2009 BMW 535I XDRIVE width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 17 of 294

At a glance
15Reference
Controls
Driving tips
Communications
Navigation
Entertainment
Mobility
1Microphone for hands-free mode for tele-
phone
* and for voice command
system
*24
2Reading lamps113
3SOS: initiating
an emergency request253
4Interior lamps112
5Glass sunroof
*, electric43
Panorama glass sunroof45
6Passenger airbag status lamp101
7Control Display16
Displays for menu navigation
8Hazard warning flashers
9Central locking system35
10Automatic climate control114
11Changing
>radio station172
>track168
12Ejecting
>navigation DVD
*142
>audio CD182
13Programmable memory buttons22
14Drive for navigation DVDs
*14215Drive for audio CDs182
16Switching Entertainment sound output on/
off and adjusting volume168
18Controller16
Can be turned, pressed, or moved in four
directions
19Opening start menu on Control Display17
20Selecting AM or FM waveband
21Selecting radio, CD and CD changer Temperature setting, left/
right115
Automatic air distribution and
volume115
Cooling function117
AUC Automatic recirculated-air
control117
Recirculated-air mode117
Maximum cooling117
Air volume116
Defrosting windows and removing
condensation116
Rear window defroster116
17
Heated seats*53
Active seat ventilation
*54
Adjusting active backrest
width
*49
Active seat
*54
PDC Park Distance Control
*90
DTC Dynamic Traction Control92
Opening luggage compartment lid/
tailgate
*36,37
Page 50 of 294
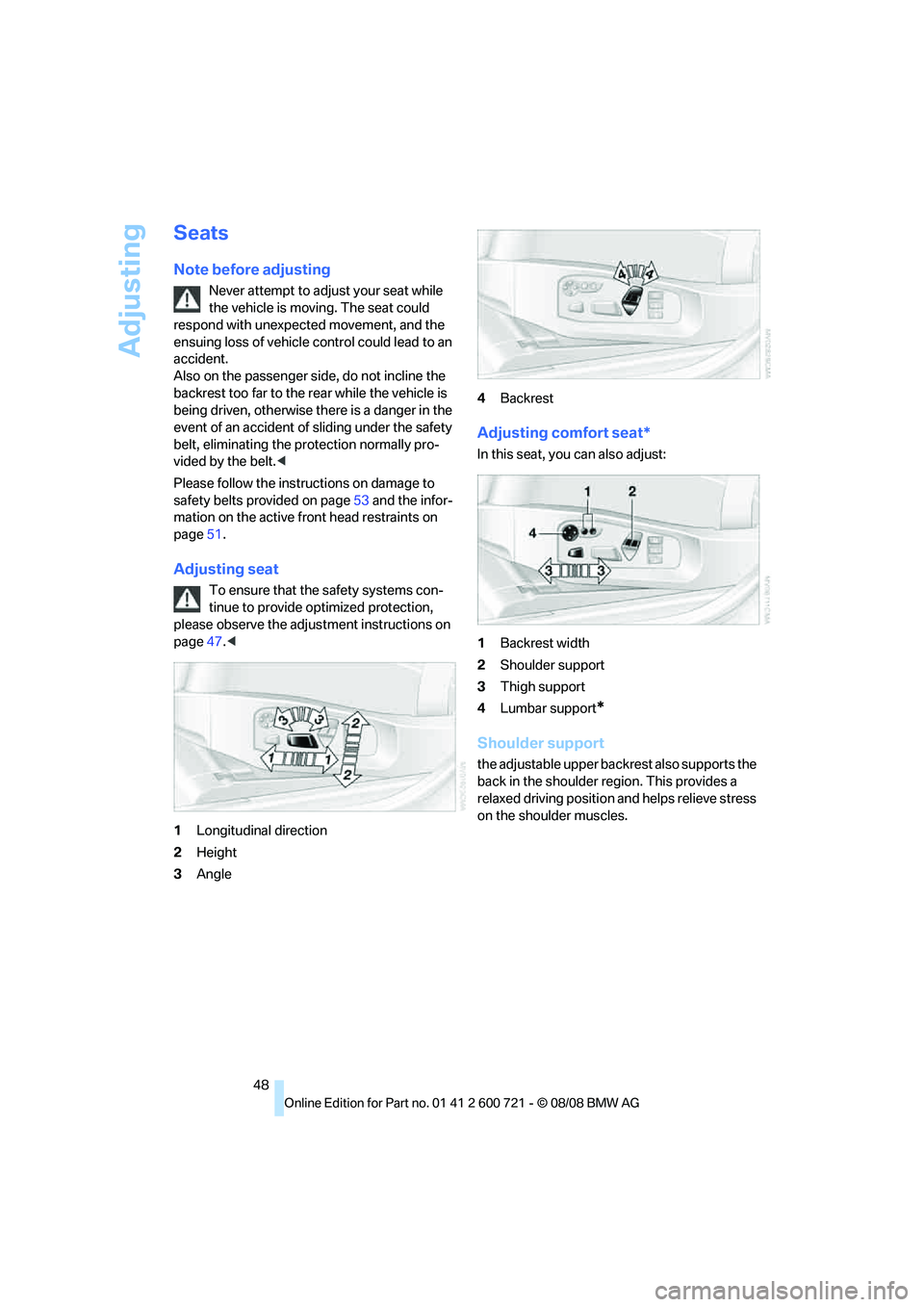
Adjusting
48
Seats
Note before adjusting
Never attempt to adjust your seat while
the vehicle is moving. The seat could
respond with unexpected movement, and the
ensuing loss of vehicle control could lead to an
accident.
