2007 SUZUKI SWIFT Dtc
[x] Cancel search: DtcPage 53 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
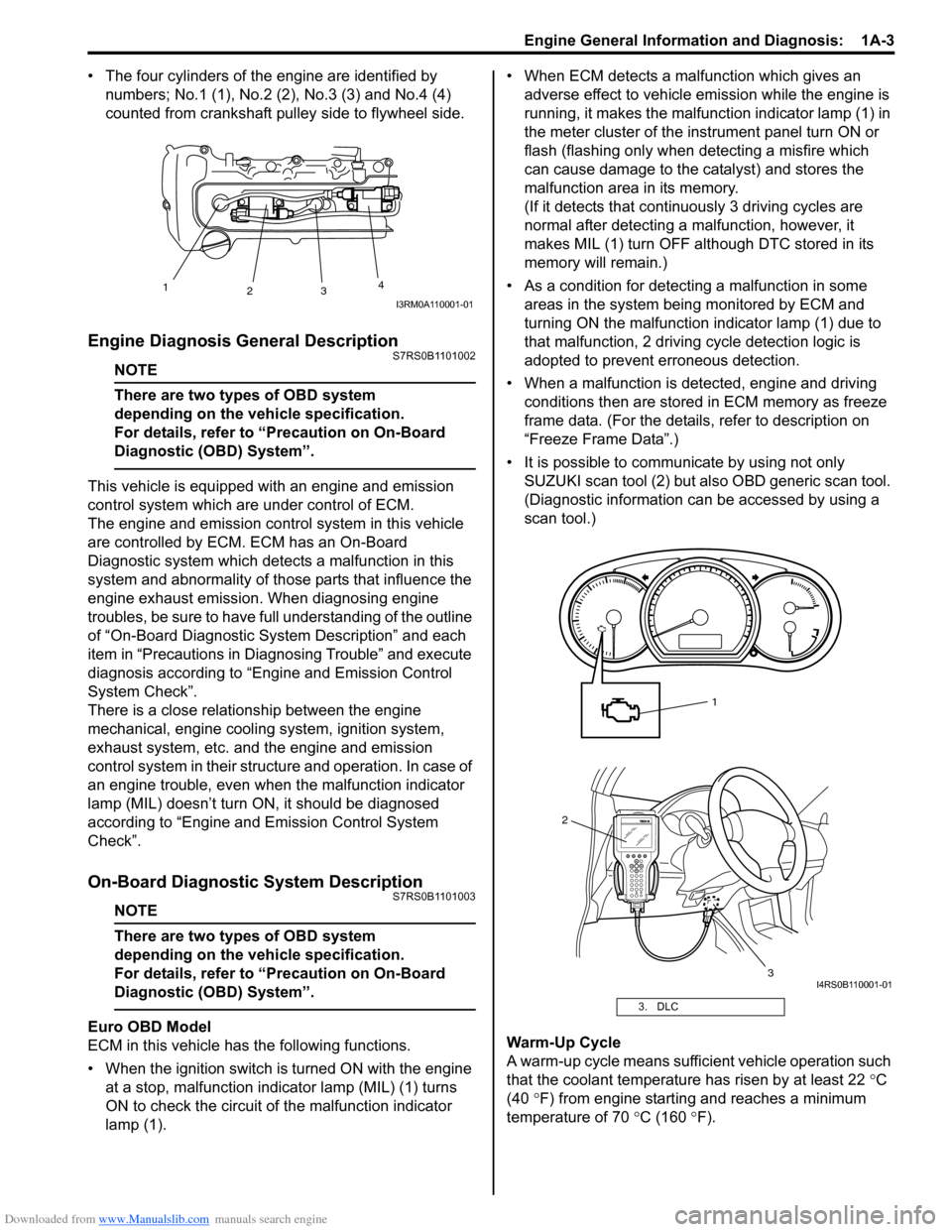
• The four cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2 ), No.3 (3) and No.4 (4)
counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Engine Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B1101002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission
control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle
are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board
Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this
system and abnormality of those parts that influence the
engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine
troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “Engine and Emission Control
System Check”.
There is a close relationship between the engine
mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system,
exhaust system, etc. and the engine and emission
control system in their structure and operation. In case of
an engine trouble, even when the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed
according to “Engine and Emission Control System
Check”.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B1101003
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Euro OBD Model
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1). • When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the inst rument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that contin uously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficie nt vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 ° F).
