2010 JAGUAR XFR ecu
[x] Cancel search: ecuPage 2684 of 3039

7 RH accelerometer 8 LH accelerometer 9 RJB (rear junction box) 10 BJB (battery junction box)
System Operation
The pedestrian protection system is operational when the vehicle is traveling at speeds between approximately 20 km/h (12.4
mph) and 45 km/h (28 mph). A vehicle speed signal is received by the pedestrian protection system control module over the
high speed CAN bus.
The system is able to determine if contact is made with a pedestrian or another object, such as a traffic cone, using signals
from accelerometers mounted behind the front bumper. When the system determines contact is made with a pedestrian it fires
the actuators to lift the rear of the hood approximately 130 mm within 35 ms of the 'fire' signal.
When an impact condition is registered, the pedestrian protection system control module outputs an impact signal on the high
speed CAN bus. This signal is used by the RJB to initiate the hazard warning lamps. If this occurs, the hazard warning lamp switch is disabled for the remainder of the current ignition cycle.
If the pedestrian protection system control module detects a fault with the system, it outputs a message on the high speed
CAN bus to the instrument cluster message center. On receipt of this, the message center will display the message 'CHECK PEDESTRIAN SYSTEM'.
The pedestrian protection system control module also stores the VIN (vehicle identification number). If a new control module
is fitted to the vehicle the Jaguar approved diagnostic tool must be used to program the unit with the vehicles VIN.
When the vehicle is delivered from the factory the pedestrian protection system is in a 'safe' plant mode. Normal operating
mode should be activated using the Jaguar approved diagnostic tool during the Pre-Delivery Inspection (PDI) prior to delivery
to the customer. For additional information, refer to the PDI manual.
If any damage is caused to the front of the vehicle, be it cosmetic or structural, repairs must be carried out in line with the
processes contained in the workshop manual. Failure to carry out the correct repair process could compromise operation of the
pedestrian protection system. Refer to GTR for the latest information.
The vehicle must be left for 1 minute after disconnecting the battery before any work can be carried out on the pedestrian
protection system.
Failure Mode Detection
In service, if any fault is detected, or any part of the system is recognized as not being present, the message center displays
the warning 'Check Pedestrian System'.
The bonnet deployment actuators are non-serviceable components, and if they must be replaced due to a fault, or due to
having been deployed, or following any other accident, their barcode labels must be read and recorded in the service database
against the vehicle VIN for security purposes.
After deployment of the pedestrian protection system, the vehicle must be stopped as soon as it is safe to do so. The hazard
warning lamps will be activated and can only be switched off by pressing the engine START/STOP button to turn the engine off
and on again. A warning message 'CHECK PEDESTRIAN SYSTEM' will appear on the message center and the vehicle should be
transported to the nearest dealer/authorised repairer. The vehicle must not be driven when the bonnet has been deployed.
NOTE: If the warning message 'CHECK PEDESTRIAN SYSTEM' appears in the message center when the bonnet has not
been deployed, the vehicle should be taken to the nearest dealer/authorised repairer immediately. It can be driven.
If any significant damage occurs to the front bumper it should be inspected by a dealer/authorised repairer as soon as
possible.
CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The control module is mounted below the hood release lever behind the side trim in the left hand front footwell.
The deployment signal is received from the pedestrian protection system control module. The second-generation system
adopted for XF is all-new to Jaguar and, although similar, differs from that introduced on XK by having an accelerometer-based
sensing system rather than a contact-sensing system. The accelerometer-based system is supplied by Bosch. Mounted very
close to the skin of the bumper, it examines the characteristics of vibration waves caused by impact. Its response time is
quicker, because it does not rely on the front of the bumper being loaded. It uses the 'saved' time to make more complex
decisions, and so has fewer error states. The speed of vehicle and the length of the bonnet define the time available to get
the bonnet into its deployed and stabilized position. It is possible, therefore, to create a time-line counting back from the
predicted moment of head impact to the time when the deployment signals need to be sent. That in turn defines a time from
first contact to decision time.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2712 of 3039
NOTE: Any attached body parts that require accurate alignment and fitting must be incorporated in this step; for
instance bumpers, seals, headlamps, rear lamps and lock assembly components. If this is not done carefully it may
result in water leaks, wind noises and substantial follow-on work.
