2010 SATURN VUE wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 171 of 398

Infotainment System 7-5
©SEEK¨:Press to go to the
previous or to the next station.
To scan stations, press and hold
either arrow for a few seconds until
a beep sounds. The radio goes to a
station, plays for a few seconds,
then goes to the next station. Press
either arrow again to stop scanning.
The radio only seeks and scans
stations with a strong signal that are
in the selected band.
4(Information) (XM™ Satellite
Radio Service, MP3, and RDS
Features): Press to display
additional text information related to
the current FM-RDS station, XM
station, or MP3 song. If information
is available, the song title
information displays on the top line
of the display and artist information
displays on the bottom line. When
information is not available, “NO
INFO” displays.
Storing a Radio Station as a
Favorite
Drivers are encouraged to set up
their radio station favorites while the
vehicle is in P (Park). Tune to
favorite stations using the presets,
favorites button, and steering wheel
controls. See Steering Wheel
Controls on page 5‑3.
FAV (Favorites): A maximum of
36 stations can be programmed as
favorites using the six pushbuttons
positioned below the radio station
frequency labels and by using the
radio favorites page button (FAV
button). Press to go through up to
six pages of favorites, each having
six favorite stations available per
page. Each page of favorites can
contain any combination of AM, FM,
or XM stations, if equipped. The balance/fade and tone settings
that were previously adjusted, are
stored with the favorite stations.
To store a station as a favorite:
1. Tune to a radio station.
2. Press FAV to display the page
where to store the station.
3. Press and hold one of the six pushbuttons until a beep
sounds. When that pushbutton is
pressed and released, the
station that was set, returns.
4. Repeat the steps for each radio station to be stored as a favorite.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 174 of 398

7-8 Infotainment System
Storing a Radio Station as a
Favorite
Drivers are encouraged to set up
their radio station favorites while the
vehicle is in P (Park). Tune to
favorite stations using the presets,
favorites button, and steering wheel
controls. SeeSteering Wheel
Controls on page 5‑3.
FAV (Favorites): A maximum of
36 stations can be programmed as
favorites using the six pushbuttons
positioned below the radio station
frequency labels and by using the
radio favorites page button (FAV
button). Press to go through up to
six pages of favorites, each having
six favorite stations available per
page. Each page of favorites can
contain any combination of AM, FM,
or XM stations.
The balance/fade and tone settings
that were previously adjusted, are
stored with the favorite stations. To store a station as a favorite:
1. Tune to a radio station.
2. Press FAV to display the page
where to store the station.
3. Press and hold one of the six pushbuttons until a beep
sounds. When that pushbutton is
pressed and released, the
station that was set, returns.
4. Repeat the steps for each radio station to be stored as a favorite.
To setup the number of favorites
pages:
1. Press MENU to display the radio setup menu.
2. Press the pushbutton located below the FAV 1-6 label.
3. Select the desired number of favorites pages by pressing the
pushbutton located below the
displayed page numbers. 4. Press FAV, or let the menu time
out, to return to the original main
radio screen showing the
radio station frequency labels
and to begin the process of
programming favorites for the
chosen amount of numbered
pages.
XM™ Radio Messages
XL (Explicit Language
Channels): These channels, or any
others, can be blocked at a
customer's request, by calling
1-800-852-XMXM (9696).
XM Updating: The encryption code
in the receiver is being updated, and
no action is required. This process
should take no longer than
30 seconds.
No XM Signal: The system is
functioning correctly, but the vehicle
is in a location that is blocking the
XM™ signal. When the vehicle is
moved into an open area, the signal
should return.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 184 of 398
7-18 Infotainment System
Phone
Bluetooth
Vehicles with a Bluetooth system
can use a Bluetooth capable cell
phone with a Hands Free Profile to
make and receive phone calls. The
system can be used while the key is
in ON/RUN or ACC/ACCESSORY
position. The range of the Bluetooth
system can be up to 9.1 m (30 ft.).
Not all phones support all functions,
and not all phones are guaranteed
to work with the in-vehicle Bluetooth
system. See www.gm.com/bluetooth
for more information on compatible
phones.
