Page 286 of 828
13-51793-00
E-EGR valve
Receives the electric signal from the ECU to
control the valve.
E-EGR cooler and bypass valve
The cooler lowers the high temperature of the
exhaust gas and the bypass valve directly
supplies the exhaust gas to the intake duct
without passing through the EGR cooler to
reduce the emission of exhaust gas before
warming up the engine.
2) Location and Components
HFM sensor
Used as a main map value to control the EGR.
The coolant temperature, engine rpm, engine
load, intake air temperature (HFM: decreased
at 60˚C or more), atmospheric pressure
(atmospheric pressure sensor: altitude
compensation) are used as auxiliary map
values.
EGR pipe
Transports the exhaust gas from the EGR
cooler and EGR bypass valve to the intake
duct.
See the section "Engine control" for E-EGR
valve control logic.
EGR cooler
EGR bypass
For details, see the section "Engine control". *
Page 289 of 828

13-8
3) Control Logic
The EGR system controls the EGR amount based on the map values shown below:
Main map value: Intake air volume
Auxiliary map value: ※
※
Compensation by the coolant temperature
Compensation by the atmospheric pressure: Altitude compensation
Compensation by the boost pressure deviation (the difference between the requested value
and the measured value of boost pressure)
Compensation by the engine load: During sudden acceleration
Compensation by the intake air temperature -
-
-
-
-
The engine ECU calculates the EGR amount by adding main map value (intake air volume) and
auxiliary map value and directly drives the solenoid valve in the E-EGR to regulate the opening
extent of the EGR valve and sends the feedback to the potentiometer.
(1) Operating conditions
Intake air temperature: between -10 and 50℃
Atmospheric pressure: 0.92 bar or more
Engine coolant temperature: between 0 and 100°C
When there is no fault code related to EGR -
-
-
-
(2) Shut off conditions
Abrupt acceleration: with engine speed of 2600 rpm or more
When the engine is idling for more than 1 minute
Vehicle speed: 100 km/h or more
Engine torque: 380 Nm or more -
-
-
-
Page 306 of 828
15-30000-00
1. ENGINE DATA LIST
Data Unit Value
Coolant temperature℃ 0.436 V (130℃) to 4.896 V (-40℃)
Intake air temperature℃ -40 to 130℃ (varies by ambient air
temperature or engine mode)
Idle speed rpm750 ± 20
Engine load % 18~25%
Mass air flow kg/h 16 to 25 kg/h
Throttle position angle°TA 0° (Full Open) to 78° (Close)
Engine torque Nm varies by engine conditions
Injection time ms 3 to 5ms
Battery voltage V 13.5 V to 14.1 V
Accelerator pedal position 1 V 0.4. to 4.8V
Accelerator pedal position 2 V 0.2 to 2.4 V
Throttle position 1 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Throttle position 2 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Oxygen sensor mV 0 to 5 V
A/C compressor switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Full load 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Gear selection (A/T) 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Knocking control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Brake switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Cruise control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Page 308 of 828
15-50000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensorEGR valveFuel temperature
sensor
Electric throttle bodyKnock sensor
(2 ea)
Coolant temperature
sensor
T-MAP sensorD20DTR ECU
E-VGT actuator
Water sensorGCU (Preglow control
unit)
E-EGR bypass valve
Page 310 of 828
15-70000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
CAN
- ABS & ESP
- GCU
- Instrument
cluster
- TCUSwirl valve position
sensor
Differential
pressure sensorE-EGR valve
position sensorCamshaft position
sensorCoolant
temperature senso
r
Exhaust gas
temperature senso
r
HFM sensorOxygen sensorT-MAP sensor
Crankshaft position
sensor
Accelerator pedal
sensorThrottle position
sensorKnock sensor
-Auto cruise switch
- Rear right wheel
speed (without ABS)
- Refrigerant pressure
sensor
- Clutch pedal signal
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Water sensor
Page 314 of 828
15-110000-00
b. Pilot Injection
Injection before main injection. Consists of 1st and 2nd pilot injection, and Pre-injection
Inject a small amount of fuel before main injection to make the combustion smooth. Also, called
as preliminary injection or ignition injection. This helps to reduce Nox, engine noise and vibration,
and to stabilize the idling.
The injected fuel volume is changed and stopped according to the coolant temperature and
intake air volume.
Pilot injection is much earlier than main injection due to higher engine rpm
Too small injection volume (insufficient injection pressure, insufficient fuel injection volume
in main injection, engine braking)
System failure (fuel system, engine control system) -
-
-
Pilot injection
Main injection
Combustion pressure with pilot injection
Combustion pressure without pilot injection 1.
2.
1a.
2b. Stop conditions
Combustion pressure characteristic curve for pilot injection ▶
Page 315 of 828
15-12
c. Main Injection
The power of the vehicle is determined by the main fuel injection volume.
