2009 SKODA FABIA technical data
[x] Cancel search: technical dataPage 128 of 259

Passive Safety127
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
SafetyPassive SafetyBasic informationDriving the safe way
Passive safety measures reduce the risk of injury in accident situa-
tions.In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject of
passive safety in your vehicle. We have combined everything here which you
should be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and
safety of children. It is therefore important, in particular, to comply with the notes
and warnings in this section for your own interest and in the interest of those trav-
elling with you.
WARNING
•
This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle
for the driver and his occupants. You will find further information on safety,
which concerns you and those travelling with you, in the following chapters
of this Owner's Manual.
•
The complete on-board literature should always be in the vehicle. This
applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Safety equipment
The safety equipment is part of the occupant protection and it can
reduce the risk of injuries in accident situations.“Do not put at risk” your safety and the safety of those travelling with you . In the
event of an accident, the safety equipment can reduce the risk of injuries. The
following list contains part of the safety equipment in your vehicle:
•
three-point seat belts for all the seats;
•
belt force limiters for front seats;
•
belt tensioners for front seats;
•
seat belt height adjusters for front seats;
•
front airbags for the driver and the front passenger*;
•
side airbags*;
•
head airbags*;
•
anchoring points for child seat using the “ISOFIX” system;
•
anchoring points for child seat using the “Top Tether” system;
•
head restraints adjustable for height;
•
adjustable steering column.
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally protect you
and those travelling with you in accident situations. The safety equipment does not
protect you or the people travelling with you, if you or your occupants adopt an
incorrect seated position or the equipment is not correctly adjusted or used.
Fo r t h i s re a s o n y o u w i l l b e p ro v i d e d w i th i n fo rm a ti o n o n w hy t h i s e q u i p m e nt i s v e r y
important, how it protects you and the occupants, what should be observed when
using the equipment and how you and the people travelling with you can make full
use of the existing safety equipment. This Owner's Manual contains important
warning notes, which you and those travelling with you should pay attention to in
order to reduce a risk of injury.
Safety concerns everybody!
s3f4.1.book Page 127 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 130 of 259

Passive Safety129
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident, we
recommend the following setting.
•
Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance between the steering wheel and
your chest is at least 25 cm ⇒page 128, fig. 140.
•
Position the driver seat in the forward/back direction so that you are able to fully
press the pedals with your legs at a slight angle.
•
Adjust the seat backrest so that you are able to reach the highest point of the
steering wheel with your arms at a slight angle.
•
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same
level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 141.
•
Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 134, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
Driver seat adjustment ⇒page 62, “Adjusting the front seats”.
WARNING
•
The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
•
The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering
wheel ⇒page 128, fig. 140. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you -
hazard!
•
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the
outer edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering
wheel firmly in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle
of the steering wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases,
injuries to the arms, the hands and the head can occur when the driver
airbag is deployed.
•
Ensure that there are no objects in the footwell as any objects may get
behind the pedals during a driving or braking manoeuvre. You would then
no longer be able to operate the clutch, to brake or accelerate.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from
the dash panel so that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety
when an airbag is deployed.For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of
an accident, we recommend the following setting.•
Adjust the front passenger seat as far as possible to the rear.
•
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same
level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 141.
•
Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 134, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated ⇒page 145,
“Deactivating airbags”.
Adjusting the passenger seat ⇒page 62, “Adjusting the front seats”.
WARNING
•
The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
Fig. 141 The correct head
restraint adjustment for the
driver
WARNING (continued)
s3f4.1.book Page 129 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 132 of 259

