Page 244 of 828

07-4
2. MAINTENANCE
1) Level Check
Park the vehicle on a level ground and apply the parking brake. Stop the engine and wait more
than 5 minutes.
Pull out the dipstick and wipe it with a clean cloth. Reinsert it all the way.
Pull out it again and check the oil level.
The oil level should be between the maximum (Max) mark and minimum (Min) mark on the oil
dipstick. Oil should be replenished before the level goes below the minimum mark. -
-
-
Operating vehicle with insufficient amount of oil can damage the engine. Make sure the engine
oil level is correct and add oil if necessary.
2) Replenishment
If the level gets to the lower point, open the filler cap on top of the cylinder block and add the
genuine oil without exceeding the level of the upper mark.
Recheck the oil level after 5 minutes.
Regularly check the engine oil level and add Ssangyong genuine engine oil if necessary.
Clean the dipstick with clean cloth so that any foreign materials cannot get into the engine.
The oil should not go above the upper mark on the dipstick.
The engine oil may be consumed more if the engine is new. -
-
-
-
Engine oil dipstick
Engine oil filler
Page 247 of 828

08-4
2. INSPECTION
Problem Possible Cause Action
Coolant level is
too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the coolant auxiliary tank
- Leak from the heater core- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
- Change the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose
connections
- Damaged coolant hose- Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Change the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal
seal- Change the gasket
- Change the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Change the water inlet cap
gasket
- Change the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Change the cylinder head gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective coolant auxiliary tank or
tank cap- Change the thermostat
- Change the water pump
- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Change cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Change the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 258 of 828

09-8
(3) Starting with jumper cable
If the battery is weak or terminated, the battery from another vehicle can be used with jumper
cables to start the engine.
Connecting order ▶
The positive (+) terminal of the discharged battery
The positive (+) terminal of the booster battery
The negative (-) terminal of the booster battery
Connect one end of the other jumper cable to the body of the discharged vehicle, such as the
engine block or a front towing hook. 1.
2.
3.
4.
Starting ▶
Prepare a set of jumper cables.
Place another vehicle that has the same 12 V of power near to the discharged vehicle.
Switch off all electrical accessories for the discharged vehicle.
Apply the parking brake and shift the transaxle to the P position (automatic transaxle) or neutral
(N) position (manual transaxle).
Connect the jumper cables.
Try to start the discharged vehicle while accelerating the engine rpm in the booster vehicle.
Attempt to start the engine with the discharged battery.
After starting the engine, carefully disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse sequence of
connection. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Page 270 of 828
11-31461-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Capacity 12 V, 2.3 kW
Engagement Meshed type
Rotating direction Clockwise
Pinion gear manufacturing Cooled forging
Solenoid operating voltage Max. 8 V
Weight 2.5 kg
Bracket manufacturing Aluminum die casting
Page 309 of 828
15-6
2. SYSTEM OPERATION
1) Input/Output of ECU
(1) ECU Block diagram
Page 318 of 828

