2010 ASTON MARTIN V8 VANTAGE OBD port
[x] Cancel search: OBD portPage 741 of 947

Diagnostic Ports
Appendix & Glossary20-1-2 Workshop Manual May 2007
Appendix & Glossary
Diagnostic Ports (20.01)
Diagnostic ports are provided for:
•OBD II
• Body - including
LHD RHD
PRNDCRUISE000000MILES00 0T10
Engine
Body
Page 849 of 947

AML EOBD System Operation Summary
Rory O’Curry Aston Martin Lagonda CONFIDENTIAL 1 May 2009
[email protected] AML EOBD Monitors 07 ROC.doc Page 3 of 43
Introduction
This document describes in detail the operation of the AML (Aston Martin Lagonda) EOBD System.
The AML EOBD System consists of a series of Mon itors designed to observe the operation of strategic
aspects of the Emission Control System. For each of the Monitors there is a detailed functional review of
the monitor's operation, a listing of the relevant malfunction codes, typical Monitor entry conditions
followed by typical malfunction thresholds.
The AML EOBD System also incorporates a Malfunction Indicator Lamp or MIL (symbol shown on the
last page). The MIL will only be used to report emi ssion related failures and to indicate emergency start-
up or Limp Home routines. It will not be used for any other purpose.
Although this document describes all the Monitors cont ained within the AML EOBD System, not ALL of
these monitors may be utilised on every vehicle built w ith the AML EOBD System. This is primarily due
to the hardware configuration of the particular vehicle in question e.g. Auto vs. Man Transmission OR
EGR vs. No EGR. Please refer to the vehicle specific documentation for details of those Monitors that will
be operational.
It is important to note that to illuminate the MIL, th e failure condition must be observed at least twice. The
first occurrence will set a 'pending code' and the second occurrence will illuminate the MIL. The only
exception to this is the Type A Misfire failure, whic h will 'flash' the MIL at the first occurrence of the
failure condition. Therefore, if an OBD reset is performed, a minimum of two trips is required to
illuminate the MIL, although the Misfire Monitor does require pre-conditioning to learn 'Profile
Correction' and will utilize three trips.
De-activation of the MIL can be achieved if, no furt her separate failure conditions are detected and 3
subsequent and sequential trips have been comp leted where the original failure condition which
illuminated the MIL initially, is no longer detected.
The MIL code will be completely erased if the same failure condition is not detected after 40 trips.
Page 860 of 947

AML EOBD System Operation Summary
Rory O’Curry Aston Martin Lagonda CONFIDENTIAL 1 May 2009
[email protected] AML EOBD Monitors 07 ROC.doc Page 14 of 43
After the vehicle is started, during vehicle acceleration, the differential pressure indicated by the DPFE
sensor at zero EGR flow is checked to ensure that both hoses to the DPFE sensor are connected. Under
this condition, the differential pressure should be zer o. If the differential pressure indicated by the DPFE
sensor exceeds a maximum threshold or falls below a minimum threshold, an upstream or downstream
DPFE hose malfunction is indicated (P1405 P1406).
EGR Hose Check Operation:
DTCs P1405, P1406
Monitor execution once per driving cycle
Monitor Sequence Done after P0402 test
Sensors OK MAF, MAP
Monitoring Duration 2 seconds to register a malfunction
Typical EGR hose check entry conditions : Minimum Maximum
EVR duty Cycle (EGR commanded off) 0% 0%
Mass Air Flow 8 lb/min
Inferred exhaust back pressure 13 in H2O
Typical EGR hose check malfunction thresholds:
DPFE sensor voltage: < -7 in H2O, > 7 in H2O
After the vehicle has warmed up and normal EGR rates are being commanded by the PCM, the low flow
check is performed. Since the EGR system is a closed loop system, the EGR system will deliver the
requested EGR flow as long as it has the capacity to do so. If the EVR duty cycle is very high (greater
than 80% duty cycle), the differential pressure indicated by the DPFE sensor is evaluated to determine the
amount of EGR system restriction. If the differential pr essure is below a calibratable threshold, a low flow
malfunction in indicated (P0401).