Make sure that edges line up with adjacent parts and check that gaps are consistent (compare left and right-hand
sides). Make sure that the shape of the vehicle is retained.
Secure the new part
NOTE: The need for subsequent follow-on work can be significantly reduced if aligning and tack-welding are carried
out with due care.
Depending on accessibility the following methods for securing are available:
- Grip pliers (set of).
- Screw clamp (set of).
- Self-tapping screws.
- Tack welds.
Use a staking tool or a screwdriver to Make sure that the edges of sectional replacements of profiled parts line up. The
edge is then tack welded to Make sure that it lines up.
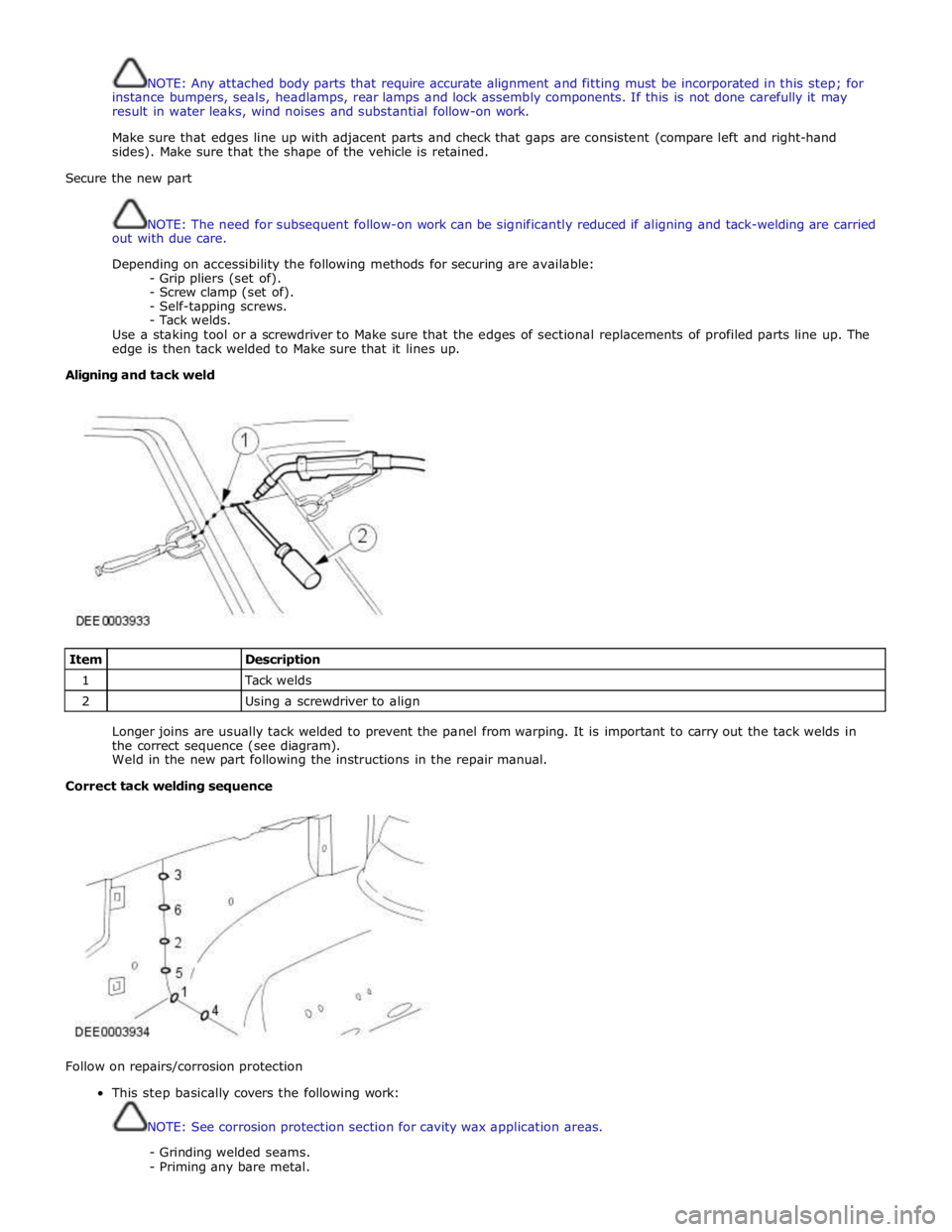
Aligning and tack weld
Item
Description 1
Tack welds 2
Using a screwdriver to align
Longer joins are usually tack welded to prevent the panel from warping. It is important to carry out the tack welds in
the correct sequence (see diagram).
