2009 AUDI S6 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 259 of 398
Mounting and releasing the anchorage hook
If you use a child restraint system with hooks or other
latches attached to adjustable straps.
Mounting
- Press the anchorage hook wit h the spring catch re lease
onto the lower anchorage so that the anchorage hook locks into place .
- Pull on the anchorage hook to make sure that it has
securely engaged the lower anchorage.
- Tighten the strap following the child restraint manufac
turer 's instructions.
Releasing
- Loosen the tens ion on the strap following the child
restraint manufacturer's instructions .
- Depress the spring catch on the hook. - Hold the spring catch in depressed posit ion .
- Move the hook in the direction of the vehicle floor so that
there is enough space to release the anchorage hook
from the lower anchorage.
& WARNING
• Improper installation of child restraints will increase the risk of
injuries in a crash.
• Always refer to the child restraints manufacturer's instructions
for proper instaHation of the child restraint and proper use of the
lower anchorages or safety belts in your vehicle. •
Safety first
Tether anchors
Child Safety
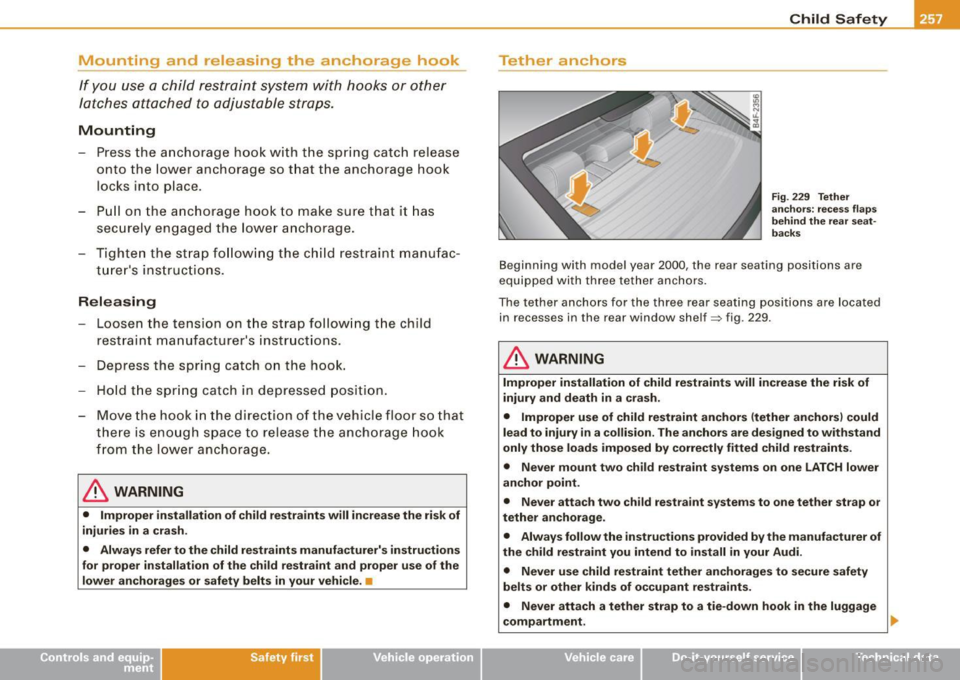
Fig. 229 Tether
anchors: recess flaps
behind the rear seat
backs
B eginning with mod el year 2000 , th e re ar sea ting posi tions are
equipped with three tether anchors.
The tether anchors for the three rear seating positions are located in r ecess es in the r ear window shelf~ fig . 229.
& WARNING
Improper installation of child restraints will increase the risk of
injury and death in a crash.
• Improper use of child restraint anchors (tether anchors) could
lead to injury in a collision. The anchors are designed to withstand
only those loads imposed by correctly fitted child restraints.
• Never mount two child restraint systems on one LATCH lower
anchor point.
• Never attach two child restraint systems to one tether strap or
tether anchorage.
• Always follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer of
the child restraint you intend to install in your Audi.
• Never use child restraint tether anchorages to secure safety
belts or other kinds of occupant restraints.