1
23 4
I3RM0A110001-01
3. DLC
2
3
1
I4RS0B110001-01
Page 54 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-4 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Driving Cycle
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup and engine
shutoff.
2 Driving Cycle Detection Logic
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is
stored in ECM memory (in t he form of pending DTC) but
the malfunction indicator lamp does not light at this time.
It lights up at the second detection of same malfunction
also in the next driving cycle.
Pending DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored
temporarily at 1 driving cycle of the DTC which is
detected in the 2 driving cycle detection logic.
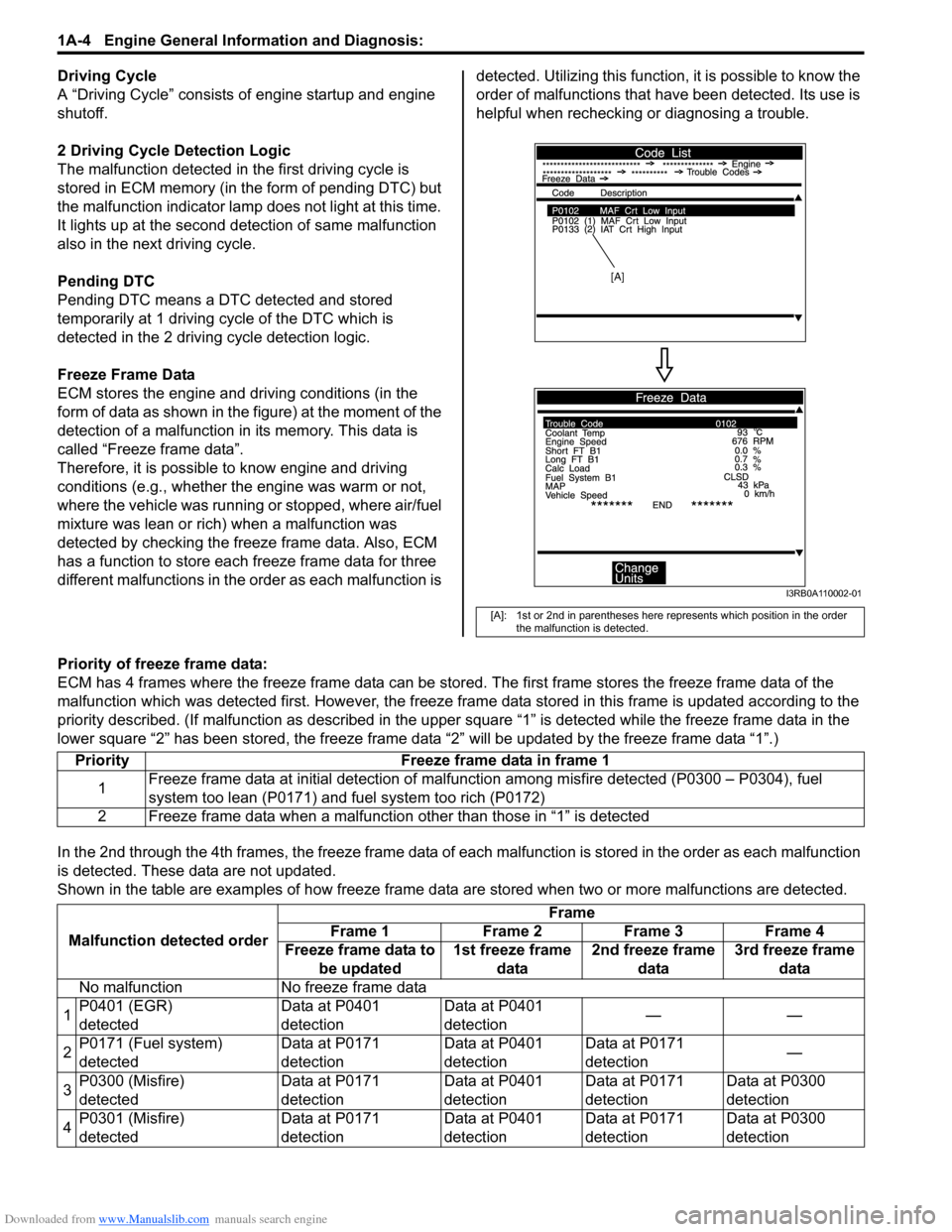
Freeze Frame Data
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the
form of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the
detection of a malfunction in its memory. This data is
called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving
conditions (e.g., whether the engine was warm or not,
where the vehicle was running or stopped, where air/fuel
mixture was lean or rich) when a malfunction was
detected by checking the freeze frame data. Also, ECM
has a function to store each freeze frame data for three
different malfunctions in the order as each malfunction is detected. Utilizing this function,
it is possible to know the
order of malfunctions that ha ve been detected. Its use is
helpful when rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
Priority of freeze frame data:
ECM has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stor ed. The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the
malfunction which was detected first. Howe ver, the freeze frame data stored in this frame is updated according to the
priority described. (If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” is detected while the freeze frame data in the
lower square “2” has been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by the freeze frame data “1”.)
