2011 SKODA FABIA technical data
[x] Cancel search: technical dataPage 129 of 220

Attaching child seat using the “Top Tether” system
Fig. 117 Rear seat: Top Tether
IIn certain countries national legal provisions also require the equipment of the
rear seat with fixing eyes for child seat using the “Top Tether” system
⇒
fig. 117.
Always perform the installation and removal of the child seat using the “Top Teth-
er” system as stated in the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat. WARNING
● Attach the child seats with the “Top Tether” system only to the points pro-
vided for this purpose
⇒ fig. 117.
● On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
anchorage points.
● Pay attention to the important safety information regarding the use of
child seats ⇒ page 121. Note
Store the remaining part of the belt for the “Top Tether” system in a textile pock-
et, which is located at the child seat. 127
Transporting children safely Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 130 of 220

Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology Electronic stability programme (ESP)
General General
The ESP aids you in maintaining control of your vehicle in situations in which the
vehicle is driving at its dynamic limits, such as entering a curve fast. The risk of
skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on
the conditions of the road surface. The system operates at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
●
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
● Traction control system (TCS),
● Antilock brake system (ABS),
● Brake Assist,
● Uphill Start Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts
a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It al-
so processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive
sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle about its vertical axis, the lateral ac-
celeration of the vehicle, the braking pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual be-
haviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the car beginning to skid, the
ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is
braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front
wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle
to break away) while occurs this is on the inner rear wheel of a vehicle which
tends to understeer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle
is accompanied by noises. During an intervention of the system, the warning light
flashes quickly in the
instrument cluster.
The ESP system cannot be switched off, only the TCS system can be switched off
by pressing the button ⇒ fig. 118 . The warning light
⇒ page 24 lights up if the
TCS system is switched off.
The warning light lights up permanently if there is a fault in the ESP system.
The fact that the ESP system operates together with the ABS means that the ESP
warning light will also come on if the ABS system is not operating properly.
If the warning light comes on immediately after starting the engine, the ESP
system can be switched off for technical reasons. In this case, the ESP system can
be switched on again by switching the ignition on and off. If the warning light
goes out, the ESP system is fully functional again. WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the vehi-
cle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your style of
driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation. This par-
ticularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident! Note
● All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve prob-
lem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can
lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒ page 169,
Accessories, changes and replacement of parts
.128
Intelligent Technology
Page 131 of 220

Electronic Differential Lock (EDL and XDL)
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual wheel from
slipping.
Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part of the
driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sen-
sors. Should only
one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will
be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function
brakes the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to
the other driven wheel. This control process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in order to
avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being
braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as
a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
XDL function (Fabia RS and Fabia Combi RS only)
The XDL function is an extension to the electronic differential lock. The XDL func-
tion does not respond to traction, but to the relief of the inner front wheel during
fast cornering. An active brake intervention on the brake of the inner wheel pre-
vents it from spinning. Thus, the traction is improved and the vehicle continues to
follow the desired track. WARNING
● Depress the accelerator carefully when accelerating on uniformly slippery
road surfaces, such as ice and snow. The driven wheels might still spin despite
the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
● You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road sur-
face and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL. The
increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than other-
wise - risk of an accident! Note
● If the ABS or ASR or, where applicable, ESP indicator light lights up, the EDl
may have a fault. Have the vehicle inspected by your specialist garage as soon as
you can.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL ⇒
page 169
,
Accessories, changes and replacement of parts.
Traction control system (TCS) The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spin-
ning when accelerating.
Fig. 118 TCS switch
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble. £ 129
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 133 of 220

