2009 NISSAN TIIDA 4 wheel drive
[x] Cancel search: 4 wheel drivePage 12 of 4331

AT
N
O P
PRECAUTIONS
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER" INFOID:0000000004803451
The Supplemental Restraint System such as “A IR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along
with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severi ty of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. This system includes seat belt switch inputs and dual stage front air bag modules. The SRS
system uses the seat belt switches to determine the front air bag deployment, and may only deploy one front
air bag, depending on the severity of a collision and w hether the front occupants are belted or unbelted.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in the SRS and SB section of this Service Man-
ual.
WARNING:
• To avoid rendering the SRS inoper ative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death in
the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed by
an authorized NISSAN/INFINITI dealer.
• Improper maintenance, including in correct removal and installation of the SRS can lead to personal
injury caused by unintentional act ivation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air Bag
Module, see the SRS section.
• Do not use electrical test equipm ent on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses can be identi fied by yellow and/or orange harnesses or har-
ness connectors.
• When working near the Airbag Diagnosis Sensor Un it or other Airbag System sensors with the Igni-
tion ON or engine running, DO NOT use air or el ectric power tools or strike near the sensor(s) with a
hammer. Heavy vibration could activate the sensor( s) and deploy the air bag(s), possibly causing
serious injury.
• When using air or electric power tools or hammers , always switch the Ignition OFF, disconnect the
battery, and wait at least 3 minutes before performing any service.
Precaution Necessary for Steering Wh eel Rotation After Battery Disconnect
INFOID:0000000004305289
NOTE:
• This Procedure is applied only to models with Intell igent Key system and NVIS/IVIS (NISSAN/INFINITI
VEHICLE IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM - NATS).
• Remove and install all control units after disconnecti ng both battery cables with the ignition knob in the
″ LOCK ″ position.
• Always use CONSULT-III to perform self-diagnosis as a part of each function inspection after finishing work.
If DTC is detected, perform trouble diagnosis according to self-diagnostic results.
For models equipped with the Intelligent Key system and NVIS/IVIS, an electrically controlled steering lock
mechanism is adopted on the key cylinder.
For this reason, if the battery is disconnected or if the battery is discharged, the steering wheel will lock and
steering wheel rotation will become impossible.
If steering wheel rotation is required when battery pow er is interrupted, follow the procedure below before
