2010 JAGUAR XFR Xenon
[x] Cancel search: XenonPage 486 of 3039

2 Main piston 3 Tube 4 Bypass valve (closed) 5 Piston and rod assembly ACCELEROMETERS
Three accelerometers are used in the adaptive dynamics system. The accelerometers are located as follows:
One each on the rear edge of the radiator support panel.
One in the luggage compartment, in the rear LH corner adjacent to the rear lamp assembly.
The accelerometers measure acceleration in the vertical plane and output a corresponding analogue signal to the adaptive
damping module. The algorithms in the adaptive damping module calculate the heave, pitch and roll motions of the vehicle,
which are used by the module to control road induced body modes.
Each accelerometer is connected to the adaptive damping module via three wires, which supply ground, 5 V supply and signal
return.
The sensing element comprises a single parallel plate capacitor, one plate of which moves relative to the other dependant on
the force (acceleration) applied. This causes the capacitance to change as a function of applied acceleration. This capacitance
is compared with a fixed reference capacitor in a bridge circuit and the signal is processed by means of a dedicated integrated
circuit to generate an output voltage that varies as a function of applied acceleration. The sensors output a signal voltage of
approximately 1 V/g ± 0.05 V/g.
SUSPENSION HEIGHT SENSORS
Four suspension height sensors are used in the adaptive dynamics system, two for the front suspension and two for the rear
suspension. A front suspension height sensor is attached to each side of the front subframes and connected by a sensor arm
