2009 JAGUAR XF ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 3 of 36

Technical Training
NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine 04/14/2009
3-1
Engine Management System
Table of Contents
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Engine Control Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Crankshaft Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Camshaft Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . 14
Knock Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Mass Air Flow Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Temp. / Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor . . . . 18
Throttle Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Heated Oxygen Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Ambient Air Temperature Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Ignition Coils . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Fuel Tank Canister Purge Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Viscous Fan Control (Land Rover only) . . . . . . . 29
Controller Area Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
On-Board Diagnostic Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Crankcase Ventilation System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Page 4 of 36

3-2
04/14/2009 NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine
Technical Training
Overview
Engine Management System
OVERVIEW
The 5.0-Liter V8 normally aspirated (NA) and super-
charged (SC) engines are managed by the engine control
module (ECM), which controls the following:
• Engine fuel metering
• Ignition timing
• Camshaft timing
• Camshaft Profile Switching (CPS)
• Closed loop fuel metering
• Knock control
• Idle speed control
• Emission control
• On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)
• Interface with the immobilization system
• Speed control
The ECM controls the engine fuel metering by provid-
ing sequential fuel injection to all cylinders. Ignition is
controlled by a direct ignition system, provided by eight
coil-on-plug (COP) units. The ECM is able to detect and
correct for ignition knock on each cylinder and adjust the
ignition timing for each cylinder to achieve optimum
performance.
The ECM uses a torque-based strategy to generate the
torque required by driver demand and the other vehicle
control modules, using input from various sensors to cal-
culate the required torque. The ECM also interfaces with
other vehicle electronic control modules to obtain addi-
tional information (road speed from the ABS control
module, for example). The ECM processes these signals
and determines how much torque to generate, using vari-
ous actuators to supply air, fuel, and spark to the engine
(electronic throttle, injectors, coils, etc.).
Page 5 of 36

Technical Training
NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine 04/14/2009
3-3
Engine Management System
Overview
NA Component Location: Front of Engine
NP10V8089
THROTTLE BODY
MANIFOLD ABS
OLUTE PRESSURE S ENSOR
ENGINE
CONTROL MODULE
FUEL INJECTOR
IGNITION COIL
MASS AIR FLOW SENS OR
CAMS HAFT POS ITION
S ENS ORS
VARIABLE CAMS HAFT TIMING
S OLENOIDS
OIL LEVEL / TEMPERATURESENS OR CAMS
HAFT POS ITION
S ENS ORS
VARIABLE CAMSHAFT TIMING
S OLENOIDS MASS AIR FLOW
SENS OR
Page 7 of 36

Technical Training
NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine 04/14/2009
3-5
Engine Management System
Overview
SC Component Location: Front of Engine
NP10V8091
THROTTLE BODY
MANIFOLD ABS
OLUTE PRESSURE S ENSOR
ENGINE
ENGINECONTROL MODULECONTROL MODULEENGINE
CONTROL MODULE
FUEL INJECTOR
IGNITION COIL
MASS AIR FLOW SENS OR
CAMS HAFT POS ITION
S ENS ORS
VARIABLE CAMS HAFT TIMING
S OLENOIDS
OIL LEVEL / TEMPERATURESENS OR CAMS
HAFT POS ITION
S ENS ORS
VARIABLE CAMSHAFT TIMING
S OLENOIDS MASS AIR FLOW
SENS OR
Page 10 of 36

3-8
04/14/2009 NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine
Technical Training
Engine Control Module
Engine Management System
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
The ECM is supplied with battery voltage from a 5A fuse and an ignition supply from the ECM relays through\
a 15A
fuse, both located in the CJB. A regulator located within the ECM supplies a 5V current to internal compone\
nts such
as the microprocessor unit. Other components or functions requiring full\
battery voltage are controlled by external
relays or internal switching modules.
The microprocessor within the ECM receives signals from different components and control modules and uses a pro-
gram within the ECM software to interpret the signal information and issue signals which relate t\
o how the engine
components and functions should be controlled. The ECM communicates with other control modules via bidirectional
Controller Area Network (CAN) communication interfaces.
The ECM uses the following inputs and outputs:
Inputs
• Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• Fuel rail high-pressure sensor
• Mass air flow (MAF) sensors (2)
• Knock sensors (4)
• Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
• Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
• Electronic throttle position sensor
• Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
• Cooling fan speed
• Upstream Universal Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen (UHEGO) sensors (2)
• Brake switch
• Speed control cancel/suspend switch
• Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (integrated into the MAF) (2)
• Ambient air temperature (AAT) sensor
• Engine oil level and temperature sensor
• Temperature and manifold absolute pressure (TMAP) sensor (SC only)
Outputs
• Throttle Actuator
• Coil-on-plug (COP) ignition coils (8)
• Upstream Universal Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen (UHEGO) sensors (2)
• Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO2S) (2)
• Direct injection fuel injectors (8)
• Variable camshaft timing (VCT) solenoids (4)
• Camshaft profile switching (CPS) solenoids (2)
• Intake manifold tuning solenoid
• Carbon canister purge valve
• Fuel pump relay
• Starter relay
• A/C condenser fan relay
• ECM main relay viscous fan control
• Generator control
• Air flap solenoid (SC only)
• Pump control diagnostics
• Diagnostic Monitoring of Tank Leakage (DMTL)
Page 12 of 36