Weld in the new part following the instructions in the repair manual.
Correct tack welding sequence
Follow on repairs/corrosion protection
This step basically covers the following work:
NOTE: See corrosion protection section for cavity wax application areas.
- Grinding welded seams.
- Priming any bare metal.
Page 2716 of 3039
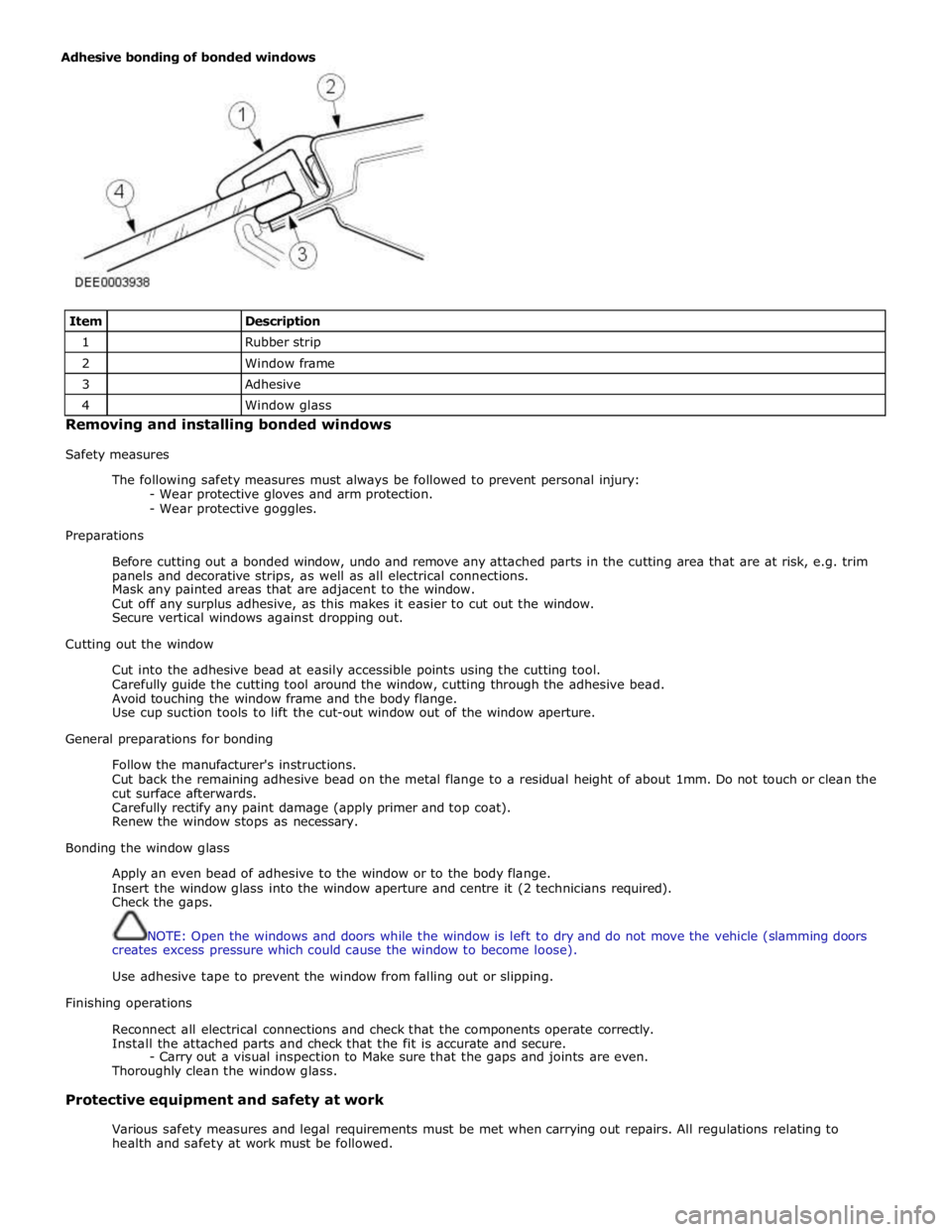
Item
Description 1
Rubber strip 2
Window frame 3
Adhesive 4
Window glass Removing and installing bonded windows
Safety measures
The following safety measures must always be followed to prevent personal injury:
- Wear protective gloves and arm protection.
