2014 AUDI Q7 wheel size
[x] Cancel search: wheel sizePage 190 of 340

188 Airbag system
conditions is impossible in all conceiva
ble situations that may happen during
the useful life of your vehicle.
- The Advanced Airbag System can deploy
in accordance with the "low risk" option
under the U.S. Federal Standard if a child
that is heavier than the typical one-year
old child is on the front passenger seat
and the other conditions for airbag de
ployment are met.
-Accident statistics have shown that chil
dren are generally safer in the rear seat
area than in the front seating position.
- For their own safety, all children, espe
cially 12 years and younger, should al
ways ride in the back properly restrained
for their age and size.
Advanced front airbag system
Your vehicle is equipped with a front Advanced
Airbag System in compliance with United
States Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
208 as applicable at the time your vehicle was
manufactured.
The front Advanced Airbag System supple ments the safety belts to provide additional
protection for the driver's and front passeng
er's heads and upper bodies in frontal crashes .
The airbags inflate only in frontal impacts
when the vehicle deceleration is high enough.
The front Advanced Airbag System for the
front seat occupants is not a substitute for
your safety belts. Rather, it is part of the over
all occupant restraint system in your vehicle.
Always remember that the airbag system can
only help to protect you, if you are sitting up
right , wearing your safety belt and wearing it
properly. This is why you and your passengers
must always be properly restrained, not just
because the law requires you to be.
The Advanced Airbag System in your vehicle has been certified to meet the "low risk" re
quirements for 3 and 6 year-old children on
the passenger side and very small adults on
the driver side. The low risk deployment crite
ria are intended to help reduce the risk of in- jury through interaction with the front airbag
that can occur, for example, by being too close to the steering wheel and instrument
panel when the airbag inflates.
In addition, the system has been certified to
comply with the "suppression" requirements
of the Safety Standard, to turn off the front
airbag for infants 12 months old and younger
who are restrained on the front passenger
seat in child restraints that are listed in the Standard
~ page 206, Child restraints and
Advanced Airbags .
"Suppression" requires the front airbag on the
passenger side to be turned off if:
- a child up to about one year of age is re
strained on the front passenger seat in one
of the rear-facing or forward-facing infant
restraints listed in Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard 208 with which the Ad
vanced Airbag System in your vehicle was
certified. For a listing of the child restraints
that were used to certify your vehicle's com
pliance with the US Safety Standard
~page 206,
-weight less than a threshold level stored in
the control unit is detected on the front pas
senger seat.
When a person is detected on the front pas senger seat, weighing more than the total
weight of a child that is about 1 year old re
strained in one of the rear-facing or forward
facing infant restraints (listed in Federal Mo
tor Vehicle Safety Standard 208 with which
the Advanced Airbag System in your vehicle
was certified), the front airbag on the passen ger side may or may not deploy.
The
PASSENGER AIR BAG OFF light comes on
when the electronic control unit detects a to
tal weight on the front passenger seat that re quires the front airbag to be turned off. If the
PASSENGER AIR BAG OFF light does not
come on, the front airbag on the passenger
side has not been turned off by the control
unit and can deploy if the control unit senses
an impact that meets the conditions stored in
its memory.
ll-
Page 207 of 340

-Always install rear-facing child safety
seats on the rear seat.
- If you must install a rearward facing
child safety seat on the front passenger
seat in exceptional circumstances and
the
PASSENGER AIR BAG OFF light does
not come on and stay on, immediately
install the rear-facing child safety seat in
a rear seating position and have the air
bag system inspected immediately by
your Audi dealer.
_& WARNING
If, in exceptional circumstances, you must
install a forward-facing child restraint on
the front passenger's seat:
- Always make sure the forward-facing
seat has been designed and certified by its manufacturer for use on a front seat
with a passenger front and side airbag.
- Always follow the manufacturer's in
structions provided with the child safety
seat or carrier.
- Always move the passenger seat into its
rearmost position in the seat's fore and
aft adjustment range, as far away from
the airbag as possible before installing
the child restraint. The backrest must be
adjusted to an upright position .
- Always make sure that the
PASSENGER
AIR BAG OFF
light comes on and stays
on all the time whenever the ignition is
switched on.