3-10
04/14/2009 NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine
Technical Training
Relays
Engine Management System
RELAYS
Main Relay
The main Engine Management System (EMS) relay is
not a main power input; it is used to initiate the power-up
and power-down routines within the ECM.
This input comes from the engine junction box (EJB).
When the ignition is turned on 12V is applied to the igni-
tion sense input. The ECM then starts its power-up rou-
tines and turns on the ECM main relay, the main power
to the ECM and its associated system components.
When the ignition is turned OFF, the ECM will maintain
its powered-up state for several seconds (or up to 20
minutes in extreme cases when cooling fans are
required) while it initiates its power-down routine and,
on completion, will turn off the ECM main relay.
The main relay is located in the EJB. The operation of
the main relay is controlled by the ECM, which provides
a ground path for the main relay coil, energizing the
relay and closing the relay contacts.
The main relay supplies battery voltage to the following
engine sensors and actuators:
• Throttle position (TP) sensor (through ECM)
• Fuel injectors
• Ignition coils
• Coil capacitor
• CPS solenoids
• All heated oxygen sensors
• Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve
• Diagnostic Monitoring of Tank Leakage (DMTL)
Failure Modes
• Relay drive open circuit
• Short circuit to battery voltage or ground
• Component failure
Failure Symptoms
• Engine will not start
Starter Relay
The starter motor relay is located in the EJB. Operation
of the starter motor relay is controlled by the ECM,
which provides a ground path for the relay coil, energiz-
ing the relay and closing the relay contacts. When the
relay contacts are closed, battery voltage is supplied,
through the starter motor relay, to the starter module
solenoid coil.
The starter solenoid is energized and connects the starter
motor with a direct battery feed to operate the starter
motor.
Once the engine has started, the ECM removes the
starter motor relay ground, opening the relay contacts
and terminating the battery feed to the starter solenoid,
which in turn stops the operation of the starter motor.
NOTE:
Diagnose using Jaguar Land Rover approved
diagnostic equipment.
Page 15 of 36
Technical Training
NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine 04/14/2009
3-13
Engine Management System
Camshaft Position Sensor
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position (CMP) sensors are magneto-
resistive element (MRE) sensors, which have digital out-
put with zero speed recognition. They show a high signal
if the camshaft position target is directly in front of the
sensor, and low if the camshaft position target is not in
front of the sensor.
There are four common sensors, one per camshaft.
Failure Modes
• Sensor open circuit
• Short circuit to vehicle battery supply or ground
• Mechanical fitting and integrity of the sensor
• Camshaft wheel tolerances/camshaft end float excessive
• Camshaft and crankshaft misalignment/valve timing error
• Camshaft wheel magnetized/residual magnetism
• Speed signal correlation with crankshaft sensor input
• Incorrect air gap between camshaft and sensor
NOTE:
If both the CKP sensor and the CMP sensor fail,
the engine will stall or not start.
Failure Symptoms
• Ignition timing reverting to the base mapping, with no cylinder correction
• VCT is disabled
NP10V8096
NP10V8097
NP10V8098
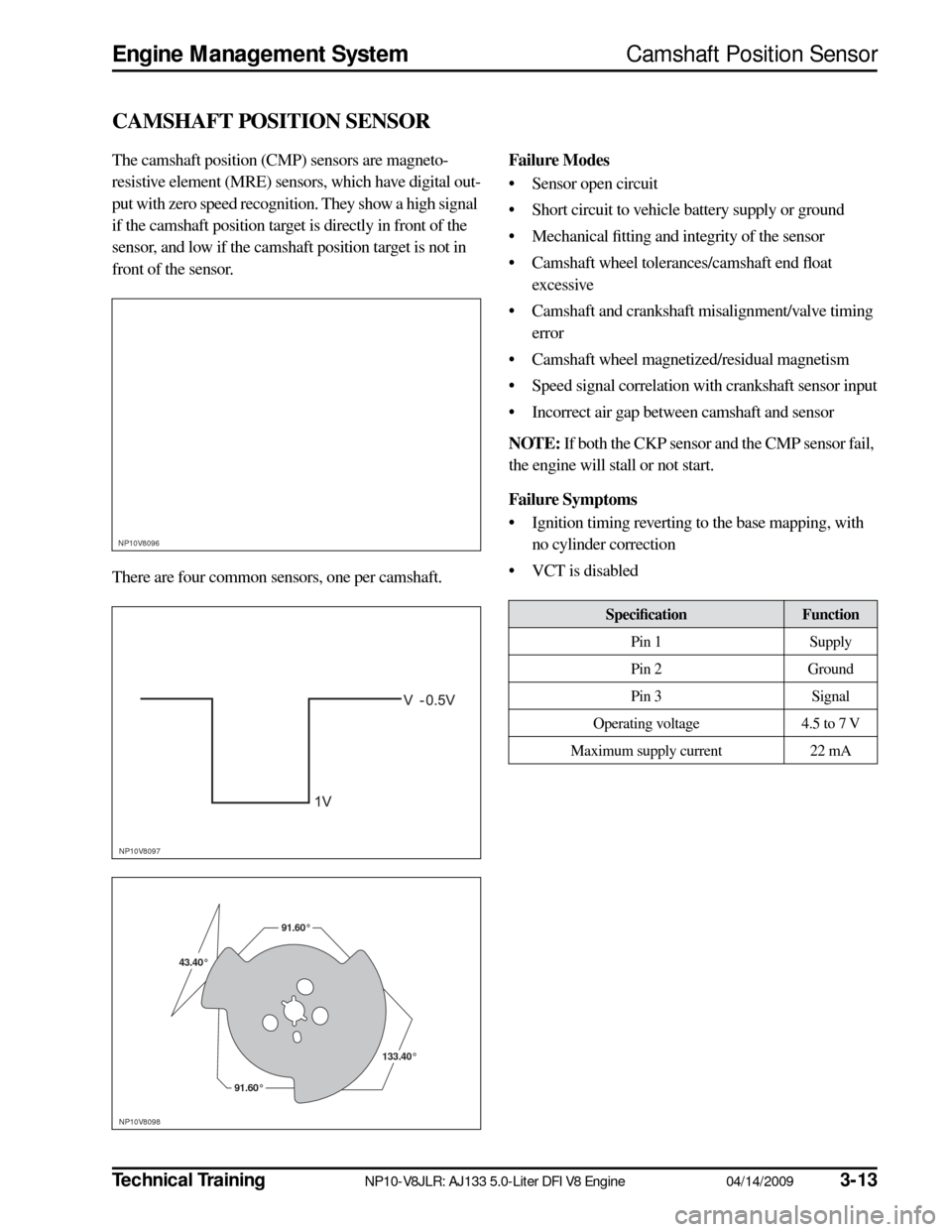
43.40°43.40°43.40° 91.60°
91.60°
133.40°133.40°
91.60°
133.40°
91.60°
91.60°91.60°
Specification
Function
Pin 1 Supply
Pin 2 Ground
Pin 3 Signal
Operating voltage 4.5 to 7 V
Maximum supply current 22 mA
Page 17 of 36

