Page 298 of 484

WARNING! (Continued)
•The ABS cannot prevent the natural laws of phys-
ics from acting on the vehicle, nor can it increase
braking or steering efficiency beyond that af-
forded by the condition of the vehicle brakes and
tires or the traction afforded.
•The ABS cannot prevent accidents, including
those resulting from excessive speed in turns,
following another vehicle too closely, or hydro-
planing. Only a safe, attentive, and skillful driver
can prevent accidents.
•The capabilities of an ABS equipped vehicle must
never be exploited in a reckless or dangerous
manner that could jeopardize the user’s safety or
the safety of others.
All vehicle wheels and tires must be the same size and
type and tires must be properly inflated to produce
accurate signals for the computer.
ELECTRONIC BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Your vehicle is equipped with an advanced electronic
brake control system that include ABS (Anti-Lock Brake
System), TCS (Traction Control System), BAS (Brake
Assist System), and ESP (Electronic Stability Program).
All four of these systems work together to enhance
vehicle stability and control in various driving condi-
tions.
ABS (Anti-Lock Brake System)
This system aids the driver in maintaining vehicle control
under adverse braking conditions by controlling hydrau-
lic brake pressure. This prevents wheel lock-up to help
avoid skidding on slippery surfaces during braking.
Refer to “Anti-Lock Brake System” in Section 5 of this
manual.
296 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 303 of 484
ESP is synchronized (refer to Synchronizing ESP), see
your authorized dealer as soon as possible to have the
problem diagnosed and corrected.
NOTE:
•The ESP/TCS Indicator Light and the ESP/BAS Mal-
function Indicator Light will turn on momentarily
each time the ignition switch is turned ON.
•Each time the ignition switch is turned ON, the ESP
system will be on even if it was turned off previously.
•The ESP control system will make buzzing or clicking
sounds when it is active. This is NORMAL; the sounds
will stop when ESP becomes inactive following the
maneuver that caused the ESP activation.
TIRE SAFETY INFORMATION
Tire Markings
1 — U.S. DOT Safety Stan-
dards Code (TIN)4 — Maximum Load
2 — Size Designation 5 — Maximum Pressure
3 — Service Description 6 — Treadwear, Traction and Temperature Grades
STARTING AND OPERATING 301
5
Page 304 of 484