Faults in the brake surface
If you notice that the braking distance has suddenly become longer and that the
brake pedal can be depressed further, it is possible that a brake circuit of the dual-
circuit brake system has failed. Drive, in such cases, to the nearest specialist ga-
rage without delay in order to have the problem rectified. Drive at a reduced
speed while on your way to the dealer and adapt your style of driving to the high-
er brake pedal pressure required.
Low brake fluid level
An insufficient level of brake fluid may result in problems in the brake system. The
level of the brake fluid is monitored electronically
⇒ page 26, Brake system .WARNING
● Only apply the brakes for the purpose of drying and cleaning the brake
discs if the traffic conditions permit this. Do not place any other road users in
jeopardy.
● When retrospectively mounting a front spoiler, solid wheel hubs etc. one
must ensure that the air supply to the front wheel brakes is not reduced oth-
erwise the braking system could run too hot.
● Allow for the fact that new brake pads do not achieve their full braking ef-
ficiency until approximately 200 kilometres. New brake pads must be first
“run in ”
before they develop their optimal friction force. You can, however,
compensate for this slightly reduced braking force by increasing the pressure
on the brake pedal. This guideline also applies to any new brake pads installed
at a future date. CAUTION
● Never allow the brakes to rub by applying slight pressure if you do not wish to
brake the vehicle. This causes the brakes to overheat and can also result in a lon-
ger braking distance and excessive wear.
● Before negotiating a steep downhill section, please reduce your speed, shift
down into the next lower gear (manual gearbox) or select a lower driving stage
(automatic gearbox). This enables you to make full use of the braking power of
the vehicle and reduces the strain on the brakes. Any additional braking should be
done intermittently, not continuously. Note
The brake light flashes automatically in case of an emergency braking at speeds
greater than 60 km/h or with the intervention of the ABS, which lasts longer than
1.5 seconds. After the speed was reduced below 10 km/h or the vehicle was stop-
ped, the brake light stops flashing and the hazard warning light system switches
on. The hazard warning light system is switched off automatically after accelerat-
ing or driving off again.
Brake booster The brake booster boosts the pressure which you generate with the brake pedal.
The necessary pressure is only generated when the engine is running.
WARNING
● Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary.
● The brake booster only operates when the engine is running. Greater
physical effort for braking is required when engine is switched off. Because if
you do not stop as normal, this can cause an accident and severe injuries.
● While stopping or braking with a vehicle with a petrol engine and manual
transmission in the low rev range, press down on the clutch pedal. If you fail
to do so, the result may be an impairment of the function of the power brake.
You will apply a greater force to the brake pedal which you are usde to - dan-
ger of accident!
Antilock brake system (ABS) ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking.
General
The ABS contributes significantly to enhancing the active safety of your vehicle.
Compared to a car not fitted with the ABS brake system, you are able to retain op-
timal steering ability even during a full brake application on a slippery road surface
because the wheels do not lock up.
You must not expect, however, that the braking distance will be shorter under all
circumstances as a result of the ABS. The braking distance for example on gravel
and fresh snow, when you should anyway be driving slowly and cautiously, will be
longer. £ 131
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 135 of 220
The uphill start assist is active as of a 3 % slope, if the driver door is closed. It is
always active on slopes when in forward or reverse start off. When driving down-
hill, it is inactive.
Electrohydraulic power steering The power steering enables you to steer the vehicle with less physical force.
The steering characteristics can be changed by a specialist garage.
You will place great stresses on the power steering system if the steering is
turned to full lock when the vehicle is stationary. Turning the steering to full lock
in such a situation will be accompanied by noises.
It is still possible to fully steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the en-
gine is not running (vehicle being towed in). The only difference is that greater
physical effort is required.
It is possible that the hydraulic pump of the power steering will not run due to the
low vehicle network voltage if the battery has gone flat and the engine must star-
ted with the help off jump leads. This condition will be indicated by lighting up of
the warning light.
The power steering operates again if the battery is charged to a specific range
when engine is running. It also operates again, if the engine can be started with
its own battery.
If there is a fault in the power steering, the warning light lights up in the instru-
ment cluster
⇒ page 20. WARNING
Contact your specialist garage if the power steering is defective. CAUTION
Never leave the steering wheel at full lock for more than 15 seconds when the en-
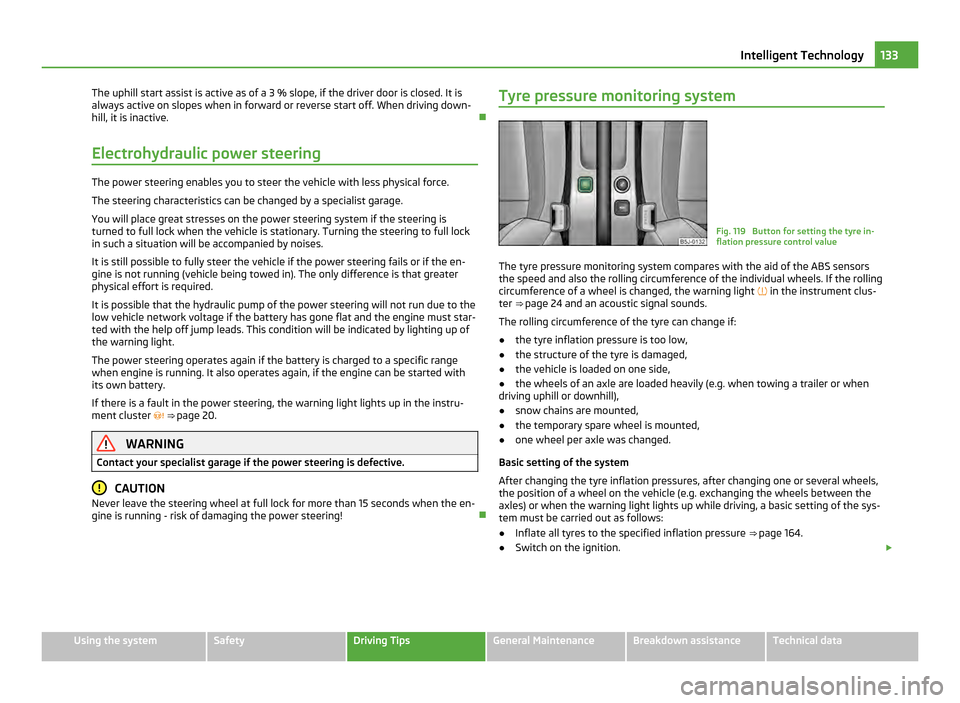
gine is running - risk of damaging the power steering! Tyre pressure monitoring system Fig. 119 Button for setting the tyre in-
flation pressure control value
The tyre pressure monitoring system compares with the aid of the ABS sensors
the speed and also the rolling circumference of the individual wheels. If the rolling
circumference of a wheel is changed, the warning light in the instrument clus-
ter ⇒ page 24 and an acoustic signal sounds.
The rolling circumference of the tyre can change if:
● the tyre inflation pressure is too low,
● the structure of the tyre is damaged,
● the vehicle is loaded on one side,
● the wheels of an axle are loaded heavily (e.g. when towing a trailer or when
driving uphill or downhill),
● snow chains are mounted,
● the temporary spare wheel is mounted,
● one wheel per axle was changed.
Basic setting of the system
After changing the tyre inflation pressures, after changing one or several wheels,
the position of a wheel on the vehicle (e.g. exchanging the wheels between the
axles) or when the warning light lights up while driving, a basic setting of the sys-
tem must be carried out as follows:
● Inflate all tyres to the specified inflation pressure ⇒ page 164.
● Switch on the ignition. £ 133
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 137 of 220

