Page 546 of 751
08-94411-01
Under View (4WD, Automatic Transmission)
Rear suspension
1. SUSPENSION
The suspension is the device to connect the axle and vehicle. It absorbs the vibrations and impacts from
road surface, which enhances the comforts, driving force, braking force and drivability.
Front suspension
Page 553 of 751
09-4
2. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) Terms and Definition
CBS: Conventional Brake System
ABS: Anti-Lock Brake System
EBD: Electronic brake-Force Distribution
ESP: Electronic Stability Program
ABD: Automatic Braking Differential
ASR: Acceleration Slip Regulation
AYC: Active Yaw Control (Understeer and Oversteer Control)
HBA: Hydraulic Brake Assistant
ARP: Active Rollover Protection
HSA: Hill Start Assistant
Brake pad: Brake pad is a component of disk brakes used in automotive and other applications.
Brake pad is steel backing plates with friction material bound to the surface that faces the brake disc.
Brake disc: The brake disc is a device for slowing or stopping the rotation of a wheel while it is in
motion.
Brake caliper: To stop the wheel, friction material in the form of brake pads (mounted on a device
called a brake caliper) is forced hydraulically against both sides of the disc. Friction causes the disc
and attached wheel to slow or stop.
Brake master cylinder: The brake master cylinder is a control device that converts non-hydraulic
pressure (commonly from a driver's foot) into hydraulic pressure, in order to move other device(s)
which are located at the other end of the hydraulic system, such as one or more slave cylinders. As
piston(s) move along the bore of the master cylinder, this movement is transferred through the
hydraulic fluid, to result in a movement of the slave cylinder(s). The hydraulic pressure created by
moving a piston (inside the bore of the master cylinder) toward the slave cylinder(s) compresses the
fluid evenly, but by varying the comparative surface-area of the master cylinder and/or each slave
cylinder, one will vary the amount of force and displacement applied to each slave cylinder (relative to
the amount of force and displacement that was applied to the master cylinder). -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
FunctionVehicle with CBS
Vehicle with ABS/EBD Vehicle with ESP
ABS
Not appliedApplied
Applied EBD Applied
ABD
Not applied ASR
AYC
HBA
ARP
2) Functions
Page 559 of 751

09-10
This section describes the noise phenomena occurred possibly in the brake system operation.
Distinguish between the information given below and the actual problems and then, inspect the vehicle
and take appropriate measures.
Noise symptoms and Causes -
Symptom 1. If depressing the brake pedal when the engine is cold, "screeching" sound always
occurs and, after driving for a while, the sound disappears..
This usually occurs in the morning. When the temperature goes down, the dew condensation
phenomenon sets moisture on the brake disc as the window frost forms. Due to this moisture, the iron
within the brake disc and pad oxidizes, forming undetectable micro-rusts on the disc surface. When
starting the engine under this condition, noise may sound due to the friction of micro-rusts. When
operating the brake several times, the disc temperature goes up and the micro-rusts come off and the
noise goes away. Depending on the driving conditions, noise gets louder when slightly depressing the
brake pedal and oppositely, noise is smaller when deeply depressing the brake pedal. This is simply a
physical phenomenon, called "morning effect" in professional terms, and does not imply any problems
with the brake system.
Symptom 2. Slip or screech after the brake pad replacement.
This usually occurs when the bed-in is not made between the disc and the pad's friction material. The
bed-in is a state that the brake system normally works and gives no noise out, when, after about 300 km
city driving, the contact area of the pad friction material is enlarged and the disk is in complete contact
with the pad's friction material. Therefore, for some time after the brake disk/pad replacement, the brake
system poorly operates or noise (abnormal sound) occurs due to the partial contact.
Symptom 3. "Groaning" sound occurs in the automatic transmission vehicle when slightly taking the foot
off the brake pedal to slowly start after waiting for the signal, or slightly depressing the brake pedal.
This is the noise "Creep groan" that occurs when, in both the automatic and manual transmission,
slightly releasing the brake pedal in the neutral gear at downhill roads.
It frequently occurs at the low braking power and low speed, through the following process. When
operating the brake system at low speed and low pressure, adhesion and slip repeatedly take place
between the brake disk and the friction material, and this makes the braking power inconstant, instantly
increasing or decreasing, and gives out the brake noise.
It is also a physical phenomenon and has no relation with the brake performance.BRAKE OPERATION AND NOISE ▶
Page 655 of 751
13-54620-01
1. OVERVIEW
The speed-sensitive power-assisted steering system can automatically adjust the boosts according to
the speed changes, automatically induct the high-speed or low-speed status, and relatively adjust the
reasonable steering boosts, enhance the operation precision, reduce the driving pressure of drivers. No
matter for steering, parking or reversing, it becomes much easier. The adjustable safety steering column
attached possesses the functions of electrically adjusting height and transverse position, has brought
much more abundant and comfortable spaces for legs, and has provided the great convenience to get in
or out the car.
The Speed Sensitive Power Steering (SSPS) unit controls the SSPS solenoid vale in steering gear box
to get proper power steering force.