Voice Recognition
The Bluetooth system uses voice
recognition to interpret voice
commands to dial phone numbers
and name tags.
Noise:Keep interior noise levels to
a minimum. The system may not
recognize voice commands if there
is too much background noise. When to Speak:
A short tone
sounds after the system responds
indicating when it is waiting for a
voice command. Wait until the tone
and then speak.
How to Speak: Speak clearly in a
calm and natural voice.
Audio System
When using the in‐vehicle Bluetooth
system, sound comes through the
vehicle's front audio system
speakers and overrides the audio
system. Use the audio system
volume knob, during a call, to
change the volume level. The
adjusted volume level remains in
memory for later calls. To prevent
missed calls, a minimum volume
level is used if the volume is turned
down too low.
Bluetooth Controls
Use the buttons located on the
steering wheel to operate the
in‐vehicle Bluetooth system. See
Steering Wheel Controls
on
page 5‑3for more information.
J/0(Push To Talk) : Press to
answer incoming calls, confirm
system information, and to start
speech recognition.
− /
K(Phone On Hook): Press to
end a call and to cancel an
operation.
Pairing
A Bluetooth enabled cell phone
must be paired to the in‐vehicle
Bluetooth system first and then
connected to the vehicle before it
can be used. See the cell phone
manufacturers user guide for
Bluetooth functions before pairing
the cell phone. If a Bluetooth phone
is not connected, calls will be made
using OnStar
®Hands‐Free Calling,
if available. Refer to the OnStar
owner's guide for more information.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 205 of 398

Driving and Operating 9-1
Driving and
Operating
Driving Information
Driver Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Driving Environment . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Vehicle Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Defensive Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Drunk Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Control of a Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
Off-Road Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-6
Loss of Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-7
Off-Road Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-8
Driving on Wet Roads . . . . . . . 9-18
Highway Hypnosis . . . . . . . . . . . 9-18
Hill and Mountain Roads . . . . . 9-19
Winter Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-20
If the Vehicle is Stuck . . . . . . . . 9-22
Vehicle Load Limits . . . . . . . . . . 9-22
Starting and Operating
New Vehicle Break-In . . . . . . . . 9-27
Ignition Positions . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-28
Retained AccessoryPower (RAP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-29 Starting the Engine . . . . . . . . . . 9-29
Engine Coolant Heater . . . . . . . 9-30
Shifting Into Park . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-31
Shifting Out of Park . . . . . . . . . . 9-33
Parking Over Things
That Burn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-33
Engine Exhaust
Engine Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
Running the Vehicle WhileParked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
Automatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission . . . . . 9-35
Manual Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-37
Drive Systems
All-Wheel Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-38
Brakes
Antilock BrakeSystem (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-38
Parking Brake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-39
Ride Control Systems
Traction Control System (TCS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-40
StabiliTrak System . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
Cruise Control
Cruise Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-42
Object Detection Systems
Rear Vision Camera (RVC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-44
Fuel
Fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-47
Recommended Fuel . . . . . . . . . 9-48
Gasoline Specifications . . . . . . 9-48
California FuelRequirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-48
Fuels in Foreign Countries . . . 9-49
Fuel Additives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-49
Filling the Tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-50
Filling a Portable Fuel Container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
Towing
General TowingInformation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
Driving Characteristics and Towing Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-53
Trailer Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-56
Towing Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . 9-60
Trailer Sway Control (TSC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-60
Conversions and Add-Ons
Add-On ElectricalEquipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-61
ProCarManuals.com
Page 206 of 398

9-2 Driving and Operating
Driving Information
Driver Behavior
Whenever we drive, we are taking
on an important responsibility. This
is true for any motor
vehicle—passenger car, van, truck,
sport utility. Driver behavior, the
driving environment, and the
vehicle's design all affect how well a
vehicle performs. But statistics show
that the most important factor, by
far, is how we drive.
Knowing how these three factors
work together can help you
understand how your vehicle
handles and what you can do to
avoid many types of crashes,
including a rollover crash.
The single most important thing is
this: everyone in the vehicle,
including the driver, should buckle
up. See Safety Belts
on page 3‑10.
