2007 SUZUKI SWIFT Gear oil
[x] Cancel search: Gear oilPage 355 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-3
6) Start engine and warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
Be sure to shift transaxle gear shift lever in
“Neutral” (shift select lever in “P” range for
A/T vehicle), set parking brake and block
drive wheels.
7) After warming up, raise engine speed to 4,000 r/min. and measure oil pressure.
Oil pressure specification
More than 270 kPa (2.7 kg/cm2, 39.8 psi) at 4,000
r/min. (rpm)
8) After checking oil pressure, stop engine and remove oil pressure gauge and attachment.
9) Before reinstalling oil pressure switch (2), be sure to
wrap its screw threads with sealing tape (1) and
tighten switch to specified torque.
NOTE
If sealing tape edge is bulged out from screw
threads of switch, cut it off.
Tightening torque
Oil pressure switch (a): 13 N·m (1.3 kgf-m, 9.5
lb-ft) 10) Start engine and check oil pressure switch for oil
leakage. If oil leakage is found, repair it.
11) Connect oil pressure switch coupler (1).
Repair Instructions
Heat Exchanger ComponentsS7RS0B1506001
I2RH0B150005-01
I2RH0B150006-01
3
4
5
7
6
(a)
2
1
I6RS0B151001-02
1. Heat exchanger inlet No. 1 hose 4. Gasket7. O-ring
: Apply engine oil.
2. Heat exchanger outlet No. 1 hose 5. Heat exchanger stand bolt : 22 N⋅m (2.2 kgf-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
3. Heat exchanger 6. Oil filter adapter case : Do not reuse.
Page 400 of 1496
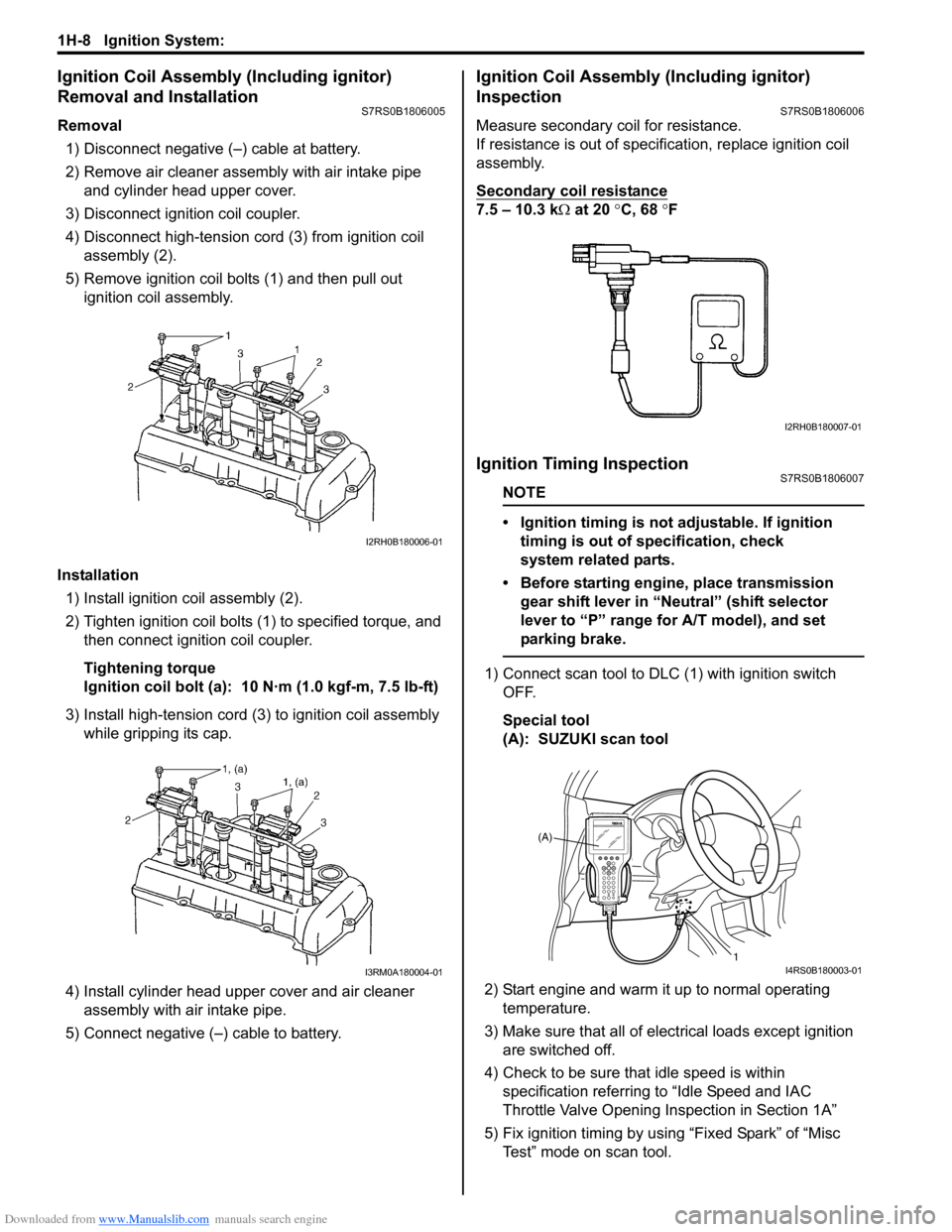
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-8 Ignition System:
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1806005
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe and cylinder head upper cover.
