2008 SUZUKI SWIFT esp start
[x] Cancel search: esp startPage 629 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-55
Sensor Calibration (Using SUZUKI Scan Tool)1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position and confirm that
only any of DTC(s) C1075, C1076 and/or C1077 is
detected. If any other DTC are detected, repair the
detected DTC.
4) Park and level the vehicle with parking brake, stop engine with ignition switch ON, set steering in
straight and without step ping on the brake pedal.
NOTE
Hold the above condition in Step 4) to
calibrate sensor correctly until sensor
calibration is completed.
5) Select menu “SENSOR CALIBRATION” under
“MISC. TEST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool and
calibrate sensor. Refer to scan tool operator's
manual for further derails.
6) After completing the calibra tion, turn ignition switch
to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool
from DLC. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration (Not Using
SUZUKI Scan Tool)
1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect battery terminals and/or fuse and start engine.
NOTE
When power is not supplied to the steering
angle sensor by removing battery or fuse,
DTC C1075 is detected and SLIP indicator
lamp (1) flashes.
If DTC other than C1075 is detected, SLIP
indicator lamp flushes and other indicator
illuminate. In that case, repair the detected
DTC first.
3) Drive vehicle straight on level ground at 15 km/h (9.5 mph) or above for few seconds without spinning
wheels. And confirm that SLIP indicator lamp is OFF.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection
S7RS0B4606027
CAUTION!
Never disassemble ESP ® hydraulic unit /
control module assembly, loosen blind plug
or remove motor. Pe rforming any of these
prohibited services will affect original
performance of ESP ® hydraulic unit / control
module assembly.
Check hydraulic unit for fluid leakage.
If any, repair or replace.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
1
I6RS0B460028-02
Page 675 of 1496
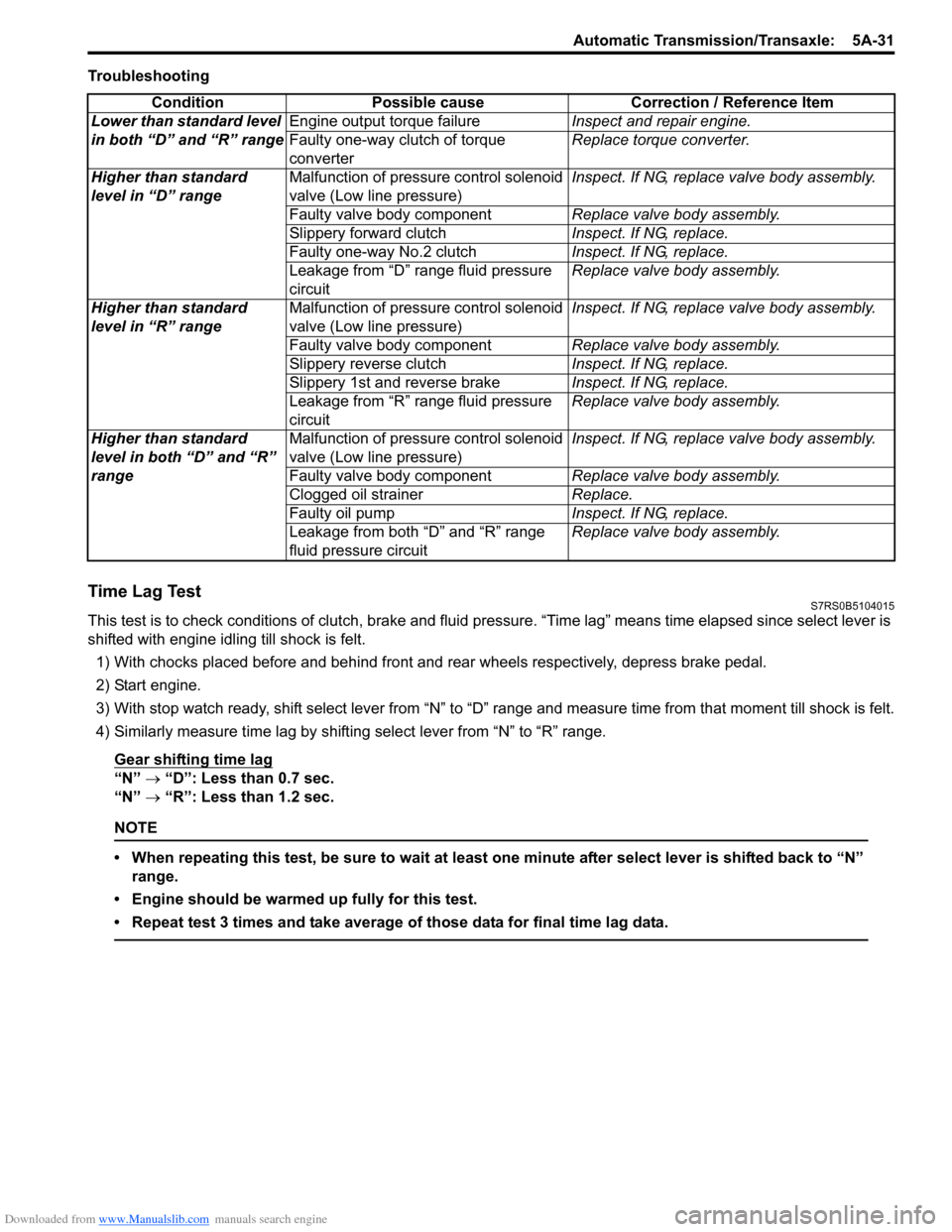
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-31
