2008 MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 38 of 241

HEATER CONTROL
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-6
HEATER CONTROLM2551000900421
HEATER CONTROLLER
.
The features of the heater controller described below
have been designed for better appearance, easier
operation, and enhanced visibility.
•Each dial for the air outlet switching, fan volume
control, and temperature adjustment has been
enlarged to enhance operability.
•Ring lights have been adopted to inside the dials
to enhance appearance during nighttime.
cles with automatic A/C>
•AUTO and OFF positions of the fan volume con-
trol dial have been exchenged with one another.
This change prevents the dial to pass the AUTO
position when the fan volume control is turned
OFF, and eliminates the necessity of manual
reselection when switching the inside/outside air
selection manually, thus enhancing the operabil
-
ity.
•When the air outlet switching dial and fan volume
control dial are turned to the AUTO position, the
A/C switch has been made to automatically turn
ON to enhance convenience. (Using the custom
-
ize function, this function can be cancelled. Refer
to
P.55-7.)
AC608071AC608070
AC608069AC608068
AC608329
Outside/Inside air
selection switch
Maximum
A/C position
Temperature adjustment knob
A/C switch
Blower knob
Rear window defogger switch
Mode selection knob
selection switch
Temperature
adjustment knobBlower knob
A/C switch
Rear window
defogger switch
Mode selection knob
Outside/Inside air
selection switch
Temperature adjustment knob
A/C switch
Blower knob
Mode selection knob
Rear window defogger switch
selection switch
Temperature
adjustment knobBlower knob
A/C switch
Mode selection knob
Rear window
defogger switch
AB
Page 101 of 241

SENSOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-8
SENSORM2132001000565.
MASS AIRFLOW SENSOR
Mass airflow sensor is installed in the air intake hose. Mass air-
flow sensor is composed of an extremely small heatsensing
resistor. The mass airflow sensor controls the amount of elec
-
tric current flowing into the heat sensing resistor to keep the
heat sensing resistor at a constant temperature to the intake air
temperature. The faster the air flow speed, the higher the mass
flow rate.Because the amount of heat transfer from the heat
sensing resistor to the air increases, the mass airflow sensor
increases the amount of electric current to the heat sensing
resistor. Thus, the amount of electric current increases in
accordance with the air mass flow rate. The mass airflow sen
-
sor measures the air mass flow rate by detecting the amount of
electric current. The mass airflow sensor amplifies the detected
electric current amount and outputs it into the ECM. ECM uses
this output current and engine speed to calculate and decide
basic fuel injection time. Sensor properties are as shown in the
figure.
.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Intake air temperature sensor is built in to the mass airflow sen-
sor. Intake air temperature sensor detects intake air tempera-
ture through thermistor's resistance change and outputs the
voltage according to intake air temperature to ECM. ECM uses
this output voltage to compensate fuel injection control and
ignition timing control. Sensor properties are as shown in the
figure.
AK602252AC
Sensing areaSilicon substrate
Heat sensing
resistor
Intake air
Diaphragm
AK602221AG
From MFI relay
Mass airflow sensorECMOutput current mA
Mass flow g/s
AK602253AC
Sensory part
(thermistor)
Page 114 of 241

SENSOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-21
.
GENERATOR FR TERMINAL
Generator turns ON/OFF the power transistor in the voltage
regulator to adjust current flow in the field coil according to
alternator output current. In this way generator's output voltage
is kept adjusted (to about 14.7 V). The ratio of power transistor
ON time (ON duty) is output from generator FR terminal to
ECM. ECM uses this signal to detect generator's output current
and drives throttle actuator control motor according to output
current (electric load). This prevents change in idle speed due
to electric load and helps maintain stable idle speed.
.