Also on the passenger side, do not incline the
backrest too far to the rear while the vehicle is
being driven, otherwise there is a danger in the
event of an accident of sliding under the safety
belt, eliminating the protection normally pro-
vided by the belt.<
Please follow the instructions on damage to
safety belts provided on page53 and the infor-
mation on the active front head restraints
on
page51.
Adjusting seat
To ensure that the safety systems con-
tinue to provide optimized protection,
please observe the adjustment instructions on
page47.<
1Longitudinal direction
2Height
3Angle4Backrest
Adjusting comfort seat*
In this seat, you can also adjust:
1Backrest width
2Shoulder support
3Thigh support
4Lumbar support
*
Shoulder support
the adjustable upper backrest also supports the
back in the shoulder region. This provides a
relaxed driving position and helps relieve stress
on the shoulder muscles.
Page 51 of 294

Controls
49Reference
At a glance
Driving tips
Communications
Navigation
Entertainment
Mobility
Lumbar support*
You can also adjust the contour of the backrest
to obtain additional support in the lumbar
region.
The upper hips and spinal column receive sup-
plementary support to help you maintain a
relaxed, upright sitting position.
>Increase or decrease curvature: press front
or rear section of switch.
>Shift curvature up or down: press upper or
lowers section of switch.
Adjusting active backrest width*
First set a comfortable backrest width, see
above. Based on the backrest width set, the lat-
eral support is automatically adapted to the cur-
rent driving situation.
The adaptation of the backrest width and the
speed of the adjustment vary depending on the
program. You can select from among three pro-
grams from comfort to sport.
Button with three LEDs
Press button once per program:
>"Comfort": one LED
>"Normal": two LEDs
>"Sport": three LEDsTo deactivate: Press button longer.
Button with one LED
Press the button repeatedly until the desired
program is shown on the Control Display. The
LED in the button lights up.
To deactivate: Press button longer.
Easy entry/exit*
To facilitate entry and exit, the backrest width
temporarily opens all the way.
Seat, mirror and steering
wheel memory*
You can store and request two different posi-
tions for the driver's seat and passenger seat
*,
exterior rearview mirrors, and steering wheel.
Page 57 of 294

Controls
55Reference
At a glance
Driving tips
Communications
Navigation
Entertainment
Mobility
Objects reflected in the mirror are closer than
they appear. Do not estimate the distance of
following traffic based on what you see in the
mirrors, otherwise there is an increased acci-
dent risk.<
1Adjusting
2Switching to the other mirror or to the auto-
matic curb monitor
3Folding mirrors in and out
*
Storing the mirror positions, refer to Seat, mir-
ror and steering wheel memory on page49.
Adjusting manually
You can also adjust the mirrors manually by
pressing against the outer edges of their mirror
glass.
Folding mirrors in and out*
Pressing button3 allows you to fold mirrors
in and out up to a speed of approx. 20 mph/
30 km/h. This is advantageous, for example, in
car washes, narrow streets or for bringing mir-
r o r s t h a t ha v e b e e n m a nu ally folded in back into
the correct position. Mirrors that were folded in
are folded out automatically at a speed of
approx. 25 mph/40 km/h.
Before going through a car wash, fold the
mirrors in manually, or with button 3, oth-
erwise they could be damaged, depending on
the width of the car wash system.<
Automatic heating
Below a certain outdoor temperature, both
exterior mirrors are heated whenever the
engine is running or the ignition is switched on.