• Never attach a tether strap to a tie-down hook in the luggage
compartment.
Vehicle care I I irechnical data
Page 264 of 398

___ ln_ t _e_ ll-'"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
Intelligent technology
Notice about data recorded by
vehicle control modu les
Your vehicle is not equipped with an Event Data Recorder (EDR),
installed by some manufacturers for the express purpose of
capturing data for retrieval after an accident or crash event . EDR's
are sometimes called "crash recorders" .
Some state laws restrict the retrieva l or downloading of data stored
by EDR's that were insta lled in a vehicle for the express purpose of
retrieving data after an accident or crash event without the owner's
consent.
Although your vehicle is not equipped with an EDR, it is equipped
with a number of electronic control modules for various vehicle systems such as, for example, engine function, emission control, as
well as for the airbags and safety belts.
These electronic control modules also record vehicle-related data during norma l vehicle operation for diagnost ic and repair purposes .
The recording capacity of the electronic control modules is limited
to data (no sound is recorded) and only a small amount of data is
actually recorded over a very limited period of time and stored when
a system fault or other condition is sensed by a control unit. Some
of the data then stored may relate to vehicle speed, direction, braking as well as restraint system use and performance in the
event of a crash or other condition . Stored data can only be read and
down loaded with special equipment .•
Electron ic Stabilizat ion Program (ESP)
General =nformation
The ESP improves the vehicle stability.
(
Fi g. 232 C ente r
co nso le w it h ES P
swi tch
ESP is designed to he lp you maintain vehic le control in situations
where the car approaches the limits of "grip", especia lly when
accelerating and cornering. ESP reduces the risk of skidding and
improves stabil ity under all road conditions .
T he system operates across the entire speed range in combination
with the ABS system. If the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) malfunc
tions, the ESP wil l also shut down .
How th e sys te m w ork s
The Anti -Lock Brake System (ABS) , Electronic Differential Lock (EDU
and the Anti-Slip Regulation System (ASR) are integrated in the e lec
tronic stabi lization program . In addition to the data provided by
these functions, the ESP control unit requires additional measure ment data provided by high performance sensors . The rotational
speed of the vehic le about its vertical axis, vehicle acce leration in
the fore-and-aft and lateral directions, the brake pressure and the steering angle are al l measured .
Page 265 of 398

The direction in which the driver wishes to travel is determined with
t he aid of the steering angle and vehicle speed and is continua lly
compared with the actual behavior of the vehicle. If the two do not
match, for example, when the vehic le starts hydrop laning on a wet
road, ESP will automatically brake the appropriate whee l to correct
the prob lem.
The vehicle is then stab ilized by the forces acting on the whee l
during braking. If the vehicle is
oversteering (rear tends to skid out
of the turn), the brakes are mainly app lied on the wheel that is on
the outside of the curve. In the case of a vehicle that is
understeering
(tendency to sl ide out of the curve), the brakes are applied at the
rear wheel that is on the inside of the curve . An acoustic signal indi
cates when ESP brake application cuts in
~ & .
The system operates across the entire speed range in combination
with the ABS system
~ page 266 . If the Anti -Lock Brake System
(ABS) malfunctions, the ESP wi ll be out of action as well.
Ac tivat ing
When you turn on the eng ine, ESP will automatically be activated
and will perform a se lf -test . As soon as the test is comp leted, the
system is in norma l operating mode.
You can activate a deactivated ESP or deactivated ESP/ASR if required by pressing the~
page 262, fig. 232 button . When they are
activated, the message
E S P/AS R on appears briefly in the display.
D eactiv ating
The ESP should normally be activated al l the time . If necessary, you
can deactivate An ti- Slip Regulation (ASR) or the E lectronic Stabiliza
tion Program (ESP) by pressing the button~
page 262, fig. 232 .
• Dea ct iv at ing A SR: Tap the button . In certain exceptional situa
tions (e.g. driving with t ire chains) , the Anti-Sl ip Regulation (ASR)
can be deactivated ~
page 264. The message ASR off appears in the
display as we ll.