Troubleshooting
Time Lag TestS7RS0B5104015
This test is to check conditions of clutch, brake and fluid pressure. “Time lag” means time elapsed since select lever is
shifted with engine idling till shock is felt.
1) With chocks placed before and behind front and rear wheels respectively, depress brake pedal.
2) Start engine.
3) With stop watch ready, shift select lever from “N” to “D” range an d measure time from that moment till shock is felt.
4) Similarly measure time lag by shifting select lever from “N” to “R” range.
Gear shifting time lag
“N” → “D”: Less than 0.7 sec.
“N” → “R”: Less than 1.2 sec.
NOTE
• When repeating this test, be sure to wait at least one minute after select lever is shifted back to “N”
range.
• Engine should be warmed up fully for this test.
• Repeat test 3 times and take average of those data for final time lag data.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Lower than standard level
in both “D” and “R” range Engine output torque failure
Inspect and repair engine.
Faulty one-way clutch of torque
converter Replace torque converter.
Higher than standard
level in “D” range Malfunction of pressure control solenoid
valve (Low line pressure) Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Slippery forward clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.2 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Leakage from “D” range fluid pressure
circuit Replace valve body assembly.
Higher than standard
level in “R” range Malfunction of pressure control solenoid
valve (Low line pressure) Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Slippery reverse clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Slippery 1st and reverse brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Leakage from “R” range fluid pressure
circuit Replace valve body assembly.
Higher than standard
level in both “D” and “R”
range Malfunction of pressure control solenoid
valve (Low line pressure)
Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Clogged oil strainer Replace.
Faulty oil pump Inspect. If NG, replace.
Leakage from both “D” and “R” range
fluid pressure circuit Replace valve body assembly.