and sensor link to the related lower lateral arm of the front suspension. A rear suspension height sensor is attached to each
side of the rear subframe and connected by a sensor arm and sensor link to the related upper control arm of the rear
suspension. On each suspension height sensor, the sensor arm and sensor link convert linear movement of the suspension into
rotary movement of the sensor shaft.
The sensors are also used for the static dynamic headlamp leveling system on vehicles fitted with xenon headlamps.
The suspension height sensors measure suspension displacement at each corner of the vehicle and output a corresponding
analogue signal to the adaptive damping module. The algorithms in the adaptive damping module calculate the position,
velocity and frequency content of the signals and use the results for wheel control.
Each suspension height sensor is connected to the adaptive damping module via three wires, which supply ground, 5 V supply
Page 2019 of 3039
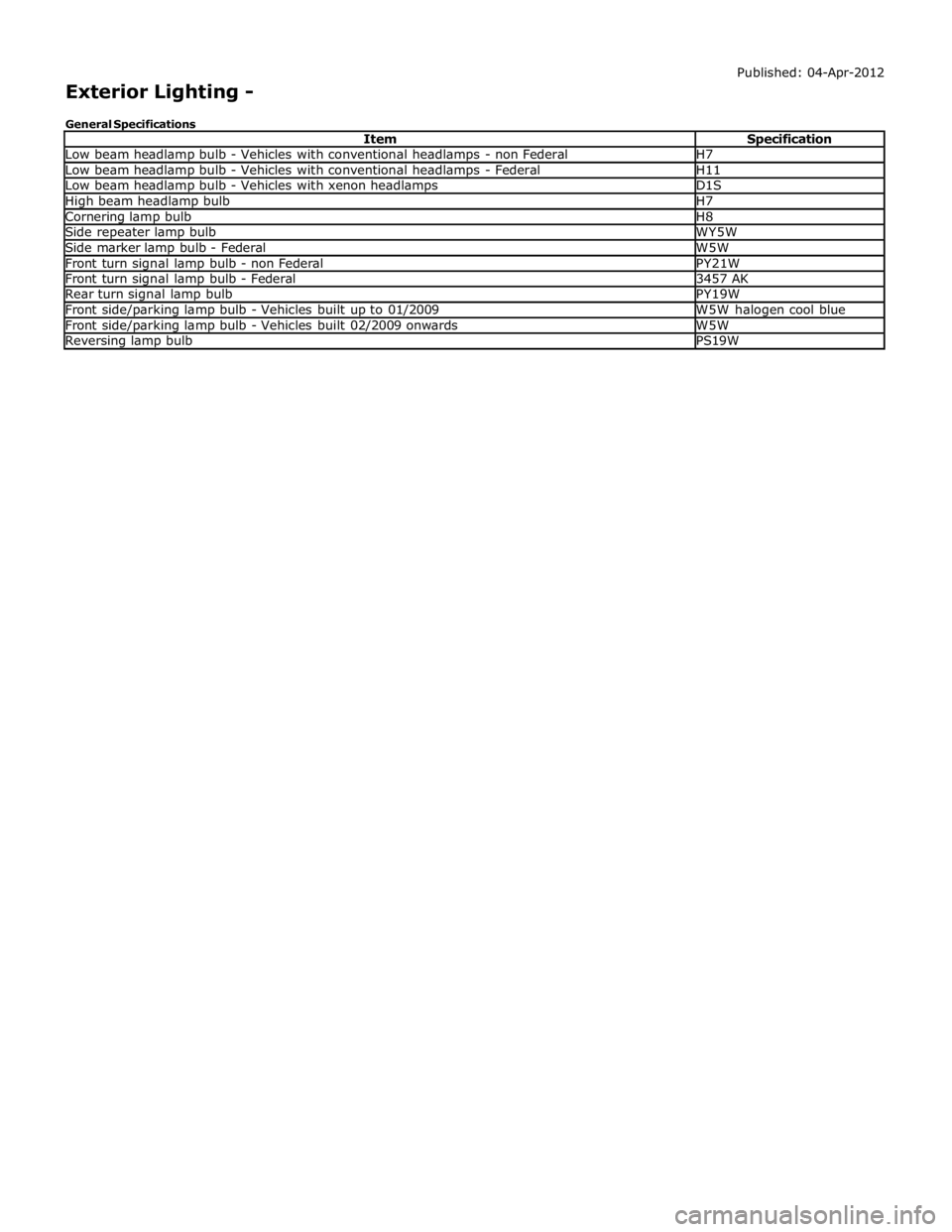
Low beam headlamp bulb - Vehicles with conventional headlamps - non Federal H7 Low beam headlamp bulb - Vehicles with conventional headlamps - Federal H11 Low beam headlamp bulb - Vehicles with xenon headlamps D1S High beam headlamp bulb H7 Cornering lamp bulb H8 Side repeater lamp bulb WY5W Side marker lamp bulb - Federal W5W Front turn signal lamp bulb - non Federal PY21W Front turn signal lamp bulb - Federal 3457 AK Rear turn signal lamp bulb PY19W Front side/parking lamp bulb - Vehicles built up to 01/2009 W5W halogen cool blue Front side/parking lamp bulb - Vehicles built 02/2009 onwards W5W Reversing lamp bulb PS19W