3) Disconnect ignition coil coupler.
4) Disconnect high-tension cord (3) from ignition coil assembly (2).
5) Remove ignition coil bolts (1) and then pull out ignition coil assembly.
Installation 1) Install ignition coil assembly (2).
2) Tighten ignition coil bolts (1) to specified torque, and then connect igni tion coil coupler.
Tightening torque
Ignition coil bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
3) Install high-tension cord (3) to ignition coil assembly while gripping its cap.
4) Install cylinder head upper cover and air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe.
5) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection
S7RS0B1806006
Measure secondary coil for resistance.
If resistance is out of specification, replace ignition coil
assembly.
Secondary coil resistance
7.5 – 10.3 k Ω at 20 °C, 68 ° F
Ignition Timing InspectionS7RS0B1806007
NOTE
• Ignition timing is not adjustable. If ignition
timing is out of specification, check
system related parts.
• Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), and set
parking brake.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition are switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within specification referring to “Idle Speed and IAC
Throttle Valve Opening Inspection in Section 1A”
5) Fix ignition timing by using “Fixed Spark” of “Misc Test” mode on scan tool.
I2RH0B180006-01
I3RM0A180004-01
I2RH0B180007-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B180003-01
Page 403 of 1496
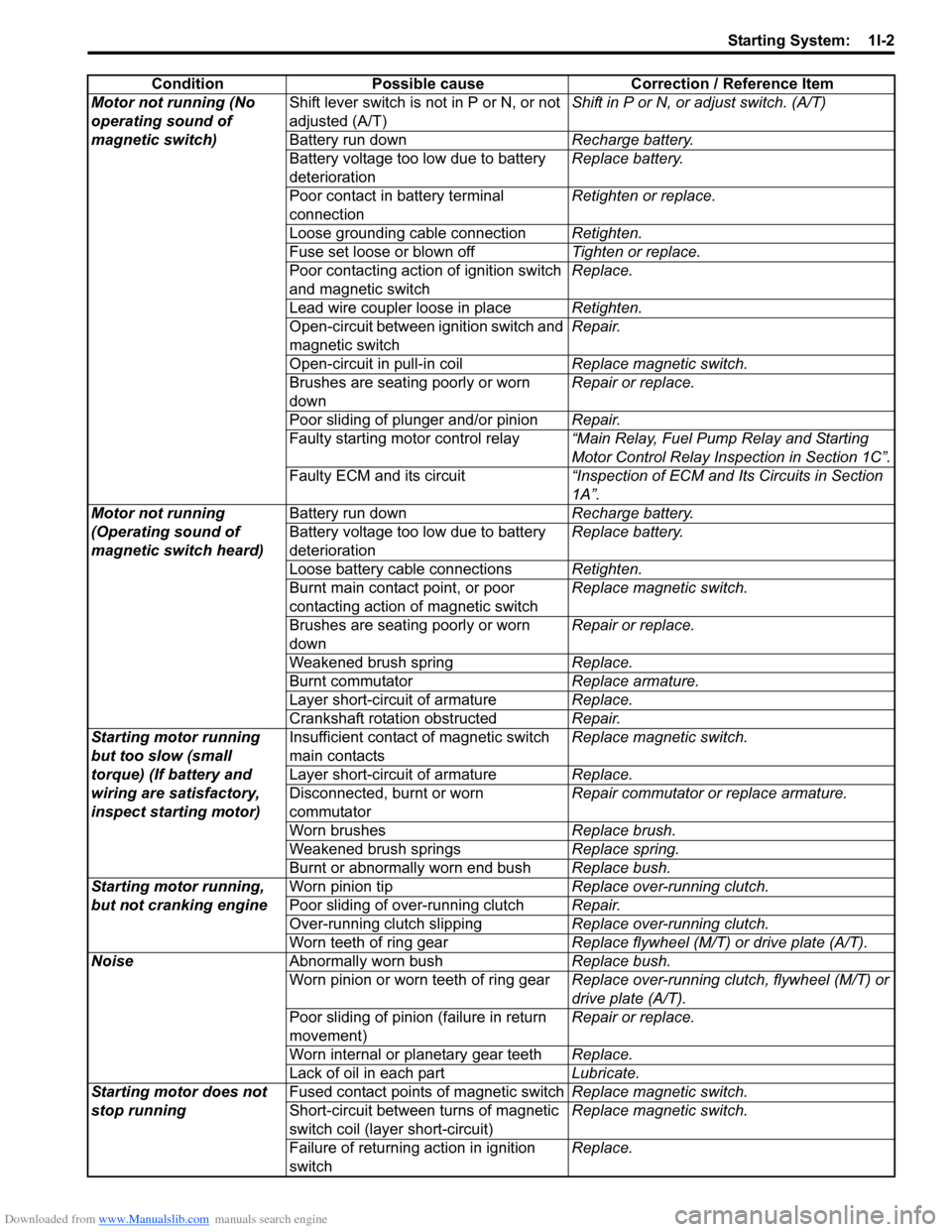
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Starting System: 1I-2
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Motor not running (No
operating sound of
magnetic switch) Shift lever switch is not in P or N, or not
adjusted (A/T)
Shift in P or N, or
adjust switch. (A/T)
Battery run down Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery
deterioration Replace battery.
Poor contact in battery terminal
connection Retighten or replace.
Loose grounding cable connection Retighten.
Fuse set loose or blown off Tighten or replace.
Poor contacting action of ignition switch
and magnetic switch Replace.
Lead wire coupler loose in place Retighten.