Page 689 of 1496
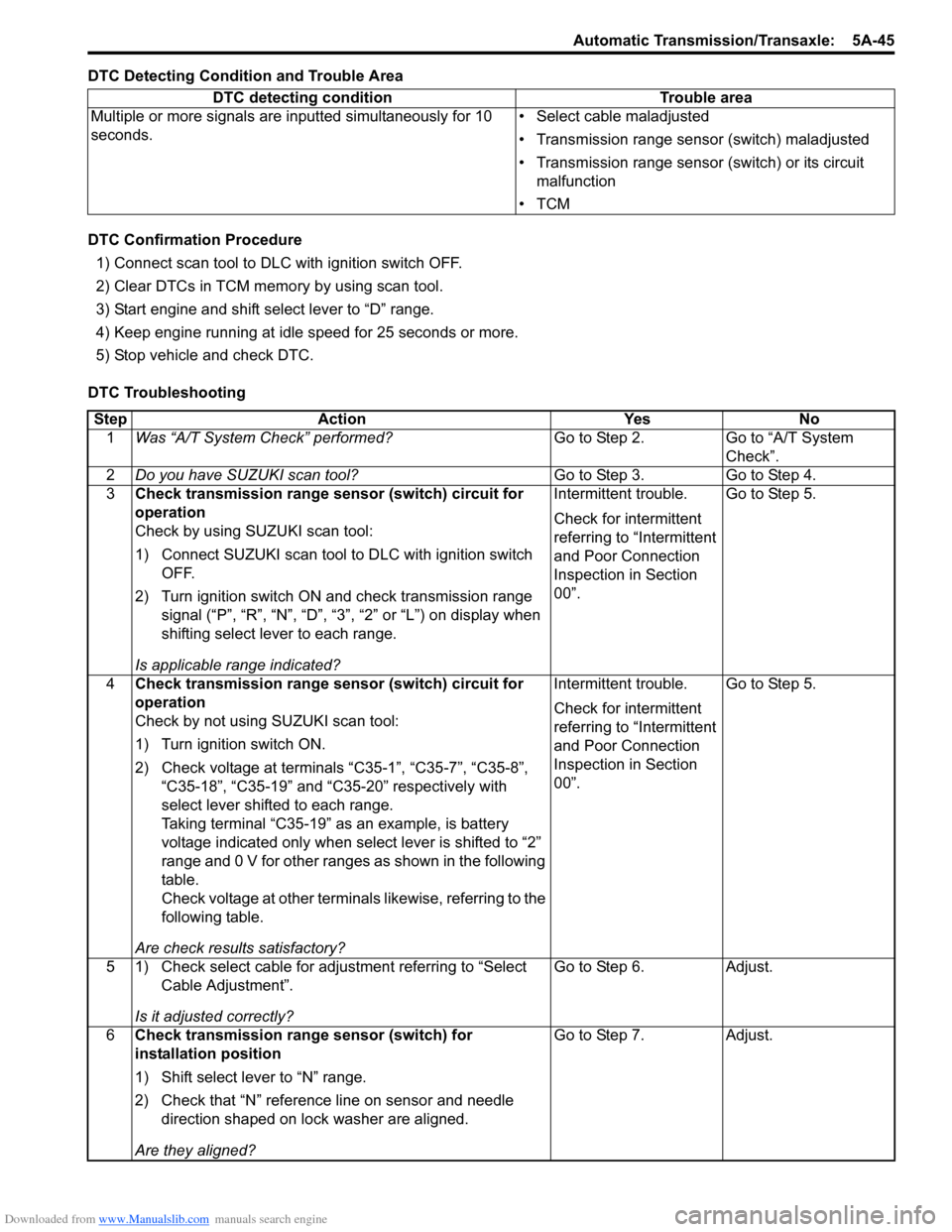
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-45
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTCs in TCM memo ry by using scan tool.
3) Start engine and shift select lever to “D” range.
4) Keep engine running at idle speed for 25 seconds or more.
5) Stop vehicle and check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Multiple or more signals are inputted simultaneously for 10
seconds. • Select cable maladjusted
• Transmission range sensor (switch) maladjusted
• Transmission range sensor (switch) or its circuit
malfunction
•TCM
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “A/T System Check” performed? Go to Step 2.Go to “A/T System
Check”.
2 Do you have SUZUKI scan tool? Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Check transmission range sensor (switch) circuit for
operation
Check by using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with ignition switch
OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check transmission range signal (“P”, “R”, “N”, “D”, “3”, “2” or “L”) on display when
shifting select lever to each range.
Is applicable range indicated? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.
Go to Step 5.
4 Check transmission range sensor (switch) circuit for
operation
Check by not using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminals “C35-1”, “C35-7”, “C35-8”,
“C35-18”, “C35-19” and “C35-20” respectively with
select lever shifted to each range.
