2008 MERCEDES-BENZ E-CLASS SALOON tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 41 of 401
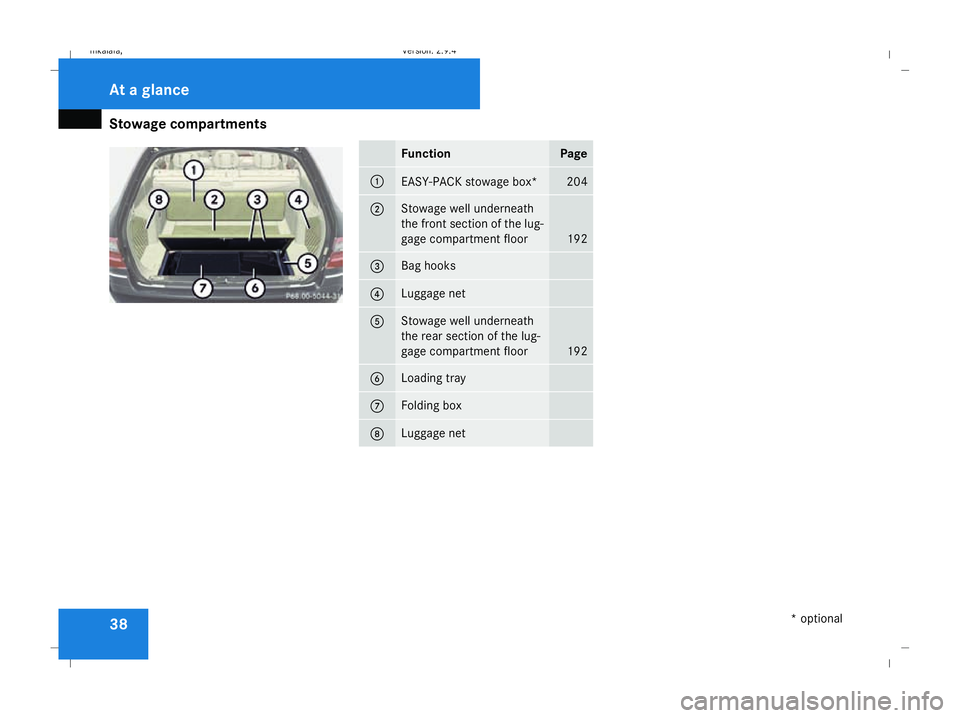
Stowage compartments
38 Function Page
1
EASY-PACK stowage box* 204
2 Stowage well underneath
the front section of the lug-
gage compartment floor
192
3 Bag hooks
4 Luggage net
5 Stowage well underneath
the rear section of the lug-
gage compartment floor
192
6 Loading tray
7 Folding box
8 Luggage netAt a glance
* optional
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4 2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 38Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 43 of 401

Occupant safety
40 Occupant safety
Notes on occupant safety
Seat belts, together with belt tensioners, belt
force limiters and airbags, are coordinated
restraint systems. They reduce the risk of
injury in defined accident situations and
thereby increase occupant safety. However,
seat belts and airbags generally do not pro-
tect against objects penetrating the vehicle
from the outside.
To ensure that the restraint systems can
deliver their full potential protection, you
should ensure that:
R the seat and head restraint are adjusted
properly (Y page 77)
R the seat belt has been fastened properly
(Y page 95)
R the airbags can inflate properly if they are
deployed (Y page 43)
R the steering wheel is adjusted properly
(Y page 89)
R the restraint systems have not been modi-
fied
i An airbag increases the protection of
vehicle occupants wearing a seat belt. However, airbags are only an additional
restraint system which complements, but
does not replace, the seat belt. All vehicle
occupants must wear their seat belt cor-
rectly at all times, even if the vehicle is
equipped with airbags. This is because - on
the one hand - airbags are not deployed in
all types of accident, as in some situations
airbag deployment would not increase the
protection afforded to vehicle occupants,
provided they are wearing their seat belt
correctly. On the other hand, airbag deploy-
ment only provides increased protection if
the seat belt is worn correctly because:
R
the seat belt helps to keep the vehicle
occupant in the best position in relation
to the airbag
R for example, in a head-on collision, the
seat belt can more adequately prevent
the occupant from being propelled
towards the force of the impact, and is
thus better suited to prevent injury
Therefore, in accident situations where an
airbag is deployed, it only provides protec-
tion in addition to the seat belt if the seat
belt is being worn correctly. G
Risk of accident and injury
Always have maintenance work carried out
at a qualified specialist workshop which
has the necessary specialist knowledge
and tools to carry out the work required.