Passive Safety131
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
•
sit to the side;
•
lean out of the window;
•
put the feet out of the window;
•
put the feet on the dash panel;
•
put the feet on the seat upholstery;
•
transport somebody in the footwell;
•
have the seat belt not fastened when driving;
•
occupy the luggage compartment.
WARNING
•
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
•
Before setting off, please adopt the correct seated position and do not
change this seated position while the car is moving. Also advise your occu-
pants to adopt the correct seated position and not to change this seated
position while the car is moving.
s3f4.1.book Page 131 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 134 of 259
Seat belts133
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
The physical principle of a frontal collisionThe physical principle of a frontal accident can be explained quite simply:
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy
depends essentially on the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the vehicle and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an acci-
dent.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50 km/hour,
the forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily
exceed 10.000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
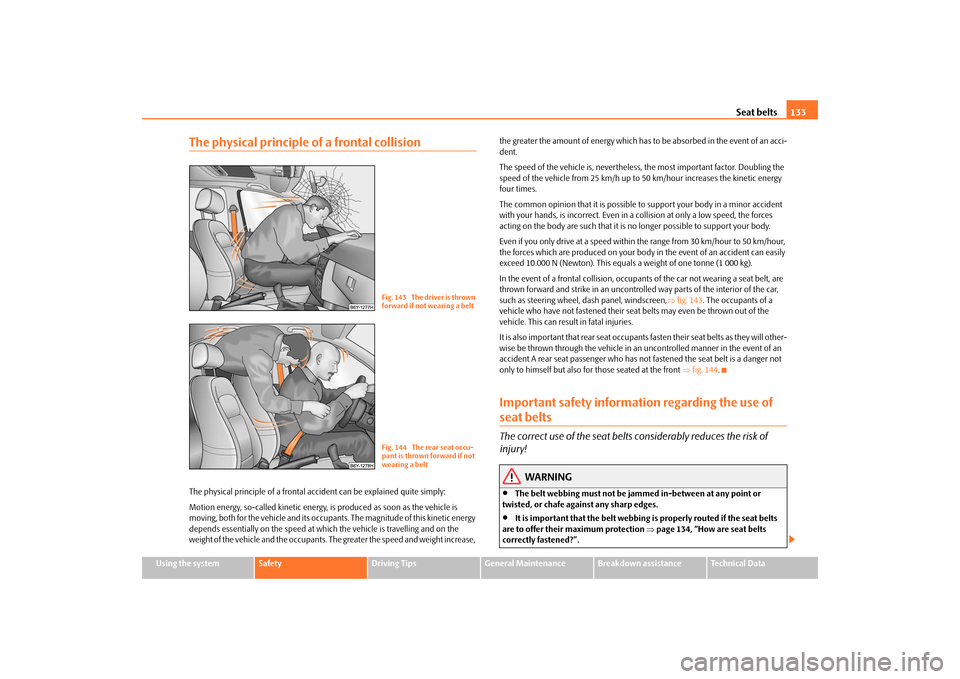
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the car,
such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen,⇒fig. 143. The occupants of a
vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out of the
vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will other-
wise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event of an
accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a danger not
only to himself but also for those seated at the front ⇒fig. 144.
Important safety information regarding the use of seat beltsThe correct use of the seat belts considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or
twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
•
It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer their maximum protection ⇒page 134, “How are seat belts
correctly fastened?”.
Fig. 143 The driver is thrown
forward if not wearing a beltFig. 144 The rear seat occu-
pant is thrown forward if not
wearing a belt
s3f4.1.book Page 133 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 136 of 259

