Page 113 of 212

107
Driving and operation
Save energy – more kilometres
Please observe the running-in hints on the
previous page and the tips for saving
energy on the following pages.
Good, technically correct and economical
driving ensures maximum durability and
performance for your vehicle.
Overrun cut-off
The fuel supply is automatically cut off
during overrun, e.g. when the vehicle is
driven with a gear engaged but no throttle
application. Overrun cut-off is deactivated
if catalytic converter temperature is high.
Vehicles with turbocharged engine
Flow-generated noises may be audible if
the accelerator is released quickly on
account of air flow in the turbocharger.
Engine speed
Drive in a low engine speed range for each
gear as much as possible. Warming up
Allow the engine to warm up while driving.
Do not warm it up by letting it run at idling
speed. Do not apply full throttle until the
engine has reached operating
temperature.
In automatic mode, the manual
transmission automated 3 does not shift to
the higher gears after a cold start until
higher engine speeds are reached. This
allows the catalytic converter to quickly
reach the temperature that is required for
optimum pollutant reduction.
Correct gear selection
Do not race your engine whilst in neutral or
with a low gear selected. Driving too fast in
individual gears as well as stop-and-go
traffic increases engine wear and fuel
consumption.
Change down
When decreasing speed, shift down into
the next lowest gear. Do not slip the clutch
with a high-revving engine. This is
especially important when hill climbing. Cooling fan
The cooling fan is controlled via a
thermoswitch and therefore only runs if
necessary.
The cooling fan automatically switches on
when the diesel particle filter is being
cleaned 3 depending on the engine.
Pedals
Do not place any objects in the foot well
which could slip under the pedals and
inhibit the pedal travel.
To ensure the pedal travel is uninhibited,
there must be no mats in the area of the
pedals.
Battery care
When driving slowly or when the vehicle is
stationary, e.g. in slow urban traffic, stop-
and-go traffic or traffic jams, turn off all
unnecessary electrical loads where
possible (e.g. heated rear window, heated
front seats, etc.).
Declutch when starting in order to relieve
the strain on the starter and the battery.
Page 114 of 212

108 Driving and operationSaving Fuel, Protecting the
Environment Trend-setting technology
Environmentally friendly and mainly
recyclable materials were used when your
vehicle was being developed and
manufactured. The production methods
used to make your vehicle are also
environmentally-compatible.
Recycling of production wastes keeps the
circulation of material closed. Reduction of
energy and water requirements also helps
to conserve natural resources.
A highly advanced design means that your
vehicle can be easily disassembled at the
end of its working life, and the individual
materials separated for subsequent re-use.
Materials such as asbestos and cadmium
are not used. The refrigerant in the air
conditioning system 3 is CFC-free.
New painting techniques employ water as
a solvent. End-of-life vehicle recovery
Information on end-of-life vehicle recovery
centres and the recycling of end-of-life
vehicles is available at www.opel.com.
Energy and environment-conscious
driving
zHigh noise levels and exhaust emissions
are often a result of driving without due
attention to saving energy and
protecting the environment.
zYou should therefore drive with energy in
mind: "more kilometres – less fuel".
Reduce the noise level and exhaust
emissions by adopting an environment-
conscious driving style. This is extremely
worthwhile and improves the quality of
life.
Fuel consumption depends to a great
extent on your own personal driving
style. The following hints are intended to
help you consume fuel at a rate that is as
close as possible to the specified levels
3186.
Check your vehicle’s fuel consumption
every time you refuel. This facilitates
early detection of any irregularities
causing increased fuel consumption. Warming up
zFull throttle and warming up at idle
speed increase wear, fuel consumption,
exhaust emission, the amount of
pollutant in the exhaust and the amount
of noise.
zDrive off immediately after starting.
Warm up the engine by running it at
moderate engine speeds.
Uniform speed
zHectic driving significantly increases fuel
consumption, the exhaust emissions, the
proportion of pollutant in the exhaust
gas and the noise level.
zDo not accelerate and brake
unnecessarily. Drive at uniform speed,
watching the road.
Avoid frequent starting off and stopping
e.g. at traffic lights, in short distance
traffic and in queues of traffic by means
of clever planning. Select roads with
good traffic flow.
Idling
zThe engine also consumes fuel when
idling.
zIf you have to wait for more than one
minute, it is worthwhile switching off the
engine. Five minutes of idling
corresponds to approximately one
kilometre of driving.
Page 115 of 212