(D Tips
Always replace child restraints that were
installed in a vehicle during a crash. Dam
age to a child restraint that is not visible
could cause it to fail in another collision
situation.
Advanced front airbag system and children
Your vehicle is equipped with an "Advanced
Airbag System" in compliance with United
States Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
Child Safety 205
(FMVSS) 208 as applicable at the time your
vehicle was manufactured.
The Advanced Airbag system in your vehicle
has been certified to meet the "low-risk" re
quirements for 3- and 6-year old children on
the passenger side and small adults on the driver side. The low risk deployment criteria
are intended to reduce the risk of injury
through interaction with the airbag that can
occur, for example, by being too close to the
steering wheel and instrument panel when
the airbag inflates . In addition, the system
has been certified to comply with the "sup
pression" requirements of the Safety Stand
ard, to turn off the front airbag for infants up
to 12 months who are restrained on the front
passenger seat in child restraints that are list
ed in the Standard.
Even though your vehicle is equipped with an
Advanced Airbag system, all children, espe cially those 12 years and younger, should al
ways ride in the back seat properly restrained
for their age and size. The airbag on the pas
senger side makes the front seat a potentially dangerous place for a child to ride . The front
seat is not the safest place for a child in a for
ward-facing child safety seat. It can be a very
dangerous place for an infant or a larger child
in a rearward-facing seat .
Advanced Airbags and the weight
sensing mat in the front seat
The Advanced Airbag System in your vehicle
detects the presence of an infant or child in a
child restraint on the front passenger seat us
ing the weight -sensing mat in the seat cush
ion and the sensor below the safety belt latch
on the front passenger seat that measures the
tension on the safety belt.
The weight -sensing mat measures total
weight of the child and the child safety seat
and a child blanket on the front passenger seat. The weight on the front passenger seat
is related to the design of the child restraint
and its "footprint", the size and shape of the
bottom of the child restraint as it sits on the ..,.
•
•
Page 227 of 340

A WARNING 1-=
-ESC, ABS, ASR and EDL cannot overcome
the laws of physics. This is espec ially im
portant on slippery or wet roads. If the
systems begin act ing to stab ilize your ve
hicle, you should immediately change
your speed to match the road and traffic conditions. Do not let the increased sa fe
ty provided by these systems tempt you
to take r isks. Doing so will increase the
risk of a loss of vehicle control, collision
and ser ious persona l injuries.
- Always adapt your speed to road, traffic
and weather conditions. The risk of los
ing control of the vehicle increases when
dr iv ing too fast, especially through
curves and on slippery or wet roads, and
w hen driving too close to vehicles up
ahead. ESC, ABS, the b rake assist sys
tem, ASR and EDL cannot prevent co lli
sions.
Switching on/off --- -
Intellig ent technolog y 225
-Always accelerate with special care on
even, smooth surfaces such as those that
are wet or covered with ice and snow.
The drive wheels can spin even with
these assistance systems that cannot al
ways he lp to reduce the risk of loss of ve
hicle control.
@ Tips
- ABS and ASR only work correctly when
all four wheels are equipped with identi
cal tires. D iffe rent tire sizes can lead to a
reduction in engine powe r.
- Yo u may hear noises when the systems
descr ibed are working.
- If the ind icator light
DJ or ~ (USA
mode ls)/ ii] (Canada models) appears,
there may be a malfunction~
page 16,
¢page 18.
•
•
ESC turns on automatically when you start the engine .
. ...---------.,
--------------
Fig. 230 Upper center conso le : ~ O FF button
The fo llow ing situations are exceptions where
it may be useful to switch on offroad mode to
allow the whee ls to spin: -
Rocking the vehicle to free it when it is stuck
- Dr iving in deep snow or on loose ground
- Driving with snow chains
- Dr iving on roug h terrain when much of the
car's weight is lifted off the whee ls (ax le ar
ticu lation)
- Dr iving downhi ll wh ile braking on loose
ground
Page 231 of 340

Replacing wh eels/ tire s
Vehicles w ith all-wheel drive must a lways
have tires of the same size. Also avoid tires
with different tread depths. For details see
page ¢
page 284, New tires and replacing
tires and wheels .