starting the repair operation.
OPERATION PROCEDURE 1. Connect both battery cables. NOTE:
Supply power using jumper cables if battery is discharged.
2. Use the Intelligent Key or mechanical key to turn the ignition switch to the ″ACC ″ position. At this time, the
steering lock will be released.
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released and the steering wheel can be
rotated.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
5. When the repair work is completed, return the ignition switch to the ″LOCK ″ position before connecting
the battery cables. (At this time, the steering lock mechanism will engage.)
6. Perform a self-diagnosis check of al l control units using CONSULT-III.
Page 40 of 4331
AT
N
O P
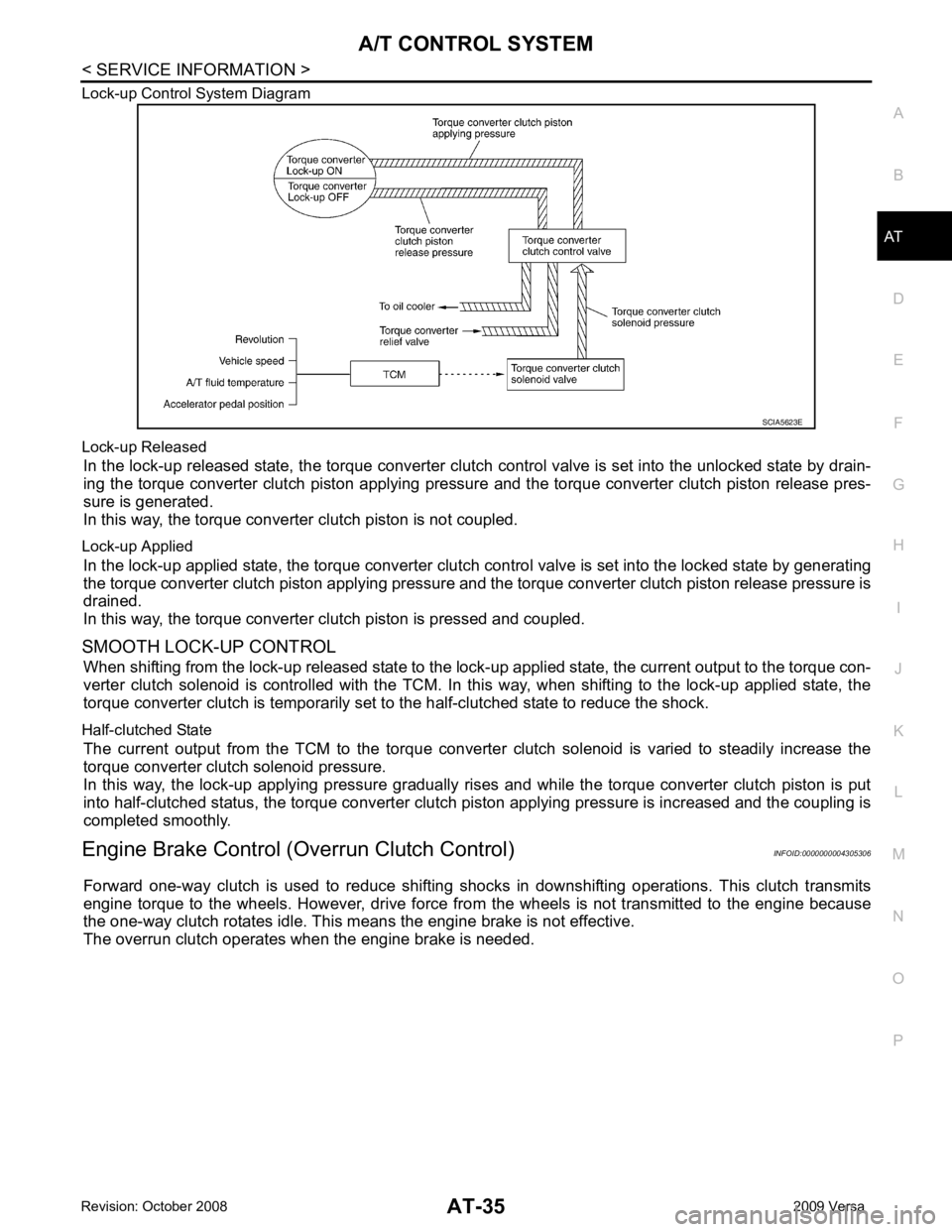
Lock-up Control System Diagram
Lock-up Released In the lock-up released state, the torque converter clutch control valve is set into the unlocked state by drain-
ing the torque converter clutch piston applying pressure and the torque converter clutch piston release pres-
sure is generated.
In this way, the torque converter clutch piston is not coupled.
Lock-up Applied In the lock-up applied state, the torque converter clutch control valve is set into the locked state by generating
the torque converter clutch piston applying pressure and t he torque converter clutch piston release pressure is
drained.
In this way, the torque converter clutch piston is pressed and coupled.
SMOOTH LOCK-UP CONTROL When shifting from the lock-up released state to the lock- up applied state, the current output to the torque con-
verter clutch solenoid is controlled with the TCM. In this way, when shifting to the lock-up applied state, the
torque converter clutch is temporarily set to the half-clutched state to reduce the shock.
Half-clutched State The current output from the TCM to the torque converte r clutch solenoid is varied to steadily increase the
torque converter clutch solenoid pressure.
In this way, the lock-up applying pressure gradually rises and while the torque converter clutch piston is put
into half-clutched status, the torque converter clutch piston applying pressure is increased and the coupling is
completed smoothly.
Engine Brake Control (Overrun Clutch Control) INFOID:0000000004305306
Forward one-way clutch is used to reduce shifting shoc ks in downshifting operations. This clutch transmits
engine torque to the wheels. However, drive force fr om the wheels is not transmitted to the engine because
the one-way clutch rotates idle. This means the engine brake is not effective.
The overrun clutch operates when the engine brake is needed.
Page 56 of 4331
AT
N
O P
Inspections Before Trouble Diagnosis
INFOID:0000000004305319
A/T FLUID CHECK
Fluid Leakage and Fluid Level Check Check fluid leakage and check the fluid level. Refer to AT-17, " Checking A/T Fluid " .
Fluid Condition Check Check the A/T fluid condition.