109
Driving and operation
Overrun
zThe fuel supply is automatically shut off
during overrun, e.g. when the vehicle is
being driven down long gradients or
when braking 3107.
zTo enable the overrun cut-off to come
into action and save fuel, do not
accelerate or declutch during overrun.
Correct gear selection
zHigh revs increase engine wear and fuel
consumption.
zDo not race your engine. Avoid driving at
high engine speeds.
Making use of the tachometer helps to
save fuel. Drive in a low engine speed
range for each gear as much as possible
with uniform engine speeds. Drive as
often as possible in top gear, select the
next higher gear as soon as possible,
and only change down when the engine
is no longer running perfectly smoothly.
High speed
zThe higher the speed, the higher the
consumption and the noise level. At top
speed, you consume a great deal of fuel
and produce excessive noise and
exhaust emissions. zSlightly releasing the accelerator pedal
results in distinct fuel savings with no
major loss of speed.
Drive at no more than around three
quarters of maximum speed and you will
use up to 50 % less fuel, without losing a
great deal of time.
Tyre pressure
zInadequate tyre pressure, leading to
higher road resistance, costs money in
two ways: for more fuel and increased
tyre wear.
zRegular checks (every 14 days) pay off.
Electrical loads
zThe power consumption of electrical
equipment increases fuel consumption.
zSwitch off all auxiliary electrical loads
(e.g. air conditioning3, heated rear
window) when not needed.
Roof racks
zDue to air resistance, a roof load can
increase fuel consumption by approx.
1 l/100 km.
zRemove them if they are not being used. Repair and maintenance
zImproper repairs or adjustment and
maintenance work can increase fuel
consumption. Do not carry out work on
the engine yourself.
You may out of ignorance infringe
environmental laws by not disposing of
materials properly.
Appropriate parts might not be recycled.
Contact with some of the materials
involved may pose a health hazard.
zWe recommend that repair and
maintenance be entrusted to your Opel
Partner.
Extreme driving conditions
zGoing up steep slopes, cornering, driving
on poor roads and winter driving all
increase fuel consumption.
Fuel consumption increases dramatically
in urban traffic and at winter
temperatures, especially on short trips
when the engine operating temperature
is not reached.
zFollowing the instructions given above
will minimise consumption under these
conditions.
Page 116 of 212

110 Driving and operationFuels, refuellingFuel consumption
Fuel consumption is determined under
specific driving conditions 3186.
Special equipment increases the weight of
the vehicle. As a result, they can increase
fuel consumption and reduce the specified
maximum speed.
There is increased friction between engine
and transmission parts during the first
1000 kilometres. This increases fuel
consumption. Fuel for petrol engines
Only use unleaded fuel that complies with
DIN EN 228.
Fuels with ethanol content greater than 5 %
may only be used if the vehicle has been
specifically developed and approved for
these fuels.
Use fuel with the recommended octane
rating (value in bold 3184). Use of fuel
with too low an octane rating can reduce
engine power and torque and slightly
increases fuel consumption. Fuel for diesel engines
Only use diesel fuel that complies with
DIN EN 590. The fuel must have low
sulphur content (max. 50 ppm).
Do not use marine diesel oils, heating oils
or entirely or partially plant-based diesel
fuels, such as rape seed oil or bio diesel,
Aquazole and similar diesel-water
emulsions. Diesel fuels must not be diluted
with fuels for petrol engines.
The flow and filterability of diesel fuel are
temperature-dependent. When
temperatures are low, refuel with diesel fuel
with guaranteed winter properties.
Fuel for natural gas operation
Use natural gas with a methane content of
approx. 78-99 %. L-gas (low) has approx.
78-87 % and H-gas (high) has approx.
87-99 %. Biogas with the same methane
content can also be used if it has been
chemically prepared and desulphurised.
Liquid gas or LPG must not be used. Caution
Use of fuel with too low an octane rating
could lead to uncontrolled combustion
and engine damage.
Page 117 of 212

111
Driving and operation
Picture no: 15829t.tif
Fuel filler cap
Only a Opel Genuine fuel filler cap provides
full functionality. Diesel-engined vehicles
have special fuel filler caps.
Refuelling Fuel filler neck at right rear side of vehicle.
Picture no: 11628s.tif
With the central locking system3, the tank
flap is unlocked together with the doors3
324.
Open the tank flap. To prevent damage,
the right-hand sliding door cannot be fully
opened if the tank flap is open.
Unlock the fuel filler cap with the ignition
key 3, unscrew and suspend from tank
flap.
The fuel tank has a limiting system which
prevents overfilling of the tank.
6
9 Warning
Before refuelling, switch off engine and
any external heaters with combustion
chambers 3 (identified by sticker on
tank flap). Switch off any mobile
phones.
Follow the operating and safety
instructions of the filling station when
refueling.
9 Warning
Fuel is flammable and explosive. No
smoking. No naked flames or sparks.
If you can smell fuel in your vehicle, have
the cause of this rectified immediately
by a workshop.
Page 118 of 212