EGR Flow Check Operation:
DTCs P0401
Monitor execution once per driving cycle
Monitor Sequence Done after P1405 and P1406 tests
Sensors OK CPS, ECT, IAT, MAF, MAP, TP
Monitoring Duration minimum 70 seconds to register a malfunction
Typical EGR flow check entry conditions: Minimum Maximum
EVR Duty Cycle 80% 100%
Engine RPM 2500 rpm
Mass Air Flow Rate of Change 6% prog. loop
Inferred manifold vacuum 6 in Hg 10 in Hg
Typical EGR flow check malfunction thresholds:
DPFE sensor voltage: < 6 in H2O
EGR Monitor temporary disablement conditions ( other than entry requirements ) :
Non-operational when base feature disabled, including matching base feature temperature disablement.
Low Barometric Pressure Conditions.
Reporting of faults suppressed below 32° F to prevent mis-diagnosis due to ice. Monitor is still operational
and continues to check, reporting any faults when temperature > 32 °F.
Page 869 of 947

AML EOBD System Operation Summary
Rory O’Curry Aston Martin Lagonda CONFIDENTIAL 1 May 2009
[email protected] AML EOBD Monitors 07 ROC.doc Page 23 of 43
SAIR System Monitor – Flow Check
When the air pump is energized, the MAF sensor will show a corresponding increase in airflow. The
SAIR pump flow check monitors the MAF sensor signal and two air flow models during normal
secondary air system operation to determine if secondary air is being delivered into the exhaust system.
The SAIR pump flow test compares the actual change in MAF during the pump on and off transitions to
the expected change in airflow from the secondary air fl ow model. (A throttle body flow model is used to
"zero out" errors in the air meter and to compensate fo r transient driving conditions.) The actual airflow is
divided by the expected airflow to calculate an "On flow ratio" and an "Off flow ratio".
A flow ratio that is much less than 1.0 means that the air pump has no/low flow, or the inlet hose to the
pump is disconnected. If secondary air system operation ex tends into closed loop fuel, fuel trim feedback
is used to discriminate between low pump flow and in let hose disconnection. A low flow ratio with a lean
fuel system indicates a disconnected inlet hose. A flow ratio significantly higher than 1.0 (and/or a rich
fuel system indication) indicates that th e outlet hose from the pump is disconnected.
SAIR Diagnostic
The V8 uses the standard FORD non-intrusive monitor that has been adapted for use on a V-engine. The
detection capability is detailed below with the V8 specific modifications highlighted
P0410 - Pump inlet hose disconnection.
P0491 - Low airflow into the exhaust on Bank1. Blocked hose OR failed to open vacuum valve.
P0492 - Low airflow into the exhaust on Bank 2. Blocked hose OR failed to open vacuum
valve.
P2448 - Low airflow into the exhaust on Bank1. Disconnected outlet hose.
P2449 - Low airflow into the exhaust on Bank 2. Disconnected outlet hose.
P0412 - SAIR electrical circuit fault high/low on ecu control pin.
P2257 - SAIR electrical circuit fault high on monitor pin.
P2258 - SAIR electrical circuit fault low on monitor pin.
The determination of which bank is receiving low ai rflow is performed by monitoring the closed loop
fuelling correction supplied from the oxygen sensors. The bank that has the highest enleaning correction is
the bank that has the lowest SAIR flow. If closed loop fuelling is not active when the SAIR pump is
disabled the diagnostic cannot determ ine which bank is receiving low flow and so a fault on both banks is
raised.
The relative difference between the commanded lambda values for each bank is used to determine a
restricted flow to either bank1 or 2 due to a restricted outlet. This enables P0491, P0492 to be raised if the
flow ratio is calculated as in range.
The SAIR functional tests run when SAIR is active and the results are stored until the HEGO monitor has
completed (150-200 seconds after SAIR is off on a typical FTP74). It is only when the HEGO monitor has
completed successfully that any functional SAIR fa ults and SAIR monitor complete is reported.
Page 875 of 947
AML EOBD System Operation Summary
Rory O’Curry Aston Martin Lagonda CONFIDENTIAL 1 May 2009
[email protected] AML EOBD Monitors 07 ROC.doc Page 29 of 43
The Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) is a syst em which uses dual intake runners to supply air to
each cylinder. The secondary runners are normally closed, but the PCM opens them under high rpm
conditions when the driver is demanding additiona l power from the engine. The IMRC system can be
actuated using an electric motor or a vacuum moto r. The IMRC system is functionally checked by
monitoring the runner control plates using switches. If the actual position of the runner control plates does
not match the commanded position, a malfunction of the IMRC system is indicated (P1518, P1519).
The Swirl Control Valve (SCV) is a system which uses di fferent regions of the Intake plenum to influence
the pattern of the airflow into the combustion chamber.
It is important to note that this functional / rationality check may or may not be a MIL Code. This is
dependent on whether the EOBD Thresholds are exceeded.
IMRC / SCV System Check Operation:
DTCs P1520 (IMRC input switch electrical check)
P1518, P 1519 (IMRC stuck open functional check)
Monitor execution continuous
Monitor Sequence none
Monitoring Duration 5 seconds
Typical IMRC functional check malfunction thresholds
IMRC plates do not match commanded position (functional)
IMRC switches open/shorted (electrical)
Camshaft Position Control (also known as Variable Cam Ti ming) is a system which is able to advance and
retard camshaft timing relative to the crankshaft. Th is phasing is controlled by a duty-cycled output. The
output driver is checked electrically for opens and s horts (P1380). The system is checked functionally by
monitoring the closed loop phase control correction. If the proper phasing cannot be maintained and the
system has an advance or retard error greater than the malfunction threshold, a CPC control malfunction is
indicated (P1381, P1383).
It is important to note that the functional / rationality checks may or may not be a MIL Code. This is
dependent on whether the EOBD Thresholds are exceeded.
Camshaft Position Control System Check Operation:
DTCs P1380 (CPC output electrical check)
P1381 (CPC timing over-advanced functional check)
P1383 (CPC timing over-retarded functional check)
Monitor execution continuous
Monitor Sequence ECT > 150 oF
Monitoring Duration 5 seconds
Typical CPC functional check malfunction thresholds:
timing over-advanced/over-retard ed by > 10 crankshaft degrees
Engine CCM temporary disablement conditions ( other than entry requirements ) :
None, except CPC does not operate (and is therefore not checked) if ACT/IAT, ECT/CHT, MAF/MAP or
TP sensors are malfunctioning.