Page 2020 of 3039
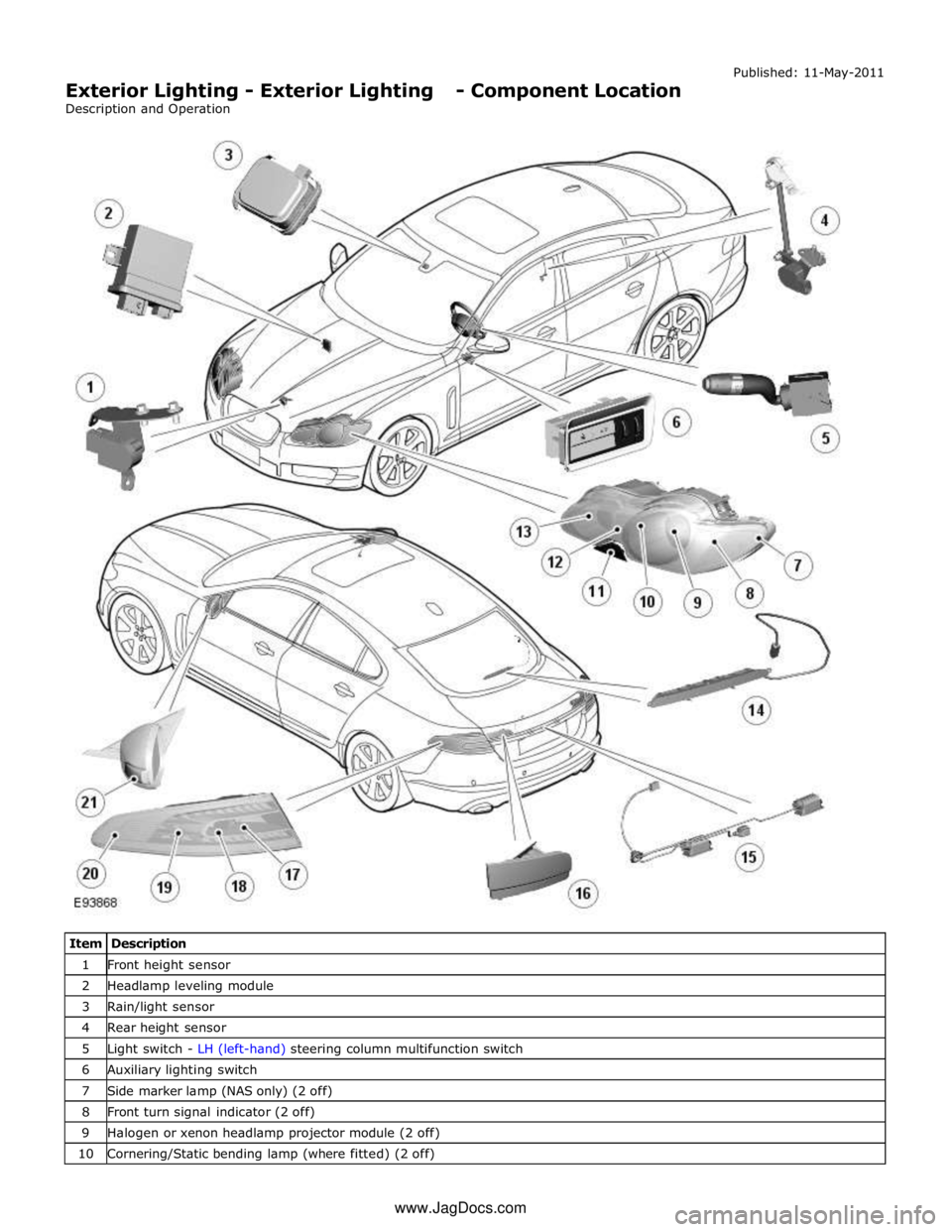
1 Front height sensor 2 Headlamp leveling module 3 Rain/light sensor 4 Rear height sensor 5 Light switch - LH (left-hand) steering column multifunction switch 6 Auxiliary lighting switch 7 Side marker lamp (NAS only) (2 off) 8 Front turn signal indicator (2 off) 9 Halogen or xenon headlamp projector module (2 off) 10 Cornering/Static bending lamp (where fitted) (2 off) www.JagDocs.com
Page 2022 of 3039

The lighting system has an 'auto' lights function which is controlled by the CJB on receipt of signals from the rain/light sensor located at the top of the windscreen. The exterior lights are turned on or off in response to ambient light signals from the
rain/light sensor on a LIN (local interconnect network) bus connection to the CJB . The auto lights can also be activated when the windshield wipers are activated by signals from the rain sensor, which is located at the top of the windshield or when the
driver activates the wipers in the fast wipe position.
Two levels of headlamp specification are available; halogen or xenon. In certain markets the headlamps feature a cornering
lamp or a static bending lamp which illuminates the area at the side of the vehicle when turning into driveways for example.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles have a side marker lamp installed in the headlamp assembly. Replacement of any
of the headlamp bulbs requires removal of the headlamp assembly.
