2008 Seat Altea XL maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 271 of 317

If and when269
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
How to jump start: descriptionIn ⇒ fig. 204, the flat battery is and the charged battery .
Jump lead terminal connections
– Switch off the ignition on both vehicles ⇒.
1. Connect one end of the red jump lead to the positive ⇒fig. 204
terminal of the vehicle with the flat battery ⇒.
2. Connect the other end of the red jump lead to the positive terminal in the vehicle providing assistance.
3. Connect one end of the black jump lead to the negative terminal on the battery of the vehicle providing assistance. 4. Connect the other end of the black jump lead to a solid metal
component which is bolted on to the engine block, or onto the
engine block itself of the vehicle with the flat battery. Do not
connect it to a point near the battery ⇒.
5. Position the leads in such a way that they cannot come into contact with any moving parts in the engine compartment.
Starting
6. Start the engine of the vehicle with the boosting battery and let
it run at idling speed.
7. Start the engine of the car with the flat battery and wait one or two minutes until the engine is “running”.
Removing the jump leads
8. Before you remove the jump leads, switch off the headlights (if they are switched on).
9. Turn on the heater blower and rear window heater in the vehicle with the flat battery. This helps minimise voltage peaks which are
generated when the leads are disconnected.
10. When the engine is running, disconnect the leads in reverse order to the details given above.
Connect the battery clamps so they ha ve good metal-to-metal contact with
the battery terminals.
If the engine fails to start, switch off the starter after about 10 seconds and
try again after about half a minute.
Fig. 204 How to connect
the jump leads
AA
AB
A+
A+
A-
AX
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 269 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 273 of 317

If and when271
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
Towing and tow-startingTo w - s t a r t i n g
The use of jump leads is preferable to tow-starting.We recommend that you do not tow-start your vehicle. Jump-starting
is preferable ⇒page 268.
However, if your vehicle has to be tow-started:
–Engage the 2
nd or the 3
rd gear.
– Keep the clutch pressed down.
– Switch on the ignition.
– Once both vehicles are mo ving, release the clutch.
– As soon as the engine starts, press the clutch and move the gear lever into neutral. This helps to prevent driving into the towing
vehicle.
WARNING
The risk of accidents is high when tow-starting. The vehicle being towed
can easily collide with the towing vehicle.
Caution
When tow-starting, fuel could enter the catalytic converter and damage it.
General notesPlease observe the following points if you use a tow-rope:
Notes for the driver of the towing vehicle
– Drive slowly at first until the tow-rope is taut. Then accelerate gradually.
– Begin and change gears cautiously. If you are driving an auto- matic vehicle, accelerate gently.
– Remember that the brake servo and power steering are not working in the vehicle you are towing. Brake earlier than you
would normally, but with a more gentle pressure on the brake.
Notes for the driver of the towed vehicle
– Ensure that the tow-rope remains taut at all times when towing.Tow-rope or tow-bar
It is easier and safer to tow a vehicle with a tow-bar. You should only use a
tow-rope if you do not have a tow-bar.
A tow-rope should be slightly elastic to reduce the loading on both vehicles.
It is advisable to use a tow-rope made of synthetic fibre or similarly elastic
material.
Attach the tow-rope or the tow-bar only to the towing eyes provided or a
towing bracket.
Driving style
Towing requires some experience, especially when using a tow-rope. Both
drivers should be familiar with the technique required for towing. Inexperi-
enced drivers should not attempt to tow-start or tow away another vehicle.
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 271 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 275 of 317
If and when273
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
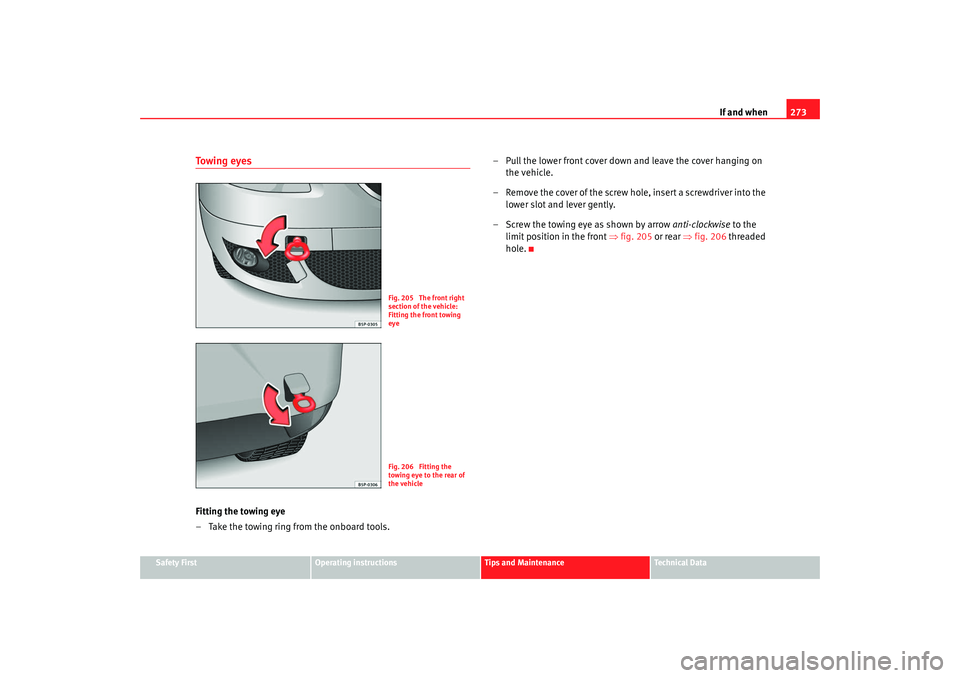
Towing eyesFitting the towing eye
– Take the towing ring from the onboard tools. – Pull the lower front cover down and leave the cover hanging on
the vehicle.
– Remove the cover of the screw hole, insert a screwdriver into the lower slot and lever gently.
– Screw the towing eye as shown by arrow anti-clockwise to the
limit position in the front ⇒fig. 205 or rear ⇒fig. 206 threaded
hole.
Fig. 205 The front right
section of the vehicle:
Fitting the front towing
eyeFig. 206 Fitting the
towing eye to the rear of
the vehicle
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 273 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 277 of 317

