Page 747 of 828
13-6
Symptom Possible Cause
Blade type wear from outer side
toward inner side of the tread
Excessive toe-in,
Deflection of knuckle arm,
Difference in tie rod length
between left and right sides
Blade type wear from inner side
toward outer side of the tread
Excessive toe-in,
Deflection of knuckle arm,
Difference in tie rod length
between left and right sides
Corrugation wear of tread
Poor wheel balance,
Loose wheel bearing,
poor wheel alignment
InsideOutside
Inside
Outside
Inside
Outside
Page 748 of 828

13-74170-09
2) Typical Inspection
Tread
Inspect the tread condition on the tire
surface and various damages resulting
from the foreign materials, crack, stone or
nail etc. If there is any damage in the tire,
repair or replace it. 1.
Wear limit 2.
Measure the depth of the tire tread. If
the depth of the tread is below the
specified value, replace the tire -
You can see the protruded part in the
groove at the point with mark "▲", which
is the indicator of the tread wear limit.
The limit of the tread wear for all season
tires are 1.6 mm, which is the same as
the general tires, but the wear limit mark
is indicated as '↓'. -
-
Wear limit 1.6 mm
Higher than recommended pressure can cause hard ride, tire bruising or damage and rapid
tread wear at the center of the tire.
Excessive tire wear over the limit of the tread wear (1.6 mm) can cause lower sliding friction
due to longer braking distance, easy tire burst by foreign materials, tire hydroplaning, and
tough brake and steering wheel handling. -
-
Page 749 of 828
13-8
Measure the dial runout and lateral
runout on both the inboard and
outboard rim flanges. - Tire inflation pressure -
Check the tire inflation pressure by
inspecting the tread width. -
Specified value 2.66 mm
Wheel runout
If wheel runout or tire runout is excessive,
it could result in abnormal wear of the tire.
Measure the runout with a dial gauge. 4.
Measure free radial runout on the tire
tread. -
Specified value 2.03 mm
If any measurement exceeds the above
specifications, replace the applicable
tires or wheels -Tire inflation pressure 3.
Specified value 32 psi
Maintaining the specified tire ressure is
essential for comfortable riding, driving
safety, and long tire life. Incorrect inflation
pressures will increase tire wear and will
impair safety, vehicle handling,
comfortable driving and fuel economy.
Always make sure that the tire inflation
pressure is correct.
Proper
inflationProper
inflationOver
inflation
Tread width Tread width Tread width
Page 750 of 828
13-94170-09
Wheel balance 5.
Check the wheel balance when the
wheel is unbalanced or the tire is
repaired.
The total weight of the wheel weight
should not exceed 150 g.
Ensure that the balance weight installed
is not projected over 3mm from the
wheel surface.
Use the specified aluminum wheel
balance weights for aluminum wheels.
Weight balance can be added by 5 g.
There are two types of weight balance,
tape type and adhesion type. -
-
-
-
-
-
Make sure to read the manual of the
manufacturer thoroughly before using
wheel balance tester. -
Change tire location
To avoid uneven wear of tires and to
prolong tire life, inspect and rotate your
tires every 5,000 km. 6.
Mixing tires could cause to lose control while driving. Be sure to use the same size and type
tires of the same manufacturer on all wheels. -
Page 751 of 828
13-10
5. COMPONENTS
Alloy wheel
Alloy wheel
Steel wheel
Cap assembly - wheel
Cap assembly - wheel
Nut (127.4 ~ 156.8 Nm)
Tire 1.
2.
3.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Page 753 of 828
13-12
OVM Tools
Location ▶
Valve insertSpare tire
Jack (pantograph jack)
Wheel wrench
Jack connection
Driver (+, -)
Spanner 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Page 756 of 828

13-154170-09
During driving, the rotating tire repeats deformation and restoring movement in is tread. This
happens when the tire pressure is low in high speed driving.
However, when the wheel rotating speed is fast, the tire is deformed even before it is restored to
its original shape and the trembling wave appears on the tread portion. If this symptom lasts for
an extended period of time, the tire can be blown out in a short period of time.
If the standing wave symptom occurs on the tire, rubber on the tread comes off and eventually
the tire can be blown out which is very dangerous. When driving at high speed, the inflation
pressure should be increased to decrease heat generation due to extension and contraction
motion, to decrease hydroplaning and to prevent standing wave.
To prevent this symptom, it is recommended to increase the tire pressure 10 ~ 30 % higher than
the specified pressure value in high speed driving.