Main injection calculates the fuel volume based on pilot injection. The calculation uses the value
for accelerator pedal position, engine rpm, coolant temperature, intake air temperature, boost
pressure, boost temperature and atmospheric pressure etc.
d. Post Injection
Injection after main injection. Consists of After injection, Post 1, Post 2 injection.
Post injection reduces PM and smoke from exhaust gas. No actual output is generated during
these injections, instead, fuel is injected to the unburned gas after main injection to enable fuel
activation. The PM amount in the emission and smoke can be reduced through these processes.
Only up to 5 types of injections can be performed within 1 cycle. If these 7 injections are all
performed, fuel economy and emission performance becomes poor.
Page 316 of 828
15-130000-00
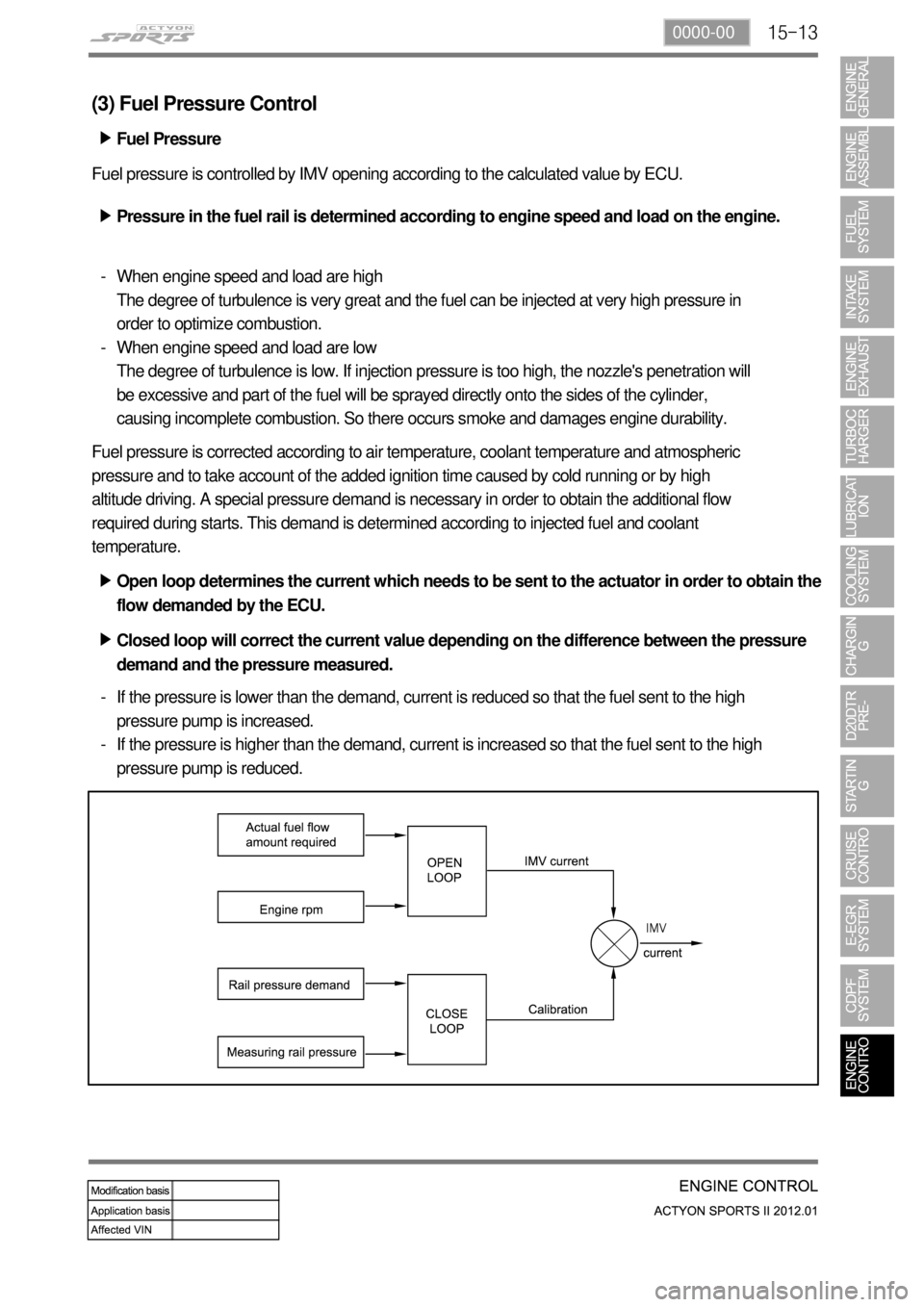
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine. ▶
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in
order to optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will
be excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder,
causing incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability. -
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric
pressure and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high
altitude driving. A special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow
required during starts. This demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant
temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain the
flow demanded by the ECU. ▶
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured. ▶
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced. -
-Fuel Pressure ▶