In fact, most serious injuries and
fatalities to unbelted occupants can
be reduced or prevented by the use of safety belts. In a rollover crash,
an unbelted person is significantly
more likely to die than a person
wearing a seat belt. In addition,
avoiding excessive speed, sudden
or abrupt turns, and drunken or
aggressive driving can help make
trips safer and avoid the possibility
of a crash, especially a rollover
crash. This section provides many
useful tips to help you drive more
safely.
Driving Environment
You can also help avoid a rollover or
other type of crash by being
prepared for driving in inclement
weather, at night, or during other
times where visibility or traction may
be limited, such as on curves,
slippery roads, or hilly terrain.
Unfamiliar surroundings can also
have hidden hazards.
To help you learn more about
driving in different conditions, this
section contains information about
city, freeway, and off-road driving,
as well as other hints for driving in
various weather conditions.
Vehicle Design
According to the U.S. Department of
Transportation, utility vehicles have
a significantly higher rollover rate
than other types of vehicles. Utility
vehicles do have higher ground
clearance and a narrower track or
shorter wheelbase than passenger
cars, to make them more capable
for off-road driving. Specific design
characteristics like these give the
driver a better view of the road, but
also give utility vehicles a higher
center of gravity than other types of
vehicles. This means that you
should not expect a utility vehicle to
handle the same way a vehicle with
a lower center of gravity, like a car,
would in similar situations.
But driver behavior factors are far
more often the cause of a utility
vehicle rollover than are
environmental or vehicle factors.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 209 of 398

Driving and Operating 9-5
If the engine ever stops while the
vehicle is being driven, brake
normally but do not pump the
brakes. If the brakes are pumped,
the pedal could get harder to push
down. If the engine stops, there will
still be some power brake assist but
it will be used when the brake is
applied. Once the power assist is
used up, it can take longer to stop
and the brake pedal will be harder
to push.
Adding non‐dealer/non‐retailer
accessories can affect vehicle
performance. SeeAccessories and
Modifications on page 10‑3.
Steering
Electric Power Steering
If the vehicle has the electric power
steering system and the engine
stalls while driving, the power
steering assist system will continue to operate until you are able to stop
the vehicle. If power steering assist
is lost because the electric power
steering system is not functioning,
the vehicle can be steered but it will
take more effort.
If you turn the steering wheel in
either direction several times until it
stops, or hold the steering wheel in
the stopped position for an
extended amount of time, you may
notice a reduced amount of power
steering assist. The normal amount
of power steering assist should
return shortly after a few normal
steering movements.
The electric power steering system
does not require regular
maintenance. If you suspect
steering system problems and/or the
Service Vehicle Soon light comes
on, contact your dealer/retailer for
service repairs.
Hydraulic Power Steering
If the vehicle has the hydraulic
power steering system and power
steering assist is lost because the
engine stops or the power steering
system is not functioning, the
vehicle can be steered but it will
take more effort.
Steering Tips
It is important to take curves at a
reasonable speed.
Traction in a curve depends on the
condition of the tires and the road
surface, the angle at which the
curve is banked, and vehicle speed.
While in a curve, speed is the one
factor that can be controlled.
If there is a need to reduce speed,
do it before entering the curve, while
the front wheels are straight.
Try to adjust the speed so you can
drive through the curve. Maintain a
reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until out of the curve, and
then accelerate gently into the
straightaway.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 210 of 398
9-6 Driving and Operating
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can
be more effective than braking. For
example, you come over a hill and
find a truck stopped in your lane,
or a car suddenly pulls out from
nowhere, or a child darts out from
between parked cars and stops right
in front of you. These problems can
be avoided by braking—if you can
stop in time. But sometimes you
cannot stop in time because there is
no room. That is the time for
evasive action —steering around
the problem.
The vehicle can perform very well in
emergencies like these. First apply
the brakes. See Braking
on
page 9‑4. It is better to remove as
much speed as possible from a
collision. Then steer around the
problem, to the left or right
depending on the space available.
An emergency like this requires
close attention and a quick decision.
