2011 SKODA OCTAVIA change wheel
[x] Cancel search: change wheelPage 125 of 248

rSAP - Remote SIM access profile
After connecting the telephone with the hands-free system via the
rSAP profile,
the telephone deregisters from the GSM network, the control unit ensures the
communication with the network via the internal antenna. In the telephone only
the interface for Bluetooth ®
remains active. In this case, you can only separate
from the control unit, switch off the Bluetooth ®
connection or select the number
of the emergency call 112 (only valid for some countries).
HFP - Hands Free Profile
After connecting the telephone with the hands-free system via the HFP profile,
the telephone continues to use its GMS module and internal antenna to communi-
cate with the GSM network. WARNING
Concentrate fully at all times on your steering! As the driver you are fully re-
sponsible for road safety. Use the telephone system only to such an extent, so
that you are in full control of your vehicle at any time. Note
● The volume can be changed individually during the call at any time with the
button for setting the radio or radio navigation system or with the buttons on the
multifunction steering wheel.
● Please refer to the following guidelines ⇒ page 115, Mobile phones and two-
way radio systems.
● Should you have any questions, please contact an authorised ŠKODA Service
Partner.
Phone Phonebook A phone phonebook is part of the mobile phone preinstallation with voice control.
In the phone phonebook there are 2000 free memory locations available. Each
contact can contain up to 5 numbers. This phone phonebook can be used in line
with the mobile telephone.
On vehicles fitted with the radio navigation system Columbus, a maximum of 1000
telephone contacts are shown in the display of this appliance.
After the first connection of the telephone, the system begins to load the phone
book from the phone and the SIM card into the memory of the control unit. If the telephone book of the mobile phone contains more than 2 000 entries, the
system announces Phone book not fully loaded .
Each time the telephone has established a new connection with the hands-free
system, an update of the relevant phone book is performed. The updating can
take a few minutes. During this time the phone book, which was stored after the
last update was completed, is available. Newly stored telephone numbers are only
shown after the updating has ended.
If a telephone event (e.g. incoming or outgoing call, dialogue of the voice control)
occurs during the updating procedure, the updating is interrupted. After the tele-
phone event has ended, the updating starts anew.
Connection of the telephone with the hands-free system In order to connect a mobile phone with the hands-free system, it is necessary to
connect the telephone to the hands-free system. Detailed information on this is
provided in the operating instructions of your mobile phone. The following steps
must be carried out for the connection.
Connecting the telephone with the hands-free system via the HFP profile
–
Activate the Bluetooth ®
in your telephone and the visibility of the mobile
phone.
– Switch on the ignition.
– Select the menu Phone - Phone search in the information display and wait un-
til the control unit has ended the search.
– Select your mobile phone in the menu of the units found.
– Within 30 seconds enter the 16 digit PIN of your control unit as indicated in the
information display and confirm it according to the instructions on the display
of your telephone.
– To store a new user or to download the telephone book and the identification
data of the SIM card into the control unit, follow the instructions in the infor-
mation display and on the mobile phone.
Connecting the telephone with the hands-free system via the rSAP profile
– Activate the Bluetooth ®
in your telephone and the visibility of the mobile
phone. For certain mobile phones it is necessary to switch on first the rSAP
function.
– Switch on the ignition. £ 123
Communication Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 138 of 248

The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50 km/hour,
the forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily
exceed 10
000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the vehicle not wearing a seat belt,
are thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the
vehicle, such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen, ⇒ fig. 118 - left. The occu-
pants of a vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out
of the vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will
otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event
of an accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a dan-
ger not only to himself but also for those seated at the front ⇒ fig. 118 - right.
Important safety information regarding the use of
seat belts The correct use of the seat belts considerably reduces the risk of
injury! WARNING
● The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted,
or chafe against any sharp edges.
● It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts are
to offer their maximum protection ⇒ page 137, How are seat belts correctly
fastened?
.
● No two persons (also not children) should ever use a single seat belt to-
gether.
● The maximum protection which seat belts can offer is only achieved if you
are correctly seated ⇒
page 132, Correct seated position. WARNING (Continued)
● The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. specta-
cles, ball-point pens, keys etc.) as this may be a cause of injuries.
● Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket)
do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of the
seat belts.
● It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e. g. for
shortening the belts for smaller persons).
