Page 262 of 715

06-211914-01
Control
rangeTurbocharger
driving
mechanismControl methodEffectImproved
performance
At low
speedNarrows the
flow passage
for the exhaust
gas by folding
the vanesThe flow rate is
increased as the
exhaust gas passes
the narrow passage
→ Increased
turbine & impeller
speed, Increased
compressive forceImproved
low speed
torque
4. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
The E-VGT is designed to get more improved engine power in all ranges by controlling the turbine
as follows:
1) How it Works at Low Speed
Normal turbocharger cannot get the turbo effect because the amount of exhaust gas is not
enough and the flow speed is slow in a low speed zone, but VGT allows the flow passage of
exhaust to narrow, resulting in increasing the flow speed of exhaust gas and running the turbine
quickly and powerfully.
Therefore, as VGT can intake more air than normal turbocharger, it can give the benefit of the
increased output even in a low speed zone.
Turbocharger lag
The turbocharger is at idle speed when there is no load or it is in the normal driving condition.
During this period, the amount of exhaust gas passing through the turbine is not enough to turn
the compressor wheel (impeller) fast. Therefore, the intake air is not compressed as needed.
Because of this, it takes time for turbocharger to supply the additional power after the
accelerator pedal is depressed. This is called "turbocharger lag".Basic principle at low speed
At low speed, it utilizes the principle of
venturi.
For example, when air flows through the
venturi tube, the flow speed is faster and the
pressure is lower at the point "A". In this case,
if the inner
diameter of venturi is more narrowed, the flow
speed is so much faster (refer to the
equation). ※
Page 269 of 715

08-4
2. INSPECTION
Possible Cause Action
Coolant level
is
too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the coolant auxiliary tank
- Leak from the heater core- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
- Change the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose
connections
- Damaged coolant hose - Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Change the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal
seal- Change the gasket
- Change the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Change the water inlet cap
gasket
- Change the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Change the cylinder head gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective coolant auxiliary tank or tank
cap- Change the thermostat
- Change the water pump
- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Change cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Change the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or faulty
wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 287 of 715
10-4
1. OVERVIEW
The pre-heating system for D20DTR engine has the glow plug to the cylinder head (combustion
chamber), and improves the cold start performance and reduces the emission level.
The pre-heating resistor (air heater) is used to heat the intake air.
This enables the diesel fuel to be ignited in low temperature condition.
