2011 HONDA CR-Z airbag off
[x] Cancel search: airbag offPage 15 of 333
Quick Reference Guide
14
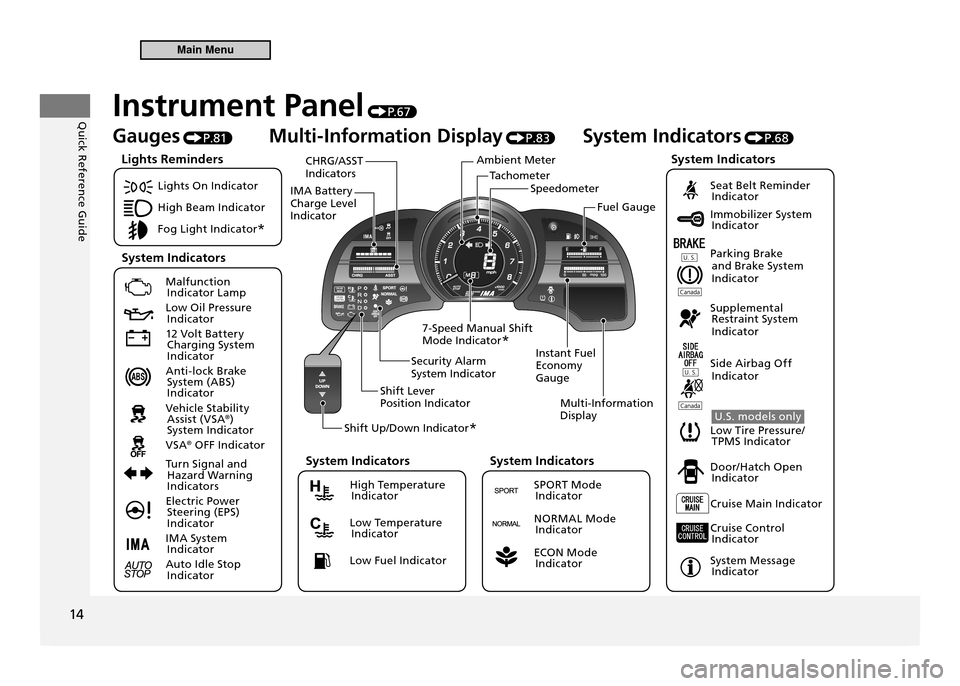
TachometerSpeedometer
Ambient Meter
IMA Battery Charge Level Indicator CHRG/ASST Indicators
Instant Fuel Economy GaugeMulti-Information Display
Security Alarm System Indicator
Shift Lever Position Indicator
Shift Up/Down Indicator *
7-Speed Manual Shift Mode Indicator
* Fuel Gauge
Instrument Panel
P. 6 7
Gauges P.81 Multi-Information Display
P.83 System Indicators
P.68
Lights On Indicator
High Beam Indicator
Fog Light Indicator *
Malfunction
Indicator Lamp
Low Oil Pressure Indicator
12 Volt Battery Charging System
Indicator
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
Indicator
Vehicle Stability Assist (VSA ®
)
System Indicator
VSA ®
OFF Indicator
Turn Signal and Hazard Warning
Indicators
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Indicator
IMA System Indicator
Auto Idle Stop Indicator
Seat Belt Reminder Indicator
Immobilizer System Indicator
Parking Brake and Brake System
Indicator
Supplemental Restraint System
Indicator
Side Airbag Off Indicator
U.S. models only
Low Tire Pressure/ TPMS Indicator
Door/Hatch Open Indicator
Cruise Main Indicator
Cruise Control Indicator
System Message Indicator
Lights Reminders
System Indicators System Indicators
High Temperature
Indicator
Low Temperature Indicator
Low Fuel Indicator
System Indicators
SPORT Mode Indicator
NORMAL Mode Indicator
ECON Mode Indicator
System Indicators
Main Menu
Page 34 of 333