● The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to pro-
tect and the risk of injury increases.
● The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
● The three-point seat belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its func-
tion reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position ⇒ page 64
.
● The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may im-
pair proper operation of the inertia reel ⇒
page 175, Seat belts.
● The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked by paper or similar objects
otherwise the belt tongue will not lock in place properly.
● Inspect the seat belts regularly to ensure they are in good condition. If you
find seat belts which have damage to the belt, the seat belt connections, to
the inertia reel or to the lock, the relevant seat belt must be replaced by a
specialist garage.
● The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not make
an attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
● Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident
and were therefore stretched, must be replaced - this is best done by a spe-
cialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The
anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
● In certain countries it is possible to use seat belts which differ in terms of
their operation from the seat belts which are described on the pages which
follow. 136
Seat belts
Page 144 of 248
WARNING (Continued)
● The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash panel
on the passenger side must not be stuck onto, covered or modified in any oth-
er way. These parts should only be cleaned with a dry cloth or a cloth mois-
tened with water. No objects such as cup holders, mobile phone mounts, etc.
may be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be located within the
immediate area.
● No modifications of any kind may be made to parts of the airbag system.
Any work on the airbag system including installing and removing system com-
ponents because of other repair work (e.g. removing the steering wheel) must
only be carried out by a specialist garage.
● Never carry out changes on the front bumper or on the body.
● Never place any objects on the surface of the front passenger airbag mod-
ule in the dash panel.
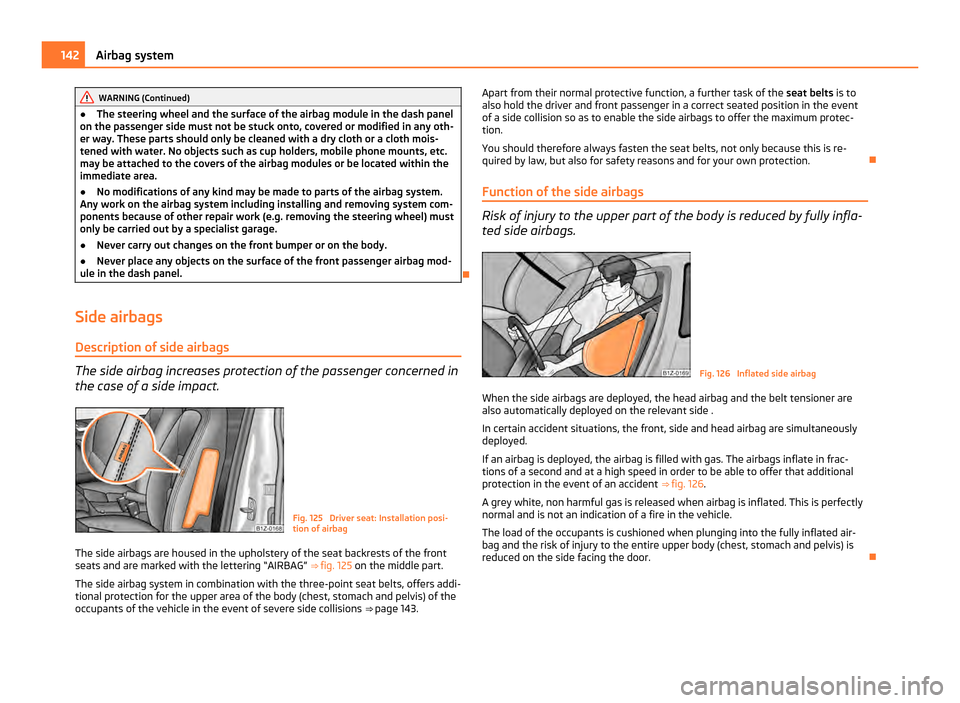
Side airbags Description of side airbags The side airbag increases protection of the passenger concerned in
the case of a side impact.
Fig. 125 Driver seat: Installation posi-
tion of airbag
The side airbags are housed in the upholstery of the seat backrests of the front
seats and are marked with the lettering “AIRBAG” ⇒ fig. 125 on the middle part.
The side airbag system in combination with the three-point seat belts, offers addi-
tional protection for the upper area of the body (chest, stomach and pelvis) of the
occupants of the vehicle in the event of severe side collisions ⇒ page 143. Apart from their normal protective function, a further task of the
seat belts is to
also hold the driver and front passenger in a correct seated position in the event
of a side collision so as to enable the side airbags to offer the maximum protec-
tion.