Taking terminal “C35-19” as an example, is battery
voltage indicated only when se lect lever is shifted to “2”
range and 0 V for other ranges as shown in the following
table.
Check voltage at other terminals likewise, referring to the
following table.
Are check results satisfactory? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.
Go to Step 5.
5 1) Check select cable for adjustment referring to “Select Cable Adjustment”.
Is it adjusted correctly? Go to Step 6.
Adjust.
6 Check transmission range sensor (switch) for
installation position
1) Shift select lever to “N” range.
2) Check that “N” reference line on sensor and needle
direction shaped on lock washer are aligned.
Are they aligned? Go to Step 7.
Adjust.
Page 691 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-47
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTCs in TCM memo ry by using scan tool.
3) Start engine and shift select lever to “D” range.
4) Start vehicle and increase vehicle speed to 40 km/h (25 mile/h) or more for 1 minutes.
5) Stop vehicle and turn ignition switch OFF.
6) Repeat Step 3) to 4) one time.
7) Stop vehicle and check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting Step Action YesNo
1 Was “A/T System Check” performed? Go to Step 2.Go to “A/T System
Check”.
2 Do you have SUZUKI scan tool? Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Check transmission range sensor (switch) circuit for
operation
Check by using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with ignition switch
OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check transmission range signal (P, R, N, D, 3, 2 or L) on display when shifting
select lever to each range.
Is applicable range indicated? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”
Go to Step 5.
4 Check transmission range sensor (switch) circuit for
operation
Check by not using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminals “C35-1”, “C35-7”, “C35-8”,
“C35-18”, “C35-19” and “C35-20” respectively with
select lever shifted to each range.
Taking terminal “C35-19” as an example, is battery
voltage indicated only when se lect lever is shifted to “2”
range and 0 V for other ranges as shown in the following
table.
Check voltage at other terminals likewise, referring to the
following table.
Are check results satisfactory? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.
Go to Step 5.
5 1) Check select cable for adjustment referring to “Select Cable Adjustment”.
Is it adjusted correctly? Go to Step 6.
Adjust.
6 Check transmission range sensor (switch) for
installation position
1) Shift select lever to “N” range.
2) Check that “N” reference line on sensor and needle
direction shaped on lock washer are aligned.
Are they aligned? Go to Step 7.
Adjust.
Page 733 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-89
A/T Fluid Level CheckS7RS0B5106002
CAUTION!
Do not use any fluid other than the specified
ATF. Use of any fluid other than the specified
ATF may cause juddering or some other
faulty condition to occur.
Level Check at Normal Operating (Hot) Temperature
– Hot Check1) Drive vehicle so that A/T fluid temperature reach the
normal operating temperature (70 – 80 °C (158 –
176 °F)).
2) Stop vehicle with engine running and place it level.
3) With select lever at “P” range, apply parking brake and place chocks against wheels.
4) Keep engine idling and shift selector slowly to “L” and back to “P” position.
5) With engine idling, pull out fluid level gauge, wipe it off with a clean cloth and put it back into place.
6) Pull out fluid level gauge (1) again and check fluid level indicated on it. The lo west fluid level should be
between FULL HOT (2) and LOW HOT (3). If it is
below LOW HOT, add SUZUKI ATF 3317 or Mobil
ATF 3309 up to FULL HOT.
Automatic transaxle fluid
SUZUKI ATF 3317 or Mobil ATF 3309
NOTE
• Do not race engine while checking fluid level, even after the engine start.
• Do not overfill. Overfilling can cause foaming and loss of fluid through breather.
Then slippage and transaxle failure can
result.
• Bringing the level from LOW HOT to FULL HOT requires 0.4 liters (0.85 / 0.70 US/Imp.
pt).
• If vehicle was driven under high load such as pulling a trailer, fluid level should be
checked about half an hour after it is
stopped.