NOTE:
•P (Passenger) - Metric tire sizing is based on U.S.
design standards. P-Metric tires have the letter “P”
molded into the sidewall preceding the size designa-
tion. Example: P215/65R15 95H.
•European-Metric tire sizing is based on European
design standards. Tires designed to this standard have
the tire size molded into the sidewall beginning with
the section width. The letter�P�is absent from this tire
size designation. Example: 215/65R15 96H.
•LT (Light Truck) - Metric tire sizing is based on U.S.
design standards. The size designation for LT-Metric tires is the same as for P-Metric tires except for the
letters “LT” that are molded into the sidewall preced-
ing the size designation. Example: LT235/85R16.
•Temporary spare tires are high-pressure compact
spares designed for temporary emergency use only.
Tires designed to this standard have the letter “T”
molded into the sidewall preceding the size designa-
tion. Example: T145/80D18 103M.
•High flotation tire sizing is based on U.S. design
standards and it begins with the tire diameter molded
into the sidewall. Example: 31x10.5 R15 LT.
302 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 306 of 484
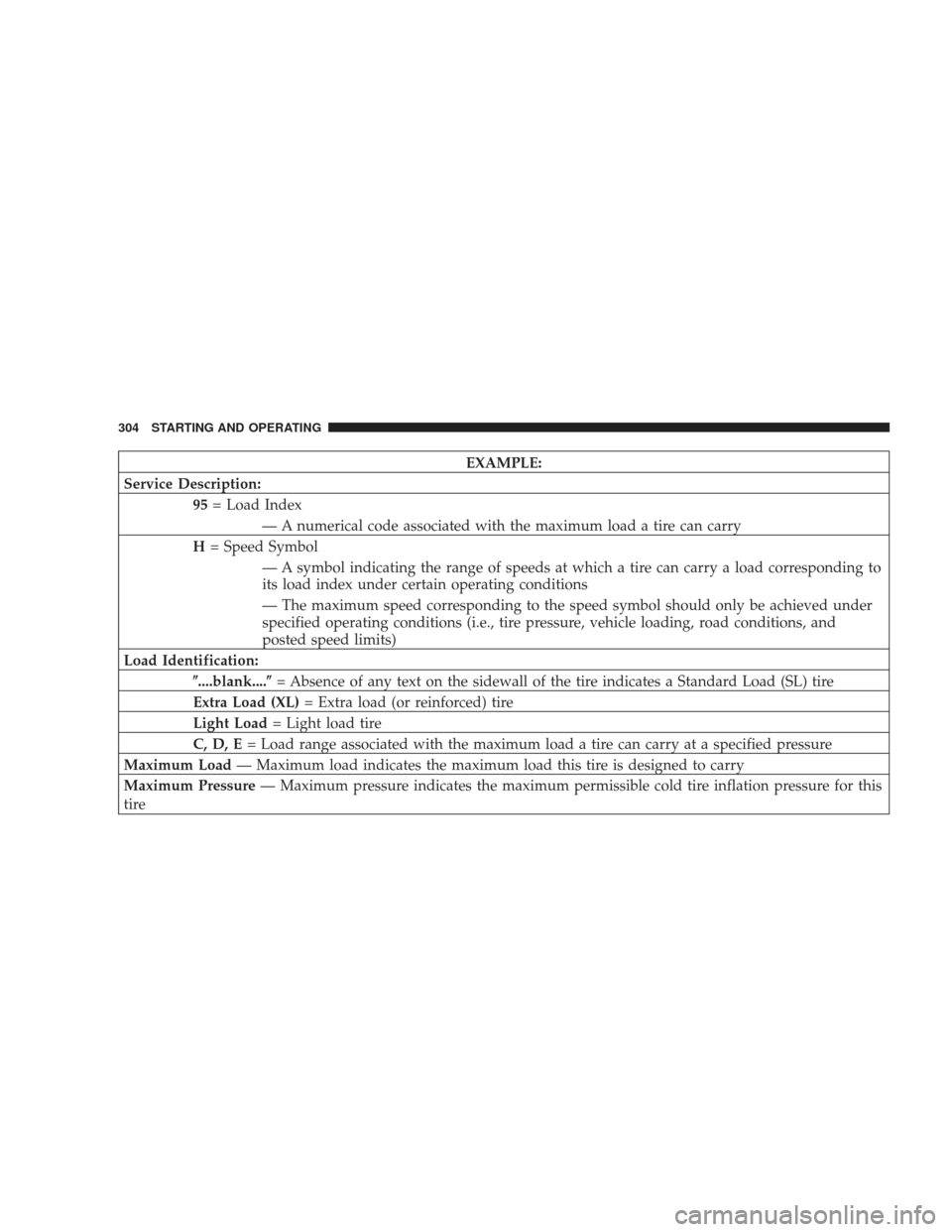
EXAMPLE:
Service Description: 95= Load Index
— A numerical code associated with the maximum load a tire can carry
H = Speed Symbol
— A symbol indicating the range of speeds at which a tire can carry a load corresponding to
its load index under certain operating conditions
— The maximum speed corresponding to the speed symbol should only be achieved under
specified operating conditions (i.e., tire pressure, vehicle loading, road conditions, and
posted speed limits)
Load Identification: \b....blank....\b = Absence of any text on the sidewall of the tire indicates a Standard Load (SL) tire
Extra Load (XL) = Extra load (or reinforced) tire
Light Load = Light load tire
C, D, E = Load range associated with the maximum load a tire can carry at a specified pressure
Maximum Load — Maximum load indicates the maximum load this tire is designed to carry
Maximum Pressure — Maximum pressure indicates the maximum permissible cold tire inflation pressure for this
tire
304 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 308 of 484
Tire Loading and Tire Pressure
Tire Placard Location
NOTE:The proper cold tire inflation pressure is listed
on the driver’s side B-Pillar.
Tire and Loading Information Placard
This placard tells you important information about
the:
1) number of people that can be carried in the vehicle
2) total weight your vehicle can carry
3) tire size designed for your vehicle
4) cold tire inflation pressures for the front, rear, and
spare tires.
Loading
The vehicle maximum load on the tire must not exceed
the load carrying capacity of the tire on your vehicle. You
will not exceed the tire’s load carrying capacity if you
adhere to the loading conditions, tire size, and cold tire
inflation pressures specified on the Tire and Loading
Information placard and in the “Vehicle Loading” section
of this manual.
NOTE: Under a maximum loaded vehicle condition,
gross axle weight ratings (GAWRs) for the front and rear
Tire and Loading Information Placard
306 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 312 of 484