Technical Training
NP10-V8JLR: AJ133 5.0-Liter DFI V8 Engine 04/14/2009
3-15
Engine Management System
Knock Sensors
KNOCK SENSORS
The ECM uses active knock control, which serves to
prevent engine damaging pre-ignition or detonation
under all operating conditions, enabling the engine to
operate without additional safety margins.
The ECM uses 4 piezo-ceramic knock sensors to determine
the point at which a cylinder is pre-detonating. Two sensors
are mounted on the intake side of each cylinder head.
Each sensor monitors engine knock by converting the
engine block noise into a suitable electrical signal, which
is then transmitted back to the ECM via a twisted-pair
cable. The signal is processed within the ECM to iden-
tify the data that characterizes knocking.
This information is compared to known signal profiles to
determine whether pre-ignition is present. If so, the
closed loop control system retards the ignition on that
cylinder for a number of cycles, after which it gradually
moves back towards its original setting.
Safety Precautions CAUTION: Terminals in sensor and connec-
tor are gold plated for corrosion/temperature
resistance. Do not probe connections.
NOTE:
Accurate orientation of the knock sensors on the
cylinder block is required to ensure correct connection to
the vehicle wiring harness.
Failure Modes
• Sensor open circuit
• Short circuit to vehicle ground or battery voltage
• Faulty component or incorrectly torqued / coming loose
• Noise on vehicle 12V supply could look like knock signal causing knock fault
• Min fault usually due to open circuit
• Max fault short circuit to battery voltage or extreme mechanical engine noise/piston slap
• ECM calculates the default value if one sensor fails on each bank of cylinders
Failure Symptoms
• Knock control is disabled and a default ‘safe ignition map’ is used
• Possible rough running and reduced engine perfor- mance
Failure Mode Behaviors
• The vehicle control system constantly checks open circuit of knock sensor. Therefore, the knock sensor
is connected to the power source via pull-up line of
the ECM.
• When short/open circuit occurs to the knock sensor signal circuit, the system detects it, sets failure flag,
and commences maximum retard control on spark
advance.
• As far as the behavior of knock sensor is concerned, however, the above-mentioned failure modes cannot
cause serious outcomes such as heat generation,
smoke emission and/or fire hazard.
NP10V8100
Specification
Function
Power Source N/A
Wiring Type Twisted Pair
Shunt Resistance 4.8M Ohms
Operating Range 3kHz – 22kHz
Mounting Torque 20Nm +/- 3.8Nm