Mercedes-Benz recommends that you use
a Mercedes-Benz Service Centre for this
purpose.
In particular, work relevant to safety or on
safety-related systems must be carried out
at a qualified specialist workshop. If this
work is not carried out correctly, the oper-
ating safety of your vehicle may be affec-
ted. There is a risk of an accident and injury. G
Risk of injury
The restraint system may not work as inten-
ded if the following components have been
modified or work on these components has
not been performed correctly:
R restraint system, consisting of the seat
belts and anchorages, belt tensioners,
belt force limiters, airbags
R wiring
R networked electronic systems
Airbags or belt tensioners could then fail,
e.g. in the event of an accident in which the Safety
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4 2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 40Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 45 of 401

Occupant safety
42
ess is pre-emptive in nature as the airbag
must be deployed during – and not at the end
of – the collision.
i Airbags are not deployed in all types of
accidents. They are controlled by complex
sensor technology and evaluation logic.
This process is pre-emptive in nature as
airbag deployment must take place during
the impact and must be adapted to provide
calculated, additional protection for the
vehicle occupants. Not all airbags are
deployed in an accident.
The different airbag systems work inde-
pendently of each other. However, the
deployment of each individual system will
depend on the type of accident determined
by the control system in the first stages of
the collision (head-on collision, side impact
and overturn) and the extent of the acci-
dent (in particular, the vehicle's rate of
deceleration or acceleration).
The rate of vehicle deceleration or accelera-
tion and the direction of the force are basi-
cally determined by:
R the distribution of forces during the colli-
sion
R the collision angle R
the deformation characteristics of the vehi-
cle
R the characteristics of the object with which
the vehicle has collided, e.g. the other vehi-
cle
Factors which can only be seen and measured
after a collision has occurred do not play a
decisive role in the deployment of an airbag,
nor do they provide an indication of it.
The vehicle may be deformed significantly,
e. g. on the bonnet or the wing, without an
airbag being deployed. This is the case if only
parts which are relatively easily deformed are
affected and the necessary deceleration does
not occur. Conversely, airbags may be
deployed even though the vehicle suffers only
minor deformations. This is the case if, for
example, very rigid vehicle parts such as lon-
gitudinal body members are affected and suf-
ficient deceleration occurs as a result.
Belt tensioners, belt force limiters The front seat belts and the outer seat belts
in the rear are equipped with belt tensioners.
!
Do not engage the seat belt tongue in the
buckle on the front-passenger seat if the
seat is not occupied. Otherwise the belt tensioner could be activated in an emer-
gency.
If the seat belt is also equipped with a belt
force limiter, the force exerted by the seat
belt on the seat occupant is reduced.
Belt tensioners tighten the seat belts in an
accident, pulling them close against the body.
i Belt tensioners do not correct incorrect
seat positions or incorrectly fastened seat
belts.
Belt tensioners do not pull occupants back
towards the backrest.
The front belt force limiters are synchronised
with the front airbags, which distribute the
forces exerted by the belt force limiters on
the occupant over a greater area.
When the ignition is switched on, the belt ten-
sioner is triggered:
R only if the restraint systems are operational
(the 1 warning lamp lights up after the
ignition is switched on and goes out once
the engine is running) (Y page 41)
R for each three-point seat belt in the front of
the vehicle when the belt tongue is
engaged in the buckle
R in the event of a head-on or rear-end colli-
sion if the vehicle decelerates or acceler- Safety
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4 2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 42Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 63 of 401

Driving safety sys
tems60 ESP
®
(Electronic Stability Program)
ESP ®
monitors driving stability and traction,
i.e. power transmission between the tyres
and the road surface.
If ESP ®
detects that the vehicle is deviating
from the direction desired by the driver, one
or more wheels are braked to stabilise the
vehicle. The engine output is also modified, if
necessary, to keep the vehicle on the desired
course within physical limits. ESP ®
assists
the driver when pulling away on wet or slip-
pery roads. ESP ®
can also stabilise the vehi-
cle during braking.
When ESP ®
intervenes, the vwarning
lamp flashes in the instrument cluster. G
Risk of accident
If the v warning lamp in the instrument
cluster flashes, proceed as follows:
R Do not deactivate ESP ®
under any cir-
cumstances.
R Only depress the accelerator pedal as far
as necessary when pulling away.
R Adapt your driving style to suit the pre-
vailing road and weather conditions.