Safe Driving
33
For Safe Driving Your Vehicle’s Safety Features
Safety Checklist
■
For the safety of you and your passenger, make a habit of checking these items each time before you drive.
After everyone has entered the vehicle, be sure both doors and the hatch are
●
closed and locked. Locking the doors and the hatch helps prevent an occupant from being ejected and an outsider from unexpectedly opening a door or the hatch.
Locking/Unlocking Doors from Inside P.1 0 2
Adjust your seat to a position suitable for driving. Be sure the seats are adjusted
●
as far to the rear as possible while allowing the driver to control the vehicle. Sitting too close to a front airbag can result in serious or fatal injury in a crash.
Adjusting the Seats P.11 9
Always wear your seat belt, and make sure you wear it properly. Confirm that
●
any passenger is properly belted as well.
Fastening the Seat Belts P. 3 7
If you choose to ignore our warnings and carry a child in this vehicle, make every
●
effort to protect them by properly using a seat belt or a child seat according to the child’s age, height, and weight.
Child Safety P. 5 6
Safety Checklist
If the door/hatch open indicator is on, a door and/ or the hatch is not completely closed. Close both doors and the hatch tightly until the indicator goes off.
Door/Hatch Open Indicator P. 7 2
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 37 of 333

Safe Driving
36
Seat Belts About Your Seat Belts
Automatic Seat Belt Tensioners
■
The driver’s and passenger’s seats are equipped with automatic seat belt tensioners to enhance safety. The tensioners automatically tighten the seat belts during a moderate to severe frontal collision, sometimes even if the collision is not severe enough to inlate the front airbags.
Automatic Seat Belt Tensioners
The seat belt tensioners can only operate once. If a tensioner is activated, the SRS indicator will come on. Have a dealer replace the tensioner and thoroughly inspect the seat belt system as it may not offer protection in a subsequent crash.
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 43 of 333

Safe Driving
42
Airbags
Airbag System Components
The front, front side, and side curtain airbags are deployed according to the direction and severity of the impact. The airbag system includes:
Two SRS (Supplemental Restraint
System) front airbags. The driver’s
airbag is stored in the center of the
steering wheel; the passenger’s airbag
is stored in the dashboard. Both are
marked “SRS AIRBAG.”
Two side airbags, one for the driver
and one for a passenger. The airbags
are stored in the outer edges of the
seat-backs. Both are marked “SIDE
A I R B A G .”
Two side curtain airbags, one for each
side of the vehicle. The airbags are
stored in the ceiling, above the side
windows. The front and rear pillars
are marked “SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG.”
An electronic control unit that
continually monitors and records
information about the sensors,
the airbag activators, the seat belt
tensioners, and driver and passenger
seat belt use when the ignition
switch is in ON
II. It also includes
emergency backup power in case
your vehicle’s electrical system is
disconnected in a crash.
Automatic seat belt tensioners. The
driver’s and passenger’s seat belts
incorporate sensors that detect
whether or not they are fastened.
A driver’s seat position sensor that
monitors the distance of the seat from
the front airbag. If the seat is too far
forward, the airbag will inflate with
less force.
Weight sensors in the passenger’s
seat. The passenger’s airbag will be
turned off if the weight on the seat is
65 lbs (29 kg) or less (the weight of an
infant or small child).
Impact sensors that can detect a
moderate to severe front or side
collision.
An indicator on the dashboard that
alerts you that the passenger’s front
airbag has been turned off.
Sensors that can detect if a child
or small statured adult is in the
deployment path of the passenger’s
side airbag.
An indicator on the instrument panel
that alerts you to a possible problem
with your airbag system or seat belt
tensioners.
An indicator on the instrument panel
that alerts you that the passenger’s
side airbag has been turned off.
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 46 of 333

Safe Driving
45
Airbags Front Airbags (SRS)
Operation
■
Front airbags are designed to inflate during a moderate-to-severe frontal collision. When the vehicle decelerates suddenly, the sensors send information to the control unit which signals one or both front airbags to inflate. A frontal collision can be either head-on or angled between two vehicles, or when a vehicle crashes into a stationary object, such as a concrete wall.
How the Front Airbags Work
■
While your seat belt restrains your torso, the front airbag provides supplemental protection for your head and chest. The front airbags deflate immediately so that they won’t interfere with the driver’s visibility or the ability to steer or operate other controls.
The total time for inflation and deflation is so fast that most occupants are not aware that the airbags deployed until they see them lying in front of them.
How the Front Airbags Work
After a front airbag inlates in a crash, you may see what looks like smoke. This is actually powder from the airbag's surface. Although the powder is not harmful, people with respiratory problems may experience some temporary discomfort. If this occurs, get out of the vehicle as soon as it is safe to do so. Although the driver's and passenger's airbags normally inlate within a split second of each other, it is possible for only one airbag to deploy. This can
happen if the severity of a collision is at the mar gin,
or threshold, that determines whether or not the airbags will deploy. In such cases, the seat belt will provide suficient protection, and the supplemental protection offered by the airbag would be minimal.
continued
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 47 of 333