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each malfunction is stored in the order as each malfunction
is detected. These data are not updated.
Shown in the table are examples of how freeze frame data are stored when two or more malfunctions are detected.
[A]: 1st or 2nd in parentheses here represents which position in the order
the malfunction is detected.
[A]
I3RB0A110002-01
Priority Freeze frame data in frame 1
1 Freeze frame data at initial detection of malfuncti
on among misfire detected (P0300 – P0304), fuel
system too lean (P0171) and fuel system too rich (P0172)
2 Freeze frame data when a malfunctio n other than those in “1” is detected
Malfunction detected order Frame
Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4
Freeze frame data to be updated 1st freeze frame
data 2nd freeze frame
data 3rd freeze frame
data
No malfunction No freeze frame data
1 P0401 (EGR)
detected Data at P0401
detectionData at P0401
detection
——
2 P0171 (Fuel system)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detection
—
3 P0300 (Misfire)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
4 P0301 (Misfire)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 56 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-6 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
For information about the following items, refer to “Euro
OBD Model: ”.
• Warm-up cycle
• Driving cycle
• 2 driving cycle detection logic
• Pending DTC
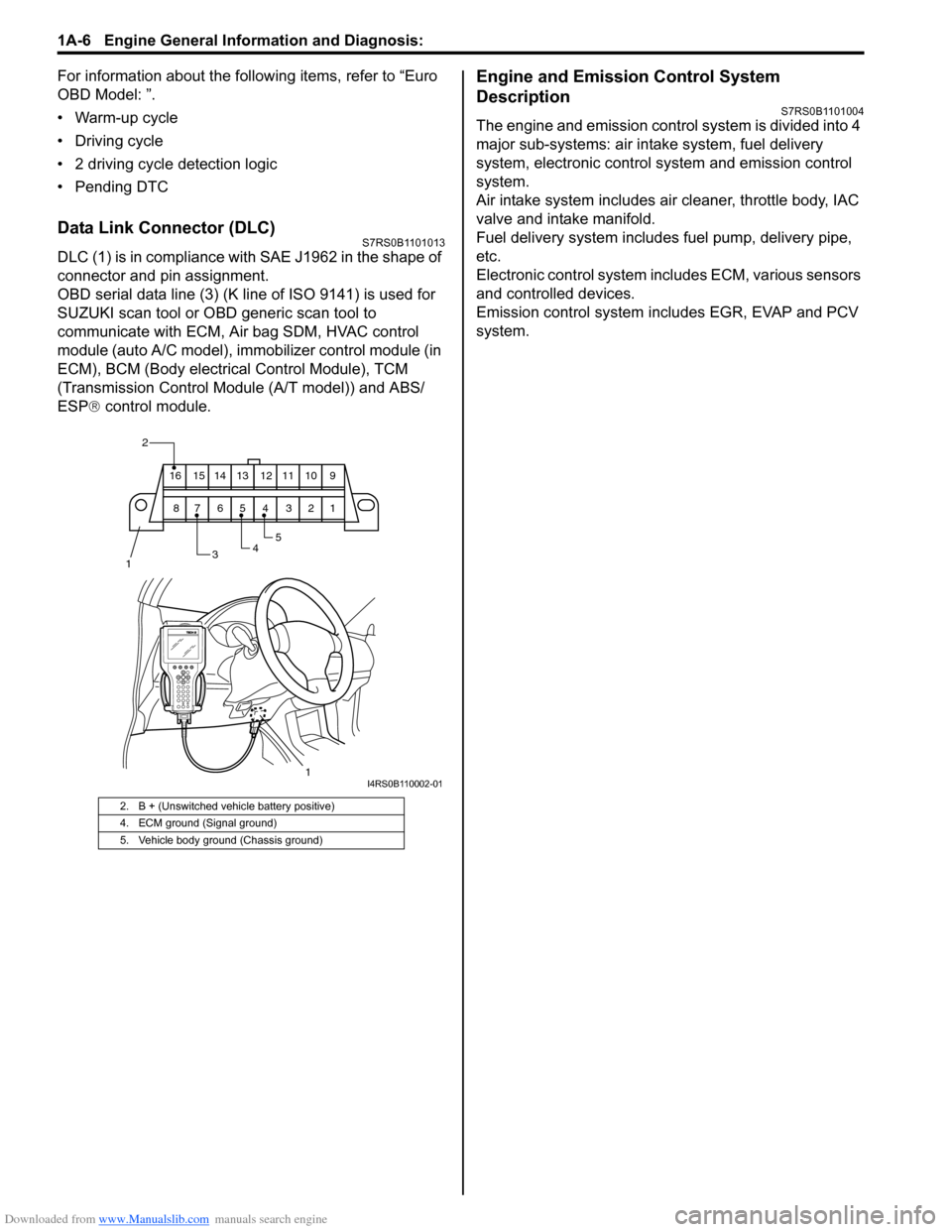
Data Link Connector (DLC)S7RS0B1101013
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAE J1962 in the shape of
connector and pin assignment.