Open-circuit between ignition switch and
magnetic switch Repair.
Open-circuit in pull-in coil Replace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn
down Repair or replace.
Poor sliding of plunger and/or pinion Repair.
Faulty starting motor control relay “Main Relay, Fuel Pump Relay and Starting
Motor Control Relay Inspection in Section 1C”.
Faulty ECM and its circuit “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits in Section
1A”.
Motor not running
(Operating sound of
magnetic switch heard) Battery run down
Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery
deterioration Replace battery.
Loose battery cable connections Retighten.
Burnt main contact point, or poor
contacting action of magnetic switch Replace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn
down Repair or replace.
Weakened brush spring Replace.
Burnt commutator Replace armature.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Crankshaft rotation obstructed Repair.
Starting motor running
but too slow (small
torque) (If battery and
wiring are satisfactory,
inspect starting motor) Insufficient contact
of magnetic switch
main contacts Replace magnetic switch.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Disconnected, burnt or worn
commutator Repair commutator or replace armature.
Worn brushes Replace brush.
Weakened brush springs Replace spring.
Burnt or abnormally worn end bush Replace bush.
Starting motor running,
but not cranking engine Worn pinion tip
Replace over-running clutch.
Poor sliding of over-running clutch Repair.
Over-running clutch slipping Replace over-running clutch.
Worn teeth of ring gear Replace flywheel (M/T) or drive plate (A/T).
Noise Abnormally worn bush Replace bush.
Worn pinion or worn teeth of ring gear Replace over-running clutch, flywheel (M/T) or
drive plate (A/T).
Poor sliding of pinion (failure in return
movement) Repair or replace.
Worn internal or planetary gear teeth Replace.
Lack of oil in each part Lubricate.
Starting motor does not
stop running Fused contact points of magnetic switch
Replace magnetic switch.
Short-circuit between turns of magnetic
switch coil (layer short-circuit) Replace magnetic switch.
Failure of returning action in ignition
switch Replace.