The tail lamp comprises two separate lamp assemblies. The turn signal indicator, side and stop lamps and reverse lamps are
located in each rear fender tail lamp assembly. The rear fog lamps are located in separate units attached to the luggage
compartment lid. A side marker lamp is fitted to the rear fender tail lamp assembly and is fitted in all markets.
Two systems of headlamp leveling are available; manual leveling which is only available on halogen headlamps and static
dynamic leveling which is available on xenon headlamps. The manual system uses a thumbwheel rheostat to adjust the
vertical alignment of the headlamps to compensate for differing vehicle loading. The static dynamic system uses height
sensors fitted to the front and rear suspension and a headlamp leveling module which periodically monitors the vehicle
attitude and adjusts the headlamp vertical alignment accordingly.
Page 2028 of 3039

resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed
CAN bus to the CJB to activate the headlamps. The reference voltage to the auto headlamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that auto headlamp or exit delay has not been selected.
AUTOLAMPS - When the lighting control switch is in the auto headlamp position, the reference voltage flows through 4 of the
resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed
CAN bus to the CJB to activate the autolamp function. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that auto headlamp has been selected.
AUXILIARY LIGHTING SWITCH
Headlamp Leveling Rotary Thumbwheel (Halogen headlamps only)
A power supply is passed to the headlamp leveling thumbwheel from the ignition relay in the EJB. Depending on the position of the thumbwheel, the voltage passes through 1, 2 or 3 resistors connected in series. The voltage through the resistors is
passed to the headlamp leveling motor controller in each headlamp. The received voltage is determined as a request for the
appropriate level position and the controller powers the headlamp level motors to the applicable position for each headlamp.
Rear Fog Lamp Switch
The instrument cluster supplies a reference voltage and return to the rear fog lamp switch. The fog lamp switch is a
non-latching, momentary switch.
When the fog lamp switch is off the reference voltage is passed through a 1Kohm resistor. The voltage through the resistor is
returned to the instrument cluster that determines that no request for fog lamp operation has been made.
When the driver presses the fog lamp switch, the reference voltage is passed through a 330 ohm resistor. The change is return
voltage is sensed by the instrument cluster which determines fog lamp operation has been requested. The instrument cluster
transmits a medium speed CAN bus signal to the RJB providing the lighting control switch is in the correct position. The RJB reacts to the message and provides a power supply to the 3 LED (light emitting diode)'s in each rear fog lamp. A fog lamp
warning lamp in the instrument cluster will also be illuminated when the fog lamps are operating.
The RJB will only activate the rear fog lamps if the headlamps are selected on or are active with auto headlamp activation. When the headlamps are turned off the fog lamps are also turned off. When the headlamps are next switched on, the fog
lamps will not be activated until the driver requests fog lamp operation.
NOTE: The fog lamps do operate when DRL (daytime running lamps) are active.
HEADLAMP LEVELING
Manual Headlamp Leveling - Halogen headlamps only
A power supply is passed to the headlamp leveling motor in each headlamp from the ignition relay in the EJB. When a signal voltage is received from the headlamp leveling rotary thumbwheel, the headlamp leveling motor controller in each headlamp
uses the power supply to operate the motors and move the headlamp to the requested position.
Static Dynamic Headlamp Leveling - Xenon headlamps only
The headlamp leveling module receives a power supply from the ignition relay in the EJB. The same power supply is also supplied to the headlamp leveling motor in each headlamp assembly. The front and rear height sensors are connected to the
headlamp leveling module and receive a power and ground from the module. Each sensor has a signal line to the headlamp
leveling module to return height information to the module. The module uses the height signals from the sensors to calculate
the vehicle attitude and supplies a signal to each motor to power the headlamp to the required position.
EXTERIOR BULB TYPE/RATING Component Description
The following table shows the bulbs used for the exterior lighting system and their type and specification.
NOTE: The tail lamps, side marker lamps, stop lamps, high mounted stop lamp and rear fog lamps are illuminated by
LED's and are non-serviceable components.