- Wear protective goggles.
Preparations
Before cutting out a bonded window, undo and remove any attached parts in the cutting area that are at risk, e.g. trim
panels and decorative strips, as well as all electrical connections.
Mask any painted areas that are adjacent to the window.
Cut off any surplus adhesive, as this makes it easier to cut out the window.
Secure vertical windows against dropping out.
Cutting out the window
Cut into the adhesive bead at easily accessible points using the cutting tool.
Carefully guide the cutting tool around the window, cutting through the adhesive bead.
Avoid touching the window frame and the body flange.
Use cup suction tools to lift the cut-out window out of the window aperture.
General preparations for bonding
Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Cut back the remaining adhesive bead on the metal flange to a residual height of about 1mm. Do not touch or clean the
cut surface afterwards.
Carefully rectify any paint damage (apply primer and top coat).
Renew the window stops as necessary.
Bonding the window glass
Apply an even bead of adhesive to the window or to the body flange.
Insert the window glass into the window aperture and centre it (2 technicians required).
Check the gaps.
NOTE: Open the windows and doors while the window is left to dry and do not move the vehicle (slamming doors
creates excess pressure which could cause the window to become loose).
Use adhesive tape to prevent the window from falling out or slipping.
Finishing operations
Reconnect all electrical connections and check that the components operate correctly.
Install the attached parts and check that the fit is accurate and secure.
- Carry out a visual inspection to Make sure that the gaps and joints are even.
Thoroughly clean the window glass.
Protective equipment and safety at work
Various safety measures and legal requirements must be met when carrying out repairs. All regulations relating to
health and safety at work must be followed. Adhesive bonding of bonded windows
Page 2732 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - Water Leaks - Water Leaks
Description and Operation
General Published: 11-May-2011
If water leaks occur after bodywork repairs, the cause can be established using the checks described below. A
systematic and logical procedure is required to locate water leaks. Before beginning extensive checks, a thorough visual
inspection must be carried out.
Visual Inspection
- The following characteristics may indicate existing leaks:
- Check the clearance and accurate fit of ancillary components such as the hood, tailgate, liftgate, doors, and so
on.
- Check for correct fit and possible damage to sealing elements such as blanking plugs, rubber door seals, and so
on.
- Check water drain holes for unhindered flow.
Various tests can be used to provide further information on possible leaks:
- Water test
- Washer test
- Road test
- Chalk (powder) test
Practical execution of tests and checks
Water test
NOTE: Never aim a jet of water directly at a rubber seal.
Carry out the water test with a second person present (in the passenger compartment).
Use variable washer nozzles (concentrated water jet to fine spray mist).
Start in the lower section and spray the whole area, working upwards in stages.
Washer test
Further tests can be carried out in the washer system.
Some leaks originate here, or only occur here.
The relevant passenger compartment should be checked using a torch during the wash procedure.
Road test
If no leaks are located during the tests above, road tests should be carried out on wet roads.
Road tests under various conditions:
- At various speeds.
- On various road surfaces (asphalt to cobbles).
- With loaded or unloaded vehicle.
- Driving through puddles (splash water).
Chalk test (powder test)
In this test, the clamping load and the bearing surface of the seal are checked.
Performing the test:
- Dust the door seal with powder or coat with chalk.
- Coat the bearing surface of the seal with a thin film of Vaseline.
- Slowly close the door and open it again.
- Check the width and continuity of the imprint on the door seal.
Other test equipment
Other equipment such as stethoscopes, UV lamps, special mirrors or ultrasound measuring instruments can be used to
locate leaks.