Level Check at Room (Cold) Temperature – Cold
Check
Fluid level can be checked temporarily at room (cold)
temperature which correspond to 20 – 30 °C (68 – 86
° F). This level check is considered to be preparation
before performing level check under normal operating
(hot) temperature. Checking procedure itself is the same
as that described in “Level Check at Normal Operating
(Hot) Temperature – Hot Check: ”. If fluid level is
between “FULL COLD” (4) and “LOW COLD” (5),
proceed to test drive. And when fluid temperature has
reached normal operating temp erature, check fluid level
again and adjust it as necessary.
CAUTION!
Fluid level check at room (cold) temperature
is recommended only for preparation of level
check under normal (hot) operating
condition.
Failure to perform fluid level check under
normal (hot) operating temperature may
result in damage to transaxle.
4. “FULL COLD” mark 5. “LOW COLD” mark
1. Fluid level gauge 2. “FULL HOT” mark 3. “LOW HOT” mark
I3RM0B510032-01
I3RM0B510032-01
Page 891 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-9
3) Start engine.
4) Read DTC according to the instructions displayed on
SUZUKI scan tool. For further details, refer to
operator’s manual for SUZUKI scan tool.
NOTE
• If communication between SUZUKI scan tool and the vehicle can not be
established, perform “Serial Data Link
Circuit Check”.
• DTC C1122 (engine speed signal failure) is indicated when ignition switch is at ON
position and engine is not running, but it
means there is nothing abnormal if
indication changes to a normal one when
engine is started.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B6304004
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) located on underside of instrument panel
at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Erase DTC according to the instructions displayed on SUZUKI scan tool. For further details, refer to
operator’s manual for SUZUKI scan tool.
5) After completing the clearance, turn ignition switch to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
DTC TableS7RS0B6304005
CAUTION!
Be sure to perform the “EPS Syst em Check” before starting troubleshooting corresponding to each
DTC.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting) Trouble area MIL
No
CODES Normal — — —
�) C1113 Steering torque sensor (Main
and Sub) circuit correlation Voltage difference between torque
sensor main signal and sub signal
is more than 0.6 V for 1 second