Page 679 of 751
14-18
4. WHEEL ALIGNMENT
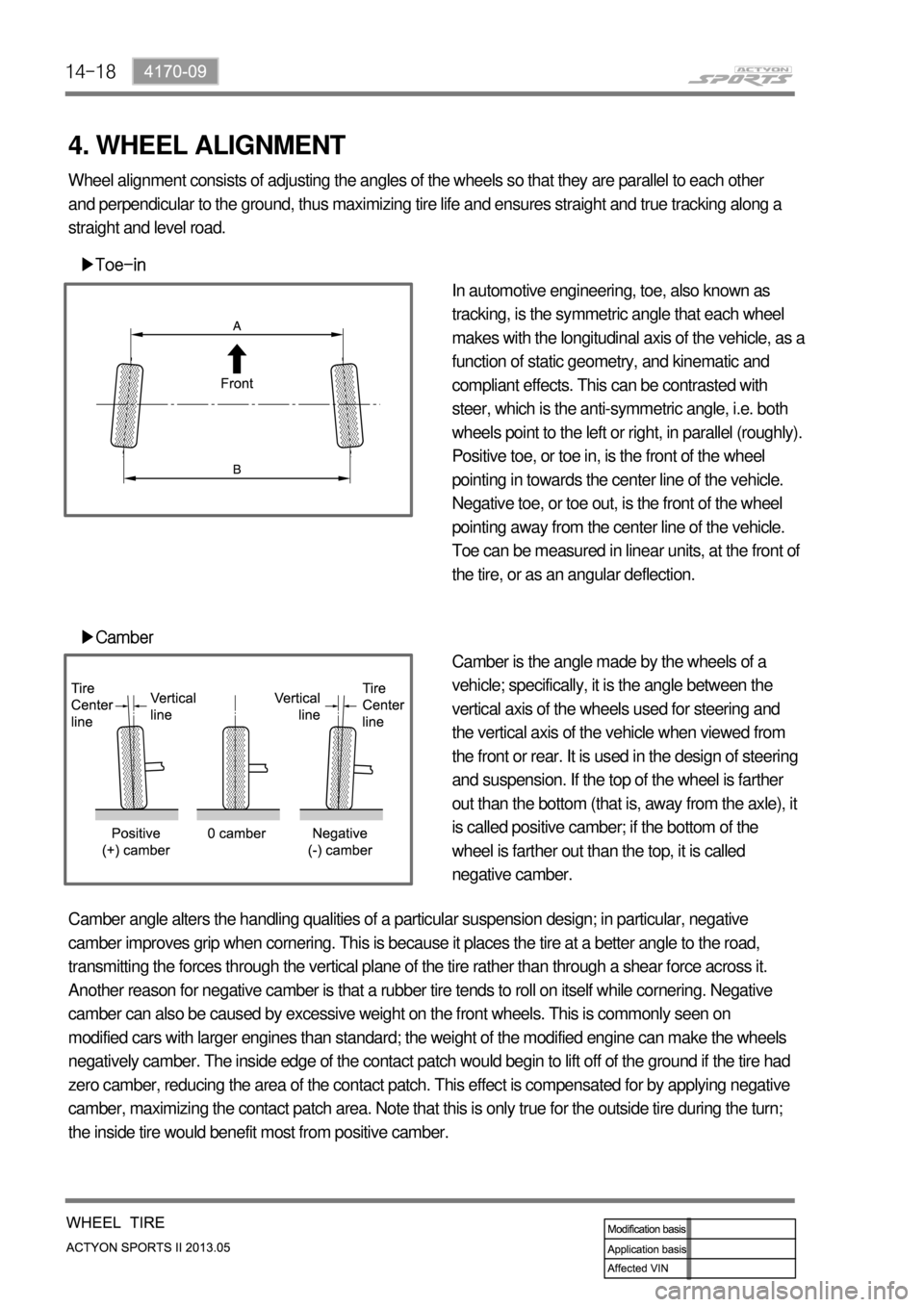
▶Toe-in
▶Camber
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as
tracking, is the symmetric angle that each wheel
makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a
function of static geometry, and kinematic and
compliant effects. This can be contrasted with
steer, which is the anti-symmetric angle, i.e. both
wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly).
Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel
pointing in towards the center line of the vehicle.
Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel
pointing away from the center line of the vehicle.
Toe can be measured in linear units, at the front of
the tire, or as an angular deflection.
Camber is the angle made by the wheels of a
vehicle; specifically, it is the angle between the
vertical axis of the wheels used for steering and
the vertical axis of the vehicle when viewed from
the front or rear. It is used in the design of steering
and suspension. If the top of the wheel is farther
out than the bottom (that is, away from the axle), it
is called positive camber; if the bottom of the
wheel is farther out than the top, it is called
negative camber. Wheel alignment consists of adjusting the angles of the wheels so that they are parallel to each other
and perpendicular to the ground, thus maximizing tire life and ensures straight and true tracking along a
straight and level road.
Camber angle alters the handling qualities of a particular suspension design; in particular, negative
camber improves grip when cornering. This is because it places the tire at a better angle to the road,
transmitting the forces through the vertical plane of the tire rather than through a shear force across it.
Another reason for negative camber is that a rubber tire tends to roll on itself while cornering. Negative
camber can also be caused by excessive weight on the front wheels. This is commonly seen on
modified cars with larger engines than standard; the weight of the modified engine can make the wheels
negatively camber. The inside edge of the contact patch would begin to lift off of the ground if the tire had
zero camber, reducing the area of the contact patch. This effect is compensated for by applying negative
camber, maximizing the contact patch area. Note that this is only true for the outside tire during the turn;
the inside tire would benefit most from positive camber.