AK602229AD
FR BS
Field coil
IC regulator
GeneratorIgnition switch-IG
Battery
ECM
Page 122 of 241
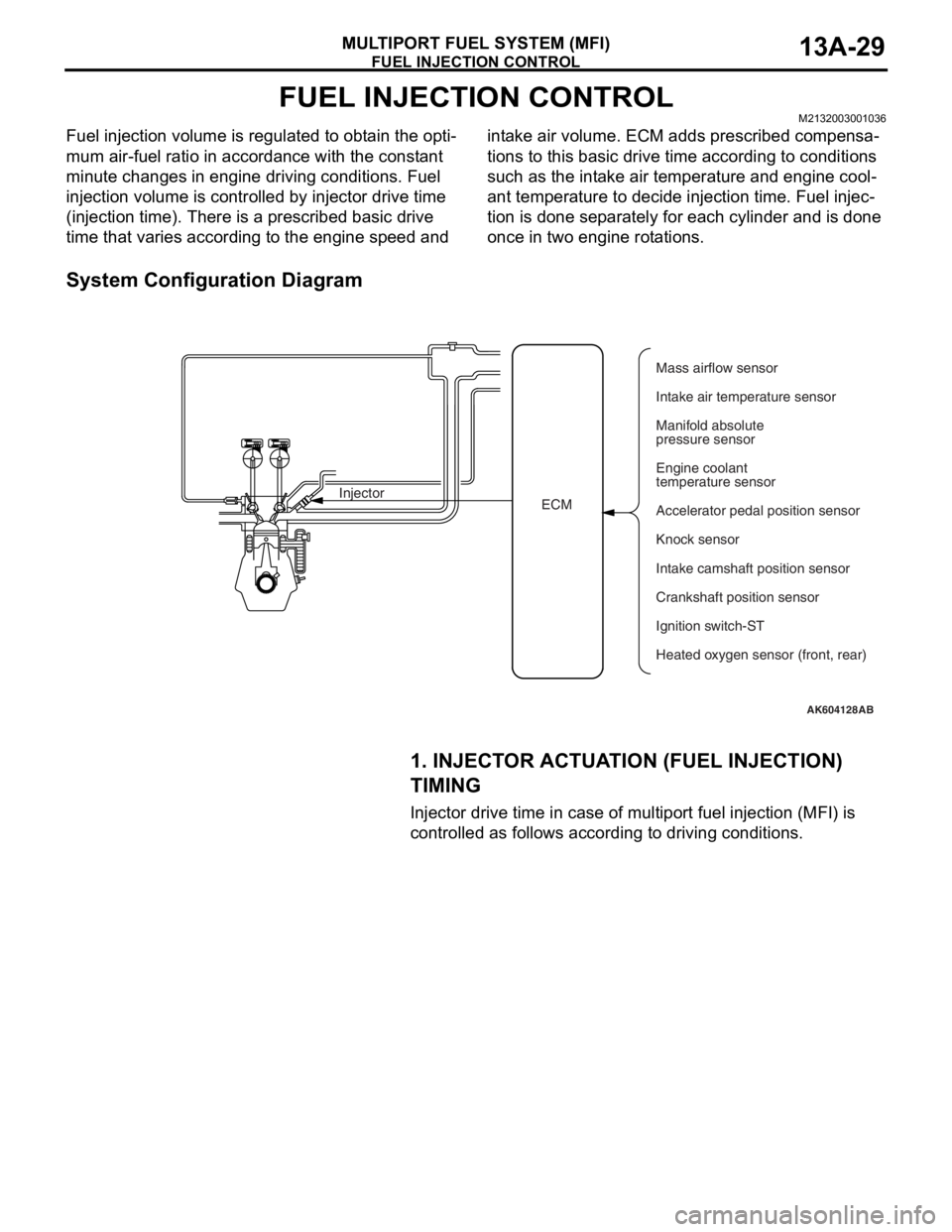
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-29
FUEL INJECTION CONTROLM2132003001036
Fuel injection volume is regulated to obtain the opti-
mum air-fuel ratio in accordance with the constant
minute changes in engine driving conditions. Fuel
injection volume is controlled by injector drive time
(injection time). There is a prescribed basic drive
time that varies according to the engine speed and intake air volume. ECM adds prescribed compensa
-
tions to this basic drive time according to conditions
such as the intake air temperature and engine cool
-
ant temperature to decide injection time. Fuel injec-
tion is done separately for each cylinder and is done
once in two engine rotations.
System Configuration Diagram
1. INJECTOR ACTUATION (FUEL INJECTION)
TIMING
Injector drive time in case of multiport fuel injection (MFI) is
controlled as follows according to driving conditions.
AK604128AB
ECM InjectorMass airflow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Accelerator pedal position sensor
Knock sensor
Intake camshaft position sensor
Ignition switch-ST
Heated oxygen sensor (front, rear) Crankshaft position sensor
Page 126 of 241
![MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-33
[Injector basic drive time]
Fuel injection is performed once per cycle for each cylinder.
Basic drive time refers to fuel injection volume (in MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-33
[Injector basic drive time]
Fuel injection is performed once per cycle for each cylinder.
Basic drive time refers to fuel injection volume (in](/manual-img/19/57326/w960_57326-125.png)
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-33
[Injector basic drive time]
Fuel injection is performed once per cycle for each cylinder.