STALL TEST
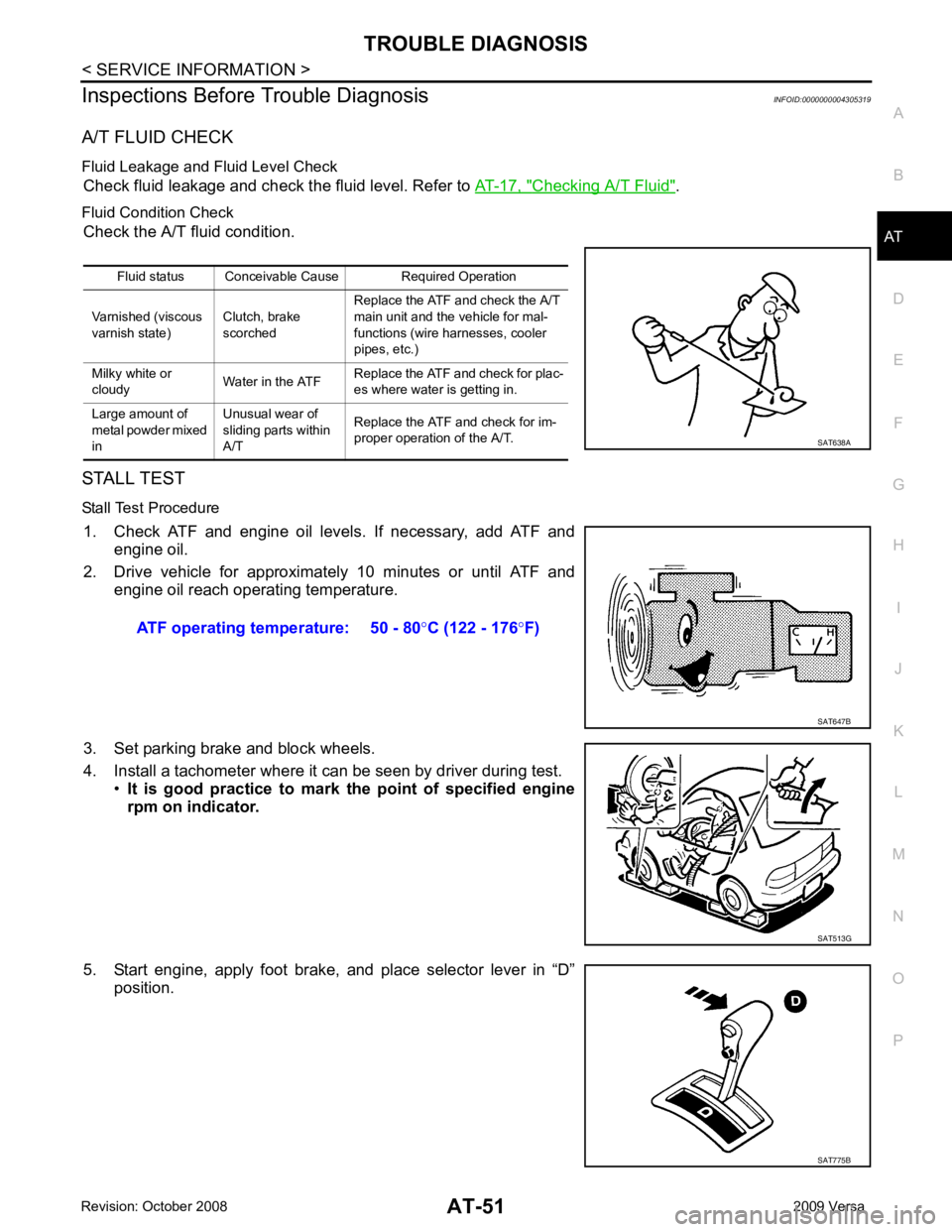
Stall Test Procedure 1. Check ATF and engine oil levels. If necessary, add ATF and engine oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approximately 10 minutes or until ATF and engine oil reach operating temperature.
3. Set parking brake and block wheels.
4. Install a tachometer where it can be seen by driver during test. •It is good practice to mark the point of specified engine
rpm on indicator.
5. Start engine, apply foot brake, and place selector lever in “D” position.Fluid status Conceivable Cause Required Operation
Varnished (viscous
varnish state) Clutch, brake
scorched Replace the ATF and check the A/T
main unit and the vehicle for mal-
functions (wire harnesses, cooler
pipes, etc.)
Milky white or
cloudy Water in the ATFReplace the ATF and check for plac-
es where water is getting in.