The vehicle could otherwise go into a skid. ESP
®
cannot reduce the risk of an accident
if you drive too fast. ESP ®
cannot override
the laws of physics.
! If the vehicle is to be towed with the front
or rear axle raised, the ignition must be
switched off (key in position 0or 1in the
ignition lock). Application of the brakes by
ESP ®
could otherwise destroy the brake
system on the front or rear axle.
! Vehicles with 4MATIC* may not be towed
with the front or rear axle raised.
i Only use wheels with the recommended
tyre sizes. Only then will ESP ®
function
properly.
Deactivating/activating ESP ® ESP
®
is activated automatically when the
engine is running.
It may be best to deactivate ESP ®
in the fol-
lowing situations:
R when using snow chains
R in deep snow
R on sand or gravel G
Risk of accident
Activate ESP ®
as soon as the situations
described above no longer apply. ESP ®
will
otherwise not be able to stabilise the vehi-
cle if the vehicle starts to skid or a wheel
starts to spin.
If you deactivate ESP ®
:
R ESP ®
no longer improves driving stability.
R engine torque is not limited and the drive
wheels are able to spin. The spinning
wheels produce a cutting effect for better
traction.
R traction control is still activated.
R ESP ®
still provides support when you
brake.
i If ESP ®
is deactivated and one or more
wheels start to spin, the vwarning lamp
in the instrument cluster flashes. In such
situations ESP ®
will not stabilise the vehi-
cle. Safety
* optional
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa
,V ersion: 2.9.4
2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 60 Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 66 of 401

Anti-theft syste
ms 63Tow-away protection*
An audible and visual alarm is triggered if your
vehicle's angle of inclination is altered while
tow-away protection is primed. This happens
if the vehicle is jacked up on one side, for
example.
Priming tow-away protection X
Lock the vehicle using the key. On vehicles
with KEYLESS GO*, the locking button on
the door handle/boot lid/tailgate can also
be used.
Tow-away protection is primed after
approximately 30 seconds.
To deactivate tow-away protection When you unlock your vehicle using the key
or KEYLESS GO
*,tow-away protection is
automatically deactivated.
Deactivate tow-away protection manually to
prevent a false alarm if your vehicle:
R is being transported
R is being loaded, e.g. onto a ferry or car
transporter
R is being parked on a movable surface, e.g.
split-level garages 1
To deactivate tow-away protection
2 Indicator lamp
X Remove the key from the ignition lock.
X Press button 1.
Indicator lamp 2lights up briefly.
X Lock the vehicle using the key. On vehicles
with KEYLESS GO*, the locking button on
the door handle/boot lid/tailgate can also
be used.
Tow-away protection remains deactivated
until the vehicle is unlocked and locked
again. Interior motion sensor*
If the interior motion sensor is primed, a vis-
ual and audible alarm is triggered if move-
ment is detected in the vehicle interior while
the vehicle is locked. This occurs, for exam-
ple, if someone breaks the side windows of
your vehicle or reaches into the vehicle's inte-
rior.
Priming the interior motion sensor X
Make sure that:
R
the side windows are closed
R the sliding/tilting sunroof* or panorama
sliding sunroof* is closed
R there are no objects, e.g. mascots, hang-
ing on the rear-view mirror or on the
grasp handles on the roof trim.
This will prevent false alarms.
X Lock the vehicle using the key. On vehicles
with KEYLESS GO*, the locking buttons on
the door handle/boot lid/tailgate can also
be used.