.&_ WARNING
Always adjust your driving to road and traf
fic conditions . Do not let the extra safety
afforded by all-wheel dr ive tempt you into
tak ing extra risks.
-Although the all-wheel dr ive is very ef
fective, always remember that braking
capacity is limited by t ire traction . You
sho uld therefore not dr ive at excessive
speeds on icy or s lippery road surfaces.
- On wet road su rfaces, be careful not to
dr ive too fast because t he front wheels
cou ld beg in to s lide on top of the wa ter
(aquaplaning). If this sho uld occ ur, you
w ill have no warning from a sudden in
crease in engine speed as with a front
whee l drive vehicle. A lways drive at
speeds wh ich are suited to the road con
ditions -risk of c rash.
Energy management
Starting ability is optimized
Energy management controls the distribution
of electrical energy and thus optimizes the
availability of electrical energy for starting
the engine.
I f a vehicle w it h a conventional energy system
i s not driven for a long pe riod of time, the bat
tery is disch arged by idling c urrent cons umers
(e .g. immobilizer) . In ce rtain c ircumstances it
can result in there being insufficient energy
ava ilab le to start the engine .
I n tell igen t energy management in your vehi
cle hand les the d istribution of electrical ener
gy . Starting abi lity is marked ly imp roved and
the life of the battery is extended.
Int ellig ent technolog y 229
Basica lly, energy management consis ts of
batte ry diagnosi s, idling cur rent manage
ment
and dynamic energy management.
Battery diagnosis
B attery diagnosis continuously de termines
the state of the battery . Sensors determine
batte ry voltage, battery current and battery
temperature . This determines the current
state of charge and the power of the battery.
Idling current management
Id lin g cur ren t man agement reduces energy
consumption while the vehi cle is standing.
With the ig nition switched off, it controls the
energy supply to the various electrical compo nents. Data from battery diagnos is is cons id
ered.
Depend ing on the battery's state of cha rge,
individual cons umers are gradually turned off
to prevent excessive discharge of the battery
and thus maintain starting capability.
Dynamic energy manag ement
While the vehicle is being driven, dynamic en
ergy management distrib utes the energy ge n
erated according to the needs of the individ u
al components. It regulates consumption, so
that more electrical energy is not being used
than is be ing generated and ensures an opti
mal state of charge for the battery .
(D Tips
-But even e nergy management cannot
negate the limits of physics. Consider
t hat the powe r and l ife of a bat tery are
l imited.
- If start ing ability is threatened, you are
informed by a warning ¢
page 230,
Driver notification in the instrument
cluster display.
•
•
Page 277 of 340

Groove
means the space between two adjacent tread
ribs.
Load rating (code)
means the maximum load that a tire is rated
to carry for a given inflation pressure. You
may not find this information on all tires be
cause it is no t req uired by law.
Maximum load rating
means the load rating for a t ire at the max i
mum permissible inflation pressure for that
tire.
Maximum loaded vehicle weight
means the sum of:
(a) Curb weight
(b) Accessory weight
(c) Vehicle capacity weight, and
(d) Production options weight
Maximum (permissible) inflation pressure
means the maximum cold inflation pressure
to which a tire may be inflated. Also called "maximum inflation pressure."
Normal occupant weight
means 150 lbs. (68 kilograms) times the
number of occupants seated in the vehicle up
to the total seating capacity of your vehicle.
Occupant distribution
means distribution of occupants in a vehicle.
Outer diameter
means the overa ll diamete r of an inflated new
tire.
Overall width
means the linear distance between the exteri
ors of the sidewalls of an inflated tire, includ
in g elevations due to labeling, decorations, or
protective bands or ribs.
Ply
means a layer of rubber-coated parallel cords.
Tires and wheels 275
Production options weight
means the combined weight of those installed
regular production options we ighing over 5
lbs. (2.3 kg) in excess of those standard items
which they replace, not previously considered
in curb weight or accessory weight, including
heavy duty brakes, ride levelers, roof rack,
heavy duty battery, and spec ial tr im .
