2012 Seat Mii technical specifications
[x] Cancel search: technical specificationsPage 197 of 308

195
In the engine compartment
Colour indicatorNecessary operations
light yellow or col-
ourlessThe electrolyte level of the vehicle's battery is too low.
Have the battery checked and, where applicable, re-
placed by a Specialised workshop.
blackThe electrolyte level of the vehicle's battery is correct.
WARNING
Working with the vehicle battery involves a risk of corrosion, explosions
and electric shock.
● Always wear protective gloves and eye protection.
● Battery acid is very corrosive and caustic. It can burn skin and cause
blindness. When handling the battery, protect yourself from splashes of
acids, above all your hands, arms and face.
● Never tilt the vehicle battery. Battery acid could spill out of the open-
ings to release gases and cause corrosion damage.
● Never open the vehicle battery.
● If battery acid splashes on you, immediately rinse your eyes and skin
abundantly with water for several minutes. Then seek medical care imme-
diately.
● If acid is swallowed by mistake, consult a doctor immediately.
Charging, replacing and connecting or disconnecting the
battery
Charging the battery
The vehicle battery should be charged by a specialised workshop only, as
batteries using special technology have been installed and they must be
charged in a controlled environment ⇒
. SEAT recommends visiting a
Technical Service. Replacing a vehicle battery
The battery has been developed to suit the conditions of its location and
has special safety features. If the battery must be replaced, consult a Tech-
nical Service for information on electromagnetic compatibility, the size and
maintenance, performance and safety requirements of the new battery in
your vehicle before you purchase one. SEAT recommends you have the bat-
tery replaced by a Technical Service.
Use only maintenance-free genuine batteries conforming to TL 825 06 and
VW 7 50 73 Standards. These standards must be dated April 2008 or later.
Vehicles fitted with the Start-Stop system are equipped with a special bat-
tery. Therefore, this battery must only be replaced by another of the same
specifications.
Disconnecting the vehicle's battery
If you must disconnect the battery from the electrical system, please note
the following:
●
Switch off the ignition and all electrical equipment.
● The vehicle must be unlocked before disconnecting the battery, other-
wise the alarm will be triggered.
● First disconnect the negative cable and then the positive ⇒
.
Connecting the vehicle's battery
● Before reconnecting the battery, switch off the engine, the ignition and
electric devices.
● First reconnect the positive cable and then the negative ⇒
.
Different control lamps may light up after connecting the battery and switch-
ing the ignition on. They will be turned off after a short trip at a speed of
between 15 - 20 km/h (10 - 12 mph). If the warning indicators remain lit,
please visit a specialised workshop to have the vehicle checked.
If the battery has been disconnected for a long time, it is possible that the
next service date is not displayed or calculated correctly ⇒ page 17. Respect
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical Data
Page 221 of 308