• Dea ctiv at ing E SP/ASR Press the button for more than 3 seconds.
With the ESP/ASR deactivated, the ESP check light comes on, see
Controls and equip
ment Safety first Vehicle operation
In
te llig ent tec hn olo gy
~ page 18 . The message ES P sw itched off appears in the disp lay as
we ll.
& WARNING
The Electroni c Stabili zation Program i s never thele ss subject to the
la ws o f physics . It is p articularl y import ant t o pay a ttent ion t o th is
f a ct on wet and slippery road s. It is ther efore important tha t y ou
a lw ays a dapt your dr iving to the c ondit ion of th e ro ad and t raffi c
c ondition s. Do n ot allow the inc rea sed safety pro vided b y th e Elec
tr on ic S ta bili zatio n Pr ogram sys tem to lull you in to acc epting
add iti onal safet y risk s. C
Electronic differential tock (EDL)
The electronic differential lock monitors the rotational
speed of the drive wheels.
Gener al note s
The electronic differential lock (EDU helps the car to start moving,
accelerate and c limb a gradient on surfaces providing poor or
almost no grip . Without EDL, this would be difficult, if not impos
sib le .
How th e sys te m wo rk s
The EDL operates automatical ly . It monitors the rotational speed of
the drive wheels on an axle with the he lp of the ABS sensors
~ page 266 . If a noticeable difference in rotational speed between
the drive wheels on one axle is detected (e.g. on slippery ground
on
one side),
the spinning wheel is braked, thereby transferring power
to the other drive wheel or whee ls (a ll -whee l drive) . Th is is done up
to a speed of about 60 mph ( 100 km/h). Noises from the brake
system signal that wheel spin is being control led .
Dr iving off
When driving off , always be sure to keep road conditions in mind as
you accelerate. If one drive wheel spins because it is on a surface
Iii>
Vehicle care Do-it-yourself service Technical data
Page 266 of 398

___ ln_ t _e_ ll-'"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
with less grip, gradually increase the pressure on the accelerator
pedal until the car starts to move.
Overheating of brakes
To prevent the disc brake of the braked wheel from overheating if
subjected to excessive loads on this wheel, the EDL cuts out tempo
rarily. The vehicle remains operational and behaves in the same way
as a vehicle without EDL.
As soon as the brake has cooled down, EDL switches on again auto
matically.
& WARNING
• When accelerating on slippery surfaces, such as on ice or snow,
always be careful when depressing the accelerator pedal. Even
with the EDL working, the drive wheels can spin and reduce your
ability to control your car. Risk of crash!
• The increased safety afforded by EDL does not mean that you
can take safety risks. Always adapt your driving style to the road
conditions and traffic situation.
[ i] Tips
If a fault occurs in the ABS, the EDL is also not functioning. This is
indicated by the ABS warning light=>
page 21. •
Ant"-Slip Regulation System (ASR)
The Anti-Slip Regulation System prevents the driven
wheels from spinning when the car is accelerating.
General notes
The Anti-Slip Regulation System (ASR) is integrated in the electronic
stabilization program (ESP). When the vehicle starts up and acceler
ates, the wheels are prevented from spinning by adjusting the engine power to match the amount of grip available from the road
surface.
How the system works
ASR
performs automatically, i.e. without the driver's intervention.
With the aid of the ABS sensors=>
page 266, ASR monitors the
speed of the driven wheels. If the wheels start to spin, the engine
torque is reduced automatically until the tires find enough grip to
lock onto the road surface. The system is active across the entire
speed range.
Th e ASR works in conjunction with the ABS. If a malfunction should
occur in the ABS, the ASR will also be out of action.
Activating
The ESP is automatically activated when the engine is started and it
performs a self -test . You can activate a deactivated ASR if required
by pressing the =>
page 262, fig. 232 button . When it is activated,
the message
ESP/ASR on appears briefly in the display. Vehicles
with front-wheel drive a deactivated ASR automatically re-activates
itself at a speed of 40 mph (70 km/h) .