The ECU receives the information such as, engine rpm, coolant temperature, engine torque, etc.,
through CAN communication during pre-heating process; and the pre-heating control unit
controls the pre-heating, heating during cranking and post-heating by the PWM control.
Glow plug
Engine ECU (D20DTR)Glow indicator
Glow plug control unit
(GCU)
Page 312 of 715
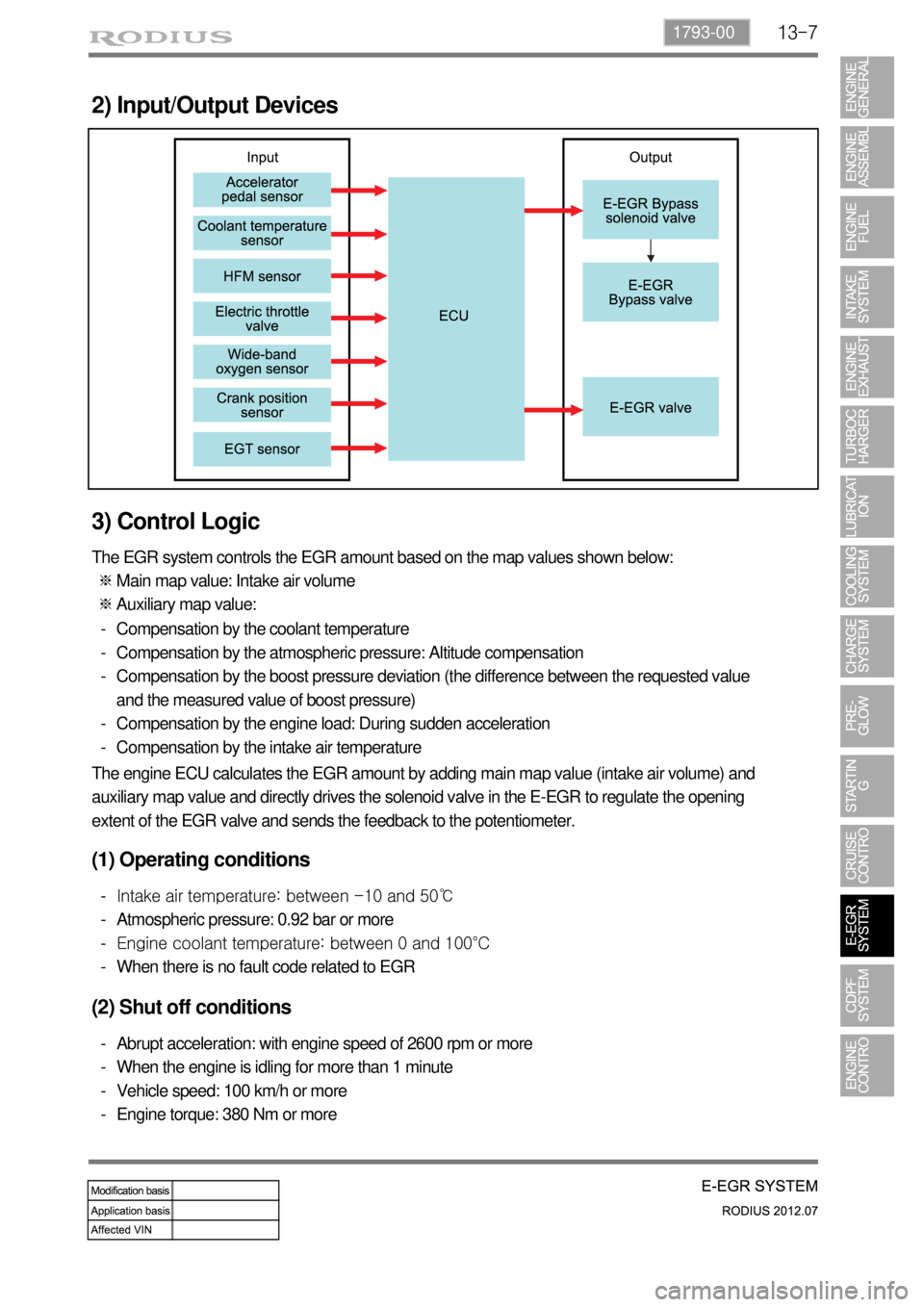
13-71793-00
2) Input/Output Devices
3) Control Logic
The EGR system controls the EGR amount based on the map values shown below:
Main map value: Intake air volume
Auxiliary map value: ※
※
Compensation by the coolant temperature
Compensation by the atmospheric pressure: Altitude compensation
Compensation by the boost pressure deviation (the difference between the requested value
and the measured value of boost pressure)
Compensation by the engine load: During sudden acceleration
Compensation by the intake air temperature -
-
-
-
-
The engine ECU calculates the EGR amount by adding main map value (intake air volume) and
auxiliary map value and directly drives the solenoid valve in the E-EGR to regulate the opening
extent of the EGR valve and sends the feedback to the potentiometer.
(1) Operating conditions
Intake air temperature: between -10 and 50℃
Atmospheric pressure: 0.92 bar or more
Engine coolant temperature: between 0 and 100°C
When there is no fault code related to EGR -
-
-
-
(2) Shut off conditions
Abrupt acceleration: with engine speed of 2600 rpm or more
When the engine is idling for more than 1 minute
Vehicle speed: 100 km/h or more
Engine torque: 380 Nm or more -
-
-
-
Page 328 of 715
15-30000-00
1. ENGINE DATA LIST
Data Unit Value
Coolant temperature℃ 130℃~-40℃
Intake air temperature℃ -40 to 130℃ (varies by ambient air
temperature or engine mode)
Idle speed rpm 700 ± 50 (P/N), 600 ± (D)
Engine load % 18~25%
Mass air flow kg/h 16 to 25 kg/h
Throttle position angle°TA 0° (Full Open) to 78° (Close)
Engine torque Nm varies by engine conditions
Injection time ms 3 to 5ms
Battery voltage V 13.5 V to 14.1 V
Accelerator pedal position 1 V 0.4. to 4.8V
Accelerator pedal position 2 V 0.2 to 2.4 V
Throttle position 1 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Throttle position 2 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Oxygen sensor V 0 to 5 V
A/C compressor switch
1=ON / 0=OFF -
Full load 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Gear selection (A/T) 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Knocking control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Brake switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Cruise control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Page 343 of 715

15-18
C. Idle Speed Controller
The idle speed controller consists of 2 principal modules:
The first module determines the required idle speed according to:
* The operating conditions of the engine (coolant temperature, gear engaged)
* Any activation of the electrical consumers (power steering, air conditioning, others)
* The battery voltage
* The presence of any faults liable to interface with the rail pressure control or the injection control. In
this case, increase the idle speed to prevent the engine from stalling.