112 Driving and operationCorrect filling depends to a large extent on
proper operation of the fuel dispensing
pump:
1. Fully insert the pump nozzle and switch it
on.
2. After the automatic cut-off, the nominal
capacity of the fuel tank can be
obtained by topping up with two doses
of fuel. Make sure the nozzle is fully
inserted.
To close, place fuel filler cap in position and
turn, overcoming the resistance until the
ratchet on the cap engages audibly. Lock
the fuel filler cap with the ignition key 3.
Close fuel tank cover. Refuelling, natural gas 3
The fuel tank filler neck for natural gas and
petrol is located on the right rear side of the
vehicle.
Picture no: 12292t.tif
Remove the cap from the natural gas filler
neck.
The tank action must be fully completed,
e.g. bleeding the filler neck.
After refuelling, refit the cap. Caution
Wipe off any overflowing fuel
immediately.
9 Warning
Care must be taken when handling
natural gas!
Before refuelling, be sure to switch off
the engine and any auxiliary heater with
combustion chamber.
Natural gas is flammable and explosive.
Therefore, avoid naked flames and
sparks when handling or in the vicinity of
natural gas. Do not smoke! This also
applies where natural gas can only be
detected by its characteristic smell.
If there is a smell of natural gas in the
vehicle, have cause established
immediately by a workshop that is
authorised to maintain natural gas
vehicles and have the problem
remedied.
9 Warning
When refuelling vehicles with natural
gas, be sure to follow the operational
and safety regulations of the filling
station.
The gas tank must only be replenished
at filling stations that refuel with
temperature compensation with a
maximum output pressure of 250 bar.
Page 119 of 212
113 Driving and operation
Refuelling when driving abroad
When refuelling in another country, please note that country-specific expressions are used
for natural gas vehicles.
German Erdgasfahrzeuge Erdgas als Kraftstoff
English NGVs = Natural Gas Vehicles CNG = Compressed Natural Gas
French Véhicules au gaz naturel
– or –
Véhicules GNVGNV = Gaz Naturel (pour) Véhicules
– or –
CGN = carburant gaz naturel
Italian Metano auto Metano (per auto)
Picture no: 16882s.tif
Fuel selector switch, natural gas 3
Switch
Y can be used to switch between
petrol and natural gas operation. A
changeover is not possible during a high
load, such as powerful acceleration or full
throttle. The status of the LED indicates
which type of fuel is in use.
As soon as the natural gas tank is empty,
the vehicle automatically switches to petrol
operation until the ignition is switched off.
This is indicated by prolonged flashing of
the LED.
6 Natural gas
operation=LED off.
Petrol operation = LED comes on.
Page 120 of 212

114 Driving and operationIf the natural gas tank is then not refilled,
petrol operation must be manually
selected the next time the engine is started.
This is necessary in order to prevent
damage to the catalytic converter
(overheating due to irregular fuel supply).
If the switch is pressed several times within
a brief period of time, a changeover
inhibitor is activated. The engine continues
with the current type of fuel. The inhibitor
remains active until the ignition is switched
off.
Minor power and torque losses are to
be expected during petrol operation,
therefore adjust driving style (e.g.
overtaking) and vehicle load (e.g. through
trailer load) accordingly.
Every 6 months, run the petrol tank down
to the reserve zone before refuelling. This is
necessary for petrol operation to obtain
the required system functionality and fuel
quality.Note:
Refuel and operate only w i t h f u e l o f a t l e a s t
95 octane (RON). Upon accidental
refuelling with petrol of an
octane rating (RON) less than 95, avoid
driving with fuel load (e.g. heavy
acceleration, full throttle), allow the tank to
reach the reserve zone and refuel with the
correct petrol.
In order to prevent corrosion in the tank,
please refuel the vehicle to the maximum
level at regular intervals.
Picture no: 6448u.tif
Catalytic converter, engine
exhaust Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter reduces the
amount of harmful substances in the
exhaust gas, such as carbon monoxide
(CO), hydrocarbons, (CH) and nitrous
oxide (NO
x).
Fuel grades other than those listed on
3110, 184 (e. g. LRP = Lead Replacement
Petrol or leaded fuel) could damage the
catalytic converter or electronic
components.
Caution
Damage to the catalytic converter or the
vehicle may result if the following points
are not observed.
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197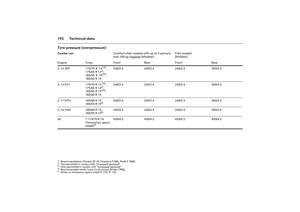 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211