Bulb Type Rating Halogen headlamp - Projector module low/high beam - Not NAS H7 55W Halogen headlamp - Projector module low/high beam - NAS only H11 60W Xenon headlamp - Projector module low/high beam - All markets D1S 35W High beam only (halogen) - High/low beam (xenon) - All markets H7 55W Front side lamps - all markets W5W Halogen cool blue (HCB) 5W Front turn signal indicators - Not NAS PY21W 21W Front turn signal indicators - NAS only 3457AK 27W Rear turn signal indicators - All markets PSY19W 19W Turn signal indicator side repeaters - All markets WY5W 5W
Page 2030 of 3039
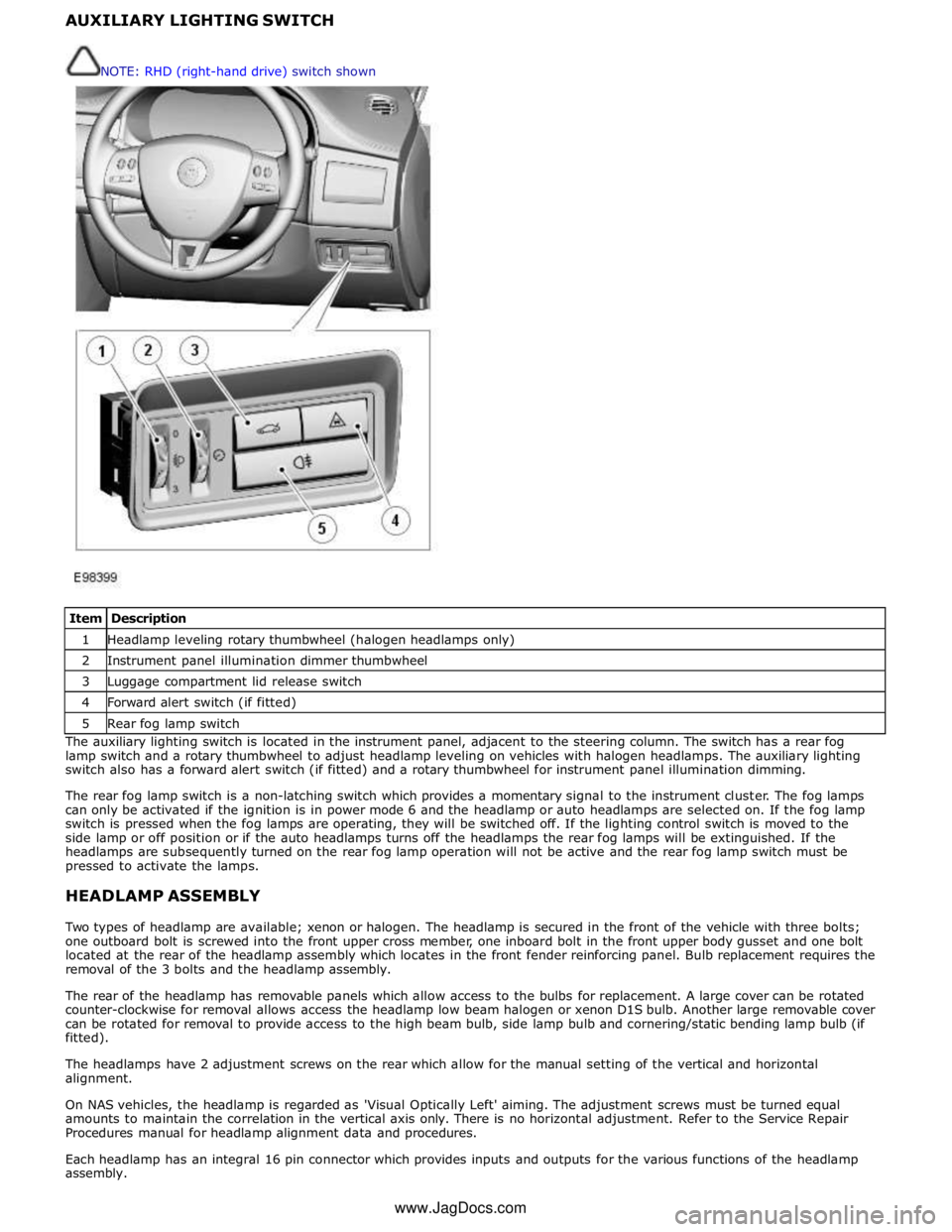
1 Headlamp leveling rotary thumbwheel (halogen headlamps only) 2 Instrument panel illumination dimmer thumbwheel 3 Luggage compartment lid release switch 4 Forward alert switch (if fitted) 5 Rear fog lamp switch The auxiliary lighting switch is located in the instrument panel, adjacent to the steering column. The switch has a rear fog
lamp switch and a rotary thumbwheel to adjust headlamp leveling on vehicles with halogen headlamps. The auxiliary lighting
switch also has a forward alert switch (if fitted) and a rotary thumbwheel for instrument panel illumination dimming.