Safe Driving
46
Airbags
Front Airbags (SRS)
When Front Airbags Should Not Deploy
■
Minor frontal crashes: Front airbags are designed to supplement seat belts and
help save lives, not to prevent minor scrapes, or even broken bones that might occur during a less than moderate-to-severe frontal crash. Side impacts: Front airbags can provide protection when a sudden deceleration
causes a driver or passenger to move towards the front of the vehicle. Side airbags and side curtain airbags have been specifically designed to help reduce the severity of injuries that can occur during a moderate-to-severe side impact which can cause the driver or passenger to move towards the side of the vehicle. Rear impacts: Head restraints and seat belts are your best protection during a
rear impact. Front airbags cannot provide any significant protection and are not designed to deploy in such collisions. Rollovers: Seat belts, and in vehicles equipped with a rollover sensor, side airbags
and side curtain airbags offer the best protection in a rollover. Because front airbags could provide little if any protection, they are not designed to deploy during a rollover.
When Front Airbags Deploy with Little or No Visible Damage
■
Because the airbag system senses sudden deceleration, a strong impact to the vehicle framework or suspension might cause one or more of the airbags to deploy. Examples include running into a curb, the edge of a hole, or other low fixed object that causes a sudden deceleration in the vehicle chassis. Since the impact is underneath the vehicle, damage may not be readily apparent.
When Front Airbags May Not Deploy, Even Though Exterior Damage
■
Appears Severe
Since crushable body parts absorb crash energy during an impact, the amount of visible damage does not always indicate proper airbag operation. In fact, some
collisions can result in severe damage but no airbag deployment because the airbags would not have been needed or would not have provided protection even if they had deployed.
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 48 of 333

Safe Driving
47
Airbags Front Airbags (SRS)
Advanced Airbags
■
Your front airbags have advanced features to reduce the likelihood of airbag related injuries to smaller occupants.
The driver's advanced front airbag system includes a seat position sensor. If the seat is too far forward, the airbag inflates with less force, regardless of the severity of the impact. The passenger's advanced front airbag system includes weight sensors. Although Honda recommends against carrying an infant or small child in the passenger seat, if the sensors detect the weight of a child (up to about 65 lbs or 29 kg), the system will automatically turn off the passenger’s front airbag.
Advanced Airbags
If there is a problem with the driver's seat position sensor, the SRS indicator will come on and the airbag will inlate with full (normal) force, regardless of the driver's seating position. For both advanced front airbags to work properly: Do not spill any liquid on or under the seats.
•
Do not put any object under the passenger’s
•
seat. Make sure any objects are positioned properly
•
on the rear loor. Improperly positioned objects can interfere with the advanced airbag sensors.All occupants should sit upright and wear their
•
seat belts properly.
Driver’s SeatPositionSensor
Passenger’s Seat
WeightSensors
Main MenuTable of Contents
Page 51 of 333

Safe Driving
50
Airbags Side Airbags
Side Airbag Cutoff System
■
To prevent a passenger from possible injury by an inflating side airbag, the passenger side airbag is automatically turned off when:
The height sensors detect a child or small statured adult is seated in the
●
passenger seat.The position sensors detect that the passenger is leaning into the deployment
●
path of the side airbag.
When the side airbag cutoff system is activated, the side airbag off indicator comes on.
Side Airbag Off Indicator P. 5 4
Side Airbag Off Indicator
■
If the side airbag off indicator comes on, have the passenger sit upright. A few seconds after the passenger is sitting properly, the side airbag will automatically be turned on, and the indicator will go off. If the passenger is a child, the indicator will remain on so long as the child is seated. Since this vehicle does not have a back seat, we recommend that you do not carry any child who is not large enough and mature enough to ride in front.
Side Airbag Cutoff System
The sensors that monitor the passenger's height and body position may not work if: The seat-back is wet
•
The passenger is touching a metal or other
•
electrical conductive objectA seat cushion is on the seat
•
The passenger is wearing thick clothing
•
Sensors that monitor the
passenger’s height.
Sensors that monitor
the passenger’s position.
Main MenuTable of Contents