General notes on the technical data 275
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
Te c h n i c a l D a t aGeneral notes on the technical dataWhat you should be aware ofGeneral notes
All data in the official vehicle documents take precedence over this data.All data in these documents are valid for the basic model as offered in Spain.
The vehicle data card included in the inspection and maintenance schedule
in the vehicles registration documents show which engine is installed in the
vehicle. The figures may be different if addition
al equipment is fitted, for different
models, for special vehicles and for other countries.
Abbreviations used in this paragraph of the Technical Data Abbreviation MeaningkW Kilowatt, engine power measurement.
bhp Brake horse power, formerly used to denote engine power
at rpm Revolutions per minute - engine speed. Nm Newton metres, unit of engine torque.
l/100 km Fuel consumption in litres per 100 kilometres g/km Carbon dioxide emission s in grams per kilometre.
CO
2
Carbon dioxide
CN Cetane number, indication of the ignition quality of the diesel.
RON Research octane number, indication of the knock resistance of petrol.
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 275 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 278 of 317

General notes on the technical data
276Vehicle identification data
The most important data are given on the type plate and the
vehicle data sticker.Vehicles for certain export countries do not have a type plate.
Type plate
The type plate is located on the left rib inside the engine compartment.
Vehicle identification number
The vehicle identification number (chass is number) can be read from outside
the vehicle through a viewer in the windscreen. This is located on the left-
hand side of the vehicle in the lower area of the windscreen. It is also located
on the right hand side of the engine compartment. Vehicle data
The data sticker is placed on the inside of the spare wheel recess in the
luggage compartment.
The following information can be fo
und in the vehicle information: ⇒fig. 209
This information also figures in the Maintenance Program. Production control number
Vehicle identification number (chassis number)
Model code number
Model designation / engine power output
Engine and gearbox code letters
Paint number / interior trim code
Optional equipment codes
Consumption values
CO
2 emissions values.
The data of 2 to 9 also figure in the Maintenance Program.
CO emissions and consumption
2
Consumption (litres/100 km) / CO
2 emissions (g/km) urban.
Consumption (litres/100 km) / CO2 emissions (g/km), road.
Consumption (litres/100 km) / CO2 emissions (g/km) combination.
Fig. 209 Vehicle data
sticker – luggage
compartment
A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9AAABAC
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 276 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 279 of 317

General notes on the technical data 277
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
How are the figures measured?Fuel consumption
The consumption and emission details shown on the vehi cle data sticker differ from one vehicle to another.The fuel consumption and CO
2 emissions of the vehicle can be found on the
vehicle data sticker.
The fuel consumption and emissions figures given are based on the weight
category of the car, which is determined according to the engine/gearbox
combination and the equipment fitted. The consumption and emission figures are calculated in accordance with the
EC test requirements 1999/100/EC. The
se test requirements specify a real-
istic test method based on normal everyday driving.
The following test conditions are applied:
Note
•
Actual consumption may vary from quoted test values, depending on
personal driving style, road and traffic conditions, the weather and the condi-
tion of the vehicle. Urban cycle
The urban cycle starts with an engine cold start. City driving is then simulated.
Extra urban cycle In the extra urban cycle the vehicle undergoes frequent acceleration
and braking in all gears, as in normal everyday driving. The
road speed ranges from 0 to 120 km/h.
Combined The average overall consumption is calculat
ed with a weighting of around 37% for the urban cycle and 63% for the extra urban
cycle.
CO2 emissions The exhaust gases are collected during both driving cycles to calculate carbon dioxide emissions. The gas composition is then
analysed to evaluate the CO
2 content and other emissions.
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 277 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 281 of 317

Technical data279
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
Te c h n i c a l d a t aChecking fluid levelsFrom time to time, the levels of the different fluids in the
vehicle must be checked. Never fill with incorrect fluids, to do
so may cause serious damage to the engine.
Radiator expansion tank
Windscreen washer fluid reservoir
Engine oil filler cap
Engine oil dipstick
Brake fluid reservoir
Vehicle battery (underneath the cover)
The checking and replenishment of the service fluids are carried out on the
components mentioned above. These operations are described in the
⇒ page 215. Overview
Further explanations, instructions and restrictions on the technical data are
contained as of
⇒page 275.
Fig. 210 Diagram for the
location of the various
elements
A1A2A3A4A5A6
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 279 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10
Page 283 of 317

Technical data281
Safety First
Operating instructions
Tips and Maintenance
Te c h n i c a l D a t a
Engine oil capacity
Petrol engine 1.4 92 kW (125 bhp)General engine data
Performance figures
Weights
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change
2.8 litres
Power output in kW (bhp) rpm 92 (125)/ 5600
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 200/ 1750-4000
No. of cylinders, capacity in cm
3
4/ 1390
Compression ratio 9,7 -0,4
Fuel Premium unleaded 95 RON or regular unleaded 91 RON
a)
a)With a slight power lossMaximum speedin km/h 194
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h in sec. 7,0
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h in sec. 10,5
Gross vehicle weight in kg 2023
Weight in working order (with driver) in kg 1478
Gross axle weight, front in kg 1004
Gross axle weight, rear in kg 1036
Permitted roof load in kg 75
altea_XL ingles.book Seite 281 Donnerstag, 13. September 2007 10:36 10