Large amount of
metal powder mixed
in Unusual wear of
sliding parts within
A/T Replace the ATF and check for im-
proper operation of the A/T. SAT775B
Page 59 of 4331
AT-54< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
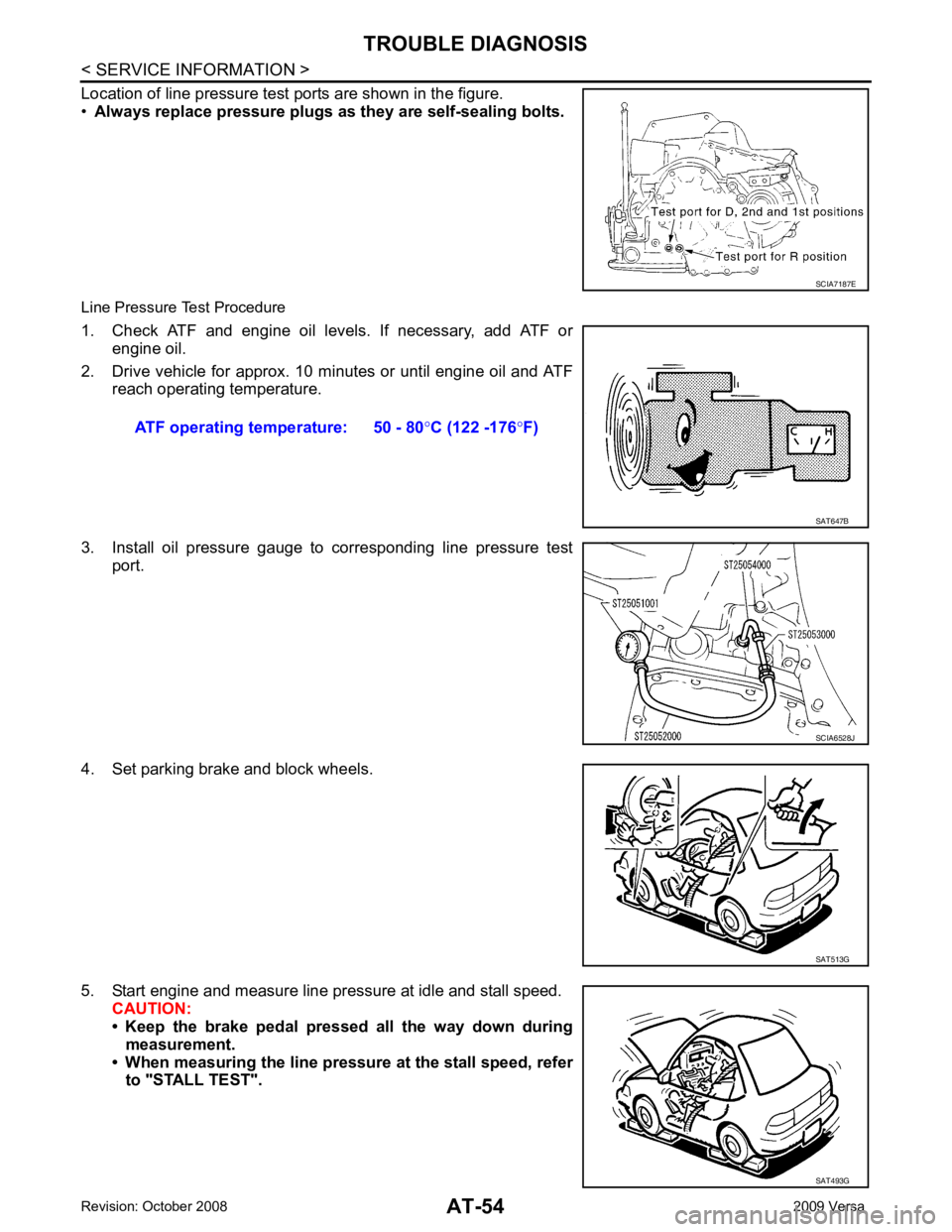
Location of line pressure test ports are shown in the figure.
• Always replace pressure plugs as they are self-sealing bolts.
Line Pressure Test Procedure
1. Check ATF and engine oil levels. If necessary, add ATF or engine oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approx. 10 minutes or until engine oil and ATF reach operating temperature.
3. Install oil pressure gauge to corresponding line pressure test port.
4. Set parking brake and block wheels.
5. Start engine and measure line pressure at idle and stall speed. CAUTION:
• Keep the brake pedal pressed all the way down during
measurement.