The interior motion sensor is primed after
approximately 30 seconds. Safety
* optional
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa
,V ersion: 2.9.4
2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 63 ZDateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 68 of 401

65
Opening and closing
...........................66
Key positions ....................................... 76
Seats .................................................... 77
Steering wheel .................................... 89
Mirrors ................................................. 91
Memory functions* .............................93
Seat belts ............................................. 95
Lights ................................................... 99
Windscreen wipers ...........................105
Side windows .................................... 107Driving and parking
..........................110
Transmission ..................................... 114
Instrument cluster ............................120
On-board computer ..........................121
Driving systems ................................ 142
Air conditioning ................................. 162
Sliding sunroof .................................. 180
Loading and stowing ........................186
Features ............................................. 207 Controls
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4
2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 65 Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 84 of 401
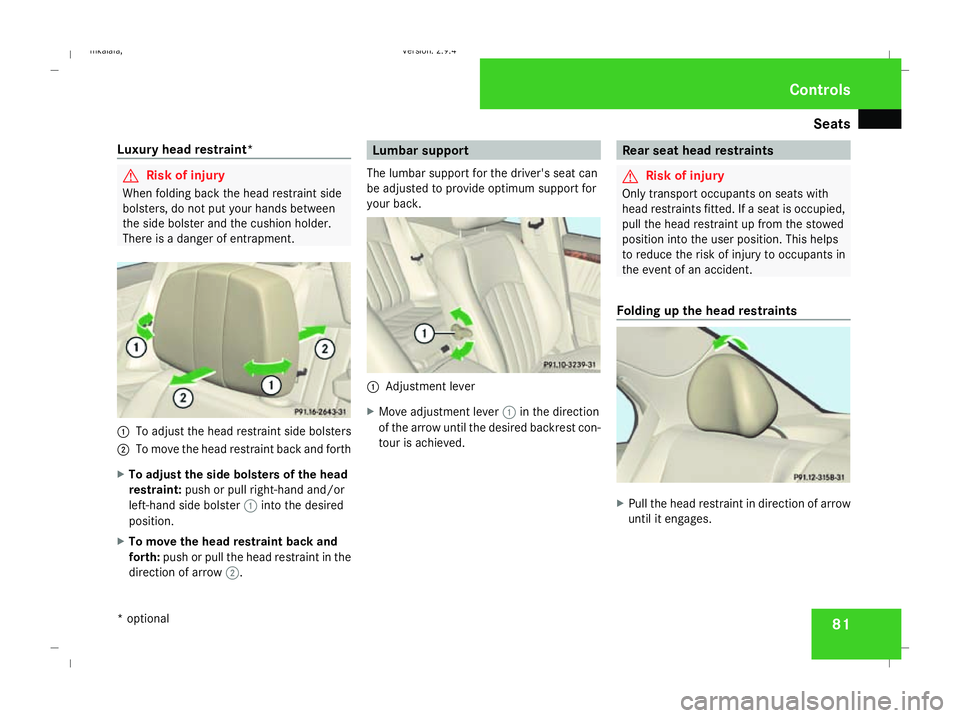
Seats
81
Luxury head restraint* G
Risk of injury
When folding back the head restraint side
bolsters, do not put your hands between
the side bolster and the cushion holder.
There is a danger of entrapment. 1
To adjust the head restraint side bolsters
2 To move the head restraint back and forth
X To adjust the side bolsters of the head
restraint: push or pull right-hand and/or
left-hand side bolster 1into the desired
position.
X To move the head restraint back and
forth: push or pull the head restraint in the
direction of arrow 2. Lumbar support
The lumbar support for the driver's seat can
be adjusted to provide optimum support for
your back. 1
Adjustment lever
X Move adjustment lever 1in the direction
of the arrow until the desired backrest con-
tour is achieved. Rear seat head restraints
G
Risk of injury
Only transport occupants on seats with
head restraints fitted. If a seat is occupied,
pull the head restraint up from the stowed
position into the user position. This helps
to reduce the risk of injury to occupants in
the event of an accident.
Folding up the head restraints X
Pull the head restraint in direction of arrow
until it engages. Controls
* optional
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4 2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 81 ZDateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight
Page 99 of 401

Seat belts
96 For this reason, check regularly that the
seat belts are not damaged or dirty.
Always have damaged seat belts or seat
belts that have been subjected to a load in
an accident replaced at a qualified special-
ist workshop. Choose a qualified specialist
workshop which has the necessary special-
ist knowledge and tools for the work
required. Mercedes-Benz recommends
that you use a Mercedes-Benz Service
Centre for this purpose.
For safety reasons, Mercedes-Benz recom-
mends that you only use seat belts which
have been approved by Mercedes-Benz for
your vehicle. 1
Belt sash guide
2 Belt tongue
3 Buckle
4 Release button Routing the belt X
Adjust the seat and move the backrest to
an almost vertical position (Y page 77).
X Pull the belt smoothly through belt sash
guide 1.
X Route the belt over the centre of the shoul-
der without twisting it.
X Engage belt tongue 2into buckle 3.
X If necessary, adjust the belt to the appro-
priate height (Y page 97).
X If necessary, pull upwards on the shoulder
section of the belt to tighten the belt across
your body.
Routing the belt X
Press release button 4and guide belt
tongue 2back towards belt sash guide
1. Controls
211_AKB; 2; 5, en-GB
mkalafa,
Version: 2.9.4 2008-02-29T16:57:07+01:00 - Seite 96Dateiname: 6515_3416_02_buchblock.pdf; preflight