Page 432 of 1496
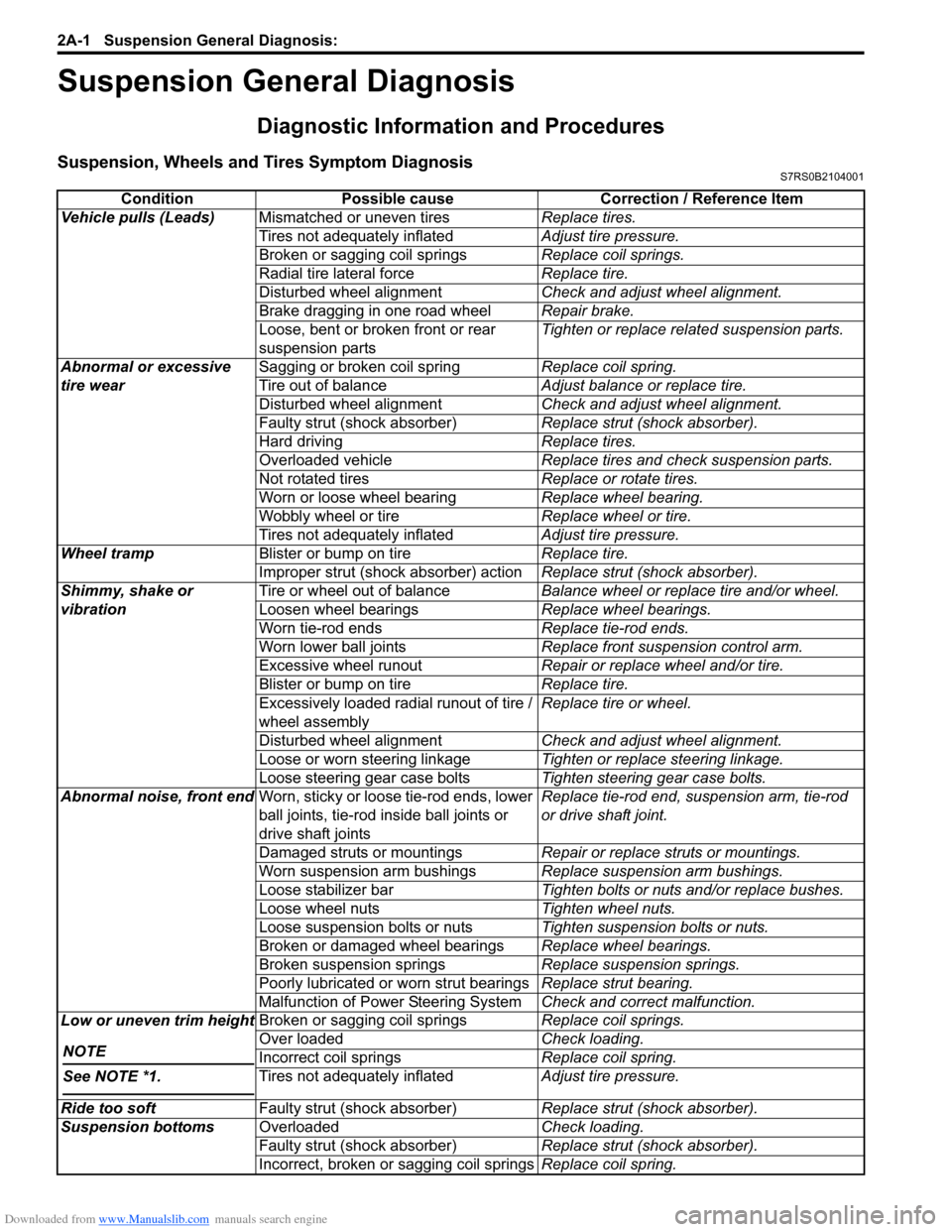
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2A-1 Suspension General Diagnosis:
Suspension
Suspension General Diagnosis
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Suspension, Wheels and Tires Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B2104001
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Vehicle pulls (Leads) Mismatched or uneven tires Replace tires.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Radial tire lateral force Replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Brake dragging in one road wheel Repair brake.
Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts Tighten or replace related suspension parts.
Abnormal or excessive
tire wear Sagging or broken coil spring
Replace coil spring.
Tire out of balance Adjust balance or replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Hard driving Replace tires.