Rectifying the leak using recommended tools, auxiliary equipment and materials
Tools and auxiliary equipment:
- Dry, absorbent cloths
- Variable washer nozzle
- Torch, fluorescent tube
- Mirror
- Compressed air
- Seal lip installer
- Wet/dry vacuum cleaner
- Sealing compound compressor
- Remover for interior trim
- Cutter blade or pocket knife
- Wedge (wood or plastic)
- Hot air blower
- Special mirror for concealed leaks
Page 2735 of 3039

Side windows
In the case of side windows, the same problems can arise as for a windscreen. The same corrective actions must therefore be
used.
Door seal
Diagnosis:
- Water ingress in the lower part of the interior door trim or in the rocker panel area.
Cause:
- The water shield fitted behind the interior door trim exists to drain off water that has entered the door via the
drainage holes, either downwards or outwards. If the water shield seal is damaged or has been fitted incorrectly,
then water can get into the passenger compartment.
- In addition to this, the drainage holes can become clogged with leaves, dirt or excess cavity protection agents.
Water gathers in the door and ingresses into the passenger compartment.
- Check water shield for damage or correct fitting.
- If the water shield needs to be re-bonded, then approved seam sealer should be used.
- Before the water shield is installed, the drainage holes must be checked for unhindered flow.
Door seals
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water into the rocker panel area
Cause:
- Insufficient clamping load between seal and door.
Corrective action:
NOTE: When adjusting the clamping load, the profile alignment of the relevant components must always be taken
into consideration.
NOTE: Do not realign the flange too far in the direction of the door, as this can reduce the bearing surface of the
seal to the door.
- Check clamping load:
- The easiest way to check the clamping load of a seal to the respective bearing surface is by means of a paper
strip test. This consists of trapping strips of paper at various points between the door and the seal, and fully
closing the door. If it is possible to pull out the paper with no great resistance, then the clamping load is too
low.
- Adjust the clamping load:
- The clamping load is normally adjusted using the striker. When doing so, the edge alignment from the door to
the side panel, or from the front door to the rear door must be taken into account.
- Another setting method is to realign the panel flange for the seal mounting. The clamping load is increased by
moving the flange towards the door.
- Check the bearing surface:
- Apply chalk evenly to the surface of the seal. Evenly coat the bearing surface of the door with Vaseline.
- Close the door fully, the lock must engage. Open the door. The imprint of the chalk (bearing surface) can be
identified in the film of Vaseline.
- The bearing surface should be at least 5mm across at all points.
Other causes:
- The door seal must completely seal the door where it meets the bodywork.
- Water can ingress directly or indirectly into the interior of the vehicle if the seal is damaged at any point.
Corrective action:
- A damaged or worn door seal must always be renewed in full.
- When renewing the seal, the following must be taken into account:
- Always fit the seal first in the area of the narrow radii (corner points).
- Next, secure the seal to the flange evenly by tapping lightly with a rubber hammer. The installed seal must not
be kinked at any point.
NOTE: The prescribed length of a seal must not be shortened.
Other cause:
- The door seal is attached to the welded flange all the way round. If this welded flange is uneven or damaged at
any point (usually in areas with small radii) then this point could be subject to leaks.
- A stretched seal carrier can also cause a leak.
- In both cases, water gets into the vehicle interior under the seal carrier.
Corrective action:
- Align the deformed welded flange using a hammer and anvil block, prevent and, if necessary, repair any paint
damage.
Sliding roof/tilting roof
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water at sliding roof aperture
Cause:
- The sliding roof/tilting roof is installed in a water trap. The water drains off via the water trap, water drain holes
and drain hoses. The drain hoses lead downwards on both sides via the A-pillar and B-pillar.
- The drain holes or drain hoses can become clogged with leaves, dirt, underbody protection and so on.
