2009 OPEL MERIVA weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 4 of 248
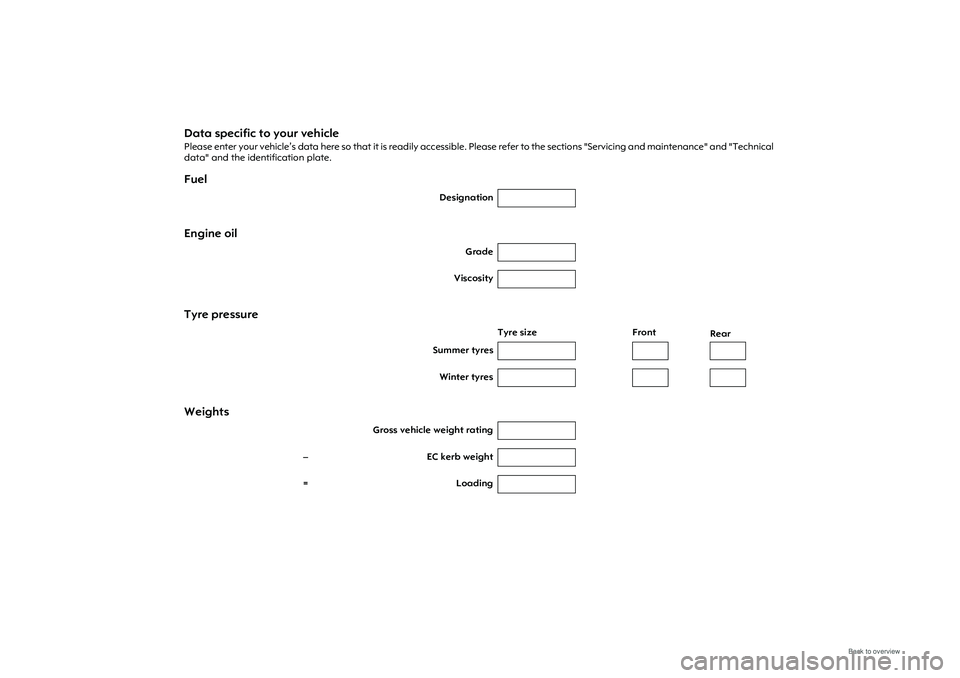
Data specific to your vehiclePlease enter your vehicle’s data here so that it is readily accessible. Please refer to the sections "Servicing and maintenance" and "Technical
data" and the identification plate. Fuel
Designation
Engine oil
Grade
Viscosity
Tyre pressure
Tyre size Front
Rear
Summer tyres
Winter tyres
Weights
Gross vehicle weight rating
– EC kerb weight
=Loading
Page 9 of 248

3
In Brief
Picture no: 13978s.tif
To adjust front seat backrests:
Turn handwheel Do not lean on seat backrest whilst
adjusting it.
Seats 344, Seat position 345.
Picture no: 13979s.tif
To adjust front seat height
3: Pull
lever
Lift lever and relieve some weight from seat
to raise it or press down on seat with body
weight to lower it.
Seats 344, Seat position 345.
Picture no: 13980s.tif
Head restraint height of front and
rear outer seats: Tip head
restraint forward to release, hold
and adjust height, engage Head restraints 346, Centre rear head
restraint 347, Head restraint position 347,
Head restraint removal 348.
Page 51 of 248

45
Seats, Interior
Picture no: 13979s.tif
Adjusting the seat height3
Lift front side lever and relieve some weight
from seat to raise it or press down on seat
with body weight to lower it.
Picture no: 16098s.tif
Adjusting the lumbar support 3
Turn side hand wheel on backrest while
relieving the load on the backrest.
Picture no: 18530s.tif
Seat position
z Sit with your buttocks as far back against
the backrest as possible. Adjust the
distance between your feet and the
pedals so that your legs are slightly
angled when pressing the pedals. Slide
the passenger seat as far back as
possible.
9 Warning
Only drive with the seat correctly
adjusted.
Page 64 of 248

58 Seats, Interior
Picture no: 14110s.tif
Notes on loading the vehicle zHeavy objects in the luggage
compartment should be placed as far
forward as possible against the properly
engaged rear seat backrests or, if the
rear seat backrests are folded down,
against the front seat backrests. If
objects are to be stacked, the heavier
objects should be placed at the bottom.
z Secure heavy objects with lashing
straps 3 attached to lashing eyes 357.
z When transporting objects with rear seat
backrests tilted forward, fit the safety net
356. z
Close luggage compartment cover 3
3 55.
z If the backrests are not folded down
when transporting objects in the
luggage compartment, they must be
engaged in an upright position 355.
z Do not allow the load to protrude above
the upper edge of the backrests.
z The warning triangle 3 and first-aid kit
(cushion) 3 must always be freely
accessible.
z Do not place any objects on the luggage
compartment cover 3 or the instrument
panel.
z No objects must be placed in the airbag
inflation area, since they could cause
injury when the systems are triggered.
z Items loaded must not prevent operation
of the pedals, hand brake and gears or
obstruct the freedom of movement of
the driver. Do not place loose objects in
the interior.
z Do not drive with luggage compartment
open when transporting bulky objects,
for example, since toxic exhaust fumes
could penetrate the interior.
z The payload is the difference between
the permitted gross vehicle weight (see
identification plate 3218) and the EC
kerb weight. z
To calculate the EC kerb weight, enter
the data for your vehicle on page 3 226.
z The EC kerb weight includes allowances
for the driver (68 kg), luggage (7 kg) and
all fluids (tank 90 % full).
z Optional equipment and accessories
increase the kerb weight.
z Weights and loads 3226.
z Driving with a roof load increases the
sensitivity of the vehicle to cross-winds
and has a detrimental effect on vehicle
handling due to the vehicle’s higher
centre of gravity. Distribute the load
evenly and secure it properly with
retaining straps. Adjust the tyre pressure
to the load conditions. Do not drive
faster than 120 km/h. Check and re-
tighten the straps frequently. Observe
country-specific regulations.
z The permissible roof load is 100 kg. The
roof load consists of the weight of the
roof rack plus the load carried.
Page 71 of 248