Page 890 of 947

Aston Martin V8 Vantage 2009 MY EOBD DocumentationAston Martin/Ford Confidential
Component/ System Fault Code Monitor Strategy
Description Malfunction Criteria Threshold Parameter Secondary Parameters Entry Parameters Time Required DTC
StorageMIL Illumin-
ation
P0300
to
P0308 Deviations in crankshaft
acceleration processed by
Neural Network Misfire
Monitor software and Catalyst
Temperature model Percentage misfire
required to exceed
Catalyst Damage
Temperature 1000 deg c
(1832 deg F) catalyst
damage threshold, per
engine bank Type A: See RPM/Load
Table FNMISPCT_97 %
Type A:
200 revs
(Continuous)Type A:
Footnote b)
Type A:
Footnote d)
Percentage misfire
required to exceed
emission thresholds Type B> 0.0323*100% Type B:
1000 revs
(Continuous)Type B/C:
Footnote a)
Type B:
Footnote c)
Percentage misfire
required to clear emission
pending code < 0.001 * 100 % Time since engine start,
value based on time and
IAT 0 + FNMISACT sec
(See Transfer Functions)
Time since PCM power up 0 sec
Time for NNMM
computation queue to fill 4 revs from initial crank
(Meets 2 rev start delay
requirement)
Engine coolant temp -7 - 115 deg C ( 20 - 240 degF )
Engine rpm 600 - 7250 rpm
Net engine torque > -81 Nm ( -60 ft lbs)
Engine torque rate of
change > -33.9Nm (-25 ft lbs/sec)
or
< 33.9Nm (25 ft lbs/sec)
Throttle position rate of
change > -30 volts/background
loop or
< 30 * 5/1024
volts/background loop
Engine rpm/load range See RPM/Load Table FNMISOK_97: Monitor
disabled when less than
0.5
Crankshaft position circuit
(PIP) OK (P0320)
Fuel shutoff for rpm or
vehicle speed limiting No fuel cutoff occurring
Fuel level > 0.15 * 100 %
Misfire Detected At
Startup P0316 Misfire detected during first
1000 engine revs since start P0316 is set in addition to
P0300 - P0308 DTC 1000 revs
(Continuous)Footnote a) Footnote c)
AICE chip failure in
PCM P0606 NNMM chip to CPU
communication fault Number of attempts 10
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Camshaft/crankshaft
synchronization
failure P1336 AICE chip reports inability to
synchronize camshaft and
crankshaft signals
(Replaces P1309) Number of attempts > 255
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Engine speed >1550rpm
<2275rpm
Engine load >0.075
<0.225
Engine coolant
temperature >68.3degC (155degF)
Transmission in 6th gear
Vehicle speed >30mph
<70mph
Maximum rate of engine
speed change <500rpm/second
In decel fuel cut
ROM checksum error P260F NNP ROM checksum error Checksum from NNP does not equal mainline
strategyNone
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Cylinder Misfire
DetectedMisfire Monitor
Footnote c)
Unable to learn
crankshaft profile P0315 Unable to learn stable
crankshaft profile Number of attempts > 6 attempts Continuous within
profile learning
entry conditionsFootnote a)
2
Page 900 of 947

Aston Martin V8 Vantage 2009 MY EOBD DocumentationAston Martin/Ford Confidential
Component/ System Fault Code Monitor Strategy
Description Malfunction Criteria Threshold Parameter Secondary Parameters Entry Parameters Time Required DTC
StorageMIL Illumin-
ation
Ratio of PIP events to
spark events seen 1 to 1 (To pass test) Increment fault counter by