The rear fog lamp switch is a non-latching switch which provides a momentary signal to the instrument cluster. The fog lamps
can only be activated if the ignition is in power mode 6 and the headlamp or auto headlamps are selected on. If the fog lamp
switch is pressed when the fog lamps are operating, they will be switched off. If the lighting control switch is moved to the
side lamp or off position or if the auto headlamps turns off the headlamps the rear fog lamps will be extinguished. If the
headlamps are subsequently turned on the rear fog lamp operation will not be active and the rear fog lamp switch must be
pressed to activate the lamps.
HEADLAMP ASSEMBLY
Two types of headlamp are available; xenon or halogen. The headlamp is secured in the front of the vehicle with three bolts;
one outboard bolt is screwed into the front upper cross member, one inboard bolt in the front upper body gusset and one bolt
located at the rear of the headlamp assembly which locates in the front fender reinforcing panel. Bulb replacement requires the
removal of the 3 bolts and the headlamp assembly.
The rear of the headlamp has removable panels which allow access to the bulbs for replacement. A large cover can be rotated
counter-clockwise for removal allows access the headlamp low beam halogen or xenon D1S bulb. Another large removable cover
can be rotated for removal to provide access to the high beam bulb, side lamp bulb and cornering/static bending lamp bulb (if
fitted).
The headlamps have 2 adjustment screws on the rear which allow for the manual setting of the vertical and horizontal
alignment.
On NAS vehicles, the headlamp is regarded as 'Visual Optically Left' aiming. The adjustment screws must be turned equal
amounts to maintain the correlation in the vertical axis only. There is no horizontal adjustment. Refer to the Service Repair