Tilting down passenger-side exterior
mirror – automatic curb monitor*
Activating
1.Slide switch into the driver's side mirror
position, arrow 1.
2.Shift into reverse or move selector lever into
position R.
The mirror glass tilts downward somewhat
on the passenger's side. This allows the
driver to see the area immediately adjacent
to the vehicle – such as a curb – when park-
ing, etc.
Deactivating
Slide switch into the passenger side mirror
position, arrow 2.
Interior rearview mirror
To reduce the dazzle effect of following vehi-
cles at night, turn the knob.
Page 60 of 294

Transporting children safely
58
Transporting children safely
The right place for children
Do not leave children unattended in the
vehicle, otherwise they could endanger
themselves and other persons, e.g. by opening
the doors.<
Children always in the rear
Accident research shows that the safest place
for children is on the rear seat.
Children younger than 13 years of age or
with a height under 5 ft/150 cm may only
be transported in the rear in child restraint sys-
tems which correspond to the age, weight and
height of the child. Otherwise there is an
increased danger of injury in an accident.<
Children 13 years of age or older must wear a
safety belt as soon as a suitable child restraint
system can no longer be used due to their age,
size and weight.
Exception for front passenger seat
Should it ever be necessary to use a child
restraint system on the front passenger
seat, the front and side airbags on the passen-
ger side must first be deactivated. Otherwise,
there is an increased risk of injury for the child if
the airbags are triggered, even with a child
restraint system.<
For more information on automatic deactivation
of the front passenger airbags, refer to
page101.
Installing child restraint
systems
Observe the child restraint system manu-
facturer's instructions for selection,
installation and use of the child restraint sys-
tems. Otherwise the degree of protection may
be reduced.<
Backrest width* on front passenger
seat
Open the backrest width setting of the
front passenger seat all the way. After
mounting the child's seat, deactivate the active
backrest width adjustment and do not call up
any memory position. Otherwise this limits the
stability of the child's seat on the front passen-
ger seat.<
1.After unlocking the vehicle, sit on the front
passenger seat and close the door to call up
the memory position.
2.Completely open the backrest width adjust-
ment, refer to page48.
3.Deactivate active backrest width adjust-
ment, refer to page49.
4.Install child's seat.
Child seat security
All rear safety belts and the safety belt for the
front passenger can be locked against pulling
out to secure child restraint systems.
Locking safety belt
1.Secure the child restraint system with the
belt.
2.Pull out the belt webbing completely.
3.Allow the belt webbing to retract and pull
taut against the child restraint system. The
safety belt is locked.
Page 138 of 294

Things to remember when driving
136 the road surface, ultimately undermining your
ability to steer and brake the vehicle.<
The risk of hydroplaning increases as the tread
depth of the tires decreases, refer also to Mini-
mum tire tread on page229.
Driving through water
Do not drive through water on the road if it
is deeper than 1 ft/30 cm, and then only at
walking speed at the most. Otherwise, the vehi-
cle's engine, the electrical systems and the
transmission may be damaged.<
Using handbrake on inclines
On inclines, do not hold the vehicle in
place for a long time by riding the clutch;
use the handbrake. Otherwise greater clutch
wear will result.<
Braking safely
Your BMW is equipped with ABS as a standard
feature. In situations that require it, it is best to
brake with full force. Since the vehicle maintains
steering responsiveness, you can still avoid
possible obstacles with a minimum of steering
effort.
Pulsation of the brake pedal, combined with
sounds from the hydraulic circuits, indicate that
ABS is in its active mode.
Do not drive with your foot resting on the
brake pedal. Even light but consistent
pedal pressure can lead to high temperatures,
brake wear and possibly even brake failure.<
Driving in wet conditions
When roads are wet or there is heavy rain,
briefly exert gentle pressure on the brake pedal
every few miles. Monitor traffic conditions to
ensure that this maneuver does not endanger
other road users. The heat generated in this
process helps dry the pads and rotors to ensure
that full braking efficiency will then be available
when you need it.
Hills
To prevent overheating and the resulting
reduced efficiency of the brake system, drive long or steep downhill gradients in the
gear in which the least braking is required. Even
light but consistent pressure on the brake can
lead to high temperatures, brake wear and pos-
sibly even brake failure.<
The braking effect of the engine can be further
increased by downshifting, if necessary all the
way down into first gear. This strategy helps
you avoid placing excessive loads on the brake
system. For information on downshifting in the
manual mode of the automatic transmission,
refer to page65.