Radial ply tire
means a pneumatic tire in which the ply cords
that extend to the beads are laid at substan
tia lly 90 degrees to the center line of the
tread .
Recommended inflation pressure
see ¢ page 2 7 4, Cold tire inflation pressure.
Reinforced tire
means a t ire design to operate at higher loads
and at h igher inflation pressures than the cor
re sp onding standard tire. Reinforced tires
may be identified as "XL", "xl", "EXTRA LOAD",
or "RF" on the sidewa ll.
Rim
means a metal support for a tire or a t ire and
tube assembly upon which the tire beads are
seated.
Rim diameter
means nom inal diameter of the bead seat. If
you change your wheel s ize, you will have to
purchase new tires to match the new rim di
ameter.
Rim size designation
means r im diameter and width .
Rim width
means nominal distance between rim flanges .
Sidewall
means that portion of a tire between the
tread and bead.
•
•
Page 279 of 340

Tires and wheels 277
Occupant loading and distribution for vehicle normal load fo r various d esignated seat ing
capaci tie s
Designated seating capacity , Vehicle normal load , number Occupant distribution in a nor-
number of occupants of occupants mally loaded vehicle
5/6*/7" 3 2 in front, 1 in second seat
Cold tire inflation pressure
Tire pressure affects the overall handling, performance and safety of a vehicle.
I
JJ
0
Fig. 249 Tire pressure labe l: located on driver 's s ide B·
p ill ar
Tire pressure genera lly refers to the amount
of air in a tire that it needs it to do its job and
safely carry the combined load of the entire
vehicle and its contents . Tire pressure is
measured in kilopasca ls (kPa), the i nte rna
tional measur ing unit and in pounds pe r
squa re i nch (PSI). Tire pressure is based in
part on the vehicle 's design and load limi t -
the greatest amount of weight that the vehi cle can carry safe ly and the t ire size . The prop
er tire pressure is frequent ly referred to as the
"recommended cold tire inflation pressure."
A ir in the tires expands when the tire heats up
because of internal friction when it flexes in
use . The tire p ressu re is higher when the tire
has warmed up than when it is "cold ."
It is the
i nflat ion p ressure i n a "cold " tire that counts.
Therefo re, you shou ld neve r let air out of a
warm tire to ma tch "cold tire infla tion pres
sure" recommendations. The t ires wo uld then
be underinflated and could fail suddenly .
M aintaining p roper t ire press ure is one of the
most impor tant things you can do to he lp
avoid sudden tire failure. Underinflated t ires
are a ma jo r cause of s udden tire failure . Keep·
ing tires at the right pressure is also impor
tant for safe and responsive vehicle handling,
-tD
-
---------------------.. ,;
•(==.: I :::; I :,,. I)@ gi n. ............ .,_____, .... -.ito._.. ____ .... _ ...
&..p0idit,101111-~--.,...,....-- ..... ~ .... ..
-··-.....
-
-Dlst<:OURS
- KPA.. a PSI
- KPA..
a PS I
- KPA.. a PSI
Fig. 2 50 Tire pressu re labe l
traction, braking and load carrying. Tire p res
sures are particularly importa nt when the
vehicle is being dr iven at higher speeds, and
th en e spe cially when heav ily load ed even
with in the permissible load-carrying capaci
ties approved for your veh icle.
The recommended tire pressures for your Audi
depend on the kind of tires on your ve hicle
and the n umbe r of passengers and/o r amount
of luggage you w ill be transporti ng.
The tire pressure label is located on the driv
er's side B -pillar . The tire pressure labe l lists
the recommended cold t ire inflat io n pressures
for t he vehicle at its maxi mum capac ity
weight and tires that were on your veh icle at
t he time it was m anufactu red.
If you wish to improve comfort wh en operat
ing the vehicle at normal load (up to 3 occu
pant s), you can adju st tire press ures to those
spe cified for n ormal vehi cle load . Before op
erating the vehicle at maximum load , you
must increase the tire pre ssure s to those
specified for ma ximum vehicle load
¢ & .
Bear in mind that the tire pressure mon itor ing
system can only monitor the tire pressures
II>
Page 280 of 340
278 Tires and wheels
you have stored. The system does not recog
nize the load condition of your vehicle.