Procedures manual for headlamp alignment data and procedures.
Each headlamp has an integral 16 pin connector which provides inputs and outputs for the various functions of the headlamp
assembly. NOTE: RHD (right-hand drive) switch shown
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2031 of 3039
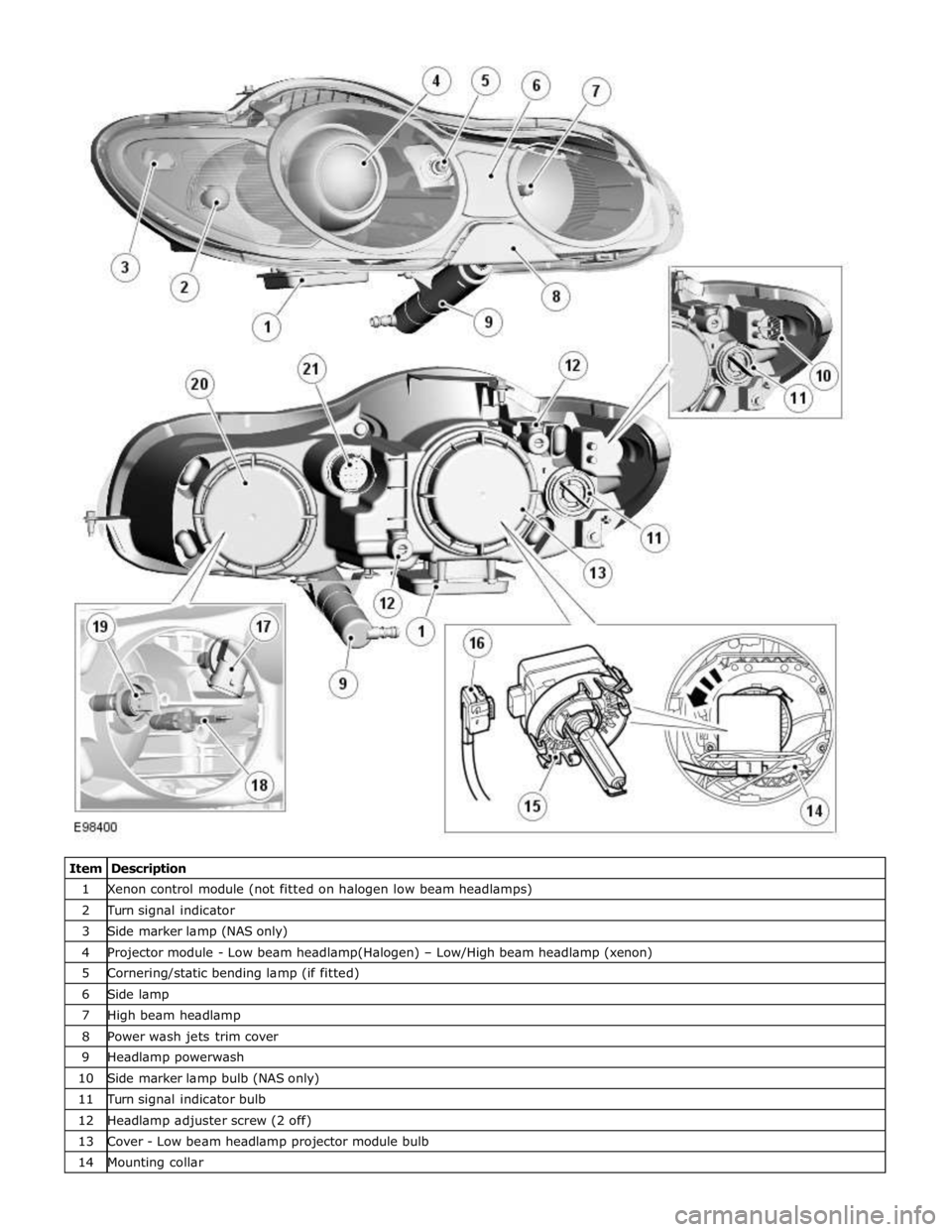
1 Xenon control module (not fitted on halogen low beam headlamps) 2 Turn signal indicator 3 Side marker lamp (NAS only) 4 Projector module - Low beam headlamp(Halogen) – Low/High beam headlamp (xenon) 5 Cornering/static bending lamp (if fitted) 6 Side lamp 7 High beam headlamp 8 Power wash jets trim cover 9 Headlamp powerwash 10 Side marker lamp bulb (NAS only) 11 Turn signal indicator bulb 12 Headlamp adjuster screw (2 off) 13 Cover - Low beam headlamp projector module bulb 14 Mounting collar
Page 2032 of 3039

15 Xenon igniter unit and bulb 16 Xenon igniter electrical connector 17 Cornering/static bending lamp bulb (if fitted) 18 Side lamp bulb 19 High beam headlamp bulb 20 Cover - Side lamp, cornering/static bending lamp (if fitted) and high beam headlamp bulbs 21 Electrical connector Bi-Xenon Headlamp
The bi-xenon headlamp uses a projector lens, similar to the halogen headlamp. The projector module comprises an ellipsoidal
lens and a reflector. The projector reflector collects the light produced by the halogen bulb and projects the light into a focal
plane containing a shield. The contour of the shield is projected onto the road by the lens. A complex surface reflector is used
for the halogen fill in high beam lamp. This type of reflector is divided into separate parabolic segments, with each segment
having a different focal length. The low and high beam bulbs are quartz halogen H7, with a rating of 55W. The bulbs are
retained in the headlamp unit with conventional wire retaining clips.