• When measuring the line pressure at the stall speed, refer to "STALL TEST". SCIA7187E
ATF operating temperature: 50 - 80
°C (122 -176 °F) SAT647B
SCIA6528J
SAT513G
SAT493G
Page 805 of 4331
BR
N
O P
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHN
ESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
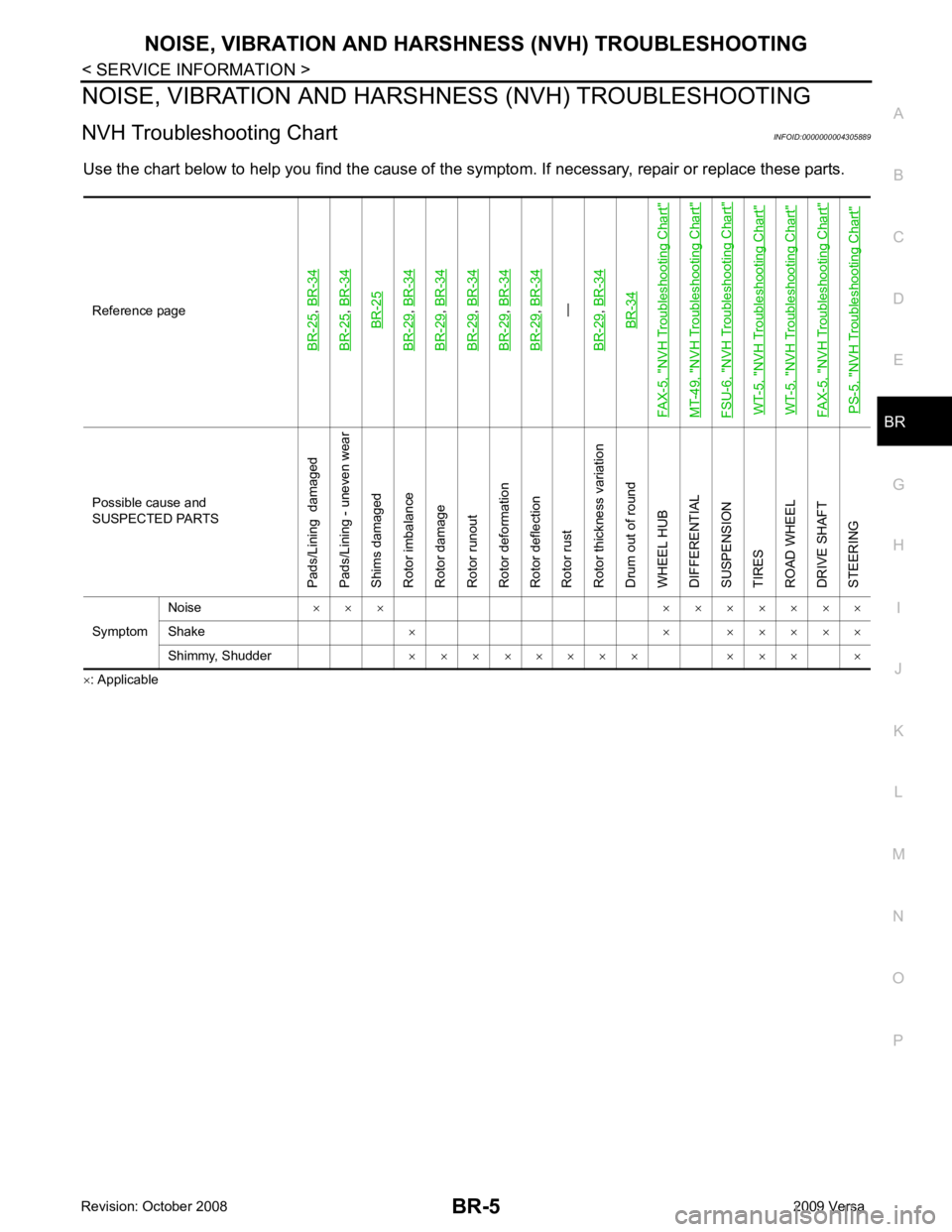
NVH Troubleshooting Chart INFOID:0000000004305889
Use the chart below to help you find t he cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
× : ApplicableReference pageBR-25
,
BR-34
BR-25
, BR-34BR-25
BR-29
, BR-34
BR-29
, BR-34
BR-29
, BR-34
BR-29
, BR-34
BR-29
, BR-34—
BR-29, BR-34BR-34
FAX-5, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
MT-49, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
FSU-6, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
WT-5, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