Basic drive time refers to fuel injection volume (injector drive
time) to achieve theoretical air-fuel ratio for the intake air vol
-
ume of 1 cycle of 1 cylinder. Fuel injection volume changes
according to the pressure difference (injected fuel pressure)
between manifold absolute pressure and fuel pressure (con
-
stant). So, injected fuel pressure compensation is made to
injector drive time for theoretical air-fuel ratio to arrive at basic
drive time.
Intake air volume of each cycle of 1 cylinder is calculated by
ECM based on the mass airflow sensor signal and crankshaft
position sensor signal. Also, during engine start, the map value
prescribed by the engine coolant temperature sensor signal is
used as basic drive time.
.
AK602279AC
Basic fuel
injection timeFuel injection pressure compensation Intake air amount per cycle per cylinder
Theoretical air-fuel ratio
Page 127 of 241
![MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the o MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the o](/manual-img/19/57326/w960_57326-126.png)
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the optimum fuel injec
-
tion volume according to driving conditions.
List of main compensations for fuel injection control
.
[Fuel limit control during deceleration]
ECM limits fuel when decelerating downhill to prevent exces-
sive rise of catalytic converter temperature and to improve fuel
efficiency.
.
[Fuel-cut control when over-run]
When engine speed exceeds a prescribed limit (6,600 r/min),
ECM cuts fuel supply to prevent overrunning and thus protect
the engine. Also, if engine speed exceeds 4,000 r/min for 15
seconds while vehicle is stationary (no load), it cuts fuel supply
and controls the throttle valve opening angle to protect the
engine.
CompensationsContent
Heated oxygen sensor feedback compensationThe heated oxygen sensor signal is used for
making the compensation to get air-fuel ratio with
best cleaning efficiency of the 3-way catalytic
converter. This compensation might not be made
sometimes in order to improve drivability,
depending on driving conditions. (Air-fuel ratio
compensation is made.)
Air-fuel ratio compensationUnder driving conditions where heated oxygen
sensor feedback compensation is not performed,
compensation is made based on pre-set map
values that vary according to engine speed and
intake air volume.
Engine coolant temperature compensationCompensation is made according to the engine
coolant temperature. The lower the engine coolant
temperature, the greater the fuel injection volume.
Acceleration/ Deceleration compensationCompensation is made according to change in
intake air volume. During acceleration, fuel injection
volume is increased. Also, during deceleration, fuel
injection volume is decreased.
Fuel injection compensationCompensation is made according to the pressure
difference between atmospheric pressure and
manifold absolute pressure. The greater the
difference in pressure, the shorter the injector drive
time.
Battery voltage compensationCompensation is made depending on battery
voltage. The lower the battery voltage, the greater
the injector drive signal time.
Learning value for fuel compensationCompensation amount is learned to compensate
feedback of heated oxygen sensor. This allows
system to compensate in accordance with engine
characteristics.
Page 130 of 241
![MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-37
2. Spark-advance control and current carrying
time control
.
[During start]
ECM initiates ignition at fixed ign MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Workshop Manual IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-37
2. Spark-advance control and current carrying
time control
.
[During start]
ECM initiates ignition at fixed ign](/manual-img/19/57326/w960_57326-129.png)
IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-37
2. Spark-advance control and current carrying
time control
.
[During start]
ECM initiates ignition at fixed ignition timing (5° BTDC) syn-
chronized with the crankshaft position sensor signal.
.
[During normal operation]
After determining the basic spark-advance based on the intake
air volume and engine speed, ECM makes compensations
based on input from various sensors to control the optimum
spark-advance and current carrying time.
List of main compensations for spark-advance control and current carrying time control
.
[Control for checking ignition timing]
During basic ignition timing set mode for M.U.T.-III actuator test
function, sparking is done with fixed ignition timing (5
° BTDC)
synchronized with crankshaft position sensor signal.
CompensationsContent
Intake air temperature compensationCompensation is made according to intake air
temperature. The higher the intake air temperature
the greater the delay in ignition timing.
Engine coolant temperature compensationCompensation is made according to engine coolant
temperature. The lower the engine coolant
temperature the greater the advance in ignition
timing.
Knocking compensationCompensation is made according to generation of
knocking. The greater the knocking the greater the
delay in ignition timing.
Stable idle compensationCompensation is made according to change in idle
speed. In case engine speed becomes lower than
target speed, ignition timing is advanced.
Delay compensation when changing shiftDuring change of shift, sparking is delayed
compared to normal ignition timing to reduce
engine output torque and absorb the shock of the
shift change.
Battery voltage compensationCompensation is made depending on battery
voltage. The lower the battery voltage the greater
the current carrying time and when battery voltage
is high current carrying time is shortened.