You should therefore always fasten the seat belts, not only because this is re-
quired by law, but also for safety reasons and for your own protection.
Function of the side airbags Risk of injury to the upper part of the body is reduced by fully infla-
ted side airbags.
Fig. 126 Inflated side airbag
When the side airbags are deployed, the head airbag and the belt tensioner are
also automatically deployed on the relevant side .
In certain accident situations, the front, side and head airbag are simultaneously
deployed.
If an airbag is deployed, the airbag is filled with gas. The airbags inflate in frac-
tions of a second and at a high speed in order to be able to offer that additional
protection in the event of an accident ⇒
fig. 126 .
A grey white, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is perfectly
normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
The load of the occupants is cushioned when plunging into the fully inflated air-
bag and the risk of injury to the entire upper body (chest, stomach and pelvis) is
reduced on the side facing the door. 142
Airbag system
Page 147 of 248

Important safety information on the head airbag
Correct use of the airbag system considerably reduces the risk of
injury! WARNING
● It is essential to always switch off ⇒ page 145 , Deactivating an airbag the
front passenger airbag when attaching a child safety seat on the front pas-
senger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel
(in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel). If this
is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal injuries if
the front passenger airbag is deployed. When transporting a child on the front
passenger seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations re-
garding the use of child safety seats.
● There must not be any objects in the deployment area of the head airbags
which might prevent the airbags from inflating properly.
● Only hang light items of clothing on the clothes hooks to the vehicle. Nev-
er leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the pockets of the items of cloth-
ing. In addition, it is not permitted to use clothes hangers for hanging up
items of clothing.
● The airbag control unit operates together with the sensors, which are at-
tached in the front doors. For this reason no adjustments must be carried out
at the doors as well as at the door panels (for example additional installation
of loudspeakers). Resulting damages can have a negative affect on the opera-
tion of the airbag system. All work on the front doors and their panels must
only be carried out by a specialist garage.
● There must not be any other persons (e.g. children) or animals between
the car occupant and the deployment area of the head airbag. In addition,
none of the occupants should lean their head out of the window when driving,
or extend their arms and hands out of the window.
● The sun visors must not be swivelled to the side windows into the deploy-
ment area of the head airbags if any objects, such as ball-point pens etc. are
attached to them. This might result in injuries to the occupants if the head air-
bag is deployed.
● Installing impermissible accessories in the area of the head airbags may
considerably impair the protection offered by the head airbag in the event of it
being deployed. When the deployed head airbag is inflated, parts of the acces- WARNING (Continued)
sories fitted may in certain circumstances be thrown into the interior of the
car and cause injuries to the occupants ⇒
page 197, Accessories, changes and
replacement of parts.
● Any work on the head airbag system including installing and removing sys-
tem components because of other repair work (e.g. removing headliner) must
only be carried out by a specialist garage.
Deactivating an airbag Deactivating airbags If any airbags have been deactivated, switch them on again as
soon as possible so that they are able to again provide their proper
protection.
There is the technical means installed within your vehicle to switch off the front,
side or head airbag (take out of commission).
This is why you should have the deactivation of the airbags carried out by a spe-
cialist garage.
On vehicles equipped with the switch for deactivation of the airbags, you can de-
activate the front passenger airbag by means of this switch ⇒
page 146.
Deactivation of airbags is envisaged only for particular instances, such as if:
● You must in exceptional cases use a child seat on the front passenger seat
where the child is seated with its back to the direction of travel (in some countries
this must be in the direction of travel due to other legal regulations applying)
⇒ page 147,
Important safety information regarding the use of child safety seats ;
● you are not able to maintain the distance of at least 25 cm between middle of
steering wheel and chest, despite the driver seat being correctly adjusted;
● special attachments are required in the area of the steering wheel because of
a physical disability;
● you have installed other seats (e.g. orthopaedic seats without side airbags).
Monitoring the airbag system
The functionality of the airbag system is also monitored electronically when one
airbag has been switched off. £ 145
Airbag system Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 157 of 248

WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the vehi-
cle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your style of
driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation. This par-
ticularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident! Note
● All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve prob-
lem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can
lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒
page 197, Ac-
cessories, changes and replacement of parts.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL and XDL) The electronic differential lock prevents an individual wheel from
slipping.