20 on each event. Set
code when counter
exceeds 200 N/A
PCM able to determine
coil Yes
Above neutral torque axis See RPM/Load Table FNMISOK_97: Monitor
disabled when less than
0.5
Difference between actual
and desired rpm > -200 rpm
Engine coolant temp -40 deg C
(> -40 deg F)
Time with solenoid at limit > 5 sec Time since engine start > 60 sec
Fuel control Closed loop
Idle state At idle
Difference between actual
and desired rpm > 100 rpm
Engine coolant temp -40 deg C
(> -40 deg F)
Time with solenoid at limit > 5 sec Time since engine start > 60 sec
Fuel control Closed loop
Idle state At idle
Vehicle ID block not
programmed P1639 VID block not programmed
with tire/axle ratio Time with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
VID Block checksum P0602 VID block checksum test failedTime with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous
KAM Failed / reset P0603 Keep Alive Memory check failed / memory was resetTime with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
RAM memory failed P0604 Random Access Memory test has failed.Time with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
ROM checksum test
failed P0605 Read Only Memory test failed Time with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
CPU Fault detected P0607 General fault with the CPU has been detectedTime with error present > 0 sec
NoneNoneContinuous
Keep Alive Memory
Power Input P1633 KAM power input voltage too
low/open circuit Time with error present > 20 sec
NoneNoneContinuous Footnote k) Footnote i)
Vehicle Speed
Sensor P0500 Invalid / missing data from
BCM BCM reports VSS failure
OR no data on CAN bus1
Time after start >2 secondsContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Commanded duty cycle on
or full-off >=0.5 * 100 % or = 0%
Signal circuit voltage Refer to Appendix for threshold calculation
Time with circuit
malfunction > 5 sec
P0330 Bank1
Sensor1 Sensor range check
Engine speed>1000rpm
P0325 Bank1
Sensor2 Sensor range check
Engine coolant temp >55degC (131degF)
P130A Bank2
Sensor2 Sensor range check
P130B Bank2
Sensor2 Sensor range check
P0460 (Range
Check) Sensor range check
Sensor input <= 7 or >= 254 A/D
counts w/in a range of
256 A/D counts
P0462 (Low) Circuit Check Sensor input< 7 A/D counts
P0463 (High) Circuit Check Sensor input> 254 A/D counts
Time with sensor out of
range > 30 sec
Sensor rationality check
(Stuck sensor) Compare fuel mass
consumed versus
observed change in gauge
readings (Min. and max.
reading) Fuel consumed (Fuel
consumed and fuel gauge
reading range are both
stored in KAM and reset
after a refuelling event or
DTC storage)> 10 %
"Fuel consumed" is
continuously calculated based
on PCM fuel pulse width
summation as a percent of
fuel tank capacity Fuel consumed (%) -
Range of fuel gauge
readings (%)
> 0.125 * 100 %
threshold at fuel tank
fill from 15% to 85%
Fuel consumed (%) -
Range of fuel gauge
readings (%) > 0.054 + 0.125 * 100
% threshold if tank
overfilled (> 85%)
Fuel consumed (%) -
Range of fuel gauge
readings (%) > 0.175 + 0.125 * 100
% threshold if tank on
reserve (< 15%)
Change in fuel level > 0.1925*100% Fuel level on the data bus N/A
Number of intermittent
