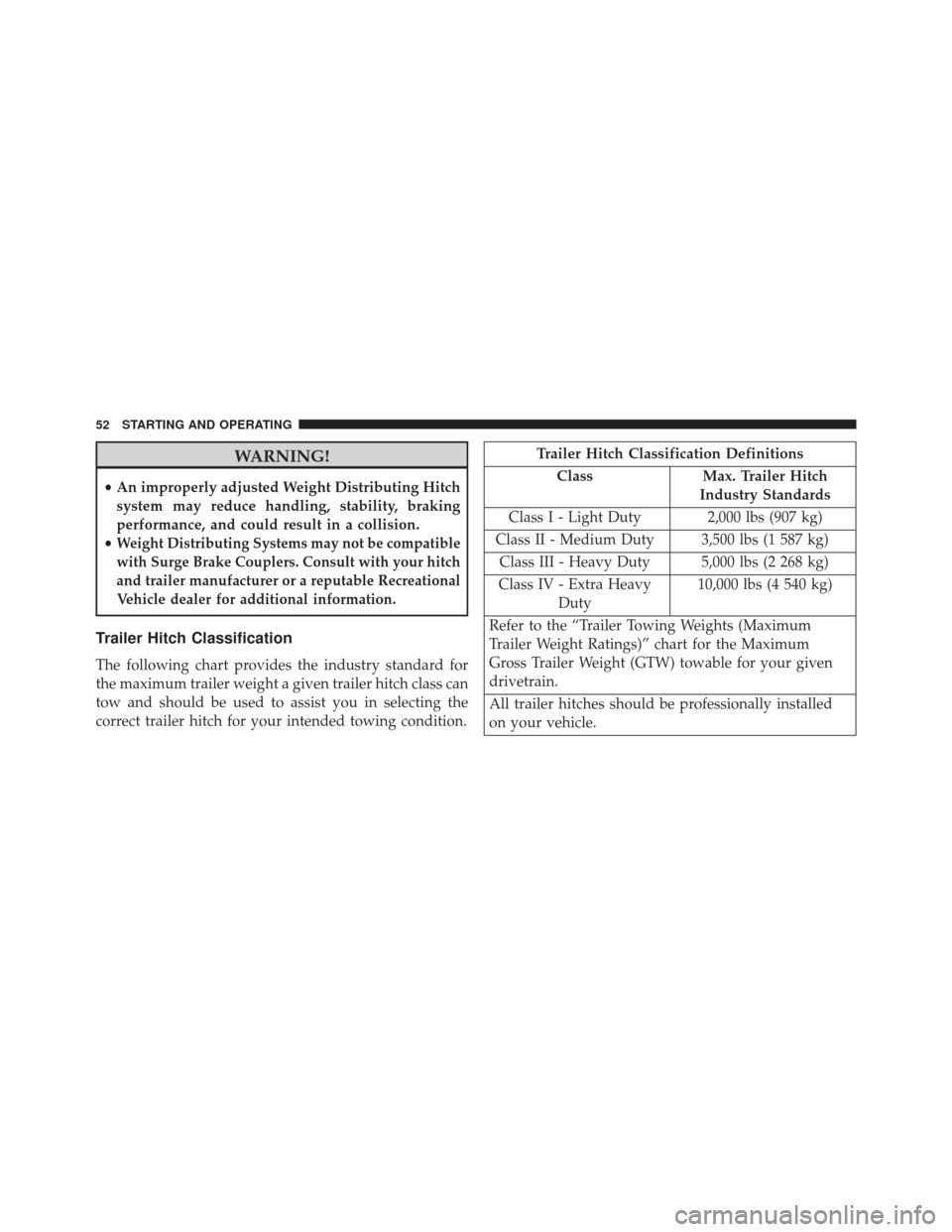
WARNING!
•An improperly adjusted Weight Distributing Hitch
system may reduce handling, stability, braking
performance, and could result in a collision.
•
Weight Distributing Systems may not be compatible
with Surge Brake Couplers. Consult with your hitch
and trailer manufacturer or a reputable Recreational
Vehicle dealer for additional information.
Trailer Hitch Classification
The following chart provides the industry standard for
the maximum trailer weight a given trailer hitch class can
tow and should be used to assist you in selecting the
correct trailer hitch for your intended towing condition.
Trailer Hitch Classification Definitions
Class Max. Trailer Hitch
Industry Standards
Class I - Light Duty 2,000 lbs (907 kg)
Class II - Medium Duty 3,500 lbs (1 587 kg) Class III - Heavy Duty 5,000 lbs (2 268 kg)
Class IV - Extra Heavy Duty 10,000 lbs (4 540 kg)
Refer to the “Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum
Trailer Weight Ratings)” chart for the Maximum
Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) towable for your given
drivetrain.
All trailer hitches should be professionally installed
on your vehicle.
52 STARTING AND OPERATING