Page 877 of 1336
Horn (high) Horn (low)
Theft deterrent horn
Theft deterrent horn
4) Horn Switch
Two horns are installed in the radiator grille at the bottom of both sides (one on each side). There is
another horn installed at the bottom of the battery tray side in the engine compartment for theft alarm.
Operating the horn switch on the steering wheel applies the power to the horn relay to operate both
horns (Dual horn). The theft deterrent horn is controlled by the BCM in armed mode regardless of the
horn relay operation.
Horn (dual horn)
Horn switch
Page 984 of 1336
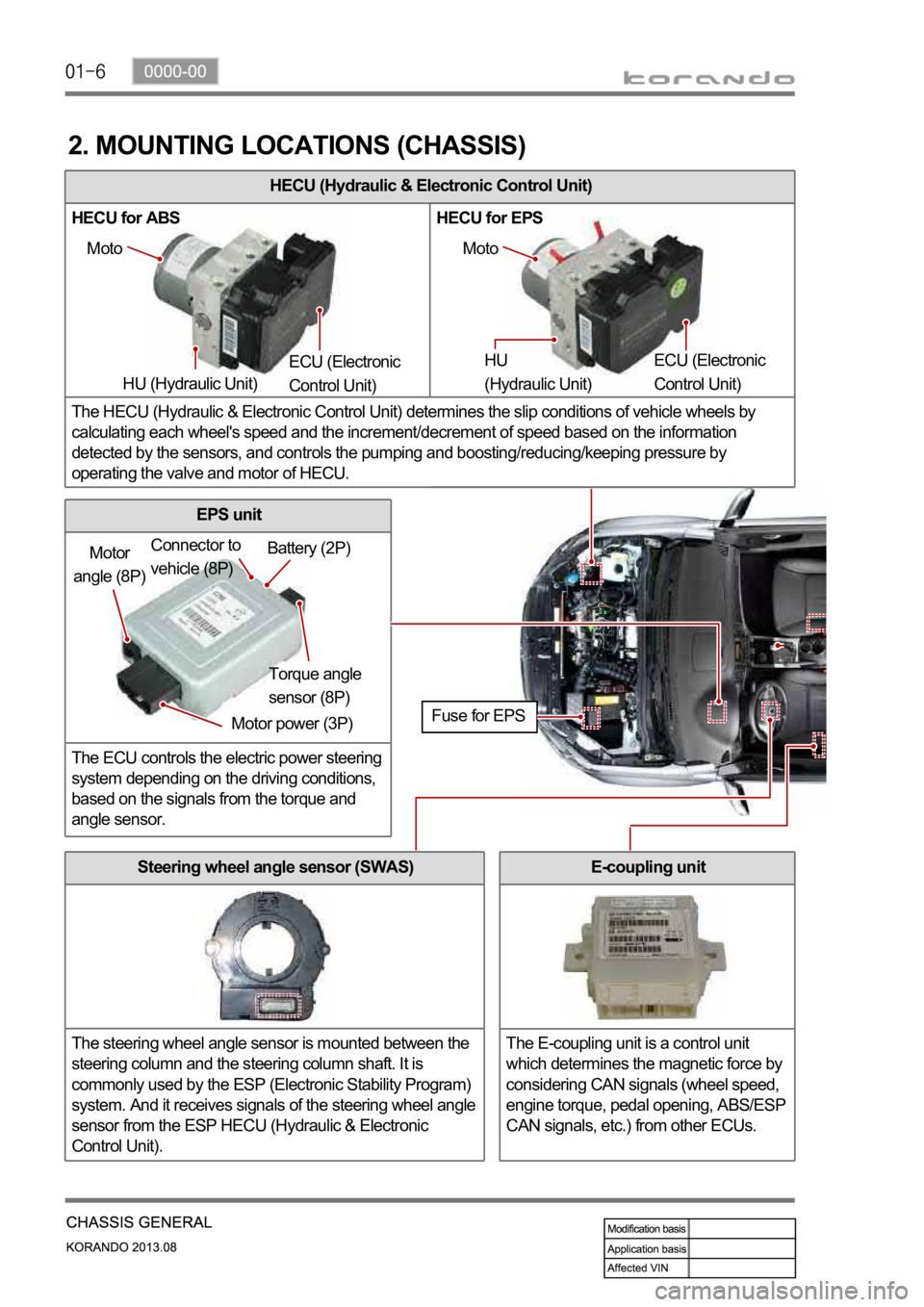
HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic Control Unit)
HECU for ABS HECU for EPS
The HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic Control Unit) determines the slip conditions of vehicle wheels by
calculating each wheel's speed and the increment/decrement of speed based on the information
detected by the sensors, and controls the pumping and boosting/reducing/keeping pressure by
operating the valve and motor of HECU.