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part of the
driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sen-
sors. Should only
one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will
be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function
brakes the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to
the other driven wheel. This control process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in order to
avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being
braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as
a vehicle not fitted with EDL. The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
XDL function (only for Octavia RS)
The XDL function is an extension to the electronic differential lock. The XDL func-
tion does not respond to traction, but to the relief of the inner front wheel during
fast cornering. An active brake intervention on the brake of the inner wheel pre-
vents it from spinning. Thus, the traction is improved and the vehicle continues to
follow the desired track.
WARNING
● Carefully depress the accelerator when accelerating on uniformly slippery
road surfaces, such as ice and snow. The driven wheels might still spin despite
the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
● You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road sur-
face and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL. The
increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than other-
wise - risk of an accident! Note
● If the ABS or ESP warning light comes on, this may also indicate a fault in the
EDL. Have the vehicle inspected by your specialist garage as soon as you can.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL ⇒
page 197, Ac-
cessories, changes and replacement of parts. 155
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 158 of 248

Traction control system (TCS)
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spin-
ning when accelerating.
Fig. 139 TCS switch
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts
a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of
the ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force transmitted to the road sur-
face is automatically adapted by reducing the engine speed. The system operates
at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS ⇒ page 158, Antilock brake system
(ABS)
. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS system.
The TCS warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on
the TCS
⇒ page 26.
During an intervention of the system, the TCS warning light flashes in the in-
strument cluster ⇒ page 26.
Switching off
You can also switch off the TCS system by pressing the ⇒ fig. 139 button, or, in ve-
hicles with ESP, by pressing the ⇒ fig. 138 button. The TCS warning light lights up
in the instrument cluster when the TCS is switched off . The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain
exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the
system.
Examples:
● when driving with snow chains,
● when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
● when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the TCS again. WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of the road
surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety offered must not tempt
you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident! Note
● All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve prob-
lem-free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can
lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the TCS ⇒
page 197, Ac-
cessories, changes and replacement of parts.
Active driver-steering recommendation (DSR) This function indicates to the driver in critical situations a steering recommenda-
tion in order to stabilise the vehicle. The active driver-steering recommendation is
activated, for example, on the right and left vehicle side when braking sharply on
different road surfaces. WARNING
Even with this function the vehicle cannot steer itself! The driver is further-
more responsible for the steering of the vehicle! 156
Intelligent Technology
Page 160 of 248

Brake booster
The brake booster boosts the pressure which you generate with the brake pedal.
The necessary pressure is only generated when the engine is running. WARNING
● Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary.
● The brake booster only operates when the engine is running. Greater
physical effort for braking is required when engine is switched off. Because if
you do not stop as normal, this can cause an accident and severe injuries.
● While stopping or braking with a vehicle with a petrol engine and manual
transmission in the low rev range, press down on the clutch pedal. If you fail
to do so, the result may be an impairment of the function of the power brake.
You will apply a greater force to the brake pedal which you are usde to - dan-
ger of accident!
Antilock brake system (ABS) ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking.
General
The ABS contributes significantly to enhancing the active safety of your vehicle.
Compared to a car not fitted with the ABS brake system, you are able to retain op-
timal steering ability even during a full brake application on a slippery road surface
because the wheels do not lock up.
You must not expect, however, that the braking distance will be shorter under all
circumstances as a result of the ABS. The braking distance for example on gravel
and fresh snow, when you should anyway be driving slowly and cautiously, will be
longer.
Operating principle
The brake pressure will be reduced on a wheel which is rotating at a speed which
is too low for the speed of the vehicle and tending to lock. This control cycle is
noticeable from a pulsating movement of the brake pedal which is accompanied
by noises. This is consciously intended to provide the driver with the information
that the wheels are tending to lock (ABS control range). You must always keep the
brake pedal depressed to enable the ABS to optimally control the brake applica-
tion in this braking range. Never interrupt the application of the brakes! As soon as the vehicle speed has increased to about 20 km/hour an automatic
test procedure is conducted during which you will be able to hear a pumping noise
for about 1 second. WARNING
● The ABS can also not overcome the physical limits of your vehicle. Please
do not forget this, particularly when driving on icy or wet road surfaces. If the
ABS is operating within the control range, adapt your speed immediately to
the conditions of the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased
safety offered by the ABS must not tempt you to take greater risks than oth-
erwise - risk of an accident!