219
Vehicle care and maintenance
Radial
Rim diameter code
Load index & speed rating
DOT tyre identification number
Severe snow conditions
Tyre ply composition and materials used
Max. load rating
Treadwear, traction and temperature grades
Max. permissible inflation pressure
Passenger vehicle tyre
Nominal width of tyre in millimetres
Ratio of height to width (aspect ratio)
Tyre code (example)MeaningMake, logotypeManufacturerProduct nameName of tyre assigned by manufacturer.P255 / 55 R 18Size:PPassenger vehicle code.255Nominal width between walls, in mm.55Height/width ratio in %RTyre type (R indicates "radial").18Rim diameter in inches109 HLoad index ⇒ page 220 and speed rating
⇒ page 220.
XL(“Reinforced”) tyres.M+S or M/S or Winter tyres code (mud and snow tyres).RADIAL TUBELESSRadial tyre without inner tube.E4 ...E-mark certifying tyre complies with internation-
al legislation followed by a number denoting the
country granting the authorisation. The authori-
sation number ( several digits) is shown below.
123456789101112
Tyre code (example)MeaningDOT BT RA TY5 1709Tyre identification number (TIN a)
, may be only on
interior wall of wheel) and date of manufacture:
DOTThe tyre complies with the legal require-
ments of the US Department of Trans-
port, responsible for tyre safety regula-
tions.
BTPlace of manufacture code.RAInformation about manufacturer and tyre
size.
TY5Manufacturer's tyre specifications.1709Date of manufacture: Week 17 of 2009.TWIThis identifies the position of the Tread Wear In-
dicator ⇒ page 215.
Made in GermanyCountry of manufacture.MAX LOAD 615 KGUS load rating, indicating maximum permitted
load per tyre.
MAX INFLATION 350 KPA
(51 PSI)US limit, indicating maximum permitted tyre
pressure.
SIDEWALL 1 PLY RAYONInformation about tyre wall components:
1 layer of rayon (artificial silk).
TREAD 4 PLIES
1 RAYON + 2 STEEL +
1 NYLONInformation about tread components:
In the example, there are 4 layers below the
tread: 1 layer of rayon (artificial silk), 2 layers of
steel reinforcement and 1 layer of nylon.
Information for the end consumer concerning the comparative values of
the established base tyres (standardised test procedures) ⇒ page 233:
TREADWEAR 220Relative service life of the tyre, with respect to
specific US standard test.
TRACTION ABraking capacity of tyre on wet surface (AA, A, B
or C).
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical Data
Page 235 of 308
233
Vehicle care and maintenance
Notes for the user Introduction
Additional information and warnings:
● Exterior detail ⇒ page 6
● Accessories, parts replacement, repairs and modifications ⇒ page 222
● ⇒ Booklet Maintenance Programme
WARNING
Failure to treat the vehicle with the correct care increases the risk of acci-
dent and injury.
● Observe legal requirements.
● Observe the Instruction Manual.
CAUTION
If you do not treat the vehicle suitably, you may cause it to be damaged.
● Observe legal requirements.
● Carry out regular maintenance of the vehicle, according to specifications
in the Maintenance Programme.
● Observe the Instruction Manual. Labels and plates
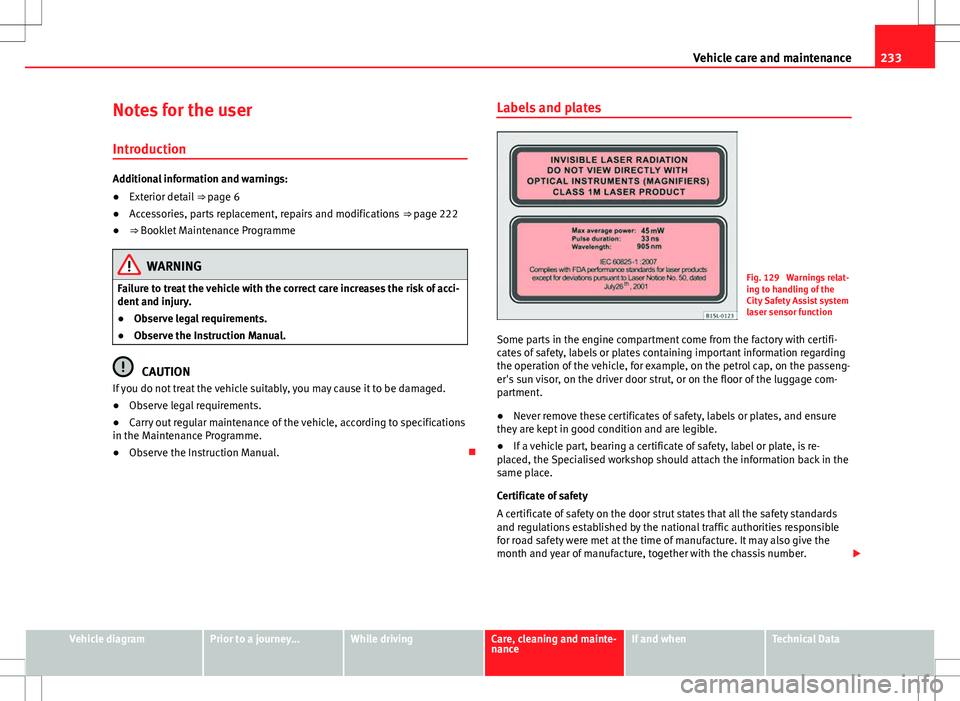
Fig. 129 Warnings relat-
ing to handling of the
City Safety Assist system
laser sensor function
Some parts in the engine compartment come from the factory with certifi-
cates of safety, labels or plates containing important information regarding
the operation of the vehicle, for example, on the petrol cap, on the passeng-
er's sun visor, on the driver door strut, or on the floor of the luggage com-
partment.
● Never remove these certificates of safety, labels or plates, and ensure
they are kept in good condition and are legible.
● If a vehicle part, bearing a certificate of safety, label or plate, is re-
placed, the Specialised workshop should attach the information back in the
same place.
Certificate of safety
A certificate of safety on the door strut states that all the safety standards
and regulations established by the national traffic authorities responsible
for road safety were met at the time of manufacture. It may also give the
month and year of manufacture, together with the chassis number.
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical Data
Page 266 of 308