WT-5, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
FAX-5, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
"
PS-5, "
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
" Possible cause and
SUSPECTED PARTS
Pads/Lining damaged
Pads/Lining - uneven wear
Shims damaged
Rotor imbalance
Rotor damage
Rotor runout
Rotor deformation
Rotor deflection
Rotor rust
Rotor thickness variation
Drum out of round
WHEEL HUB
DIFFERENTIAL
SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
DRIVE SHAFT
STEERING
Symptom Noise
× × × × × × × × × ×
Shake × × × × × × ×
Shimmy, Shudder × × × × × × × × × × × ×
Page 830 of 4331
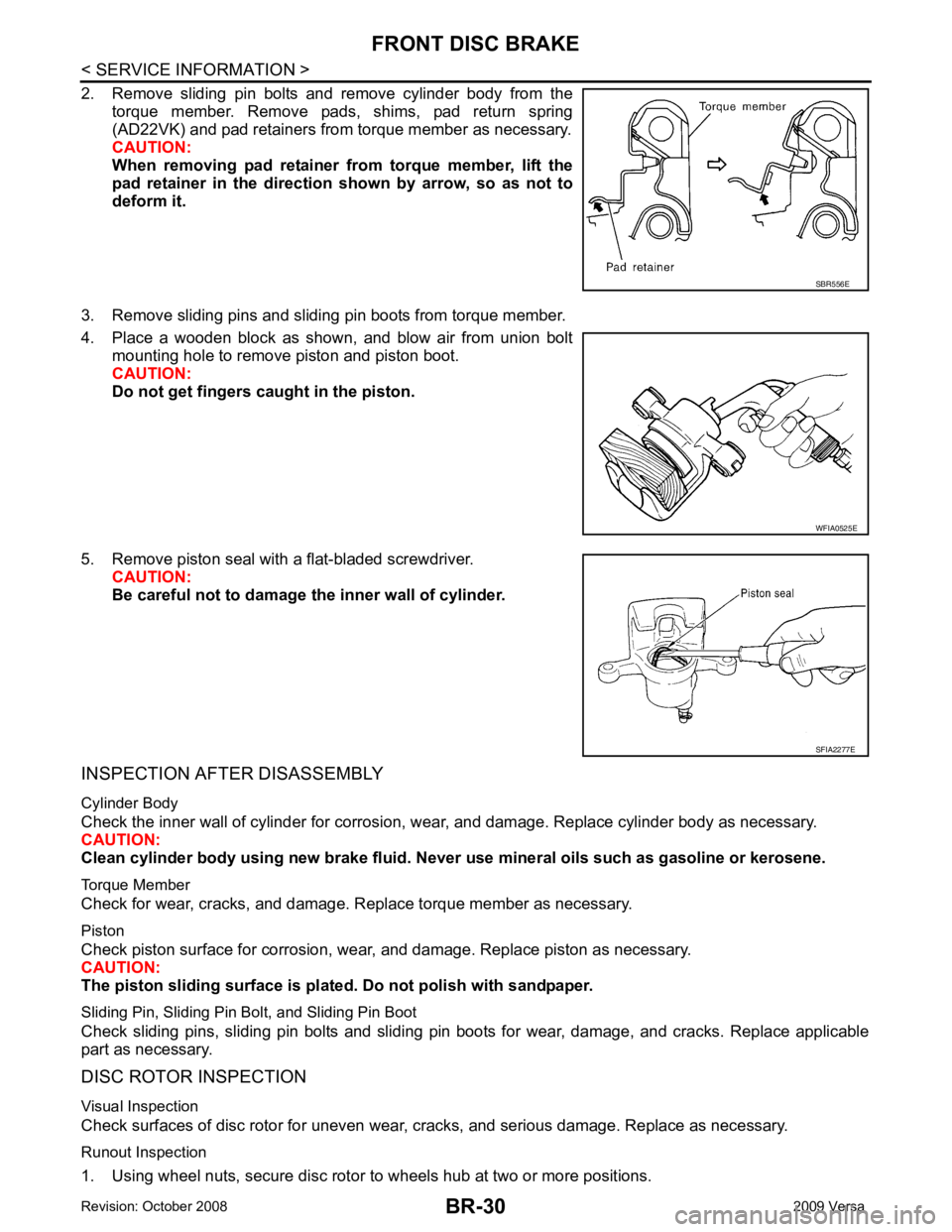
BR-30< SERVICE INFORMATION >
FRONT DISC BRAKE
2. Remove sliding pin bolts and remove cylinder body from the torque member. Remove pads, shims, pad return spring
(AD22VK) and pad retainers from torque member as necessary.