15-150000-00
A fourth correction is made according to the pressure error.
This correction is used to reduce the injection timing advance when the pressure in the rail is
higher than the pressure demand.
A fifth correction is made according to the rate of EGR.
This correction is used to correct the injection timing advance as a function of the rate of
exhaust gas recirculation. -
-
When the EGR rate increases, the injection timing advance must in fact be increased in order to
compensate for the fall in termperature in the cylinder.
A. Main Flow Control
The main flow represents the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder during the main injection.
The pilot flow represents the amount of fuel injected during the pilot injection.
The total fuel injected during 1 cycle (main flow + pilot flow) is determined in the following manner.
When the driver depress the pedal, it is his demand which is taken into account by the system
in order to determine the fuel injected.
When the driver release the pedal, the idle speed controller takes over to determine the
minimum fuel which must be injected into the cylinder to prevent the enigne from stalling. -
-
It is therefore the greater of these 2 values which is retained by the system. This value is then
compared with the lower flow limit determined by the ESP system.
As soon as the injected fuel becomes lower than the flow limit determined by the ESP system, the
antagonistic torque (engine brake) transmitted to the drive wheels exceeds the adherence
capacity of the vehicle and there is therefore a risk of the drive wheels locking.
The system thus chooses the greater of these 2 values (main flow & pilot flow) in order to prevent
any loss of control of the vehicle during a sharp deceleration.
As soon as the injected fuel becomes higher than the fuel limit determined by the ASR trajectory
control system, the engine torque transmitted to the wheels exceeds the adhesion capacity of the
vehicle and there is a risk of the drive wheels skidding. The system therefore chooses the smaller
of the two values in order to avoid any loss of control of the vehicle during accelerations.
The anti-oscillation strategy makes it possible to compensate for fluctuations in engine speed
during transient conditions. This strategy leads to a fuel correction which is added to the total fuel
of each cylinder.
A switch makes it possible to change over from the supercharge fuel to the total fuel according to
the state of the engine.
Until the stating phase has finished, the system uses the supercharged fuel.
Once the engine changes to normal operation, the system uses the total fuel. -
-
(5) Fuel Control
The main fuel is obtained by subtracting the pilot injection fuel from the total fuel.
A mapping determines the minimum fuel which can control an injector as a function of the rail
pressure. As soon as the main fuel falls below this value, the fuel demand changes to 0 because
in any case the injector is not capable of injecting the quantity demand.
Page 326 of 828
15-230000-00
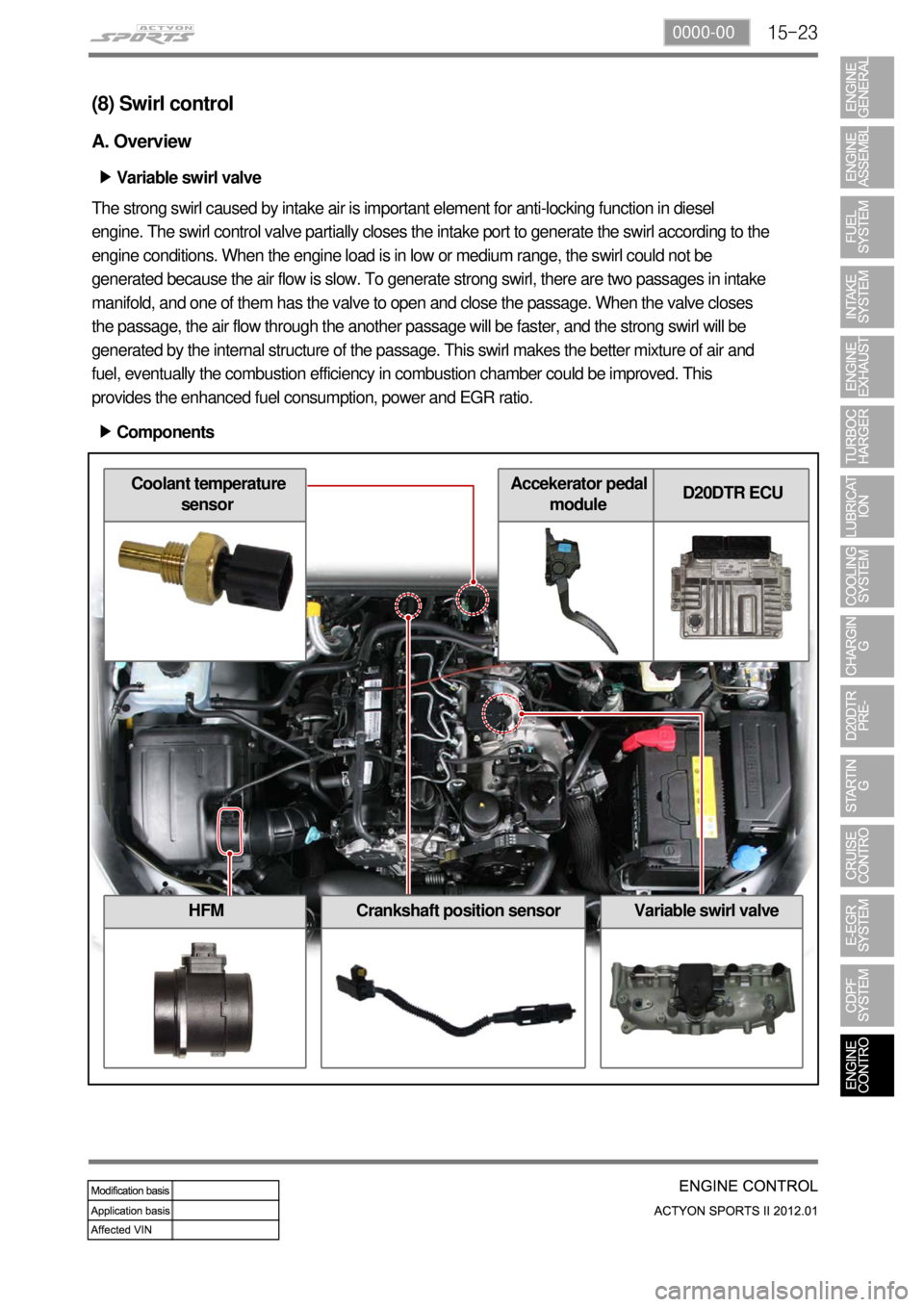
(8) Swirl control
A. Overview
Variable swirl valve ▶
The strong swirl caused by intake air is important element for anti-locking function in diesel
engine. The swirl control valve partially closes the intake port to generate the swirl according to the
engine conditions. When the engine load is in low or medium range, the swirl could not be
generated because the air flow is slow. To generate strong swirl, there are two passages in intake
manifold, and one of them has the valve to open and close the passage. When the valve closes
the passage, the air flow through the another passage will be faster, and the strong swirl will be
generated by the internal structure of the passage. This swirl makes the better mixture of air and
fuel, eventually the combustion efficiency in combustion chamber could be improved. This
provides the enhanced fuel consumption, power and EGR ratio.
Components ▶
HFMCrankshaft position sensorVariable swirl valve
Coolant temperature
sensorAccekerator pedal
moduleD20DTR ECU
Page 340 of 828

15-370000-00
HFM (intake air
temperature)Cooling fan module
DSI 6 A/T (ATF
temperature)Coolant
temperature senso
r
Refrigerant
pressure sensor
Relay box
(12) Cooling fan control
A. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine
operating conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then
circulates through water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head.
When the coolant reaches the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens.
The coolant then goes back to the radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transmission
is also cooled down through the radiator by circulating the oil through the oil pump. ECU controls
the electric cooling fans with three cooling fan relays to improve the engine torque and air
conditioning performance.
For detailed information, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning System".
B. Components
A/C compressor
D20DTR ECU