continuously. • Torque sensor signal circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle
�) C1114 Steering torque sensor
reference power supply
circuit Circuit voltage of torque sensor 5
V reference power supply voltage
is more than 5.7 V or less than 4.3
V for 1 second continuously. • Torque sensor circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle
�) C1117 Steering torque sensor
failure signal circuit low Torque sensor internal failure
signal circuit voltage is less than
1.7 V when ignition switch turned
ON.
• Torque sensor signal circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module1 driving
cycle
�) C1118 Steering torque sensor
failure signal circuit high Torque sensor internal failure
signal circuit voltage is more than
3.7 V for 1 second continuously. 1 driving
cycle
�) C1119 Steering torque sensor
power supply circuit Circuit voltage of torque sensor
main power supply
is less than
7.5 V for 1 second continuously. • Torque sensor circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle
Page 908 of 1496
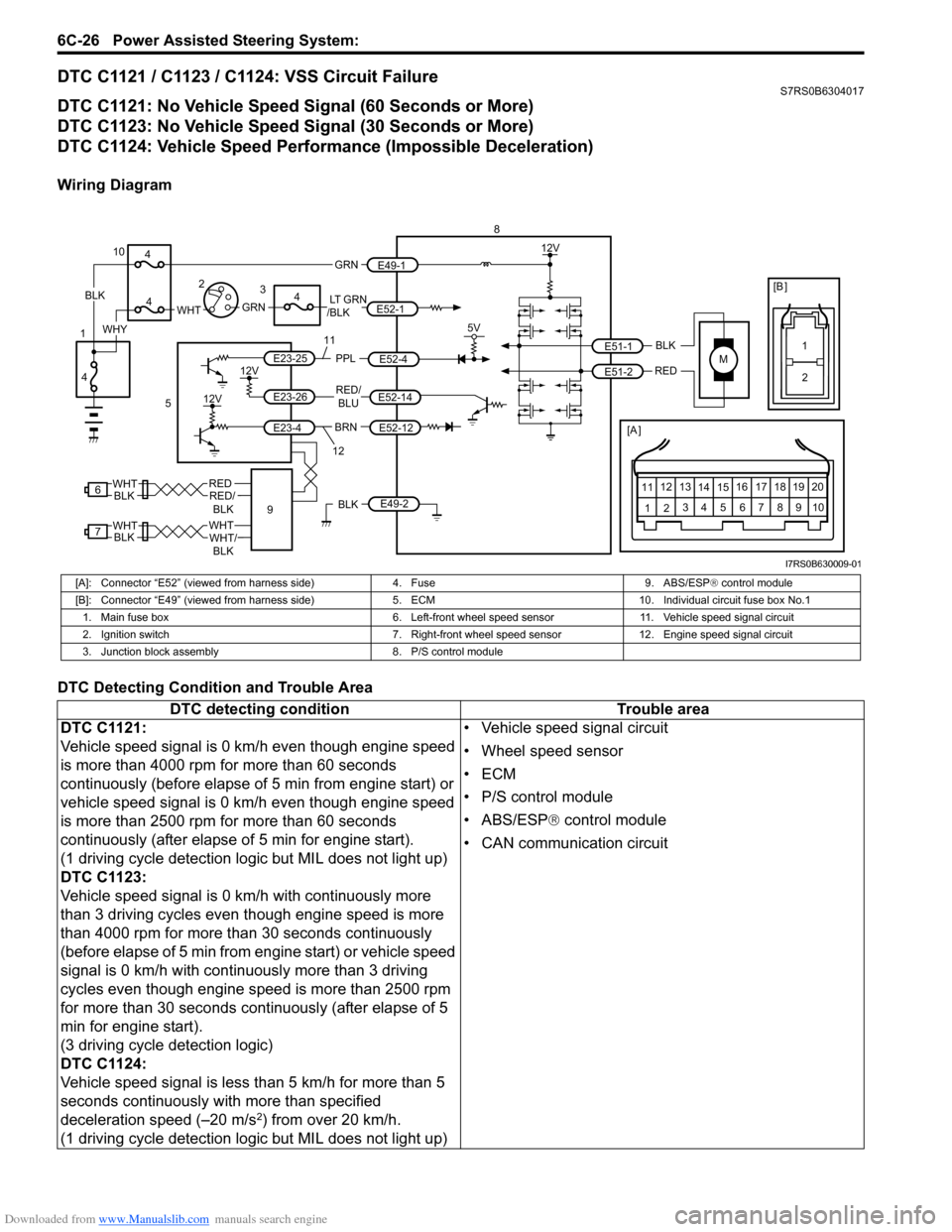
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-26 Power Assisted Steering System:
DTC C1121 / C1123 / C1124: VSS Circuit FailureS7RS0B6304017
DTC C1121: No Vehicle Speed Signal (60 Seconds or More)
DTC C1123: No Vehicle Speed Signal (30 Seconds or More)
DTC C1124: Vehicle Speed Performance (Impossible Deceleration)
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
M
BRNRED/
BLU
BLK
RED
E52-14
E52-12
E23-4
E23-26
E23-25 E51-1
E51-2
[A ]
12
3
4 5 67
89
11
10
12 13
141516
17 18 19 20
5V
PPL
E52-4
8
5
12V
E49-2BLK
12V
12V
6REDRED/ BLKWHT
7WHTWHT/BLKWHTBLK BLK
111
2
[B ]
9
LT GRN
/BLKE52-1 E49-1
GRNGRNWHTBLK
WHY
10
3
4
4
4
4
1 2
12
I7RS0B630009-01
[A]: Connector “E52” (viewed from harness side)
4. Fuse9. ABS/ESP® control module
[B]: Connector “E49” (viewed from harness si de)5. ECM 10. Individual circuit fuse box No.1
1. Main fuse box 6. Left-front wheel speed sensor11. Vehicle speed signal circuit
2. Ignition switch 7. Right-front wheel speed sensor 12. Engine speed signal circuit
3. Junction block assembly 8. P/S control module
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
DTC C1121:
Vehicle speed signal is 0 km/h even though engine speed
is more than 4000 rpm for more than 60 seconds
continuously (before elapse of 5 min from engine start) or
vehicle speed signal is 0 km/h even though engine speed
is more than 2500 rpm for more than 60 seconds
continuously (after elapse of 5 min for engine start).