The effectiveness of the tire pressure monitor
ing system w ill be impaired if yo u store nor
mal load pressures but then operate the vehi
cle at its maximum load¢.&. .
See the illustration¢
fig. 249 for the location
of the label on driver's side 8-pillar (color of
the actua l label and exact location on the ve
hicle wi ll vary slightly).
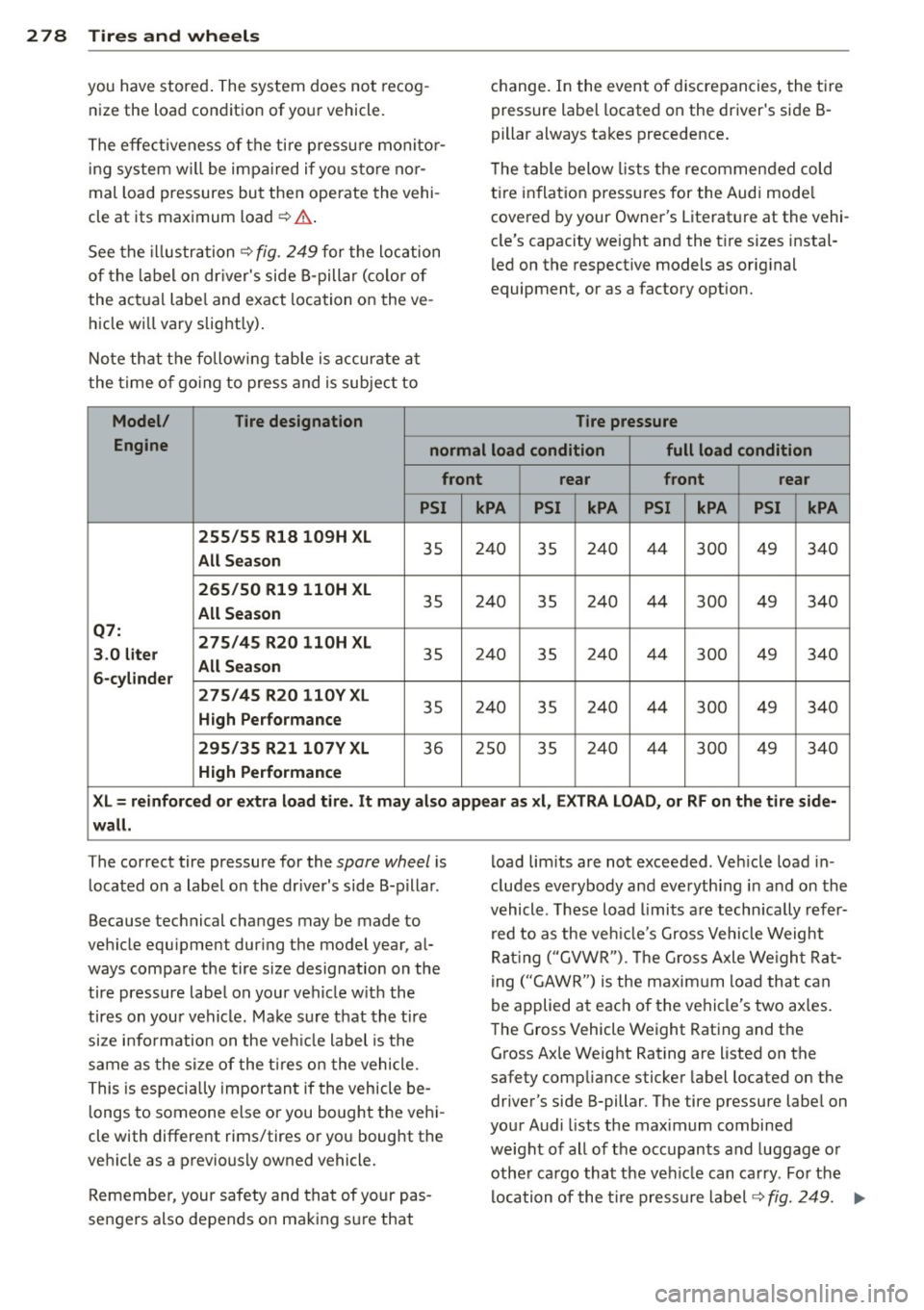
Note that the following table is accurate at
the time of going to press and is subject to
Model/ Tire designation
change. In the event of discrepancies, the tir e
pressure label located on the driver's side 8-
pillar always takes precedence.