● The normal braking system is still fully functional if there is an ABS fault.
Visit a specialist garage immediately and adjust your style of driving according
to the damage to the ABS as you will not know how great the damage is and
the limitation it is placing on the braking efficiency. Note
● A warning light comes on if a fault occurs in the ABS system ⇒ page 27.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ABS ⇒
page 197,
Accessories, changes and replacement of parts.
Brake Assist During a severe brake application (e.g. if a hazard exists), the Brake Assist increa-
ses the braking force and thus makes it possible to rapidly produce the pressure
required in the brake system.
The majority of drivers do apply the brakes in good time in dangerous situations,
but do not depress the brake pedal with sufficient pressure. Consequently, it is
not possible for the car to achieve its maximum deceleration and the car covers a
greater distance than necessary.
The Brake Assist is activated by the very quick operation of the brake pedal. In
such cases, a much greater braking pressure exists than during a normal brake ap-
plication. This makes it possible, even with a relatively low resistance of the brake
pedal, to produce an adequate pressure in the brake system in the shortest possi-
ble time, which is required for maximum deceleration of the car. You must apply
the brake pedal firmly and hold it in this position in order to achieve the shortest
possible braking distance. £158
Intelligent Technology
Page 161 of 248

The Brake Assist is able to help you achieve a shorter braking distance in emer-
gency situations by rapidly producing the pressure required in the brake system. It
fully exploits the attributes of the ABS. After you release the brake pedal, the
function of the Brake Assist is automatically switched off and the brakes operate
in the normal way.
The Brake Assist is part of the ESP system. If a fault occurs in the ESP, the Brake
Assist function is also not available. Further information on the ESP
⇒ page 154.WARNING
● The Brake Assist is also not able to overcome the physical limits of your car
in terms of the braking distance required.
● Adapt your speed to the conditions of the road surface and to the traffic
situation.
● The increased safety offered by the Brake Assist must not tempt you to
take a greater safety risk than otherwise.
Uphill Start Assist The uphill start assist makes it easier to start off on steep hills. The system assists
a start off by holding the brake pressure produced by the brake pedal actuation
for approx. 2 seconds after releasing the brake pedal. The driver can therefore
move his foot from the brake pedal to the accelerator pedal and start off on the
slope, without having to actuate the handbrake. The brake pressure drops gradu-
ally the more you operate the accelerator pedal. If the vehicle does not start off
within 2 seconds, it starts to roll back.
The uphill start assist is active as of a 5 % slope, if the driver door is closed. It is
always active on slopes when in forward or reverse start off. When driving down-
hill, it is inactive.
Electromechanical power steering The power steering enables you to steer the vehicle with less physical force.
With the electromechanical power steering, the steering assist is automatically
adapted to the speed and to the steering angle.
It is still possible to fully steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the en-
gine is not running (vehicle being towed in). The only difference is that greater
physical effort is required. If there is a fault in the power steering, the warning light
or lights up in the
instrument cluster ⇒
page 24. WARNING
Contact your specialist garage if the power steering is defective.
Tyre pressure monitoring system Fig. 140 Button for setting the tyre in-
flation pressure control value
The tyre pressure monitoring system compares with the aid of the ABS sensors
the speed and also the rolling circumference of the individual wheels. If the rolling
circumference of a wheel is changed, the warning light
in the instrument clus-
ter ⇒ page 27 and an acoustic signal sounds.
The rolling circumference of the tyre can change if:
● the tyre inflation pressure is too low,
● the structure of the tyre is damaged,
● the vehicle is loaded on one side,
● the wheels of an axle are loaded heavily (e.g. when towing a trailer or when
driving uphill or downhill),
● snow chains are mounted,
● the temporary spare wheel is mounted,
● one wheel per axle was changed.
Basic setting of the system
After changing the tyre inflation pressures, after changing one or several wheels,
the position of a wheel on the vehicle (e.g. exchanging the wheels between the
axles) or when the warning light lights up while driving, a basic setting of the sys-
tem must be carried out as follows. £ 159
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data