(1 driving cycle detection logic but MIL does not light up)
DTC C1123:
Vehicle speed signal is 0 km/h with continuously more
than 3 driving cycles even though engine speed is more
than 4000 rpm for more than 30 seconds continuously
(before elapse of 5 min from engine start) or vehicle speed
signal is 0 km/h with continuously more than 3 driving
cycles even though engine speed is more than 2500 rpm
for more than 30 seconds continuously (after elapse of 5
min for engine start).
(3 driving cycle detection logic)
DTC C1124:
Vehicle speed signal is less than 5 km/h for more than 5
seconds continuously with more than specified
deceleration speed (–20 m/s
2) from over 20 km/h.
(1 driving cycle detection logic but MIL does not light up) • Vehicle speed signal circuit
• Wheel speed sensor
•ECM
• P/S control module
• ABS/ESP®
control module
• CAN communication circuit
Page 1039 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Bag System: 8B-1
Restraint
Air Bag System
Precautions
Precautions on Service and Diagnosis of Air
Bag System
S7RS0B8200001
WARNING!
• If the air bag system and another vehicle system both need repair, SUZUKI
recommends that the air bag system be
repaired first, to help avoid unintended air
bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel, dashboard, both front seat or any other on
or around air bag system components.
Modifications can adversely affect air bag
system performance and lead to injury.
• Be sure to follow the procedures described in this section. Failure to follow
procedures could result in possible air bag
system activation, personal injury or
unneeded air bag system repairs.
• WARNING / CAUTION labels are attached on each
part of air bag system components (SDM, air bag
(inflator) modules and seat belt pretensioners). Be
sure to follow the instructions.
• Many of service procedures require disconnection of
“A/BAG” fuse and air bag (inflator) module(s) (driver,
passenger, side of both si des and curtain of both
sides) from initiator circuit to avoid an accidental
deployment.
• Do not apply power to the air bag system unless all components are connected or a diagnostic flow
requests it, as this will set a DTC.
• The “Air Bag Diagnostic S ystem Check” must be the
starting point of any air bag diagnostics. The “Air Bag
Diagnostic System Check” will verify proper “AIR
BAG” warning right operatio n and will lead you to the
correct flow to diagnose any air bag malfunctions.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect
parts replacements. • Never use air bag component parts from another
vehicle.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93
° C (200 °F) (for example, during a paint baking
process), remove the air bag system components
beforehand to avoid component damage or
unintended system activation.
• When handling the air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side of both si des and curtain of both
sides), seat belt pretensio ners (driver and passenger),
SDM, forward-sensor or side-sensor, be careful not to
drop it or apply an impact to it. If an excessive impact
was applied (e.g., SDM, forward-sensor and side-
sensor are dropped, air bag (inflator) module is
dropped from a height of 90 cm (3 ft) or more, seat
belt pretensioner (retractor assembly) is dropped from
a height of 30 cm (1 ft) or more), never attempt
disassembly or repair but replace it with a new one.
• When using electric welding, be sure to disconnect air bag (inflator) module connectors (driver, passenger,
side of both sides and curtain of both sides) and seat
belt pretensioner connectors (driver and passenger)
respectively.
• When applying paint around the air bag system related parts, use care so that the harness or
connector will not be expo sed to the paint mist.
• Never expose air bag system component parts directly to hot air (drying or baking the vehicle after
painting) or flames.
WARNING!
When performing service on or around air
bag system components or air bag wiring,
follow the procedures listed in “Disabling Air
Bag System” to temporarily disable the air
bag system.
Failure to follow procedures could result in
possible air bag system activation, personal
injury or unneeded air bag system repairs.