2. MOUNTING LOCATIONS (CHASSIS)
Moto
HU (Hydraulic Unit) ECU (Electronic
Control Unit) Moto
HU
(Hydraulic Unit) ECU (Electronic
Control Unit)
Motor
angle (8P)
Motor power (3P)Torque angle
sensor (8P) Battery (2P) Connector to
vehicle (8P)
Fuse for EPS
Steering wheel angle sensor (SWAS)
The steering wheel angle sensor is mounted between the
steering column and the steering column shaft. It is
commonly used by the ESP (Electronic Stability Program)
system. And it receives signals of the steering wheel angle
sensor from the ESP HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic
Control Unit).
EPS unit
The ECU controls the electric power steering
system depending on the driving conditions,
based on the signals from the torque and
angle sensor.
E-coupling unit
The E-coupling unit is a control unit
which determines the magnetic force by
considering CAN signals (wheel speed,
engine torque, pedal opening, ABS/ESP
CAN signals, etc.) from other ECUs.
Page 985 of 1336

0000-00
TPMS ECU
The TPMS ECU is located to the rear bumper rail
under the vehicle. It outputs the tire pressure and
cluster, based on the wheel module information
and CAN data.
G-sensor(4WD, ABS)
For the vehicle with the ABS, a speed difference
between the wheels is not noticeable as all the wheels
are slipping during abrupt braking. Therefore, the
vehicle needs the speed information from other sensors
other than the wheel speed sensor. The longitudinal
acceleration sensor (G-sensor) is used for this case. It
controls the ABS by using the signals from the sensor
during abrupt braking and acceleration.
TCU unit
The transmission control unit (TCU) is installed
under the driver seat, and controls the
transmission. The TCU is operated by the ignition
power supply and receives and processes the
following information from the inner sensors
through CAN buses.
TGS Lever assembly
The TGS communicates with TCU
(Transmission Control Unit), ECU,
ESP HECU and instrument cluster
to let the driver select the desired
transmission gear and to maintain
the desired driving condition. Also,
the tip switch is installed on the
lever knob and the steering wheel
so that the driver select the gear
manually when the shift lever is in
"M".Sensor cluster
The sensor cluster is linked to
the sensors on the unit board
and CAN interface. And they
are housed in one case and
mounted to the body.
Page 988 of 1336
Front sub frame with HPS type steering gear box assembly
The front sub frame consists of 4 body bush mountings and 2 transmission
bush mountings which reduce the vibration from the powertrain and road,
and also control the torque. And the frame is equipped with hydraulic
pressure pipe of the HPS type steering gear box.
4. SUB FRAME AND STEERING GEAR BOX LAYOUT
Front sub frame with EPS type steering gear box assembly
This kind of front sub frame system has the same mounting structure with
the frame with HPS. But the EPS type steering gear box has no hydraulic
pressure pipe since it is driven by the electric motor.