Overloaded vehicle Replace tires and check suspension parts.
Not rotated tires Replace or rotate tires.
Worn or loose wheel bearing Replace wheel bearing.
Wobbly wheel or tire Replace wheel or tire.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Wheel tramp Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Improper strut (shock absorber) action Replace strut (shock absorber).
Shimmy, shake or
vibration Tire or wheel out of balance
Balance wheel or replace tire and/or wheel.
Loosen wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Worn tie-rod ends Replace tie-rod ends.
Worn lower ball joints Replace front suspension control arm.
Excessive wheel runout Repair or replace wheel and/or tire.
Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Excessively loaded radial runout of tire /
wheel assembly Replace tire or wheel.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or worn steering linkage Tighten or replace steering linkage.
Loose steering gear case bolts Tighten steering gear case bolts.
Abnormal noise, front end Worn, sticky or loose tie-rod ends, lower
ball joints, tie-rod in side ball joints or
drive shaft joints Replace tie-rod end, su
spension arm, tie-rod
or drive shaft joint.
Damaged struts or mountings Repair or replace struts or mountings.
Worn suspension arm bushings Replace suspension arm bushings.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten bolts or nuts and/or replace bushes.
Loose wheel nuts Tighten wheel nuts.
Loose suspension bolts or nuts Tighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or damaged wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Broken suspension springs Replace suspension springs.
Poorly lubricated or worn strut bearings Replace strut bearing.
Malfunction of Power Steering System Check and correct malfunction.
Low or uneven trim height
NOTE
See NOTE *1.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Over loaded Check loading.
Incorrect coil springs Replace coil spring.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Ride too soft Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Suspension bottoms Overloaded Check loading.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Incorrect, broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil spring.
Page 483 of 1496
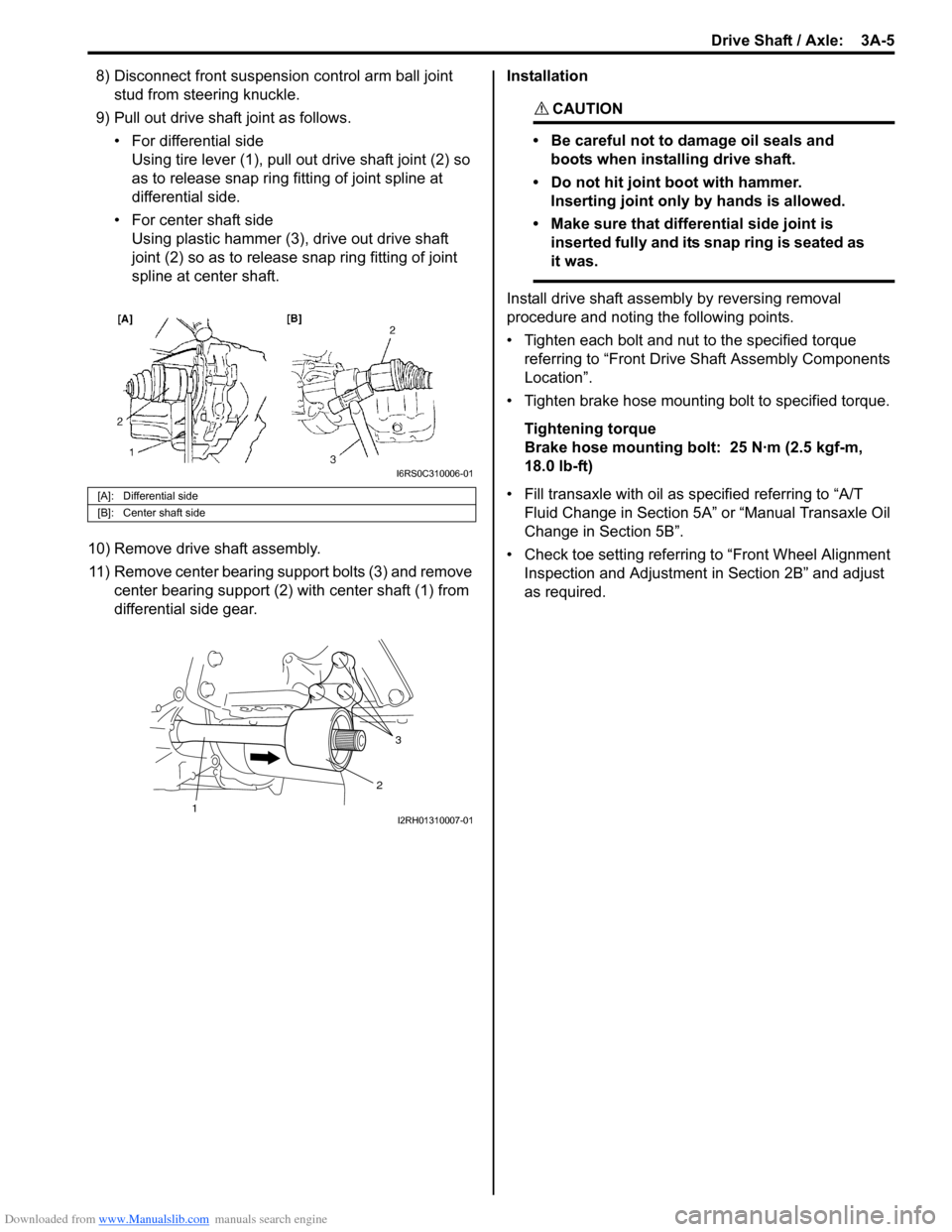
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Drive Shaft / Axle: 3A-5
8) Disconnect front suspension control arm ball joint
stud from steering knuckle.
9) Pull out drive shaft joint as follows. • For differential sideUsing tire lever (1), pull out drive shaft joint (2) so
as to release snap ring fitting of joint spline at
differential side.
• For center shaft side Using plastic hammer (3), drive out drive shaft
joint (2) so as to release snap ring fitting of joint
spline at center shaft.
10) Remove drive shaft assembly. 11) Remove center bearing support bolts (3) and remove center bearing support (2) with center shaft (1) from
differential side gear. Installation
CAUTION!
• Be careful not to damage oil seals and
boots when installing drive shaft.
• Do not hit joint boot with hammer. Inserting joint only by hands is allowed.
• Make sure that differential side joint is inserted fully and its snap ring is seated as
it was.
Install drive shaft assemb ly by reversing removal
procedure and noting the following points.
• Tighten each bolt and nut to the specified torque referring to “Front Drive Shaft Assembly Components
Location”.
• Tighten brake hose mounting bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Brake hose mounting bolt: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m,
18.0 lb-ft)
• Fill transaxle with oil as sp ecified referring to “A/T
Fluid Change in Section 5A” or “Manual Transaxle Oil
Change in Section 5B”.
• Check toe setting referring to “Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and Adjustment in Section 2B” and adjust
as required.
[A]: Differential side
[B]: Center shaft side
I6RS0C310006-01
3
2
1I2RH01310007-01
Page 646 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-2 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
CAUTION!
• Keep component parts in group for each subassembly and avoid mixing them up.
• Clean all parts with cleaning solvent thoroughly and air dry them.
• Use kerosene or automatic transaxle fluid as cleaning solvent.
• Do not use wiping cloths or rags to clean or dry parts.
• All oil passages should be blown out and checked to make sure that they are not
obstructed.
• Keep face and eyes away from solvent spray while air blowing parts.
• Check mating surface for irregularities and remove them, if any, and clean it again.
• Soak new clutch discs and brake discs in transaxle fluid for at least 2 hours before
assembly.
• Replace all gaskets and O-ring with new ones.
• Apply automatic transaxle fluid to all O- rings.
• When installing seal ring, be careful so that it is not expanded excessively, extruded or
caught.
• Replace oil seals that are removed and apply grease to their lips.
• Before installing, be sure to apply automatic transaxle fluid to sliding, rolling
and thrusting surface of all component
part. Also after installation, make sure to
check each part for proper operation.
• Always use torque wrench when tightening bolts.
• A new discs should be soaked in ATF at least 2 hours before use.
Part Inspection and Correction Table Part Inspect for Correction
Casted part,
machined part Small flaw, burr
Remove with oil
stone.
Deep or grooved
flaw Replace part.
Clogged fluid
passage Clean with air or
wire.
Flaw on installing
surface, residual
gasket Remove with oil
stone or replace
part.
Crack Replace part.
Bearing Unsmooth rotation Replace.
Streak, pitting, flaw,
crack
Replace.
Bushing, thrust
washer Flaw, burr, wear,
burning
Replace.
Oil seal, gasket Flawed or
hardened seal ring
Replace.
Worn seal ring on
its periphery or side Replace.
Piston seal ring, oil
seal, gasket, etc. Replace.
Gear Flaw, burr Replace.
Worn gear tooth Replace.
Splined part Burr, flaw, torsion Correct with oil
stone or replace.
Snap ring Wear, flaw,
distortion
Replace.
No interference Replace.
Thread Burr Replace.
Damage Replace.
Sp rin g Settling, sign of
burning Replace.
Friction plate Wear, burning,
distortion,
damaged claw Replace.
Separator plate,
retaining plate Wear, burning,
distortion,
damaged claw
Replace.
Sealing surface
(where lip
contacts) Flaw, rough
surface, stepped
wear, foreign
material
Replace.
Page 647 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-3
General Description
A/T DescriptionS7RS0B5101001
This automatic transaxle is electronic control full automatic transaxle with forward 4-speed and reverse 1-speed.
The torque converter is a 3-element, 1-step and 2-phase type and is equipped with an automatically controlled lock-up
mechanism.
The gear change device consists of a ravigneau type planet ary gear unit, 3 multiple disc type clutches, 3 multiple disc
type brakes and 2 one-way clutches.
The hydraulic pressure control device consists of a valve body assembly, pressure control solenoid valve (linear
solenoid), 2 shift solenoid va lves, TCC pressure control solenoid valve (lin ear solenoid) and a timing solenoid valve.
Optimum line pressure complying with engine torque is produced by the pressure control solenoid valve in
dependence upon control signal from transmission control module (TCM). This makes it possible to control the line
pressure with high accuracy in accordance with the engine power and running conditions to achieve smooth shifting
characteristics and high efficiency.
A clutch-to-clutch control system is prov ided for shifting between 3rd gear and 4th gear. This clutch-to-clutch control
system is made to function optimally , so that hydraulic pressure controls such as shown below are conducted.
• When upshifting from 3rd gear to 4th gear, to adjust the drain hydraulic pressure at releasing the forward clutch, a
timing solenoid valve is used to switch a hydraulic passage with an orifice to another during shifting.
• When downshifting from 4th gear to 3rd gear, to adjust the line pressure applied to the forward clutch at engaging the forward clutch, a timing solenoid valve is used to s witch a hydraulic passage with an orifice to another during
shifting.
• When upshifting from 3rd gear to 4th gear with engine throttle opened, to optimize the line pressure applied to the forward clutch at releasing the forward clutch, the learning control is processed to compensate the switching timing
of the timing solenoid at every shifting.
• When downshifting from 4th gear to 3rd gear with engine throttle opened, to optimize the line pressure applied to
the forward clutch at engaging the forw ard clutch, the learning control is processed to compensate the line pressure
at every shifting.
Employing the ravigneau type planetary gear unit and this clutch-to-clutch control system greatly simplifies the
construction to make possible a lightweight and compact transaxle.
A line pressure learning control is conducted to provide opti mum shifting time at every upshifting with engine throttle
opened. If long upshifting time is detected, the subsequent line pressure applied during upshifting is intensified. On the
contrary, if short upshifting time is detected, the subs equent line pressure applied during upshifting is weakened.
Slip controlled lock-up function
Even at a lower speed than when the TCC gets engaged completely, control over the TCC pressure control solenoid
works to cause the TCC to slip (be engaged slightly), ther eby improving the transmission efficiency. While such slip
control is being executed, the oil pressure applied to the TCC is controlled by the TCC pressure control solenoid so
that the difference between the engine speed and the input shaft speed becomes close to the specified value.
Also, during deceleration, the TCC is made to slip (be enga ged slightly) to raise the engine speed and enlarge the fuel
cut operation range so that better fuel consumption is achieved.
Due to this reason, it is absolutely necessary for the automati c transmission to use ATF suitable for slip control. Use of
any fluid other than the specified ATF may cause j uddering or some other faulty condition to occur.
Page 648 of 1496
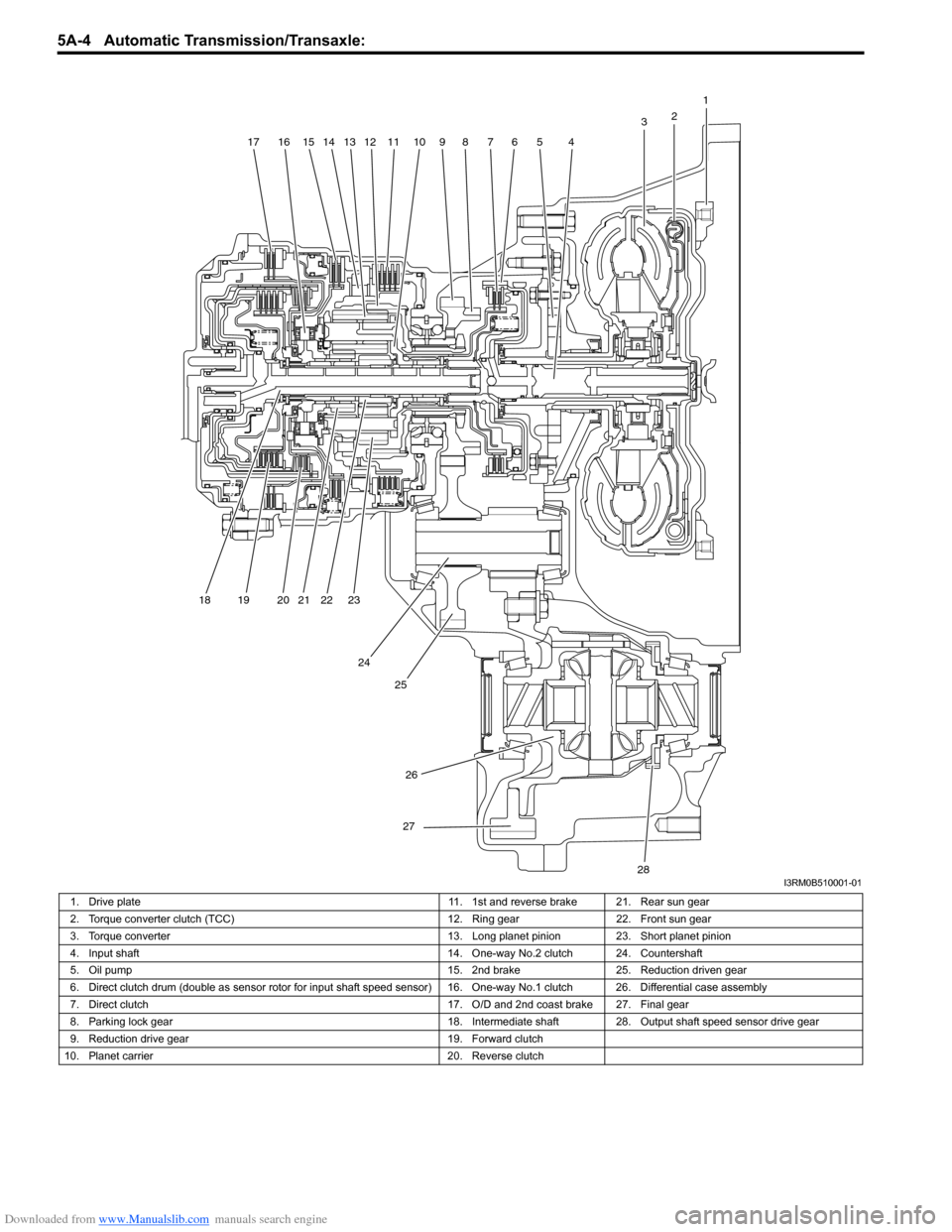
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-4 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
1
2
3
4567891011121314151617
18 19 20 21 22 23
24 25
26
27
28I3RM0B510001-01
1. Drive plate 11. 1st and reverse brake 21. Rear sun gear
2. Torque converter clutch (TCC) 12. Ring gear22. Front sun gear
3. Torque converter 13. Long planet pinion23. Short planet pinion
4. Input shaft 14. One-way No.2 clutch 24. Countershaft
5. Oil pump 15. 2nd brake25. Reduction driven gear
6. Direct clutch drum (double as sensor ro tor for input shaft speed sensor) 16. One-way No.1 clutch 26. Differential case assembly
7. Direct clutch 17. O/D and 2nd coast brake 27. Final gear
8. Parking lock gear 18. Intermediate shaft28.Output shaft speed sensor drive gear
9. Reduction drive gear 19. Forward clutch
10. Planet carrier 20. Reverse clutch