T he table below lists the recommended cold
ti re inflation pressures for the Audi mode l
covered by your Owner's Literature at the vehi
cle's capacity weight and the t ire sizes instal
l ed on the respective models as original
equipment, or as a factory option.
Tire pressure
Engine normal load condition full load condition
front rear
front rear
PSI kPA PSI kPA PSI kPA PSI kPA
255/55 Rl8 109H XL
35 240 35 240 44
300 49 340 All Season
265/50 Rl9 llOH XL
35 240
35 240
44
300 49 340 All Season
Q7: 275/45 R20 llOH XL
3 .0 liter
35 240
35 240 44
300 49 340 All Season
6-cylinder
275/45 R20 llOYXL
35 240 35 240 44 300 49 340 High Performance
295/35 R21 107V XL
36 250 35 240 44 300 49 340
High Performance
XL= reinforced or extra load tire. It may also appear as xl, EXTRA LOAD, or RF on the tire side-
wall.
The correct tire pressure for the spare wheel is
located on a label on the driver's side 8-p illar .
Because technical changes may be made to
vehicle equipment dur ing the model year, al
ways compare the tire size designation on the
tire pressure label on your vehicle w ith the
tires on your vehicle. Make sure that the tire
size info rmation on the vehicle label is the
same as the size of the tires on the vehicle.
This is especially important if the vehicle be
l ongs to someone else or you bought the vehi
cle with different rims/tires or you bought the
vehicle as a previously owned vehicle.
Remember, your safety and that of yo ur pas
sengers also depends on making s ure that load
limits are not exceeded . Veh icle load in
cludes everybody and eve ryth ing in and on the
vehicle. These load limits are techn ica lly refer
red to as the veh icle's Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating ("GVWR"). The Gross Axle We ight Rat
ing ("GAWR") is the maximum load that can
be applied at each of the vehicle's two ax les.
The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating and the Gross Axle Weight Rating are listed on the
safety comp liance sticker label located on the
driver's side 8-pillar . The tire pressure label on
your Audi lists the maximum combined
weight of all of the occupants and luggage or
other cargo that the veh icle can carry . For the
location of the tire pressure label¢
fig. 249. ..,_
Page 286 of 340

284 Tires and wheels
All-wheel drive
Vehicles with quattro must always have tires
of the same size , construction and tread type.
For details see Qpage 228.
~ WARNING
Sudden tire failure can lead to loss of con
trol, a crash and serious persona l injury!
- Never drive a vehicle when the tread on
any tire is worn down to the wear indica
tors.
- Worn tires are a safety hazard, they do
not grip well on wet roads and increase
your risk of "hydroplaning" and loss of
control.
- Always keep chemicals that can cause
tire damage , such as grease, oil, gasoline
and brake fluid away from tires .
- Tires age even if they are not being used
and can fail suddenly, especially at high
speeds. Tires that are more than 6 years
old can only be used in an emergency
and then with special care and at lower
speeds.
- Never mount used tires on your vehicle if
you a re not sure of their "previous histo
ry." Old used tires may have been dam
aged even though the damage cannot be
seen that can lead to sudden tire failure
and loss of vehicle control.
New tires and replacing tires and wheels
New tires and wheels have to be broken in .
Fig. 253 Tir e specificat ion c odes on t he s idewall o f a
t ire
No. Description
® Ratio of height to width (aspect ratio)
© Radial
® Rim diameter code
® Load index and speed rating
(J) U.S. DOT tire identification number
® Audi Original tire
® Sever snow conditions
@ Tire ply composition and materials
used
@ Maximum load rat ing
@ Treadwear, traction and temperature
grades
@ Maximum permissible inflation pres-
sure
T he tires and rims are essential parts of the
vehicle 's design . The tires and rims approved
by Audi are spec ially matched to the charac
teristics of the vehicle and can make a major .,..