Page 210 of 318

Brakes
This vehicle has disc brakes.
Disc brake pads have built-in wear
indicators that make a high-pitched
warning sound when the brake pads
are worn and new pads are needed.
The sound can come and go or be
heard all the time the vehicle is
moving, except when applying the
brake pedal firmly.
{CAUTION
The brake wear warning sound
means that soon the brakes will
not work well. That could lead to
an accident. When the brake wear
warning sound is heard, have the
vehicle serviced.
Notice: Continuing to drive
with worn-out brake pads could
result in costly brake repair. Some driving conditions or climates
can cause a brake squeal when
the brakes are first applied or
lightly applied. This does not mean
something is wrong with the brakes.
Properly torqued wheel nuts are
necessary to help prevent brake
pulsation. When tires are rotated,
inspect brake pads for wear and
evenly tighten wheel nuts in the
proper sequence to torque
specifications in
Capacities and
Speci�cations on page 11-2 .
Brake linings should always be
replaced as complete axle sets.
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer/retailer if the brake
pedal does not return to normal
height, or if there is a rapid increase
in pedal travel. This could be a sign
that brake service might be required.
Brake Adjustment
Every time the brakes are applied,
with or without the vehicle moving,
the brakes adjust for wear.
Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a vehicle is
complex. Its many parts have to be
of top quality and work well together
if the vehicle is to have really good
braking. The vehicle was designed
and tested with top-quality brake
parts. When parts of the braking
system are replaced, be sure to get
new, approved replacement parts.
If this is not done, the brakes might
not work properly. For example,
installing disc brake pads that are
wrong for the vehicle, can change
the balance between the front and
rear brakes — for the worse. The
braking performance expected can
change in many other ways if the
wrong replacement brake parts are
installed.
9-26 Vehicle Care
Page 239 of 318
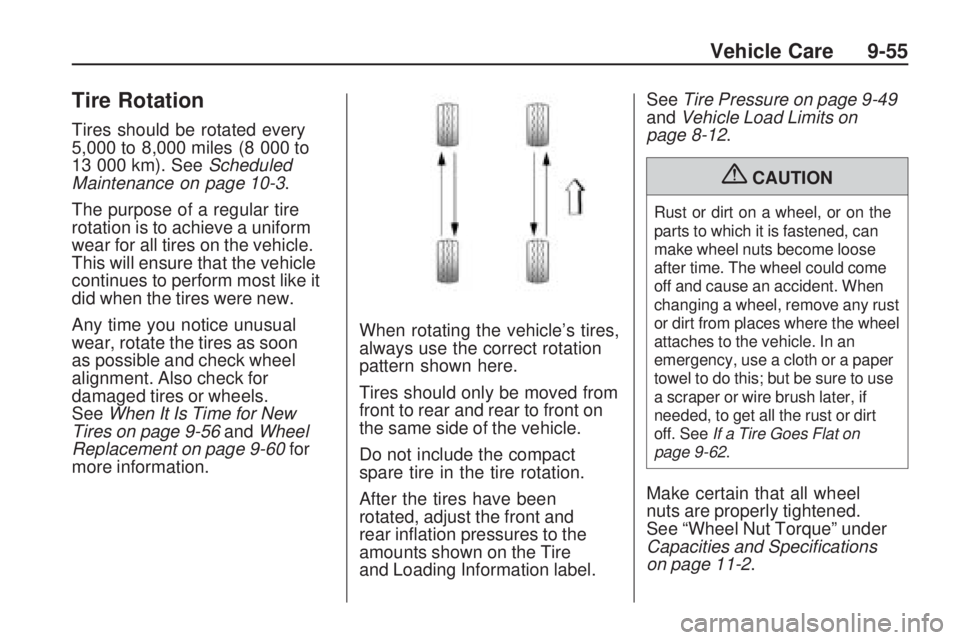
Tire Rotation
Tires should be rotated every
5,000 to 8,000 miles (8 000 to
13 000 km). SeeScheduled
Maintenance on page 10-3.
The purpose of a regular tire
rotation is to achieve a uniform
wear for all tires on the vehicle.
This will ensure that the vehicle
continues to perform most like it
did when the tires were new.
Any time you notice unusual
wear, rotate the tires as soon
as possible and check wheel
alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels.
See When It Is Time for New
Tires on page 9-56 andWheel
Replacement on page 9-60 for
more information. When rotating the vehicle’s tires,
always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Tires should only be moved from
front to rear and rear to front on
the same side of the vehicle.
Do not include the compact
spare tire in the tire rotation.