The second module is responsible for providing closed loop control of the engine's idle speed by
adapting the minimum fuel according to the difference between the required idle speed and the
engine speed. -
-
D. Flow Limitation
The flow limitation strategy is based on the following strategies:
The flow limitation depending on the filling of the engine with air is determined according to the
engine speed and the air flow. This limitation allows smoke emissions to be reduced during
stabilized running.
The flow limitation depending on the atmospheric pressure is determined according to the engine
speed and the atmospheric pressure. It allows smoke emissions to be reduced when driving at
altitude.
The full load flow curve is determined according to the gear engaged and the engine speed. It
allows the maximum torque delivered by the engine to be limited.
A performance limitation is introduced if faults liable to upset the rail pressure control or the
injection control are detected by the system. In this case, and depending on the gravity of the fault,
the system activates: -
-
-
-
Reduced fuel logic 1: Guarantees 75 % of the performance without limiting the engine speed.
Reduced fuel logic 2: Guarantees 50 % of the performance with the engine speed limited to
3,000 rpm.
Reduce fuel logic 3: Limits the engine speed to 2,000 rpm.
The system chooses the lowest of all values.
A correction depending on the coolant temperature is added to the flow limitation. This correction makes
it possible to reduce the mechanical stresses while the engine is warming up.
The correction is determined according to the coolant temperature, the engine speed and the time which
has passed since starting.
E. Superchager Flow Demand
The supercharge flow is calculated according to the engine speed and the coolant temperature. A
correction depending on the air temperature and the atmospheric pressure is made in order to increase
the supercharge flow during cold starts. It is possible to alter the supercharge flow value by adding a flow
offset with the aid of the diagnostic tool
Page 363 of 715

15-38
Relay box
A/C
compressorHFM (intake air
temperature)Cooling fan
module
MB 5 A/T (ATF
temperature)Coolant
temperature
sensor
(12) Cooling fan control
A. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transmission is also cooled down through the radiator
by circulating the oil through the oil pump. ECU controls the electric cooling fans with three cooling fan
relays to improve the engine torque and air conditioning performance.
For detailed information, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning System".
B. Components
D20DTR ECU
Refrigerant
Page 522 of 715
01-33650-01
Diameter( Torque converter) 270mm
Lockup function Yes
Gear ratios 1st 3.595
2nd 2.186
3rd 1.405
4th 1.000
5th 0.831
Reverse:
S mode / W mode3.167/1.926
Driving type 2WD(4WD)
Fluid specification Shell ATF 134
Fluid capacityapprox. 8ℓ
Selected lever
indicationP.R.N.D Mechanical
D+/D- Electrical
Parking lock systemBrake switch(signal) → TGS lever
Reverse lock systemCAN → TGS lever
Selected lever
indicationP.R.N.D Lever position
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 CAN
Oil temperature
sensorResistance: R, D0.5 ~ 2.5kΩ
Resistance: P, N20kΩ
TCU EGS 52
Shift solenoid
valve(25℃)Resistance3.8 ± 0.2Ω
Operating distance 0.2mm
Operating current 1.5 ~ 2A
Item W5A580(2WD) / W5A400(4WD)
Input torque 450Nm
1. SPECIFICATIONS