CAUTION:
When removing pad retainer fr om torque member, lift the
pad retainer in the direction shown by arrow, so as not to
deform it.
3. Remove sliding pins and sliding pin boots from torque member.
4. Place a wooden block as shown, and blow air from union bolt mounting hole to remove piston and piston boot.
CAUTION:
Do not get fingers caught in the piston.
5. Remove piston seal with a flat-bladed screwdriver. CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the inner wall of cylinder.
INSPECTION AFTER DISASSEMBLY
Cylinder Body
Check the inner wall of cylinder for corrosion, w ear, and damage. Replace cylinder body as necessary.
CAUTION:
Clean cylinder body using new brake fluid. Never use mineral oils such as gasoline or kerosene.
Torque Member
Check for wear, cracks, and damage. R eplace torque member as necessary.
Piston
Check piston surface for corrosion, wear, and damage. Replace piston as necessary.
CAUTION:
The piston sliding surface is plated . Do not polish with sandpaper.
Sliding Pin, Sliding Pin Bolt, and Sliding Pin Boot
Check sliding pins, sliding pin bolts and sliding pin boots for wear, damage, and cracks. Replace applicable
part as necessary.
DISC ROTOR INSPECTION
Visual Inspection
Check surfaces of disc rotor for uneven wear, cr acks, and serious damage. Replace as necessary.
Runout Inspection
1. Using wheel nuts, secure disc rotor to wheels hub at two or more positions. SBR556E
WFIA0525E
SFIA2277E
Page 835 of 4331
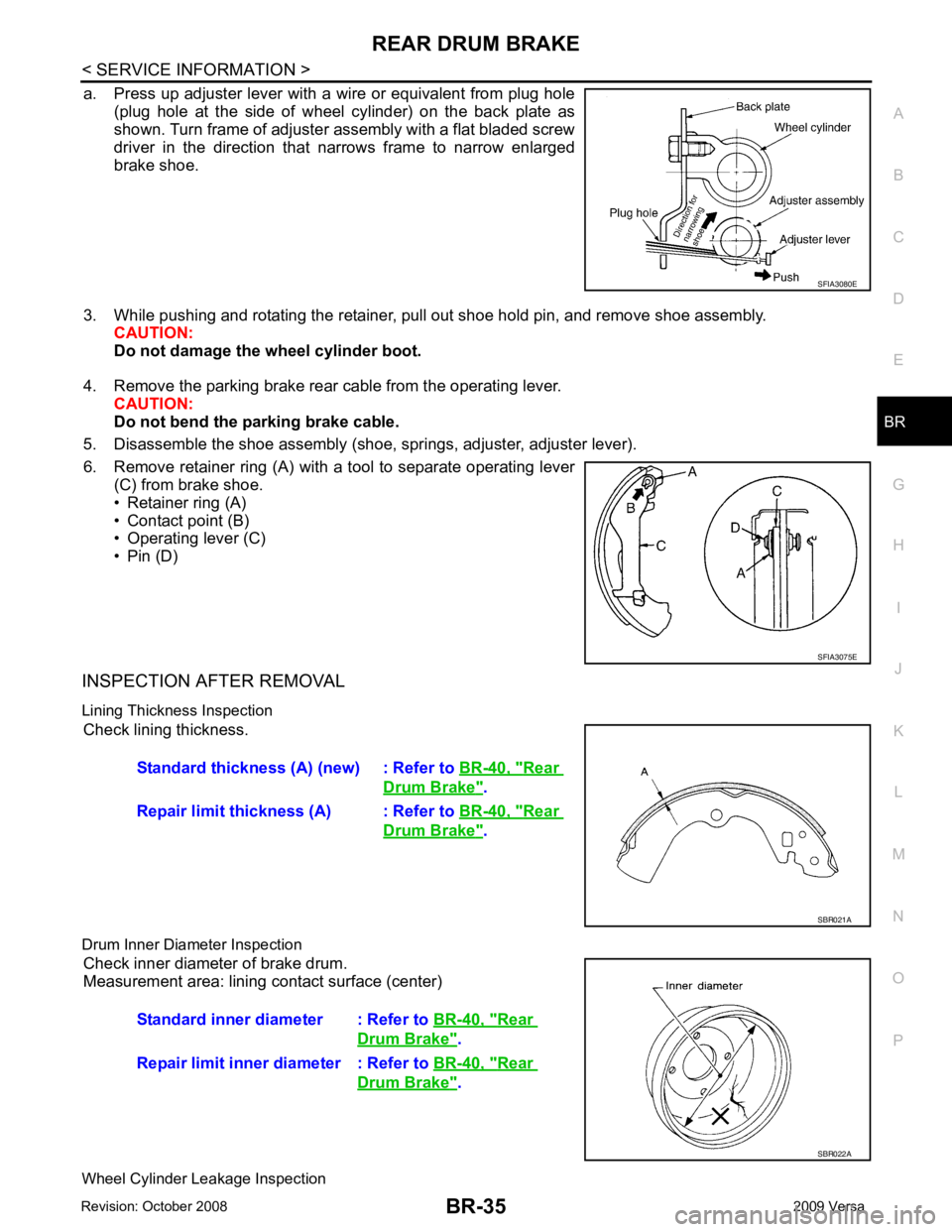
BR
N
O P
a. Press up adjuster lever with a wire or equivalent from plug hole
(plug hole at the side of wheel cylinder) on the back plate as
shown. Turn frame of adjuster assembly with a flat bladed screw
driver in the direction that narrows frame to narrow enlarged
brake shoe.