After the tires have been
rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures to the
amounts shown on the Tire
and Loading Information label.See
Tire Pressure on page 9-49
and Vehicle Load Limits on
page 8-12.
{CAUTION
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the
parts to which it is fastened, can
make wheel nuts become loose
after time. The wheel could come
off and cause an accident. When
changing a wheel, remove any rust
or dirt from places where the wheel
attaches to the vehicle. In an
emergency, use a cloth or a paper
towel to do this; but be sure to use
a scraper or wire brush later, if
needed, to get all the rust or dirt
off. See If a Tire Goes Flat on
page 9-62.
Make certain that all wheel
nuts are properly tightened.
See “Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and Speci�cations
on page 11-2.
Vehicle Care 9-55
Page 251 of 318
12. Reinstall the wheel nuts withthe rounded end of the nuts
toward the wheel. Tighten each
nut by hand until the wheel
is held against the hub.
13. Turn the jack handle counterclockwise. Lower
the jack completely.{CAUTION
Wheel nuts that are improperly
or incorrectly tightened can cause
the wheels to become loose or
come off. The wheel nuts should
be tightened with a torque wrench
to the proper torque specification
after replacing. Follow the torque
specification supplied by the
aftermarket manufacturer when
using accessory locking wheel
nuts. See Capacities and
Speci�cations on page 11-2 for
original equipment wheel nut
torque specifications.
Notice: Improperly tightened
wheel nuts can lead to brake
pulsation and rotor damage.
To avoid expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel nuts in
the proper sequence and to
the proper torque speci�cation.
See
Capacities and Specifications
on page 11-2 for the wheel nut
torque speci�cation.
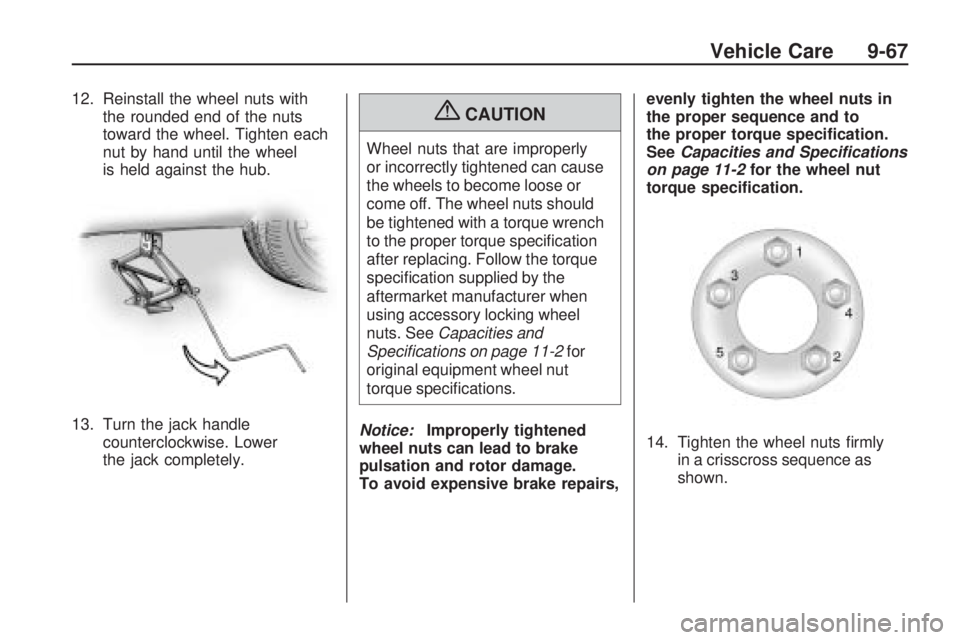
14. Tighten the wheel nuts firmly in a crisscross sequence as
shown.
Vehicle Care 9-67
Page 291 of 318
ApplicationCapacities
English Metric
Transmission, Automatic (Complete Drain and Refill) 1.8L L4 Engine 3.1 qt2.9 L
2.4L L4 Engine 3.7 qt3.5 L
Transmission, Manual (Complete Drain and Refill) 1.8L L4 Engine 2.0 qt1.9 L
2.4L L4 Engine 2.6 qt2.5 L
Wheel Nut Torque 76 lb ft103Y
All capacities are approximate. When adding, be sure to fill to the approximate level, as recommended in this
manual.
Engine Speci�cations
Engine VIN CodeTransmission Spark Plug Gap
1.8L L4 8Automatic
Manual 0.043 in (1.10 mm)
2.4L L4 0Automatic
Manual 0.043 in (1.10 mm)
Technical Data 11-3