Rear side
Front sideHPS type steering
gear box assembly
Front sub frame
assembly
Rear side
Front side
EPS type steering
gear box assembly
Front sub frame
assembly
Page 996 of 1336
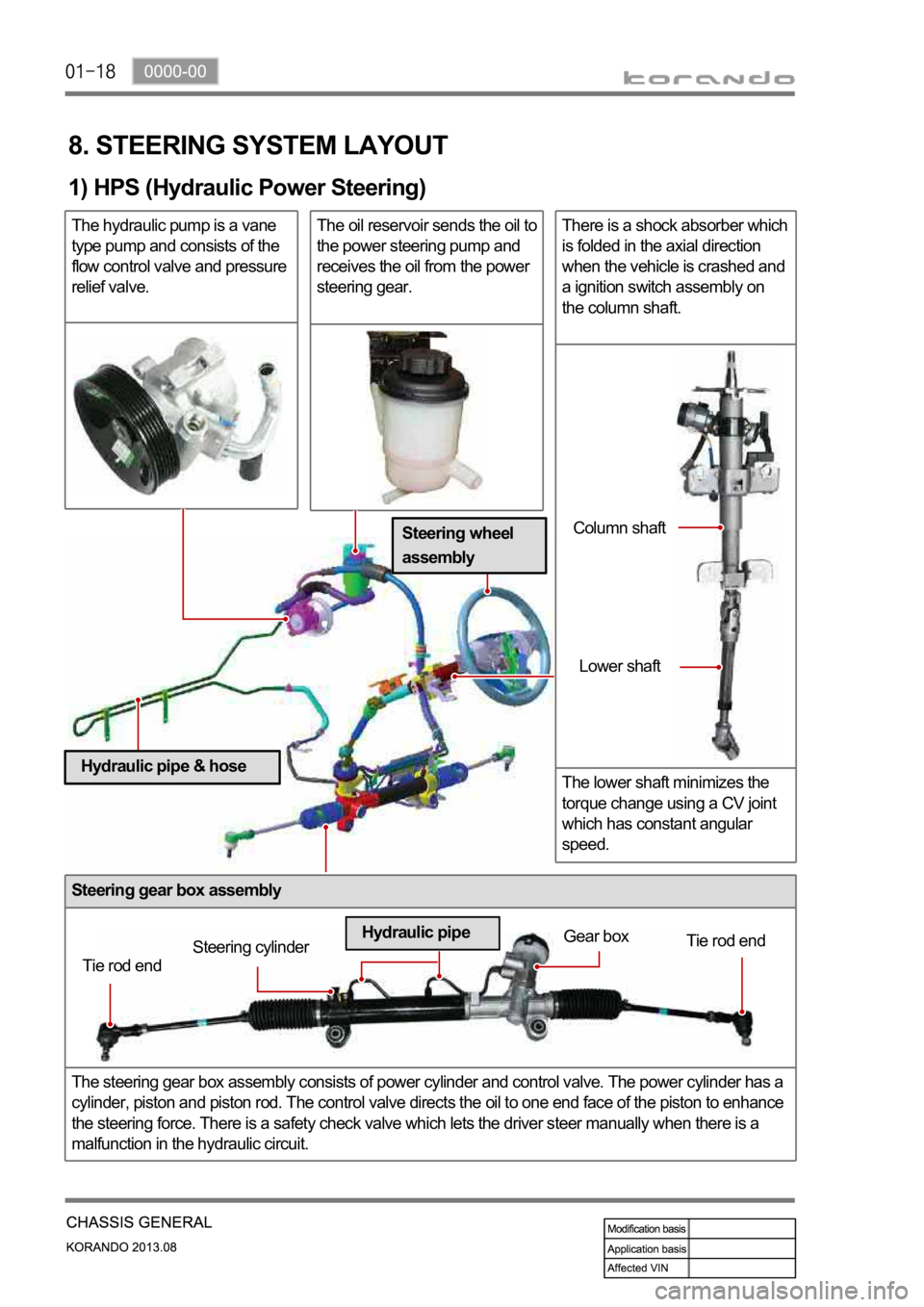
Steering gear box assembly
The steering gear box assembly consists of power cylinder and control valve. The power cylinder has a
cylinder, piston and piston rod. The control valve directs the oil to one end face of the piston to enhance
the steering force. There is a safety check valve which lets the driver steer manually when there is a
malfunction in the hydraulic circuit.