Driving and the Environment
The first 1 500 kilometres and afterwards
New engine The engine has to be run in during the first 1 500 kilometres.
Up to 1 000 kilometres
– Do not drive faster than 3/4 of the mamimum speed of the gear in use, that is
3/4 of the maximum permissible engine speed.
– Do not use full throttle.
– Avoid high engine revolutions.
– Do not tow a trailer.
From 1 000 up to 1 500 kilometres
– Increase the power output of the engine gradually up to the full speed of the
gear engaged, that is up to the maximum permissible engine revolutions.
During the first operating hours the engine has higher internal friction than later
until all of the moving parts have harmonized. The driving style which you adopt
during the first approx.1 500 kilometres plays a decisive part in the success of run-
ning in your car.
You should not drive at unnecessarily high engine revolutions even after the run-
ning-in period is complete. The maximum permissible engine speed is marked by
the beginning of the red zone on the scale of the revolutions counter. Shift up in-
to the next higher gear on a vehicle fitted with manual gearbox before the red
zone is reached. During acceleration (depressing the accelerator) exceptionally
high engine speeds are automatically reduced, yet the engine is not protected
against too high engine speeds which are caused by incorrectly shifting down the
gears resulting in a sudden increase of the engine speeds above the permitted
maximum revolutions which can lead to engine damage.
For a vehicle fitted with a manual gearbox the converse situation also applies: Do
not drive at engine revolutions which are too low. Shift down as soon as the en-
gine is no longer running smoothly. CAUTION
All the speed and engine revolution figures apply only when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature. Never rev up an engine which is cold, neither when
the vehicle is stationary nor when driving in individual gears. For the sake of the environment
Not driving at unnecessarily high engine revolutions and shifting to a higher gear
as early as possible are ways to minimise fuel consumption and operating noise
levels and protects the environment.
New tyres New tyres have to be “run in” since they do not offer optimal grip at first. You
should take account of this fact for the first 500 kilometres and drive particularly
carefully.
New brake pads Allow for the fact that new brake pads do not achieve their full braking efficiency
until approximately 200 kilometres. New brake pads must be first
“run in
” before
they develop their optimal friction force. You can, however, compensate for this
slightly reduced braking force by increasing the pressure on the brake pedal.
This guideline also applies to any new brake pads installed at a future date.
During the running-in period, you should avoid excessive stresses on the brakes.
This includes, for example, violent braking, particularly from very high speeds, and
also when crossing mountain passes.
Catalytic converter Proper operation of the emission control system (catalytic convert-
er) is of major significance for driving your vehicle in an environ-
mentally conscious way.
Please refer to the following guidelines: £ 135
Driving and the Environment Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 139 of 220