Corrective action:
Page 2879 of 3039
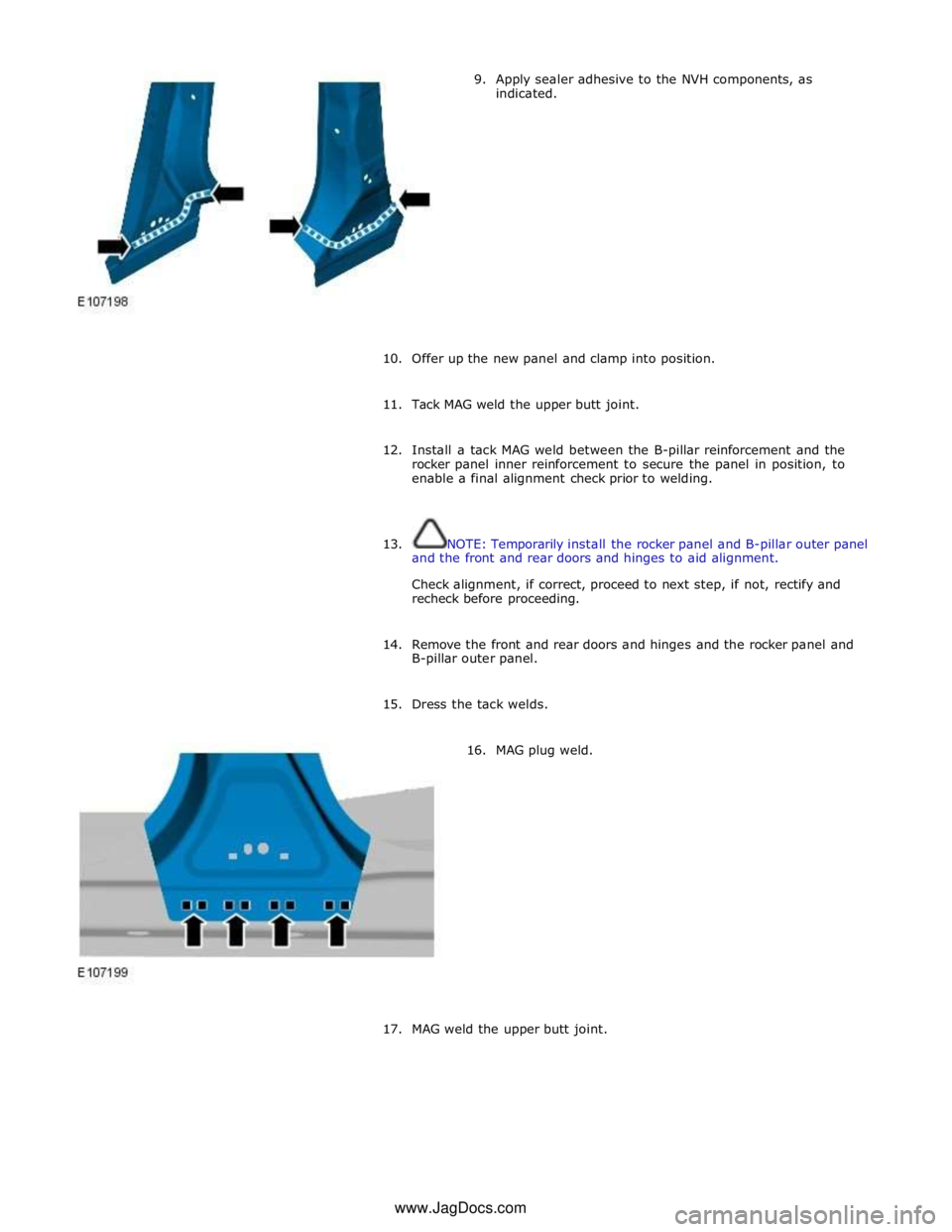
9. Apply sealer adhesive to the NVH components, as
indicated.
10. Offer up the new panel and clamp into position.
11. Tack MAG weld the upper butt joint.
12. Install a tack MAG weld between the B-pillar reinforcement and the
rocker panel inner reinforcement to secure the panel in position, to
enable a final alignment check prior to welding.
13. NOTE: Temporarily install the rocker panel and B-pillar outer panel
and the front and rear doors and hinges to aid alignment.
Check alignment, if correct, proceed to next step, if not, rectify and
recheck before proceeding.
14. Remove the front and rear doors and hinges and the rocker panel and
B-pillar outer panel.
15. Dress the tack welds.
16. MAG plug weld.
17.