8. STEERING SYSTEM LAYOUT
1) HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)
The hydraulic pump is a vane
type pump and consists of the
flow control valve and pressure
relief valve.The oil reservoir sends the oil to
the power steering pump and
receives the oil from the power
steering gear.There is a shock absorber which
is folded in the axial direction
when the vehicle is crashed and
a ignition switch assembly on
the column shaft.
The lower shaft minimizes the
torque change using a CV joint
which has constant angular
speed.
Tie rod endSteering cylinderGear box
Tie rod end
Hydraulic pipeColumn shaft
Lower shaft
Steering wheel
assembly
Hydraulic pipe & hose
Page 997 of 1336
0000-00
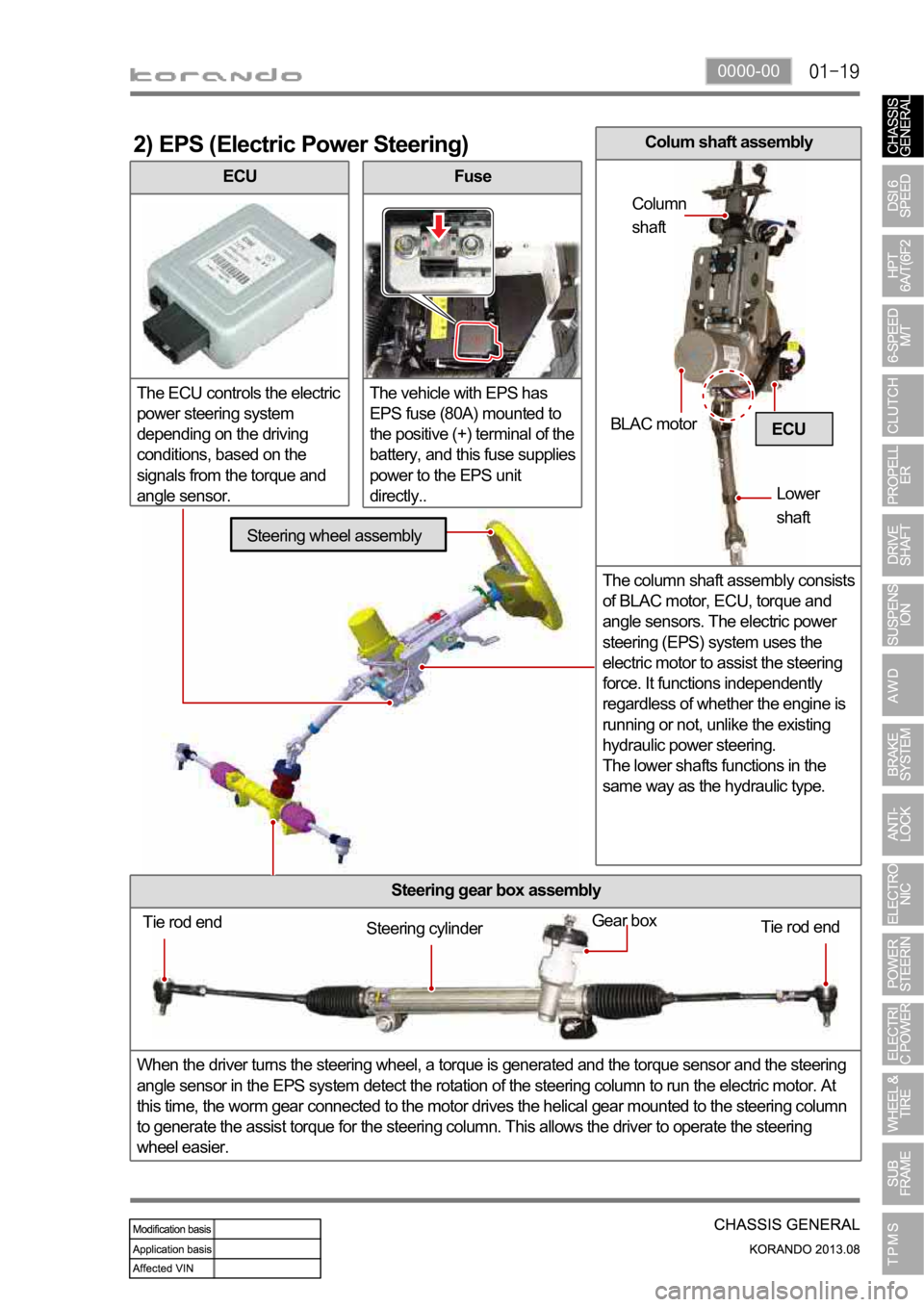
ECU
The ECU controls the electric
power steering system
depending on the driving
conditions, based on the
signals from the torque and
angle sensor.
2) EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Fuse
The vehicle with EPS has
EPS fuse (80A) mounted to
the positive (+) terminal of the
battery, and this fuse supplies
power to the EPS unit
directly..
Steering gear box assembly
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a torque is generated and the torque sensor and the steering
angle sensor in the EPS system detect the rotation of the steering column to run the electric motor. At
this time, the worm gear connected to the motor drives the helical gear mounted to the steering column
to generate the assist torque for the steering column. This allows the driver to operate the steering
wheel easier.
ECU
Tie rod end
Tie rod end Gear boxSteering cylinder
Steering wheel assembly
BLAC motor
Lower
shaft Column
shaft
Colum shaft assembly
The column shaft assembly consists
of BLAC motor, ECU, torque and
angle sensors. The electric power
steering (EPS) system uses the
electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently
regardless of whether the engine is
running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The lower shafts functions in the
same way as the hydraulic type.
Page 1000 of 1336

4) Basic Inspection
(1) Horn operation
Listen for the horn sound when pressing the horn pad on the steering wheel. -
(2) Brake operation
Check if there is any abnormal noise, unusually long braking distance, or uneven braking force. If the
brake warning lamp does not go out even after starting the engien or are flashing during driving,
have the brake system checked immediately.
Check the brake pipes and hoses for connection, oil leak, crack or interference after changing the
position of tires. When replacing the tires, check the brake disc for surface condition and wear.
Check the parking brake cable and brake operation. Shorten the checking interval if the parking
brake is used frequently. -
-
-
(3) Exhaust system
Be aware to any changes in sound or smell from the exhaust system. These may be caused by leak or
overheat. Have the exhaust system checked and repaired immediately.
Inspect the exhaust system including catalytic converter. Inspect all the components and body frame
near the exhaust system. -
-
(4) Tires
Unusual vibration of the steering wheel and seats or pulling to one side on the straight and level roads
may indicates the uneven tire inflation pressure or poor wheel balance. -
(5) Steering and suspension system
Inspect the front and rear suspension and the steering system for damage, looseness or missing
parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect the power steering line and the hoses for
connection, leak, crack and chafing. Inspect the drive axle boot and seals for damage, tear or leak.
Replace or repair the system if necessary. -
(6) Engine oil
Check the oil level when the engine is still warm and add the specified engine oil if necessary. -
(7) Coolant
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir, coolant conditions (contamination, foreign material),
and hoses for damage and leak. Replace or add the Ssangyong genuine coolant, if needed. -
(8) Engine drive belt
Check all drive belts on the engine for wear, crack and looseness. Retighten or replace the belt, if
needed. -
Page 1101 of 1336

4890-00
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) What is ABS?
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation. But,
ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
2) What is EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)?
EBD is an automobile brake technology that automatically varies the amount of force applied to each of a
vehicle's brakes, based on road conditions, speed, loading, etc. Always coupled with anti-lock braking
systems, EBD can apply more or less braking pressure to each wheel in order to maximize stopping
power whilst maintaining vehicular control. EBD does not operate when ABS is working. ABS effect according to braking conditions
Braking on split road Maneuvering while braking