OBD serial data line (3) (K line of ISO 9141) is used for
SUZUKI scan tool or OBD generic scan tool to
communicate with ECM, Air bag SDM, HVAC control
module (auto A/C model), immobilizer control module (in
ECM), BCM (Body electrical Control Module), TCM
(Transmission Cont rol Module (A/T model)) and ABS/
ESP ® control module.
Engine and Emission Control System
Description
S7RS0B1101004
The engine and emission control system is divided into 4
major sub-systems: air in take system, fuel delivery
system, electronic control sy stem and emission control
system.
Air intake system includes air cleaner, throttle body, IAC
valve and intake manifold.
Fuel delivery system includes fuel pump, delivery pipe,
etc.
Electronic control system incl udes ECM, various sensors
and controlled devices.
Emission control system includes EGR, EVAP and PCV
system.
2. B + (Unswitched vehicle battery positive)
4. ECM ground (Signal ground)
5. Vehicle body ground (Chassis ground)
2
345
1
910111213141516
12345678
1I4RS0B110002-01
Page 58 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
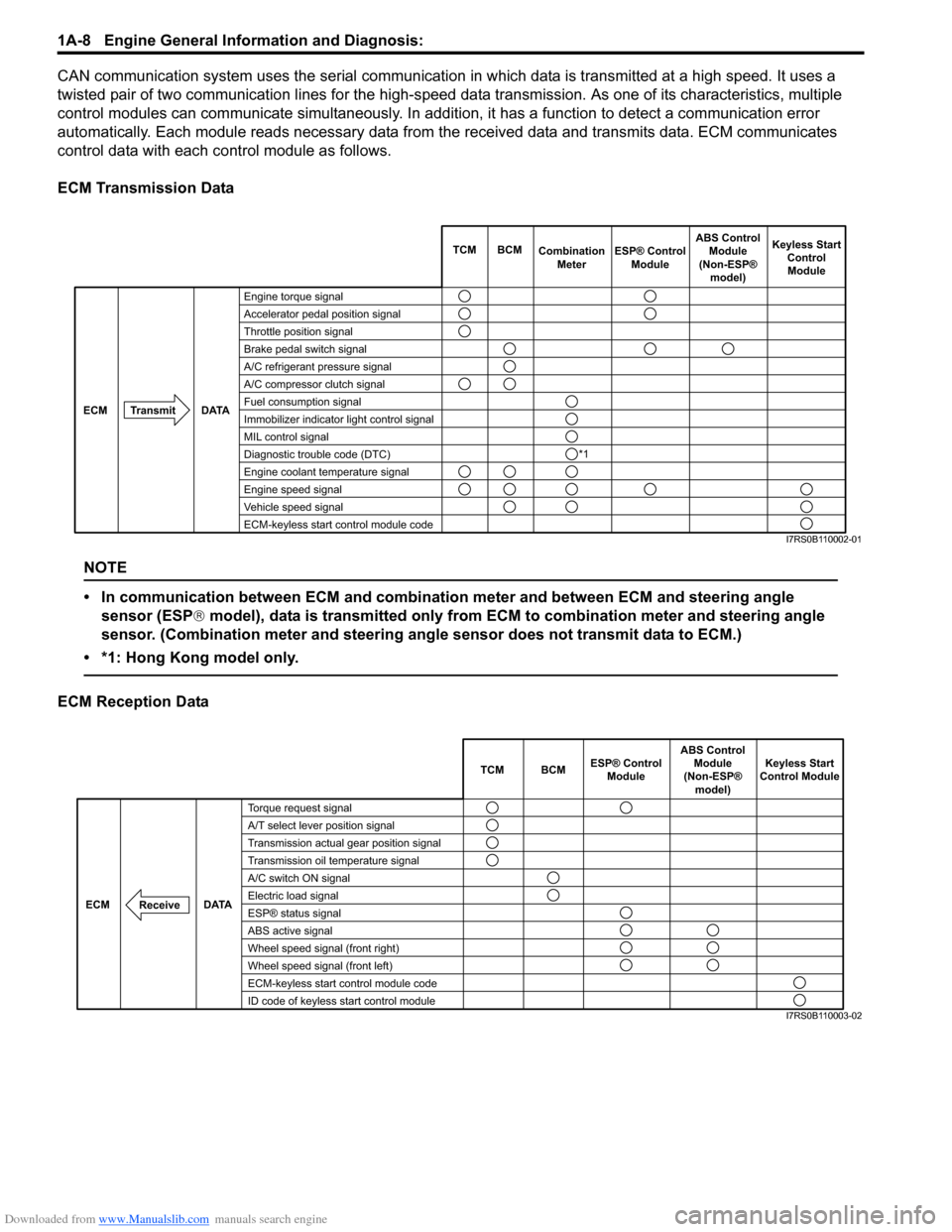
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed da ta transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
ECM Transmission Data
NOTE
• In communication between ECM and combination meter and between ECM and steering angle sensor (ESP ® model), data is transmitted only from ECM to combination meter and steering angle
sensor. (Combination meter and steering angle sensor does not transmit data to ECM.)
• *1: Hong Kong model only.
ECM Reception Data
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position signal
Throttle position signal
Brake pedal switch signal
A/C refrigerant pressure signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Fuel consumption signal
Immobilizer indicator light control signal
MIL control signal
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Engine coolant temperature signal