264Practical information
Changing bulbs
Introduction
Changing bulbs requires a certain amount of manual skill. If you are unsure,
SEAT recommends that you consult a Technical Service or request assis-
tance from a specialist. In general a specialist is needed if, in addition to
the bulbs, other vehicle components require removal.
You should store spare light bulbs in the vehicle for safety-relevant lights.
Spare bulbs may be obtained from the Official dealers and workshops. In
some countries, it is a legal requirement to carry spare bulbs in the vehicle.
Driving with faults and blown bulbs on the vehicle exterior lighting is
against the law.
Additional bulb specifications
The specifications of some headlamp bulbs and bulbs for the tail lamps fit-
ted at the factory may be different to those of conventional bulbs. Bulb in-
formation is displayed on the bulb socket or on the bulb itself.
Additional information and warnings:
● Exterior detail ⇒ page 6
● Lights and visibility ⇒ page 84
● Working in the engine compartment ⇒ page 180
● Vehicle tools ⇒ page 246
● Fuses ⇒ page 261
WARNING
If the road is not well-lit and the vehicle is not clearly visible to other
drivers, there is a risk of accident.
WARNING
Failure to replace bulbs correctly may cause serious accidents.
● Before carrying out any work in the engine compartment please read
and observe the warnings ⇒ page 180. In any vehicle, the engine com-
partment is a hazardous area and could cause severe injury.
● The bulbs H4, HB4 and H7 are pressurised and might explode on
changing them.
● Only replace the bulbs concerned when they have cooled.
● Never replace bulbs alone if you are not familiar with the operations
necessary. If you are not sure about procedures then visit a Specialised
workshop to carry out the necessary work.
● Never touch the bulb glass directly. Fingerprints will be evaporated by
the heat of the operating bulb thus “fogging” up the reflector.
● The headlamp frameworks in the engine compartment and the tail
lamps contain sharp elements. Always protect your hands when chang-
ing bulbs.
CAUTION
After changing a bulb, if the rubber covers are not replaced correctly on the
headlamp framework, the electrical installation may be damaged, especial-
ly if water is allowed to enter.
Page 282 of 308

280Description of specifications
Technical Data
Description of specifications
Technical specifications
Introduction
The information in your vehicle's official documentation al-
ways take precedence over the information in the current in-
struction manual. The Maintenance Programme vehicle data or the official vehicle documents
show which engine is installed in the vehicle.
All the technical data provided in this documentation is applicable to the
basic model. The figures indicated here may be different depending on the
additional equipment added to the vehicle or the vehicle version, in addi-
tion to special vehicles for other markets.
Additional information and warnings:
● Transporting ⇒ page 97
● Ecological driving ⇒ page 144
● Fuel ⇒ page 177
● Engine oil ⇒ page 185
● Engine coolant ⇒ page 189
● Wheels and tyres ⇒ page 210
● Notes for the user ⇒ page 233
WARNING
Failure to observe requirements for weight, loads, dimensions and maxi-
mum speed may lead to severe accident.
Page 283 of 308