A tourist lever mechanism is located on the right hand side of the projector module. This mechanism moves a flap to blank off
a portion of the beam spread to enable the vehicle to be driven in opposite drive hand markets without applying blanking
decals to the headlamp lens. The beam is changed by removing the access cover at the rear of the lamp assembly and moving
a small lever located near the bulb holder, at the side of the projector.
NOTE: The tourist lever is not fitted to NAS vehicles.
WARNING: The Xenon system generates up to 30000 volts and contact with this voltage could lead to fatality. Make sure
that the headlamps are switched off before working on the system.
The following safety precautions must be adhered to when working on the xenon low beam headlamp system:
DO NOT attempt any procedures on the xenon headlamps when the lights are switched on.
Handling of the D1S xenon bulb must be performed using suitable protective equipment; for example gloves and
goggles. The glass part of the bulb must not be touched.
Xenon bulbs must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
Only operate the bulb in a mounted condition in the projector module installed in the headlamp.
The xenon headlamp is known as 'bi-xenon' because it operates as both a low and high beam headlamp unit. The xenon lamp,
or High Intensity Discharge (HID) lamp as they are sometimes referred to, comprises an ellipsoidal lens with a solenoid
controlled shutter to change the beam output from low to high beam.
NOTE: If the lighting control switch is in the 'off' position, both the xenon lamp and the halogen high beam lamp will
operate when the high beam 'flash' function is operated.
The xenon headlamp system is controlled by the CJB using a control module for each headlamp and an igniter. The control modules and the igniters provide the regulated power supply required to illuminate the bulbs through their start-up phases of
operation.
The xenon headlamp is a self contained unit located within the headlamp assembly. The unit comprises a reflector, an adaptor
ring, the lens, a shutter controller and the xenon bulb, which together forms an assembly known as the projector module. The
reflector is curved and provides the mounting point for the xenon bulb. The bulb locates in a keyway to ensure the correct
alignment in the reflector and is secured by a plastic mounting ring. The bulb is an integral component of the igniter and is
electrically connected by a connector located in the igniter unit.
The shutter controller is a solenoid which operates the shutter mechanism via a lever. The shutter is used to change the beam
projection from low beam to high beam and vice versa.
The xenon bulbs illuminate when an arc of electrical current is established between 2 electrodes within the bulb. The xenon
gas sealed in the bulb reacts to the electrical excitation and the heat generated by the current flow to produce the
characteristic blue/white light.
To operate at full efficiency, the xenon bulb goes through 3 full stages of operation before full output for continuous operation
is achieved. The 3 phases are; start-up phase, warm-up phase and continuous phase.
In the start-up phase, the bulb requires an initial high voltage starting pulse of up to 30000 volts to establish the arc. This is
produced by the igniter. The warm-up phase begins once the arc is established. The xenon control module regulates the supply
to the bulb to 2.6A which gives a lamp output of 75W. During this phase, the xenon gas begins to illuminate brightly and the
environment within the bulb stabilizes, ensuring a continual current flow between the electrodes. When the warm-up phase is
complete, the xenon control module changes to continuous phase. The supply voltage to the bulb is reduced and the operating
power required for continual operation is reduced to 35W. The process from start-up to continuous phase is completed in a very
short time.
The xenon control modules (one per headlamp) receive an operating voltage from the CJB when the headlamps are switched on. The modules regulate the power supply required through the phases of start-up.
The igniters (one per headlamp) generate the initial high voltage required to establish the arc. The igniters have integral coils
which generate high voltage pulses required for start-up. Once the xenon bulbs are operating, the igniters provide a closed
circuit for the regulated power supply from the control modules.