Seat belts135
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
– Slowly pull the belt webbing at the tongue of the lock over your chest
and pelvis ⇒.
– Insert the tongue of the lock into the seat belt buckle belonging to the
seat until it is heard to lock in place.
– Pull on the belt to check that it has also reliably engaged in the lock.Each three-point seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. This inertia reel offers
you complete freedom of movement if the belt is unreeled slowly. If the brakes are
applied suddenly, the inertia reel will block. The belts also block when the car accel-
erates, when driving downhill and when cornering.
Expectant mothers must also wear the seat belt ⇒.
WARNING
•
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across your neck but
must run approximately over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly
against the chest. The lap part of the belt must run across the hip and must
never be routed across the stomach. It must always fit snugly ⇒page 134,
fig. 145. Adjust the belt webbing as required.
•
The lap part of the belt should be positioned as low as possible at the
pelvis of an expectant mother in order to avoid exerting any pressure on the
lower abdomen.
•
Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents.
•
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body
is moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
•
Only insert the lock tongue into the lock which is the correct one for your
seat. This will affect the protection which the belt offers and increase the risk
of an injury.
Seat belt height adjuster on the front seatsThe seat belt height adjuster makes it possible for you to adapt the
routing of the front three-point seat belt in the area of the shoulder to
match your body size.
– To adjust the belt height press the height adjuster and move it up or
down ⇒fig. 147.
– Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster
has correctly locked in place.
WARNING
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the belt
is positioned approximately across the middle of your shoulder - on no
account across your neck.
Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing on the front seats by
adjusting the height of the seat*.
Fig. 147 Front seat: Seat belt
height adjuster
s3f4.1.book Page 135 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 138 of 259

Seat belts137
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
•
When disposing of vehicle or parts of the system, it is important to comply with
the national legal requirements.
s3f4.1.book Page 137 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 140 of 259

Airbag system139
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
When are the airbags deployed?The airbag system is designed in such a way that the driver and the front passenger
airbag* are deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity.
In the case of a violent side crash, the side airbag* in the front seat and the head
airbag* on the side on which the collision occurs are deployed.
It is also possible under certain special accident situations that the front as well as
the side airbags and head airbags* are deployed at the same time.
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions, in the
case of rear-end collisions and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to state globally which deployment conditions apply to the airbag
system in every situation as the circumstances which exist in the case of accidents
vary greatly. An important role in this case, for example, is played by factors such as
the type of object against which the vehicle impacts (hard, soft), the angle of impact,
the vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which occurs
during a collision. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates
the relevant restraint system. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is meas-
ured during the collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified
in the control unit, the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well
suffer severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The airbags are not deployed if:•
ignition is switched off;
•
a minor frontal collision;
•
a minor side collision;
•
a rear-end collision;
•
Rollover of the vehicle.Note
•
A grey white or red, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is
perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
•
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
−the interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
contact position),
−the hazard warning light is switched on;
−All the doors are unlocked.
Front airbagsDescription of the front airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belt!
Fig. 149 Driver airbag in the
steering wheelFig. 150 Front passenger
airbag in the dash panel
s3f4.1.book Page 139 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 142 of 259

Airbag system141
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to injuries if
the sitting position or seated position is not correct ⇒ in “Important safety
information regarding the front airbag system” on page 141.
Important safety information regarding the front airbag system
Correct use of the airbag system considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•
Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
•
For the driver and front passenger it is important to maintain a distance
of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel or dash panel ⇒fig. 152. Not main-
taining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be
able to properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head restraints
must always also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of the occu-
pant.
•
It is essential to always switch off ⇒page 145, “Deactivating airbags” the
front passenger airbag when attaching a child safety seat on the front
passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of
travel (in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel). If this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal
injuries if the front passenger airbag is deployed. In certain countries
national legal provisions also require that the side or head passenger
airbags be deactivated. When transporting a child on the front passenger
seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
•
There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned
between the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag.
•
The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash
panel on the passenger side must not be stuck onto, covered or modified in
any other way. These parts should only be cleaned with a dry cloth or a cloth
moistened with water. No objects such as cup holders, mobile phone
mounts, etc. may be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be
located within the immediate area.
•
No modifications of any kind may be made to parts of the airbag system.
Any work on the airbag system including installing and removing system
components because of other repair work (e.g. removing the steering
wheel) must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
•
Never carry out changes on the front bumper or on the body.
•
Never place any objects on the surface of the dash panel on the front
passenger side.
Fig. 152 Safe distance to
steering wheel
WARNING (continued)
s3f4.1.book Page 141 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM