2007 SUZUKI SWIFT fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 91 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-41
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK) Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s) “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Low oil pressure Improper oil viscosity “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Engine noise – Valve
noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Improper valve lash “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem and guide “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or broken valve spring “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Warped or bent valve “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Page 92 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-42 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine noise – Piston,
ring and cylinder noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine noise –
Connecting rod noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn rod bearing “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crank pin “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose connecting rod nuts “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation in Section
1D”
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Engine noise –
Crankshaft noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Worn bearing “Main Bearings Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crankshaft journal “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose bearing cap bolts “Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”
Excessive crankshaft thrust play “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine overheating Inoperative thermostat “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance “Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator “Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system “Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control
System Check” or “Rad
iator Cooling Fan High
Speed Control System Check”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Blown cylinder head gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 94 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-44 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine hesitates –
Momentary lack of
response as accelerator
is depressed. Can occur
at all vehicle speeds.
Usually most severe when
first trying to make
vehicle move, as from a
stop sign.Spark plug faulty
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Surge – Engine power
variation under steady
throttle or cruise. Feels
like vehicle speeds up
and down with no change
in accelerator pedal. Leaky or loosely connected high-tension
cord
“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (excess carbon
deposits, improper gap, burned
electrodes, etc.) “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Variable fuel pressure “Fuel Pressure Check”
Kinky or damaged fuel hose and lines
Faulty fuel pump (clogged fuel filter)
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of MAF sensor “MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Excessive detonation –
Engine makes
continuously sharp
metallic knocks that
change with throttle
opening. Sounds like pop
corn popping. Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection of high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Clogged fuel filter (faulty fuel pump) or
fuel lines “Fuel Pressure Check” or “Fuel Pump and Its
Circuit Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold or
throttle body gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT
sensor or MAF sensor “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High”, “ECT Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C” or “MAF and IAT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Excessive combustion chamber
deposits “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D” and/or “Piston Pins
and Connecting Rods In
spection in Section
1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 253 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-203
Fuel Pressure CheckS7RS0B1104083
System Diagram
Special tool
(A): 09912–58442
(B): 09912–58432
(C): 09912–58490
I3RM0A110081-01
1. Injector2. Delivery pipe 3. Fuel filter and fuel pump
Page 254 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-204 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
NOTE
Before using following flow, check to make sure that battery voltage is higher than 11 V. If battery
voltage is low, pressure becomes lower than specification even if fuel pump and line are in good
condition.
StepAction YesNo
1 Fuel pressure check
1) Check fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure
Inspection in Section 1G”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 2.
Go to Step 5.
2 Fuel pressure check
1) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature.
2) Keep engine speed at 4000 rpm.
Does fuel pressure show about the same value as Step 1? Go to Step 3.
Go to Step 8.
3 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for fuel leakage.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace
defective part.
4 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Faulty fuel pressure
regulator.
Repair or replace
damaged or damaged
part.
5 Was fuel pressure higher than specification in Step 1? Go to Step 6.Go to Step 7.
6 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Faulty fuel pressure
regulator.
Repair or replace
damaged or damaged
part.
7 Fuel pump operating sound check
1) Remove fuel filler cap and th en turn ON ignition switch.
Can you hear operating sound? Go to Step 8.
Faulty fuel pump.
8 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Clogged fuel filter, faulty
fuel pump, faulty fuel
pressure regulator or
fuel leakage from hose
connection in fuel tank.Repair or replace
defective part.
Page 287 of 1496
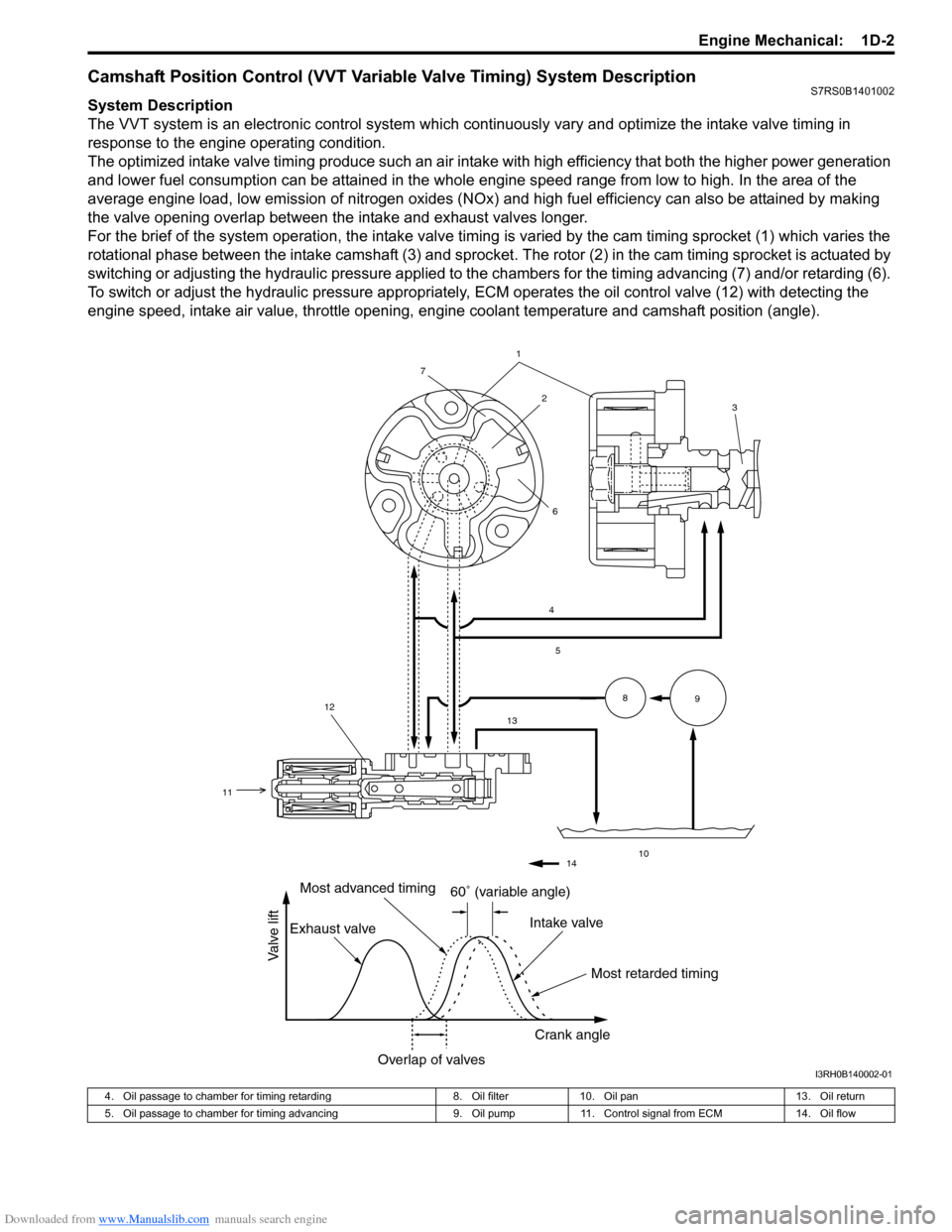
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 376 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-1 Fuel System:
Engine
Fuel System
Precautions
Precautions on Fuel System ServiceS7RS0B1700001
WARNING!
Before attempting service of any type on fuel system, the following should be always observed in
order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury.
• Disconnect negative cable at battery.
• Do not smoke, and place no smoking signs near work area.
• Be sure to have CO
2 fire extinguisher handy.
• Be sure to perform work in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames (such as gas hot heater).
• Wear safety glasses.
• To relieve fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank, remove fuel filler cap from fuel filler neck and then
reinstall it.
• As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pr essure even after stopping engine, loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel. Before loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief
Procedure”.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when the fuel line is disconnected. In order to reduce the risk of personal injury, cover a shop cloth to the fitting to be disconnected. Be sure to put that cloth
in an approved container after disconnecting.
• Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
• Note that fuel hose connection varies with each type of pipe. Be sure to connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting”.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
• When installing inje ctor or fuel feed pipe, lubr icate its O-ring with gasoline.
General Description
Fuel System DescriptionS7RS0B1701001
CAUTION!
This engine requires the unleaded fuel only.
The leaded and/or low lead fuel can result in
engine damage and reduce the effectiveness
of the emission control system.
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank,
fuel pump assembly (with fuel filter, fuel level gauge, fuel
pressure regulator, fuel feed line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Fuel Delivery System DescriptionS7RS0B1701002
The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel
pump assembly (with built-in f uel filter and fuel pressure
regulator), delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump,
sent into delivery pipe and injected by the injectors.
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel
filter and fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is filtered and
its pressure is regulated before being sent to the feed
pipe.
The excess fuel at fuel pressure regulation process is
returned back into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the
fuel vapor line into the EVAP canister.
For system diagram, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Page 377 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Fuel System: 1G-2
Fuel Pump DescriptionS7RS0B1701003
The fuel pump (1) is an in-tank type electric pump.
Incorporated in the pump assembly are;
a fuel filter (2) and a fuel pressure regulator (3) are
included and a fuel level gauge (4) is attached.
Addition of the fuel pressure regulator to the fuel pump
makes it possible to mainta in the fuel pressure at
constant level and ECM controls compensation for
variation in the intake manifold pressure.
Schematic and Routing Diagram
Fuel Delivery System DiagramS7RS0B1702001
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Fuel Pressure InspectionS7RS0B1704001
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk or fire
and personal injury.
1) Relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to
“Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure”.
2) Disconnect fuel feed hose from fuel delivery pipe.
3) Connect special tools and hose between fuel feed hose (1) and fuel delivery pipe as shown in figure,
and clamp hoses securely in order to ensure that no
leaks occur during checking.
Special tool
(A): 09912–58442
(B): 09912–58432
(C): 09912–58490
1
3
2
4
I6RS0C170001-01
4
6 7
8
12
2 3
11
10
5
1
9
I6RS0C170002-01
1. Fuel tank
5. Fuel injector9. EVAP canister
2. Fuel pump 6. Fuel feed line10. Fuel filter
3. Fuel pressure regulator 7. Fuel vapor line 11. Main fuel level sensor
4. Delivery pipe 8. Intake manifold12. EVAP canister purge valve
1
(C) (B)
(A)
I3RM0A170004-01