Do not drive with the clutch depressed, in
idle or with the engine switched off, other-
wise there will be no engine braking action or
support of the braking force and steering.
Never allow floor mats, carpets or any other
objects to protrude into the area of movement
of the pedals and impair their operation.<
Corrosion on brake rotors
When the vehicle is driven only occasionally,
during extended periods when the vehicle is not
used at all, and in operating conditions where
brake applications are less frequent, there is an
increased tendency for corrosion to form on
rotors, while contaminants accumulate on the
brake pads. This occurs because the minimum
pressure which must be exerted by the pads
during brake applications to clean the rotors is
not reached.
Should corrosion form on the brake rotors, the
brakes will tend to respond with a pulsating
effect that even extended application will fail to
cure.
When vehicle is parked
Condensation forms in the air conditioner sys-
tem during operation, and then exits under the
vehicle. Traces of condensed water under the
vehicle are therefore normal.
Before driving into a car wash
Fold in the exterior mirrors, refer to page55,
otherwise they could be damaged due to the
width of the vehicle.
Page 229 of 294
Mobility
227Reference
At a glance
Controls
Driving tips
Communications
Navigation
Entertainment
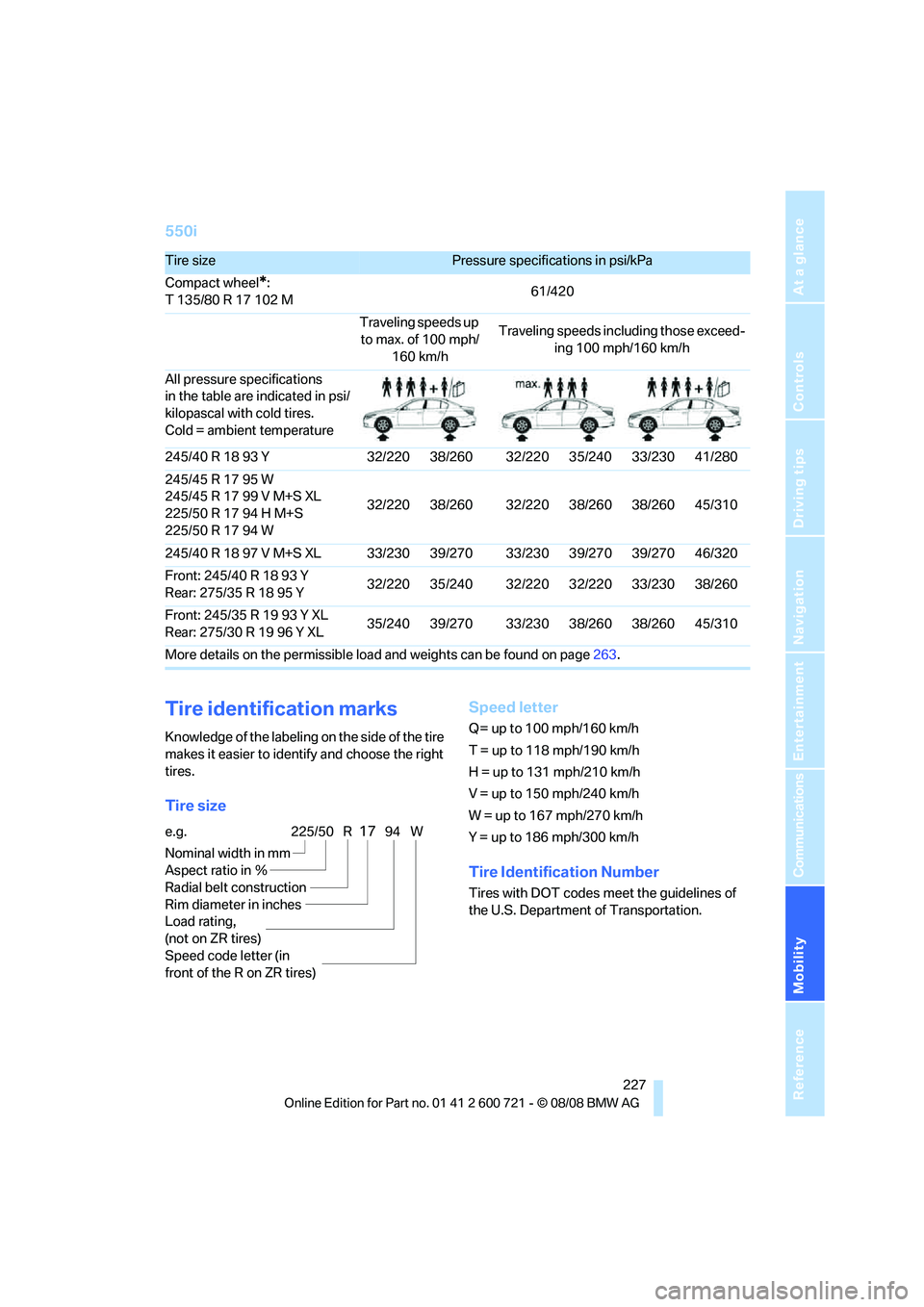
550i
Tire identification marks
Knowledge of the labeling on the side of the tire
makes it easier to identify and choose the right
tires.