281
Description of specifications
Vehicle identification data
Fig. 163 TO: Vehicle da-
ta label: in the example,
engine with code CBFA 3
. B: Identification plate
Fig. 164 Vehicle identifi-
cation number
Vehicle identification number
The vehicle identification number (chassis number) can be read from out-
side the vehicle through a viewer in the windscreen ⇒ Fig. 164. This viewer
is located in the lower part of the windscreen. The vehicle identification number (chassis number) is also stamped on the right water drain channel.
The water drain channel is located between the suspension tower and the
wing. Open the bonnet to read the vehicle identification number
.
Vehicle data plate
The vehicle data label ⇒ Fig. 163 is at the front of the spare wheel well. It
contains the following data:
Vehicle identification number (chassis number)
Vehicle type, engine power, gearbox type
Engine and gearbox code, paint number, interior equipment. In the ex-
ample, the engine has the code “CBFA” ⇒ Fig. 163.
Optional extras, PR numbers
These data are also provided in the Maintenance Programme.
Specific vehicle weight information
The instructions in the official vehicle documents take precedence. All the
technical data provided in this documentation is applicable to the basic
model. The vehicle data label in the Maintenance Programme or the vehicle
documents show which engine is installed in your vehicle.
The figures may be different depending whether additional equipment is fit-
ted, for different models and for special vehicles.
Kerb weight values shown in the following table apple for a vehicle with
driver (75 kg), liquids including a fuel tank 90% full, in addition to tools and
a spare wheel ⇒
. The kerb weight indicated increases with optional
equipment and retrofitting of accessories, while proportionally reducing car-
rying capacity.
The load is equivalent to the following weights:
1
23
4
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical Data
Page 284 of 308

282Description of specifications
● Passengers.
● Total equipment.
● Roof load, included in the carrier.
WARNING
Exceeding the maximum authorised weight and the load on the axles
could cause damage to the vehicle, accidents and serious injuries.
● The real load on the axles should never exceed the maximum permit-
ted.
● The load and its distribution in the vehicle have effects on the vehicle
handling and the braking ability. Always drive at a suitable speed.
CAUTION
Distribute the load as uniformly and as low down on the vehicle as possible.
When transporting heavy objects in the luggage compartment, these
should be placed as far forward as possible or over the rear axle to have as
little influence on handling as possible.
Information on fuel consumption
The consumption and emission values indicated do not refer to one specific
vehicle. They are only to be used to compare the values of the different ve-
hicle versions. The fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions of a vehicle not on-
ly depend on the effective use of fuel. They also depend on your driving
style and other non-technical factors.
Calculation of fuel consumption
Fuel consumption and emission values are determined according to the cur-
rent version of the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulation and are valid
for the vehicle kerb weight. The specifications do not refer to an individualvehicle. To measure the fuel consumption, two measuring cycles are carried
out on a rolling road test bed. The test criteria are as follows:
Urban cycleMeasurement of the urban cycle starts with an engine cold
start. City driving is then simulated at between 0 and 50 km/
h (0 and 31 mph).
Road cycle
In the road cycle simulation, the vehicle undergoes frequent
acceleration and braking in all gears, as in normal everyday
driving. The road speed ranges from 0 to 120 km/h (0 and
75 mph).
CombinedThe average combined consumption is calculated with a
weighting of around 37 % for the urban cycle and 63 % for
the road cycle.
CO
2 emis-
sions of the
combinationThe exhaust gases are collected during both driving cycles
to calculate carbon dioxide emissions (urban and road). The
gas composition is then analysed to evaluate the CO 2 con-
tent and other emissions.
Note
The kerb weight may vary according to the vehicle equipment. This could
raise consumption and the CO 2 emissions slightly.
Note
In practice, consumption values could be different to the values calculated
based on the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulations.
Page 285 of 308

283
Description of specifications
Engine specifications
Petrol engine 1.0 44 kW (60 PS)
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 44 (60)/ 5000-6000
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 95/ 3000-4300
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
3/ 999
Fuel 95 super RON a)
a)
Research Octane Number = Anti-detonation rating of the petrol.
Performance Maximum speed in km/h (mph) 160
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h (0-50 mph) in sec. 9,1
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h (0-60 mph) in sec. 14,4
Consumption (l/100 km) / CO
2 emissions (g/km)
Urban cycle 5,6/130
Extra-urban cycle 3,9/91
Combined 4,5/105
Weights
Gross vehicle weight in kg 1290
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 929
Gross front axle weight in kg 551
Gross rear axle weight in kg 378
Permitted roof load in kg 50
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical Data