Specified tire inflation pressure32psi
2. ABNORMAL TIRE SYMPTOM
Standing Wave ▶
Page 758 of 828
13-174170-09
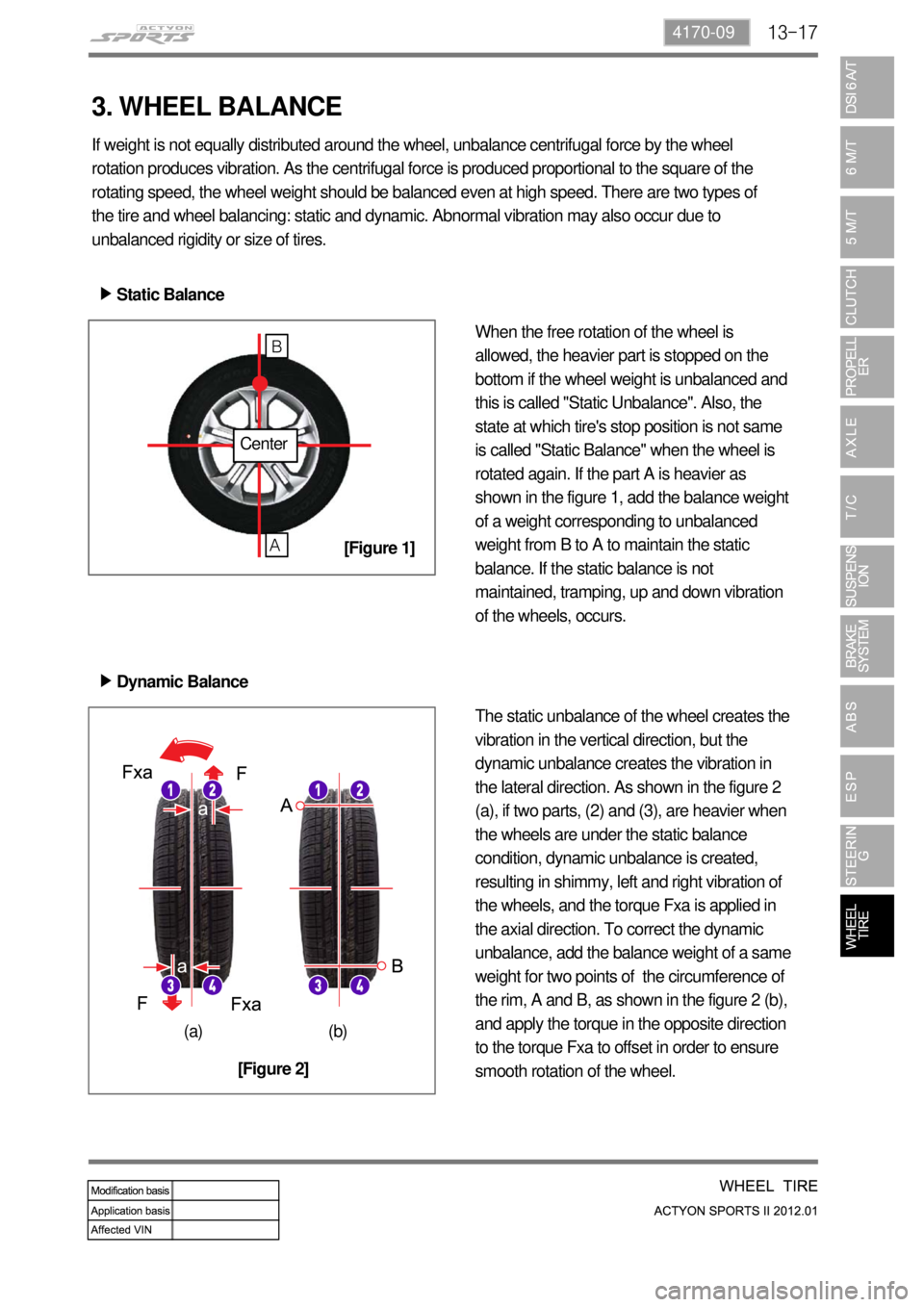
If weight is not equally distributed around the wheel, unbalance centrifugal force by the wheel
rotation produces vibration. As the centrifugal force is produced proportional to the square of the
rotating speed, the wheel weight should be balanced even at high speed. There are two types of
the tire and wheel balancing: static and dynamic. Abnormal vibration may also occur due to
unbalanced rigidity or size of tires.
Static Balance ▶
When the free rotation of the wheel is
allowed, the heavier part is stopped on the
bottom if the wheel weight is unbalanced and
this is called "Static Unbalance". Also, the
state at which tire's stop position is not same
is called "Static Balance" when the wheel is
rotated again. If the part A is heavier as
shown in the figure 1, add the balance weight
of a weight corresponding to unbalanced
weight from B to A to maintain the static
balance. If the static balance is not
maintained, tramping, up and down vibration
of the wheels, occurs.
Dynamic Balance ▶
The static unbalance of the wheel creates the
vibration in the vertical direction, but the
dynamic unbalance creates the vibration in
the lateral direction. As shown in the figure 2
(a), if two parts, (2) and (3), are heavier when
the wheels are under the static balance
condition, dynamic unbalance is created,
resulting in shimmy, left and right vibration of
the wheels, and the torque Fxa is applied in
the axial direction. To correct the dynamic
unbalance, add the balance weight of a same
weight for two points of the circumference of
the rim, A and B, as shown in the figure 2 (b),
and apply the torque in the opposite direction
to the torque Fxa to offset in order to ensure
smooth rotation of the wheel.
Center
A
B
(a) (b)
[Figure 1]
[Figure 2]
3. WHEEL BALANCE