MAG weld the upper butt joint. www.JagDocs.com
Page 3015 of 3039
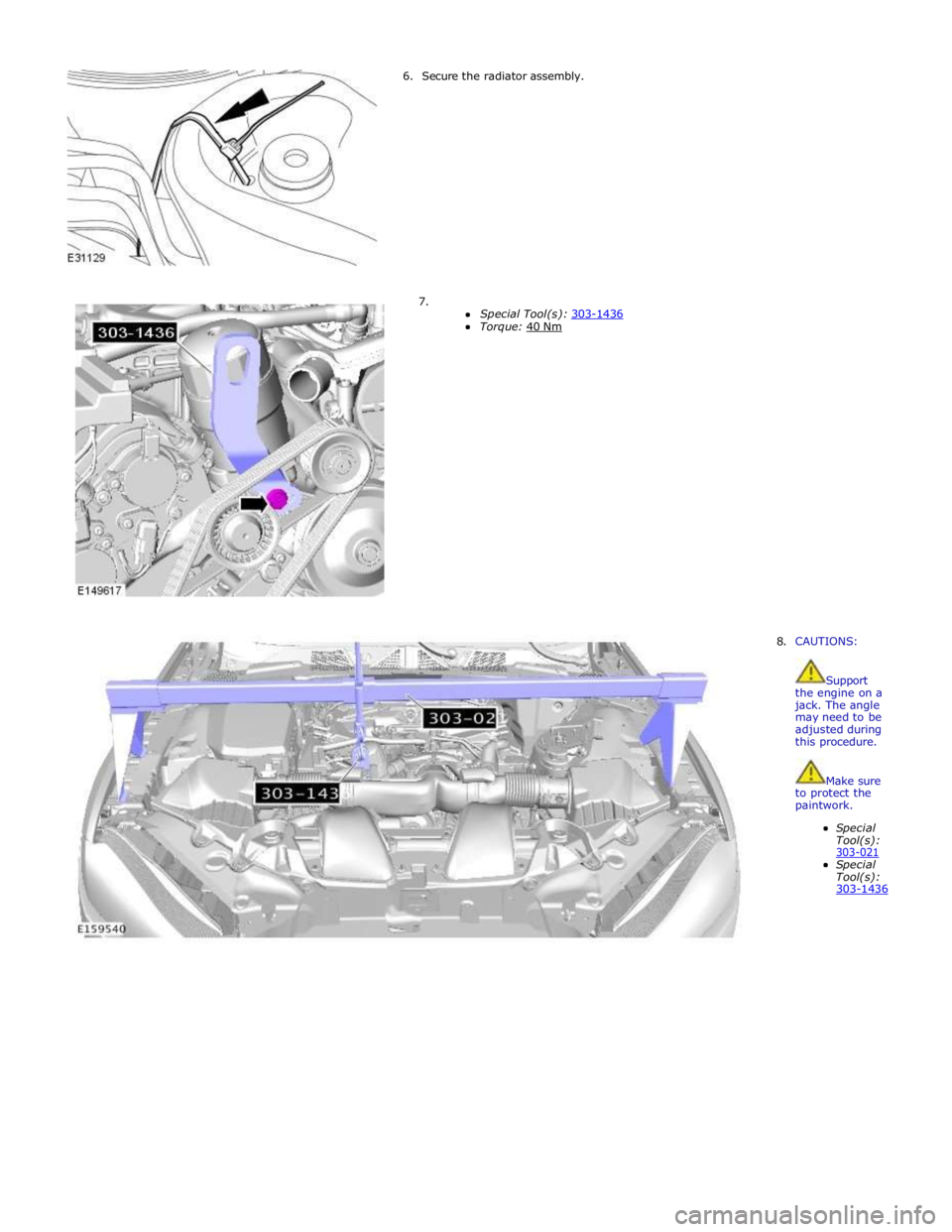
6. Secure the radiator assembly.
7.
Special Tool(s): 303-1436 Torque: 40 Nm
8. CAUTIONS:
Support the engine on a jack. The angle may need to be adjusted during this procedure.
Make sure to protect the paintwork.
Special Tool(s): 303-021 Special Tool(s): 303-1436