Deactivating
You can deactivate the ASR if required by pressing the button (for
less than 3 seconds)=>
page 262, fig. 232. With the ASR deactivated,
the ESP check light comes on, see=>
page 18. The message ASR off
appears in the display as well. On vehicles with front-wheel drive:
deactivation is possible only up to 30 mph (50 km/h) for safety
reasons . Vehicles with all -wheel drive: the ASR can be deactivated
at any speed .
The ASR should normally be activated all the time. Only in certain
exceptional situations when some slip is desirable does it make
sense to deactivate the ASR. Examples:
• when driving with tire chains
• when driving in deep snow or on loose ground and
• when rocking the vehicle loose after it has become stuck .
Page 268 of 398
___ ln_ t _e_ ll-'"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
& WARNING
• You should perform braking maneu vers for the purpose of
cleaning the brake system only if road conditions permit . Other
road u sers mu st not be put at r isk -you may cause an a ccident!
• Before des cending a steep grade, reduce speed and shift trans
mission into a lower gear or lower dr iving range . Do not ride the
brakes or hold the pedal down too long or too often. This could
cause the brake s to get hot and diminish braking effi ciency .
• Do not "ride the brakes " by resting your foot on the pedal when
you do not intend to b rake. This may cause the br ake s to ove rheat ,
premature wear and increased stopping distance.
• Under ce rtain climat ic and operating condit ions such as
passing through water , driving in heavy rain or after washing the
vehi cle , the effectiveness of the brakes can be reduced . In winter ,
ice can a ccumulate on the brake pads , linings , discs and drums .
Carefully apply bra kes fo r a test . Brakes will dry and ice coatings
will be cleaned off after a few careful brake appli cations .
• Driving for an extended period of time on salt -co vered roads
without using your brakes can also affect braking effic iency. Clean
off accumulated salt coating from brake dis cs and pads with a few
c areful brake applications .
• If you damage the front spoile r, or if you install a different
spoiler, be sure the air flow to the front brakes is not ob structed.
Otherw ise the brake sy stem could overheat reducing the effective
ness of the entire brake system .
• Failure of one bra ke cir cuit will impair the braking capability
resulting in an increased stopping distance. Avoid driving the
veh icle and have it to wed to the nearest Audi dealer or qualified
workshop . -..
Brake booster
T he b rake boost er ad ds extra b ra king powe r.
The brake booster works with vacuum pressure which is created
o nly w he n t he e ngine is ru nnin g=> & .
& WARNING
• Never let the vehicle roll to a stop with the engine shut off.
• If the brake booster is not working, for example when towing
your vehicle, or because the brake boo ster has somehow been
damaged , the brake pedal must be pressed considerably harder to
make up for the lack of booster assistance . •
Functioning of A!"lt"-Lock Brake System (ABS)
ABS p revents the wheels from locking up unde r brakin g.
Th e ABS co ntribu tes effect ively to vehicle cont ro l since it preve nts
the whee ls from
locking when the brakes are app lied. This means
t h at the ve hicle rema ins steerable and is less l ikely to s kid.
With ABS you do not need to pump the brake . Just hold the brake
pedal down .
However, do not expec t the A BS to s hor ten bra king d istance u nder
all circumstances. When driving o n grave l or on newly fallen snow
o n t op o f icy sur faces, brak ing d istance may be ev en lon ger, the re
fore, under these c ircumstances, it is especially important that you
driv e slow ly an d with gre at ca re.
How the ABS system works
An automat ic c heck is made w hen a speed o f abou t 4 mph (6 km/hl
is reached. When this happens, a pumping noise can be heard.
I f a n in div id ual wheel begins to rotate too slowly in rela tion t o
vehic le speed and tends to lock, the ABS automatically reduces
b rake p ress ure to preven t tha t w hee l from lo cking.
Page 269 of 398

This automatic adjustment process will cause a slight vibration of
the brake pedal and some noises to alert you that vehicle speed
must be adapted to existing road and traffic conditions .