3. While pushing and rotating the retainer, pull out shoe hold pin, and remove shoe assembly. CAUTION:
Do not damage the wheel cylinder boot.
4. Remove the parking brake rear cable from the operating lever. CAUTION:
Do not bend the parking brake cable.
5. Disassemble the shoe assembly (shoe, springs, adjuster, adjuster lever).
6. Remove retainer ring (A) with a tool to separate operating lever (C) from brake shoe.
• Retainer ring (A)
• Contact point (B)
• Operating lever (C)
• Pin (D)
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL
Lining Thickness Inspection Check lining thickness.
Drum Inner Diameter Inspection Check inner diameter of brake drum.
Measurement area: lining contact surface (center)
Wheel Cylinder Leakage Inspection Rear
Drum Brake " .
Repair limit thickness (A) : Refer to BR-40, " Rear
Drum Brake " .
Rear
Drum Brake " .
Repair limit inner diameter : Refer to BR-40, " Rear
Drum Brake " .
Page 845 of 4331

BRC
N
O P
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
System Component INFOID:0000000004307256
ABS Function INFOID:0000000004307257
• The Anti-Lock Brake System detects wheel revolution while braking and improves handling stability during sudden braking by electrically preventing wheel lockup. Maneuverability is also improved for avoiding obsta-
cles during emergency braking.
• If the electrical system malfunctions, the Fail-Safe function is activated, the ABS becomes inoperative and
the ABS warning lamp turns on.
• The electrical system can be diagnosed using CONSULT-III.
• During ABS operation, the brake pedal may vibrate lightly and a mechanical noise may be heard. This is
normal.
• Just after starting the vehicle, the brake pedal may vibrate or motor operating noises may be heard from the
engine compartment. This is normal due to the self check operation.
• Stopping distance may be longer than that of vehicles without ABS when vehicle drives on rough, gravel, or
snow-covered (fresh, deep snow) roads.
EBD Function INFOID:0000000004307258
• Electronic Brake Distribution is a function that detec ts subtle slippages between the front and rear wheels
during braking, and it improves handling stability by elec tronically controlling the brake fluid pressure which
results in reduced rear wheel slippage.
• If the electrical system malfunctions, the Fail-Safe function is activated, the EBD and ABS become inopera-
tive, and the ABS warning lamp and brake warning lamp are turned on.
• The electrical system can be diagnosed using CONSULT-III.
• During EBD operation, the brake pedal may vibrate lightly and a mechanical noise may be heard. This is
normal.
• Just after starting the vehicle, the brake pedal may vibrate or motor operating noises may be heard from the
engine compartment. This is normal due to the self check operation.
Fail-Safe Function INFOID:0000000004307259
CAUTION:
If the Fail-Safe function is activated, perform the Self Diagnosis for ABS system.
ABS/EBD SYSTEM In case of an electrical malfunction with the ABS, the ABS warning lamp wi ll turn on. In case of an electrical
malfunction with the EBD system, the brake warni ng lamp and the ABS warning lamp will turn on.
The system will revert to one of the follo wing conditions of the Fail-Safe function.
1. For ABS malfunction, only the EBD is operative and t he condition of the vehicle is the same condition of
vehicles without ABS system.