If holding the steering wheel at the
recommended 9 and 3 o'clock
positions, it can be turned a full
180 degrees very quickly without
removing either hand. But you have
to act fast, steer quickly, and just as
quickly straighten the wheel once
you have avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency
situations are always possible is a
good reason to practice defensive
driving at all times and wear safety
belts properly.
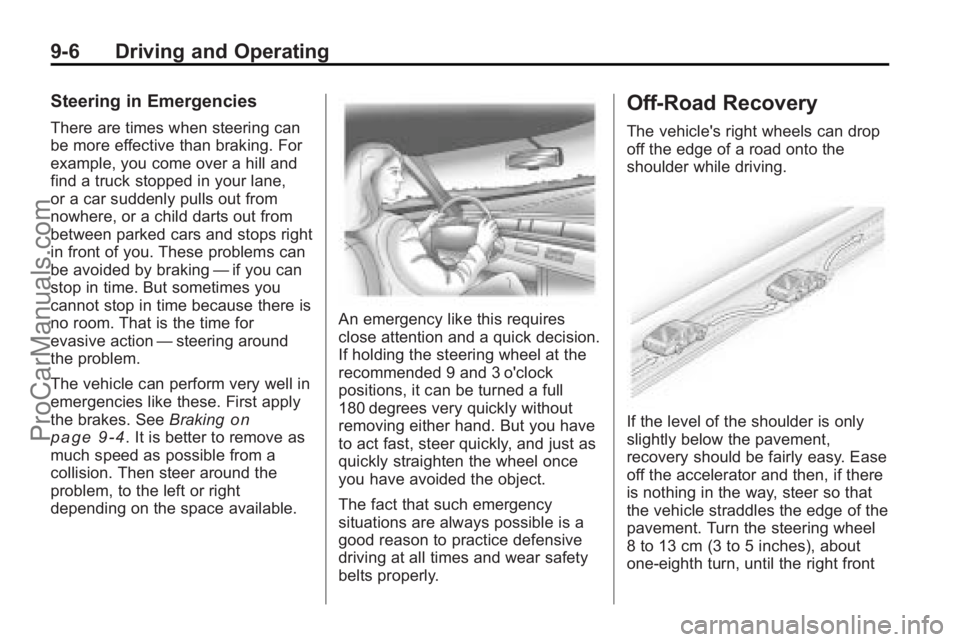
Off-Road Recovery
The vehicle's right wheels can drop
off the edge of a road onto the
shoulder while driving.
If the level of the shoulder is only
slightly below the pavement,
recovery should be fairly easy. Ease
off the accelerator and then, if there
is nothing in the way, steer so that
the vehicle straddles the edge of the
pavement. Turn the steering wheel
8 to 13 cm (3 to 5 inches), about
one-eighth turn, until the right front
ProCarManuals.com
Page 211 of 398

Driving and Operating 9-7
tire contacts the pavement edge.
Then turn the steering wheel to go
straight down the roadway.
Loss of Control
Let us review what driving experts
say about what happens when the
three control systems—brakes,
steering, and acceleration —do not
have enough friction where the tires
meet the road to do what the driver
has asked.
In any emergency, do not give up.
Keep trying to steer and constantly
seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of
the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions,
and by not overdriving those
conditions. But skids are always
possible. The three types of skids correspond
to the vehicle's three control
systems. In the braking skid, the
wheels are not rolling. In the
steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes
tires to slip and lose cornering force.
And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin.
If the vehicle starts to slide, ease
your foot off the accelerator pedal
and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start
steering quickly enough, the vehicle
may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when
water, snow, ice, gravel, or other
material is on the road. For safety,
slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to
slow down on slippery surfaces
because stopping distance is longer
and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with
reduced traction, try your best to
avoid sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing
vehicle speed by shifting to a lower
gear. Any sudden changes could
cause the tires to slide. You might
not realize the surface is slippery
until the vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues
—such as
enough water, ice, or packed snow
on the road to make a mirrored
surface —and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any Antilock Brake
System (ABS) helps avoid only the
braking skid.
ProCarManuals.com