& WARNING
Although the ABS is very effective, always remember that braking
capability is limited by tire traction. Always adjust your driving
speed according to the road and traffic conditions. Do not let the
extra safety afforded by the ABS tempt you into taking extra risks.
The ABS cannot overcome the laws of physics .
[ i ] Tips
• If ABS is not functioning properly, a warning light will come on .
See ~
page 21.
• If a fau lt occurs in the ABS, the EDL is also not functioning. This
is indicated by the ABS warning light.
Brake assistant
The brake assistant is designed to achieve the optimum
braking effect.
The brake assistant helps to increase the effective braking power
and thus to achieve a shorter stopping distance . If the driver
presses the brake pedal very quick ly, the brake assistant automati
cally boosts the braking force to the maximum level, up to the point
where the anti-lock brake function (ABS) intervenes to stop the
wheels from locking . You should then keep the brake pedal pressed
until the vehicle has braked to the required speed. The brake assis
tant switches itself off as soon as you release the brake pedal.
T he brake assistant wil l not be operative if there is a malfunction in
the ABS .
Controls and equip
ment Safety first Vehicle operation
Intelligent technology
& WARNING
Please remember that the
accident risk always increases if you
drive too fast , especially in corners or on a slippery road, or if you
follow the vehicle ahead of you too closely. Increased risk of an
accident cannot be compensated for even by the brake assistant ,
so always maintain a safe speed. •
Servotronic® -advanced power
steering system
The power steering systems uses the power of the
running engine to allow precise steering with little effort.
The advanced Servotronic ® power steering system senses the road
speed and electronically adjusts power assistance to provide
comfortab le and safe steering response exactly matched to the
vehicle speed.
Power steering will not work if the engine is off. As a result, the
steering wheel will be hard to turn.
The power steering fluid level is checked during the scheduled
maintenance services .
0 Note
If there is an electronic ma lfunction, servotronic wi ll still function
like a conventional power steering system, providing a constant
steering support force that is no longer proportionate to the vehicle
speed . This is most noticeable when turning the steering whee l at
low speeds (for examp le when parking), -more effort will be
required than usual.
• Be aware of the different than usual steering response and
adjust your steering force accordingly.
• Have the problem checked and set right by an Aud i dealer as
soon as possible. ._
Vehicle care Do-it-yourself service Technical data
Page 270 of 398
![AUDI S6 2009 Owners Manual ___ ln_ t _e_ ll-"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
[ i] Tips
• When the engine is running, never hold the steering wheel AUDI S6 2009 Owners Manual ___ ln_ t _e_ ll-"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
[ i] Tips
• When the engine is running, never hold the steering wheel](/manual-img/6/57595/w960_57595-269.png)
___ ln_ t _e_ ll-'"ig ...,_ e_ n_t _t_ e_ c_ h _ n_o _ l_o _,.g= y,_ __________________________________________ _
[ i] Tips
• When the engine is running, never hold the steering wheel
turned all the way to the right or to the left for longer than
15 seconds . The power steering pump will overheat the hydraulic
fluid if you keep holding th e steering wheel turned all th e way. This
is likely to damage the power steering system.
• If the power steering system should fail entirely, or if the engine
is not running (for example, while being towed), you will still be able
to ste er th e vehicle . However,
considerably mor e effort will be
required to do so.
• If the power steering system should have a leak, or is not func
tioning properly, contact your authorized Audi dealer immediately.
• The power steering system requires a specially formulated
hydraulic fluid. The power steering reservoir is the one located most
forward on the left side of the engine compartment=>
page 302. The
correct fluid level in the reservoir is important for proper func
tioning of the power ste ering. •
Applies to vehicles : wit h A ll Wh eel Drive
Driving with your quattro®
With All Wheel Drive, all four wheels are driven.
General information
With All Wheel Drive, power is distributed to all four wheels. This
happens automatically depending on your driving style and the
road conditions at the time . See also=>
page 263, "Electronic differ
ential lock (EDU".