65
Seats, Interior
Child restraint system
3
Follow the usage instructions for the child
restraint system.
Always comply with local or national
regulations. In some countries, the use of
child restraint systems is forbidden on
certain seats.
Selecting the right system
Your child should be transported facing the
rear in the vehicle for as long as possible.
The very weak cervical vertebrae of a child
will be under less stress in an accident if
your child is facing the rear and semi-
horizontal, than when he is sitting upright.
9 Warning
Child restraint systems must not be
carried on a passenger’s lap. Danger
to life.
Permissible options for fitting a child safety seat
1)
1)For reasons of safety, we recommend that the child safety seat be installed on one of the outer
rear seats.Weight and
age class
2)
2)We recommend the use of each system until the child reaches the upper weight limit.
On front
passenger seat On outboard seats in
the rear seats On centre
rear seat
Group 0:
up to 10 kg
or approx.
10 months
Group 0+:
up to 13 kg
or approx.
2years B
1, +
U, + U, ++
Group I:
9to18 kg
or approx.
8months
to 4 years B2, +
U, + U, ++
Group II:
15 to 25 kg
or approx.
3 to 7 years
Group III:
22 to 36 kg
or approx.
6 to 12 years X U U,
++
Page 72 of 248

66 Seats, Interior
Note
zChildren under 12 years or under 150 cm
tall should only travel in an appropriate
child restraint system.
z When transporting children, use the child
restraint systems suitable for the child’s
weight.
z Ensure correct installation of child
restraint system, see the instructions
enclosed with the system.
z The covers of the Opel child restraint
system can be wiped clean.
z Do not stick anything on the child
restraint systems and do not cover them
with any other materials.
z Only allow children to enter and exit at
the side facing away from the traffic.
z A child restraint system which has been
subjected to stress in an accident must
be replaced.
z Secure or remove child restraint systems
that are in the vehicle but not in use.
B
1= Conditional, without front
passenger airbags or with seat
occupancy recognition and Opel
child restraint systems with
transponders.
The front passenger seat must also
have a height adjusting facility:
move to highest position, slide front
passenger seat all the way back and
move front passenger seat belt
anchorage point to lowest possible
position.
B2= Conditional, without side airbag, of front passenger seat has been slid
all the way back, or with seat
occupancy recognition and Opel
child restraint systems with
transponders.
The front passenger seat must also
have a height adjusting facility:
move to highest position and slide
front passenger seat all the way
back so that the seat belt runs
towards the front from the
anchorage point.
U = Universal suitability in conjunction with three-point seat belt. + = Vehicle seat available with ISOFIX
fixings. When using ISOFIX, only
ISOFIX child restraint systems
approved for the vehicle may be
used.
++ = Only if both outboard seats are pushed back and flush with the
centre seat.
X = No child restraint system permitted in this weight class.
Page 82 of 248

76 Seats, InteriorUse of child restraint systems 3 on the
front passenger seat in vehicles with
airbag systems 3, but without seat
occupancy recognition 3
Picture no: 11704a.tif
Vehicles with front passenger airbag can
be recognised by the word AIRBAG above
the glove compartment and by the sticker
on the instrument panel on the passenger
side - see Fig. 11704 A.
Picture no: 14791s.tif
A vehicle with side airbags can be
identified by the word AIRBAG on the
outboard sides of the front seat backrests.
Seat occupancy recognition 3 372.
9 Warning
Vehicles with fron t passenger airbag 3
without side airbag 3: Child seats facing
the rear of the vehicle must not be
installed on the front passenger seat,
risk of fatal injury. Child seats facing the
direction of travel (child seats for weight
classes I, II and III, following pages) may
be installed on the front passenger seat
if the seat has been pushed back as far
as it will go and the backrest has been
adjusted such that the lap belt fits
snugly.
9 Warning
Vehicles with side airbag 3: No child
restraint system 3 may be fitted on the
front passenger’s seat; risk of fatal
injury.
Page 145 of 248

139
Driving and operation
Fuels, refuellingFuel consumption
The fuel consumption is determined under
specified driving conditions 3224.
Special equipment increases the weight of
the vehicle. As a result, they can increase
fuel consumption and reduce the specified
maximum speed.
For the first few thousand kilometres,
friction between the engine and
transmission components is higher. This
increases fuel consumption. Fuel for petrol engines
Only use unleaded fuel that complies
with DIN EN 228.
Fuels with ethanol content greater than 5 %
may only be used if the vehicle has been
specifically developed and approved for
these fuels.
Use fuel with the recommended octane
rating (value in bold
3220). Use of fuel
with too low an octane rating can reduce
engine power and torque and will slightly
increase fuel consumption. Fuel for diesel engines
Only use diesel fuel that complies
with DIN EN 590. The fuel must have low
sulphur content (maximum 50 ppm).
Do not use marine diesel oils, heating oils
or entirely or partially plant-based diesel
fuels, such as rape seed oil or bio diesel,
Aquazole and similar diesel-water
emulsions. Diesel fuels must not be diluted
with fuels for petrol engines.
The flow and filterability of diesel fuel are
temperature-dependent. When
temperatures are low, re
fuel with diesel fuel
with guaranteed winter properties.
Caution
Use of fuel with too low an octane rating
could lead to uncontrolled combustion
and engine damage.