Engine speed signal
Vehicle speed signal
ECM-keyless start control module code TCM BCM
Combination
Meter Keyless Start
ControlModule
Transmit DATA
ECM
ESP® Control
Module ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
*1
I7RS0B110002-01
TCM BCM Keyless Start
Control Module
DATA
ECM
Torque request signal
A/T select lever position signal
Transmission actual gear position signal
Transmission oil temperature signal
A/C switch ON signal
Electric load signal
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ECM-keyless start control module code
ID code of keyless start control module
Receive
ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
ESP® Control
Module
I7RS0B110003-02
Page 63 of 1496
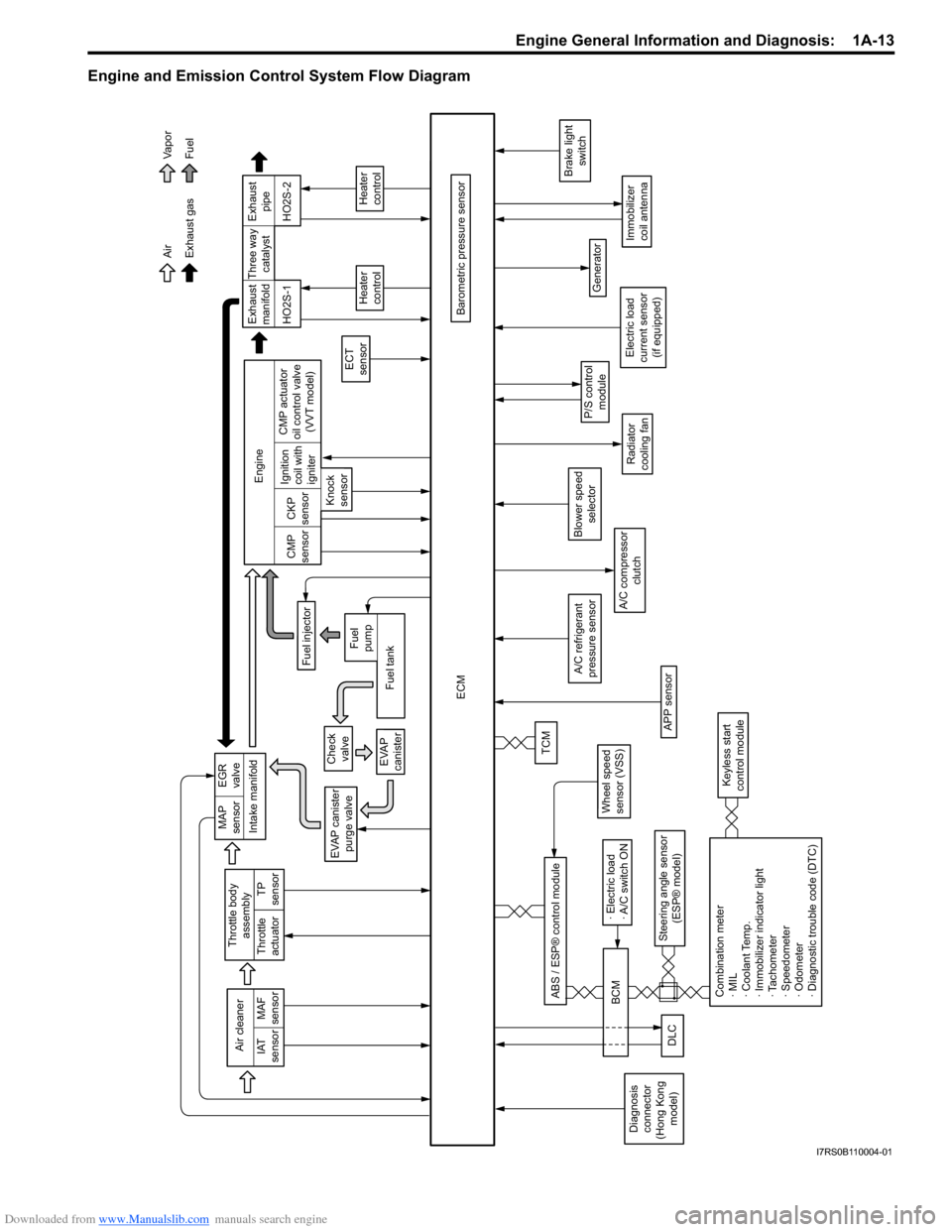
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-13
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
Intake manifold
Exhaust gas AirFuel
Va p o r
EVAP canister purge valve
ECM
Barometric pressure sensor
A/C compressor clutch
Generator
Immobilizer
coil antenna
P/S controlmodule
Brake light switch
Air cleaner
IAT
sensor MAF
sensor
A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor
TP
sensor
Throttle body
assembly
Throttle
actuator
Wheel speed
sensor (VSS)
Steering angle sensor (ESP® model)
ABS / ESP® control module
Blower speed
selector
MAP
sensor EGR
valve
Check valve
EVAP
canisterTCM
Exhaust
manifold Exhaust
pipe
Fuel injector
ECT
sensor
Heater
control
HO2S-1 HO2S-2
Engine
CMP
sensor CKP
sensor
Knock
sensor Ignition
coil with
igniter
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump CMP actuator
oil control valve (VVT model) Three way
catalyst
Heater
control
Radiator
cooling fan
Combination meter
· MIL
· Coolant Temp.
· Immobilizer indicator light
· Tachometer
· Speedometer
· Odometer
· Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Keyless start
control module
DLC
· Electric load
· A/C switch ON
BCM
Diagnosis
connector
(Hong Kong model) Electric load
current sensor (if equipped)
APP sensor
I7RS0B110004-01
Page 72 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-22 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Engine and Emission Control System CheckS7RS0B1104001
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.Step Action Yes No 1 �) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis referring to “Customer Complaint Analysis”.
Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to Step 2. Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2 �) DTC / Freeze frame data check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC) referring to “DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Print DTC and freeze
frame data or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance”, and go to
St ep 3 .Go to Step 4.
3 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 5.
4 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 8.
5 �) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to “Trouble Symptom Confirmation”.
Is trouble symptom identified? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 7.
6 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 8.
7 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 10.
8 �) Engine basic inspection and engine symptom
diagnosis
1) Check and repair according to “Engine Basic Inspection”
and “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
9 �) Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC diag. flow.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
10 �) Intermittent problems check
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to “Intermittent Problems Check”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
Go to Step 11.
Page 73 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-23
11�) Final confirmation test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test referring to “Final Confirmation Test”.
Is there any problem symptom, DTC or abnormal condition? Go to Step 6. End.
Step Action Yes No