Shifting gears and saving energy
Shifting up early saves on fuel.
Fig. 121 Fuel consumption in litres/100
km. and speed in km/h.
Manual gearbox
– Drive no more than about one length of your vehicle in first gear.
– Shift into the next higher gear when approximately 2 000-2 500 revolutions
are achieved.
An effective way of achieving good fuel economy is to shift up early . You will con-
sume more fuel if you drive at unnecessarily high revolutions in any given gear. To
shift in a fuel-efficient manner, follow ⇒
page 13
, Shift recommendation for chang-
ing gears.
Automatic gearbox
– Depress the accelerator pedal slowly. Do not depress it beyond the kickdown
position, however.
Only depress the accelerator pedal slowly if your vehicle is fitted with an automat-
ic gearbox in order to automatically select an economic driving programme. You
will achieve good fuel economy by shifting up early and shifting down late.
General
The ⇒ fig. 121 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your vehicle in
the relevant gears. Fuel consumption in 1st
gear is the highest, while that in 5th or
the 6th gear is the lowest. Note
Also use the information supplied by the multi-functional indicator ⇒ page 14.Avoiding full throttle Driving more slowly means saving fuel.
Fig. 122 Fuel consumption in litres/100
km. and speed in km/h.
Sensitive use of the accelerator will not only significantly reduce fuel consumption
but also positively influence environmental pollution and wear of your vehicle.
You should avoid exploiting the top speed of your vehicle wherever possible. Fuel
consumption, pollutant emissions and vehicle noises increase disproportionally at
high speeds.
The ⇒ fig. 122 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your vehicle.
You will cut your fuel consumption by half if you only make use three-quarters of
the possible top speed of your vehicle.
Reducing idling Idling also costs fuel.
It is worthwhile switching off the engine in a traffic jam or when waiting at a level
crossing or at traffic lights with a lengthy red phase. Even after just 30 - 40 sec-
onds you will have saved more fuel than that is needed when you start the engine
up again.
If an engine is only idling it takes much longer for it to reach its normal operating
temperature. Wear-and-tear and pollutant emissions, though, are particularly high
in the warming-up phase. This is why you should drive off right after starting the
engine. Do avoid high engine revolutions at this time, however. 137
Driving and the Environment Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data
Page 141 of 220

Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 % more fuel.
Winter tyres are also louder.
No unnecessary ballast Transporting ballast costs fuel.
The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consumption
means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to avoid trans-
porting any unnecessary ballast.
It is particularly in town traffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that the vehi-
cle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule of
thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an increase in
fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted
on just out of convenience, al-
though you no longer need it. The increased aerodynamic drag of your vehicle
causes it to use about 10% more fuel than normal at a speed of 100 - 120 km/h,
even when you are not carrying a load on the roof.
Saving electricity Generating electricity costs fuel.
– Switch off electrical components as soon as you no longer need them.
When the engine is running, the alternator generates and supplies electrical pow-
er. If more electrical components of the electrical system are switched on, more
fuel is needed to operate the alternator.
Keeping a log of your fuel consumption If you really wish to keep a close check on your
fuel consumption, it is best to en-
ter the figures in a logbook. This does not take much time but is a very worthwhile
exercise. It enables you to detect any change (positive and negative) at an early
stage and to take any appropriate action.
If you find that your fuel consumption is too high, you should reflect on how,
where and in what conditions you have driven the vehicle since you last refuelled. Environmental compatibility Environmental protection has played a major role in the design, selection of mate-
rials and manufacture of your new
ŠKODA. Particular emphasis has been paid to a
number of aspects, including:
Design measures
● Joints designed to be easily detached.
● Simplified disassembly due to the modular structure system.
● Improved purity of different classes of materials.
● Identification of all plastic parts in accordance with VDA Recommendation 260.
● Reduced fuel consumption and exhaust emission CO
2.
● Minimum fuel leakage during accidents.
● Reduced noise.
Choice of materials
● Extensive use of recyclable material.
● Air conditioning filled with CFC-free refrigerant.
● No cadmium.
● No asbestos.
● Reduction in the
“vaporisation” of plastics.
Manufacture
● Solvent-free cavity protection.
● Solvent-free protection of the vehicle for transportation from the production
plant to the customer.
● The use of solvent-free adhesives.
● No CFCs used in the production process.
● Without use of mercury.
● Use of water-soluble paints.
Trade-in and recycling of old cars
ŠKODA meets the requirements of the brand and its products regarding environ-
ment and resource protection. All new ŠKODA vehicles can be utilized up to 95
%
and always 1)
be returned. In a lot of countries sufficient trade-in networks have £1)
Subject to fulfilment of the national legal requirements. 139
Driving and the Environment Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assistance Technical data