events > 5
I/M Readiness Number of driving cycles
to clear I/M readiness flag
at extreme ambient
conditions > 1 driving cycle(s) Footnote e)
Footnote a)
Footnote c)
Footnote a) Footnote j) Footnote e)
Fuel Level Input
Noisy Continuous Footnote a)
Continuous Footnote a)
P0461
(Rationality) Sensor rationality check
(Noisy sensor)
Fuel Level Input
Stuck
P0460
(Rationality) Continuous
N/A Continuous
Calculated sensor noise
(peak to peak variation)
>0.25
KNKS Sensor
Fuel Level Input Out
Of Range NoneFootnote a) Footnote e)
Vapor Management
Valve Circuit
Malfunction P0443 Circuit continuity test, open or
shorted None
N/A Continuous
11.5< Voltage
Ignition System-
Ignition Coil Primary
Circuit Malfunction
IAC Solenoid
Underspeed Error P0507
P0506
Functional check -
overspeed error
Functional check -
underspeed error
IAC Solenoid
Overspeed Error
Footnote a) Footnote c)
Continuous
P0351
P0352
P0353
P0354
P0355
P0356
P0357
P0358
Rationality check
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Battery Voltage
12
Page 915 of 947
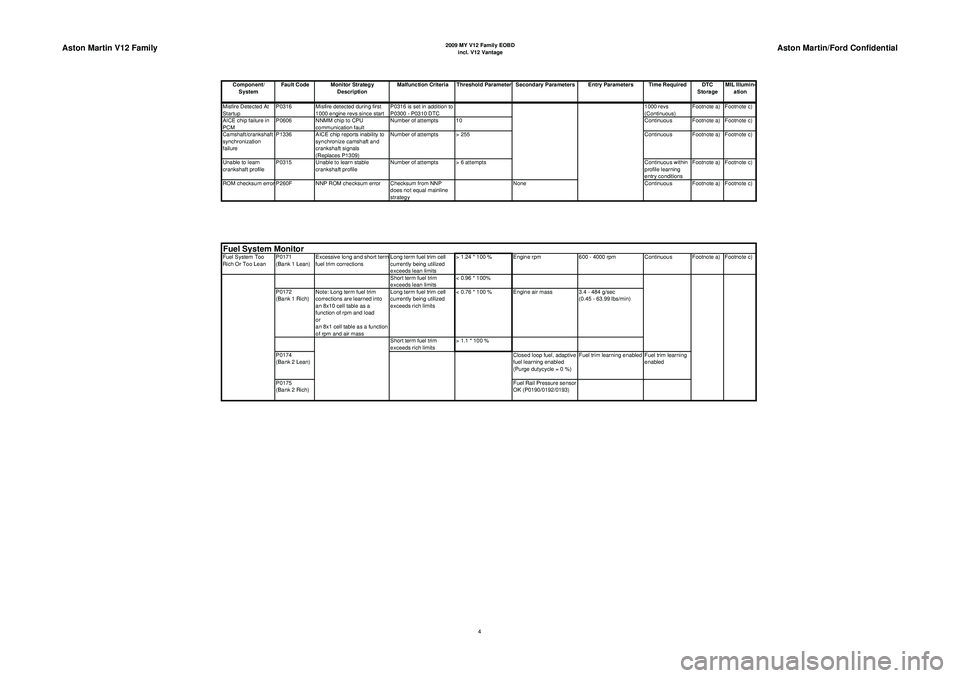
Aston Martin V12 Family
2009 MY V12 Family EOBDincl. V12 Vantage
Aston Martin/Ford Confidential
Component/ System Fault Code Monitor Strategy
Description Malfunction Criteria Threshold Parameter Secondary Parameters Entry Parameters Time Required DTC
StorageMIL Illumin-
ationMisfire Detected At
Startup P0316 Misfire detected during first
1000 engine revs since start P0316 is set in addition to
P0300 - P0310 DTC 1000 revs
(Continuous)Footnote a) Footnote c)
AICE chip failure in
PCM P0606 NNMM chip to CPU
communication fault Number of attempts 10
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Camshaft/crankshaft
synchronization
failure P1336 AICE chip reports inability to
synchronize camshaft and
crankshaft signals
(Replaces P1309) Number of attempts > 255
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Unable to learn
crankshaft profile P0315 Unable to learn stable
crankshaft profile Number of attempts > 6 attempts
Continuous within
profile learning
entry conditionsFootnote a) Footnote c)
ROM checksum error P260F NNP ROM checksum error Checksum from NNP does not equal mainline
strategyNone
Continuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Fuel System Too
Rich Or Too Lean P0171
(Bank 1 Lean)Excessive long and short term
fuel trim corrections Long term fuel trim cell
currently being utilized
exceeds lean limits> 1.24 * 100 % Engine rpm
600 - 4000 rpmContinuous Footnote a) Footnote c)
Short term fuel trim
exceeds lean limits < 0.96 * 100%
P0172
(Bank 1 Rich) Note: Long term fuel trim
corrections are learned into
an 8x10 cell table as a
function of rpm and load
or
an 8x1 cell table as a function
of rpm and air mass Long term fuel trim cell
currently being utilized
exceeds rich limits
< 0.76 * 100 % Engine air mass 3.4 - 484 g/sec
(0.45 - 63.99 lbs/min)
Short term fuel trim
exceeds rich limits > 1.1 * 100 %
P0174
(Bank 2 Lean) Closed loop fuel, adaptive
fuel learning enabled
(Purge dutycycle = 0 %)Fuel trim learning enabled Fuel trim learning
enabled
P0175
(Bank 2 Rich) Fuel Rail Pressure sensor
OK (P0190/0192/0193)Fuel S
ystem Monitor
4