Page 624 of 796
07-94411-01
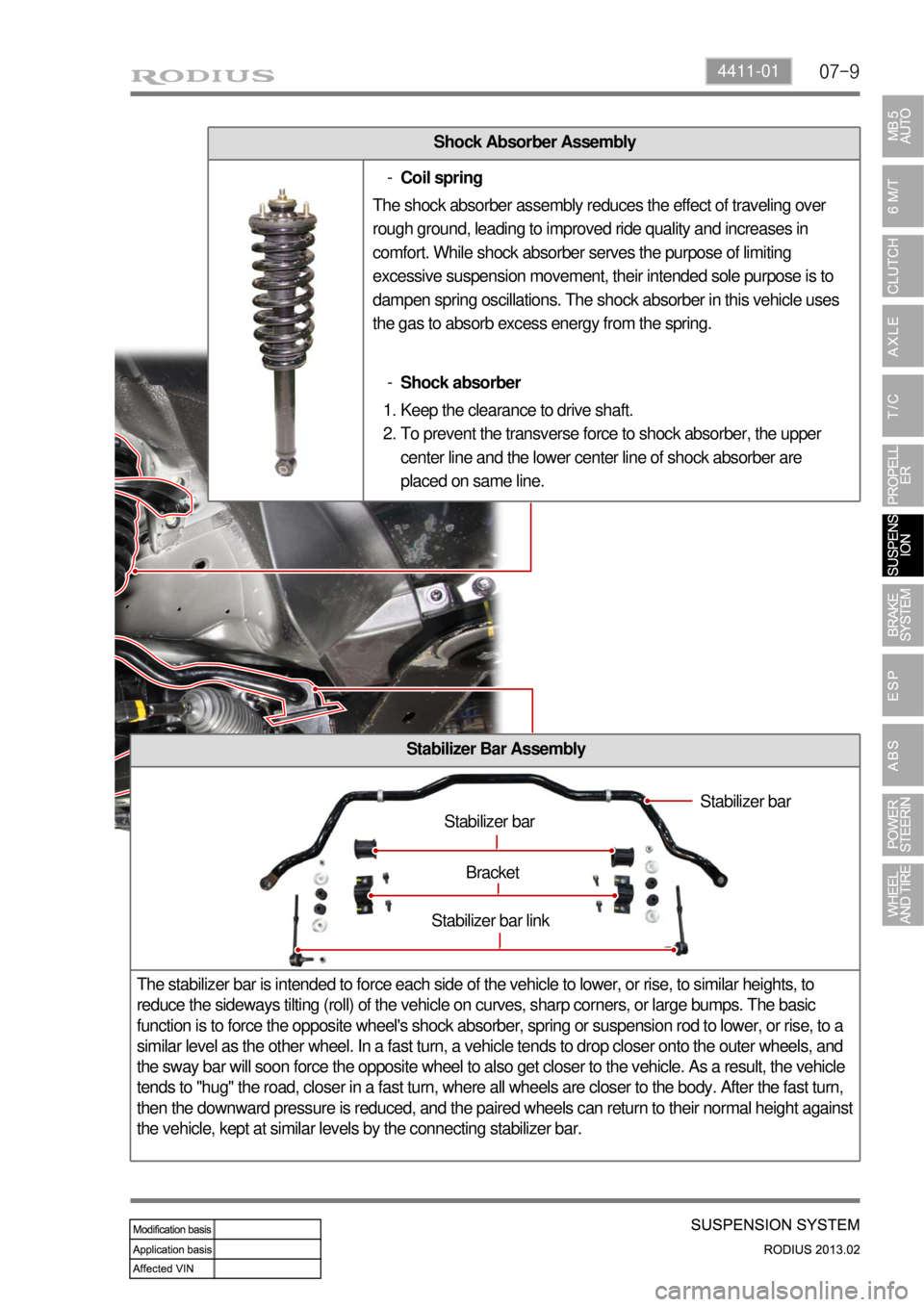
Shock Absorber Assembly
Stabilizer Bar Assembly
The stabilizer bar is intended to force each side of the vehicle to lower, or rise, to similar heights, to
reduce the sideways tilting (roll) of the vehicle on curves, sharp corners, or large bumps. The basic
function is to force the opposite wheel's shock absorber, spring or suspension rod to lower, or rise, to a
similar level as the other wheel. In a fast turn, a vehicle tends to drop closer onto the outer wheels, and
the sway bar will soon force the opposite wheel to also get closer to the vehicle. As a result, the vehicle
tends to "hug" the road, closer in a fast turn, where all wheels are closer to the body. After the fast turn,
then the downward pressure is reduced, and the paired wheels can return to their normal height against
the vehicle, kept at similar levels by the connecting stabilizer bar.
Stabilizer bar
Stabilizer bar
Bracket
Stabilizer bar link
Coil spring -
The shock absorber assembly reduces the effect of traveling over
rough ground, leading to improved ride quality and increases in
comfort. While shock absorber serves the purpose of limiting
excessive suspension movement, their intended sole purpose is to
dampen spring oscillations. The shock absorber in this vehicle uses
the gas to absorb excess energy from the spring.
Shock absorber -
Keep the clearance to drive shaft.
To prevent the transverse force to shock absorber, the upper
center line and the lower center line of shock absorber are
placed on same line. 1.
2.
Page 629 of 796

07-14
3) Caster
The angle between the vertical line and king pin, which fixes the steering knuckle and front axle,
(steering column which connects the top and bottom ball joints in the independent axle type) when
viewed the tires from the side.
CasterFront4.80˚±0.50˚
Rear -
Disadvantages:Impact from the road is transferred to the steering wheel (steering wheel turns)
Poor straightness -
- Advantages:Directional force to go straight (following control)
Restoring force of the wheel (restored to the straight ahead direction)
Prevention of wheel shimmy (wheels wobble left and right) -
-
-
Negative caster: ▶Top of the king pin is tilted forward from the vertical line of the wheel center
when viewed the tires from the side Positive caster: ▶
With considering the height difference between the wheel centers of the front and rear
wheels. (Under standard condition that the vehicle is on a level ground) Caster: ▶
Advantages:Smaller turning radius -Top of the king pin is tilted backward from the vertical line of the wheel center
when viewed the tires from the side
Page 639 of 796
08-12
Let the engine run for 1 to 2 minutes and
stop it. If the brake pedal stroke is shortened
as pumping the brake pedal, the system is
normal. If not, the system is defective. 1.
Depress the brake pedal several times with
engine off. If the brake goes down when
starting engine with pedal depressed, the
system is normal. If not, the system is
defective. 2.
If the above three checks are OK, the system is
normal. If any condition is not met, check the
valve, vacuum hose and brake booster.
3) Brake Booster
OK
NG
Engine stopped
Engine running
Depress the brake pedal when the engine is
running. If the pedal height is not changed
for 30 seconds after stopping the engine, the
system is normal. If not, the system is
defective. 3.
Page 701 of 796
12-6
2) Tire Unit Indication
Aspect ratio (%)
= Nominal section height (H) / Nominal section
width (W)
X 100
3) Tire Inflation Pressure (35 psi)
Proper inflation pressure Excessive inflation pressure Low inflation pressure
The contact area between the
ground and tire faces the tread
layer completely. Thus the driving
force and the braking force are
optimized, and the tire is worn out
evenly resulting in increased life.The contact area between the
ground and tire is not enough,
so the tire is worn out unevenly
and the tire is vulnerability to
outside influence.The contact area between the
ground and tire is excessive, so
a lot of heat is generated and
the tire is worn out unevenly
and abnormally.
Tread widthTread widthTread width
Page 745 of 796
03-6
Seat warmer switch
Sliding adjust lever
Back flat adjust lever
1. LAYOUT AND COMPONENTS
1) Components of Seat
Seat Control Switch (Driver's Seat)
Seat position control Seat height control Reclining control
Back supporter
(Driver’s seat)
Sliding control
Page 757 of 796
03-18
Headrest Height Adjustment
To adjust the height of the headrest, raise
the headrest without operating the
headrest support sleeve (A) and lower it
while pressing the headrest support
sleeve.
(However, raise the headrest while
pressing the headrest support sleeve (A)
in order to remove it.)
4. FRONT SEAT
1) To Adjust Front Seat
While the driver seat is provided as two models: a power seat and a manual seat, the manual seat is
only used for front passenger seat.
To adjust headrest ▶
To adjust headrest tilting
Move the headrest to the arrow direction
to adjust the angle.
Page 759 of 796
03-20
Power Seat
To adjust seat cushion angle
When moving the front and rear parts of the
slide switch upwards or downwards, the front
and rear up/down motors rotate the rails to
move the front and rear side of the cushion
up/down.
To adjust seat height
When moving the slide switch up/down,
the front rear up/down motor rotates the rail to
move the whole seat cushion up/down.Manual Seat
To adjust seat cushion angle and
height
Turn the adjusting knob on the side of the seat
clockwise or anticlockwise to adjust the height
or angle of the front side or rear side of the
cushion.
To adjust driver seat lumbar support
When you raise and lower the adjusting lever
on the power and manual seats, the lumbar
support goes in and out of the seat.
The lumbar support is only fitted to the vehicle without the seat air bag.
Page 762 of 796
03-237410-01
Seat cushion height adjustment
Seat moves up/down
controlled by seat height
control switch
Seatback reclining
Seat back reclining controlled
by seat reclining control switch