Tire sizeSpeed letter
Q = up to 100 mph/160 km/h
T = up to 118 mph/190 km/h
H = up to 131 mph/210 km/h
V = up to 150 mph/240 km/h
W = up to 167 mph/270 km/h
Y = up to 186 mph/300 km/h
Tire Identification Number
Tires with DOT codes meet the guidelines of
the U.S. Department of Transportation.
Tire sizePressure specifications in psi/kPa
Compact wheel
*:
T 135/80 R 17 102 M61/420
Traveling speeds up
to max. of 100 mph/
160 km/hTraveling speeds including those exceed-
ing 100 mph/160 km/h
All pressure specifications
in the table are indicated in psi/
kilopascal with cold tires.
Cold = ambient temperature
245/40 R 18 93 Y 32/220 38/260 32/220 35/240 33/230 41/280
245/45 R 17 95 W
245/45 R 17 99 V M+S XL
225/50 R 17 94 H M+S
225/50 R 17 94 W32/220 38/260 32/220 38/260 38/260 45/310
245/40 R 18 97 V M+S XL 33/230 39/270 33/230 39/270 39/270 46/320
Front: 245/40 R 18 93 Y
Rear: 275/35 R 18 95 Y32/220 35/240 32/220 32/220 33/230 38/260
Front: 245/35 R 19 93 Y XL
Rear: 275/30 R 19 96 Y XL35/240 39/270 33/230 38/260 38/260 45/310
More details on the permissible load and weights can be found on page263.
e.g.
Nominal width in mm
Aspect ratio in Ξ
Radial belt construction
Rim diameter in inches
Load rating,
(not on ZR tires)
Speed code letter (in
front of the R on ZR tires)225/50 R1794 W
Page 230 of 294

Wheels and tires
228 DOT code:
Tire age
The manufacturing date of tires is contained in
the tire coding: DOT ...1008 indicates that the
tire was manufactured in week 10 of 2008.
BMW recommends that you replace all tires
after 6 years at most, even if some tires may last
for 10 years.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Quality grades can be found where applicable
on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and
maximum section width. For example:
Tread wear 200 Traction AA
Temperature A
DOT Quality Grades
Tread wear
Traction AA A B C
Temperature A B C
All passenger car tires must conform to
Federal Safety Requirements in addition
to these grades.<
Tread wear
The tread wear grade is a comparative rating
based on the wear rate of the tire when tested
under controlled conditions on a specified gov-
ernment test course. For example, a tire graded
150 would wear one and one-half (1γ) times as
well on the government course as a tire graded
100. The relative performance of tires depends
upon the actual conditions of their use, how-
ever, and may depart significantly from the
norm due to variations in driving habits, service
practices and differences in road characteris-
tics and climate.
Traction
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are
AA, A, B, and C.
These grades represent the tire's ability to stop
on wet pavement, as measured under con-
trolled conditions on specified government test
surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked
C may have poor traction performance.
The traction grade assigned to this tire is
based on straight-ahead braking traction
tests, and does not include acceleration, cor-
nering, hydroplaning, or peak traction charac-
teristics.<
Temperature
The temperature grades are A, the highest, B,
and C, representing the tire's resistance to the
generation of heat and its ability to dissipate
heat when tested under controlled conditions
on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
Sustained high temperature can cause the
material of the tire to degenerate and reduce
tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to
a level of performance which all passenger car
tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehi-
cle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A
represent higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel than the minimum
required by law.
The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly
inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive loading, either sep-
arately or in combination, can cause heat
buildup and possible tire failure.<
RSC – run-flat tires
You will recognize run-flat tires by a circular
symbol containing the letters RSC on the side
of the tire, refer to page229.
M+S
Winter and all-season tires.
These have better winter properties than sum-
mer tires. e.g.
Manufacturer code
for tire make
Tire size and tire design
Tire age
DOT xxxx xxx 1008