Winter tires
When driving in the winter, your vehicle with All Wheel Drive has an
advantage, even with regular tires. In winter road conditions it may be advisable to mount winter tires (or all-season tires) for improved
driveability and braking: these tires must be mounted on
all four
wheels.
See also => page 333, "Winter tires".
Tire chains
Where tire chains are mandatory on certain roads, this normally
also applies to vehicles with All Wheel Drive=>
page 334, "Snow
chains".
Replacing wheels/tires
Vehicles with All Wheel Drive must always have tires of the same
si ze. Also avoid tires with different tread depths. For details see
page =>
page 329, "New tires and replacing tires and wheels".
Off-Road driving?
Your Audi does not have enough ground clearance to be used as an
off-road vehicle. It is therefore best to avoid rough tracks and
uneven terrain as much as possible. Also refer to=>
page 273.
& WARNING
Always adjust your driving to road and traffic conditions. Do not
let the extra safety afforded by All Wheel Drive tempt you into
taking extra risks.
• Although the All Wheel Drive is very effective, always
remember that braking capacity is limited by tire traction. You
should therefore not drive at excessive speeds on icy or slippery
road surfaces.
• On wet road surfaces, be careful not to drive too fast because
the front wheels could begin to slide on top of the water (aqua planing}. If this should occur, you will have no warning from a
sudden increase in engine speed as with a front-wheel drive
vehicle. Always drive at speeds which are suited to the road condi
tions -risk of crash. ,
Page 271 of 398

Energy management
Starting ability is optimized
Energy management controls the distribution of electrical
energy and thus optimizes the availability of electrical
energy for starting the engine.
If a vehicle with a conventional energy system is not driven for a
long period of time, the battery is discharged by idling current
consumers (e.g. immobilizer). In certain circumstances it can resu lt
in there being insufficient energy available to start the engine .
Intelligent energy management in your vehicle handles the distribu
tion of electrical energy . Starting ability is markedly improved and
the life of the battery is extended.
Basical ly, energy management consists of
battery di agn osis, idling
current mana gement
and dynami c en ergy management .
Batter y diagn osis
Battery diagnosis continuously deter min es the state of the battery.
Sensors determine battery vo ltage, battery current and battery
temperature . This determines the cu rrent state of charge and the
power of the battery .
Idling c urrent man ag em en t
Idling current management reduces energy consumption while the
vehicle is standing. With the ign it ion switched off, it controls the
energy supply to the various electrical components. Data from
battery diagnos is is considered .
Depending on the battery's state of charge, individual consumers
are gradually turned off to prevent excessive discharge of the
battery and thus maintain starting capability.
Dynamic energ y managem ent
While the vehic le is being driven, dynamic energy management
distributes the energy gene rated acco rding to the needs of the indi -
Controls and equip
ment Safety first Vehicle operation
In
te llig ent tec hn olo gy
vidual components . It regulates consumption, so that more e lec
trical energy is not being used than is being ge nerated and ensures
an optimal state of charge for the battery.
[ i ] Tips
• But even energy management cannot negate the limits of
physics. Consider that the power and life of a battery are limited .
• I f starting ability is threatened, you are informed by a warning
=> page 270, "Drive r notifica tion i n the instrument cluster
display" .•
What you should know
The highes t pri ority is given to main tain ing starting capa
bility.
The battery is severe ly taxed in short-distance driving, in city traffic
and during the co ld time of year. Abundant electrical energy is
required, but only a little is generated. It is also critical if the engine
is not running and elect rica l components are turned on. In this
instance energy is being consumed but none is being generated .
I t is in precisely these situations that you will notice energy manage
ment active ly regula ting the distr ibut ion of energy.
Vehicle stands fo r an extended period
If you do not drive your vehicle over a period of several days or
weeks, electrical components are gradually cut back or switched off.
This reduces energy consumption and maintains starting capability
over a longer period.
Take into considerat ion that when you un lock your veh icle, some
convenience functions, such as the remote key or power seat
adjustment, may not be availab le . T he conven ience functions will be
available again when you turn on the ignition and start the engine.
Vehicle care Do-it-yourself service Technical data