WARNING!
Overloading of your tires is dangerous. Overloading
can cause tire failure, affect vehicle handling, and
increase your stopping distance. Use tires of the
recommended load capacity for your vehicle. Never
overload them.
TIRES — GENERAL INFORMATION
Tire Pressure
Proper tire inflation pressure is essential to the safe and
satisfactory operation of your vehicle. Three primary
areas are affected by improper tire pressure:
Safety
WARNING!
•Improperly inflated tires are dangerous and can
cause accidents.
•Under-inflation increases tire flexing and can re-
sult in tire failure.
•Over-inflation reduces a tire’s ability to cushion
shock. Objects on the road and chuckholes can
cause damage that result in tire failure.
•Unequal tire pressures can cause steering prob-
lems. You could lose control of your vehicle.
•Over-inflated or under-inflated tires can affect
vehicle handling and can fail suddenly, resulting
in loss of vehicle control.(Continued)
310 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 313 of 484

WARNING! (Continued)
•Unequal tire pressures from one side of the ve-
hicle to the other can cause the vehicle to drift to
the right or left.
•Always drive with each tire inflated to the recom-
mended cold tire inflation pressure.
Economy
Improper inflation pressures can cause uneven wear
patterns to develop across the tire tread. These abnormal
wear patterns will reduce tread life resulting in a need for
earlier tire replacement. Under-inflation also increases
tire rolling resistance and results in higher fuel
consumption.
Ride Comfort and Vehicle Stability
Proper tire inflation contributes to a comfortable ride.
Over-inflation produces a jarring and uncomfortable
ride.
Tire Inflation Pressures
The proper cold tire inflation pressure is listed on the
driver’s side “B” Pillar.
Some vehicles may have Supplemental Tire Pressure
Information for vehicle loads that are less than the
maximum loaded vehicle condition. These pressure con-
ditions will be found in the “Supplemental Tire Pressure
Information” section of this manual.
The pressure should be checked and adjusted as well as
inspecting for signs of tire wear or visible damage at least
once a month. Use a good quality pocket-type gauge to
check tire pressure. Do not make a visual judgement
when determining proper inflation. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they are under-inflated.
STARTING AND OPERATING 311
5
Page 314 of 484

CAUTION!
After inspecting or adjusting the tire pressure, al-
ways reinstall the valve stem cap (if equipped). This
will prevent moisture and dirt from entering the
valve stem, which could damage the valve stem.
Inflation pressures specified on the placard are always
“cold tire inflation pressure.” Cold tire inflation pressure
is defined as the tire pressure after the vehicle has not
been driven for at least three hours, or driven less than
1 mile (1.6 km) after a three hour period. The cold tire
inflation pressure must not exceed the maximum infla-
tion pressure molded into the tire sidewall.
Check tire pressures more often if subject to a wide range
of outdoor temperatures, as tire pressures vary with
temperature changes. Tire pressures change by approximately 1 psi (7 kPa) per
12°F (7°C) of air temperature change. Keep this in mind
when checking tire pressure inside a garage, especially in
the Winter.
Example: If garage temperature = 68°F (20°C) and the
outside temperature = 32°F (0°C) then the cold tire
inflation pressure should be increased by 3 psi (21 kPa),
which equals 1 psi (7 kPa) for every 12°F (7°C) for this
outside temperature condition.
Tire pressure may increase from 2 to 6 psi (13 to 40 kPa)
during operation. DO NOT reduce this normal pressure
build up or your tire pressure will be too low.
Tire Pressures for High Speed Operation
The manufacturer advocates driving at safe speeds
within posted speed limits. Where speed limits or condi-
tions are such that the vehicle can be driven at high
speeds, maintaining correct tire inflation pressure is very
important. Increased tire pressure and reduced vehicle
312 STARTING AND OPERATING