2007 SKODA FABIA warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 139 of 242

Transporting children safely138
Child seats of group 0/0+
The optimal solution for babies of up to about 9 months old weighing up to 10 kg or babies up to about 18 months old weighi ng up to 13 kg is a child safety seat which is fastened in the opposite direction of travel ⇒fig. 127.
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of travel should not be used on the front pa ssenger seat when the vehicle is fitted with a front passenger airbag ⇒page 135, “Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat”.
WARNING
•It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag (airbags) at a specialist garage or with the switch for front passenger airbag(s)* when attaching in exceptional circumstances a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel) ⇒ page 132.
•In certain countries national legal provisions require that besides the front passenger airbag also the side or head passenger airbags are deacti- vated. Please comply with any differin g national legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
•If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat may suffer severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag or airbags are deployed.
•You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just as soon as you no longer use a child sa fety seat on the front passenger seat.
Child safety seats in Group 1
Child seats in Group 1 are for babies and small children up to 4 years of age with a weight of between 9 and 18 kilograms. It is best for children in the lower range of this group, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit with its back to the direc- tion of travel. It is best for children in the upper range of the Group 0+, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit ⇒fig. 128 in the direction of travel.
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of travel should not be used on the front pa ssenger seat when the vehicle is fitted with a front passenger airbag ⇒page 135, “Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat”.
Fig. 127 Child seats of group 0/0+
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 128 Child seat with padded table in Group 1 installed on rear seat bench facing the direc-tion of travel
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 138 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 140 of 242

Transporting children safely139
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
WARNING
•It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag (airbags) at a specialist garage or with the switch for front passenger airbag(s)* when attaching in exceptional circumstances a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel) ⇒ page 132.
•In certain countries national legal provisions require that besides the front passenger airbag also the side or head passenger airbags are deacti- vated. Please comply with any differin g national legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
•If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat may suffer severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag or airbags are deployed.
•You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just as soon as you no longer use a child sa fety seat on the front passenger seat.
Child safety seats in Group 2
For children up to about 7 years of age weighing between 15 and 25 kg the optimal solution is a child safety seat in comb ination with the three-point seat belt ⇒ fig. 129.
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulati ons regarding the use of child safety seats. Switch off the front passenger airb ag if necessary at a specialist garage or switch it off with the switch for front passenger airbag* ⇒page 132.
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately across the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly agai nst the chest. It must on no account run across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
•Please comply with any differing nati onal legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
Child safety seats in Group 3
For children of about 7 years of age weighing between 22 and 36 kg and of a height of less than 150 cm, the optimal solution is a child safety seat (seat bolster) in combination with the three-point seat belt ⇒fig. 130.
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the vehicle without a seat bolster.
Fig. 129 Child seat in Group 2 installed on the rear seat facing the direc-tion of travel
Fig. 130 Child seat in Group 3 installed on the rear seat facing the direc- tion of travel
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 139 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 141 of 242

Transporting children safely140
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats. Switch off the front passenger airb ag if necessary at a specialist garage or switch it off with the switch for front passenger airbag* ⇒page 132.
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately across the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly agai nst the chest. It must on no account run across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over th e belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
•Please comply with any differing nati onal legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
Attaching a child seat using the “ISOFIX” system*
There are two fixing eyes between the backrest and the seat itself on both
of the outer rear seats for fixing the “ISOFIX” system child seat in place.
– Insert the mounting funnels onto the locking eyes between the
backrest and seat cushion ⇒fig. 131.
– Push the notched arms of the chil d seat over the mounting funnels
into the locking eyes, until it is heard to lock ⇒fig. 132.
– Pull on both sides of the child seat!
One can mount a child safety seat using the “ISOFIX” system quickly, easily and reli- ably. Please pay close attention to instru ctions from the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.
Child seats fitted with the “ISOFIX” clamping system can only be mounted and fixed in a vehicle fitted with an “ISOFIX sy stem” when these child seats have been released for your type of vehicle according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
You can purchase child seats with the “I SOFIX” attachment system from Škoda Service Partners who will install it as well.
Complete installation instructions are enclosed with the child safety seat.
B5J-1024HFig. 131 Locking eyes (ISOFIX system)
Fig. 132 The ISOFIX child seat is pushed into the mounting funnels
AAAB
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 140 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 142 of 242
Transporting children safely141
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
WARNING
•The locking eyes have just been developed for child safety seats which use the “ISOFIX” system. You should therefore never attach other child safety seats, seat belts or objects to the locking eyes - hazard!
•Ask a Škoda Service Partner whether a child seat which you bought for another vehicle is recommended for use in a Škoda before using an “ISOFIX” system.
•Certain child seats which use the “ISO FIX” system can be attached with standard three-point seat belts. Please pay close attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.
Note
•Child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system are currently available for children weighing up to about 18 kg. This corres ponds to an age range up to 4 years.
•The child seats can also be fitted with the “Top Tether” system ⇒page 141.
Attaching child seat using the “Top Tether” system
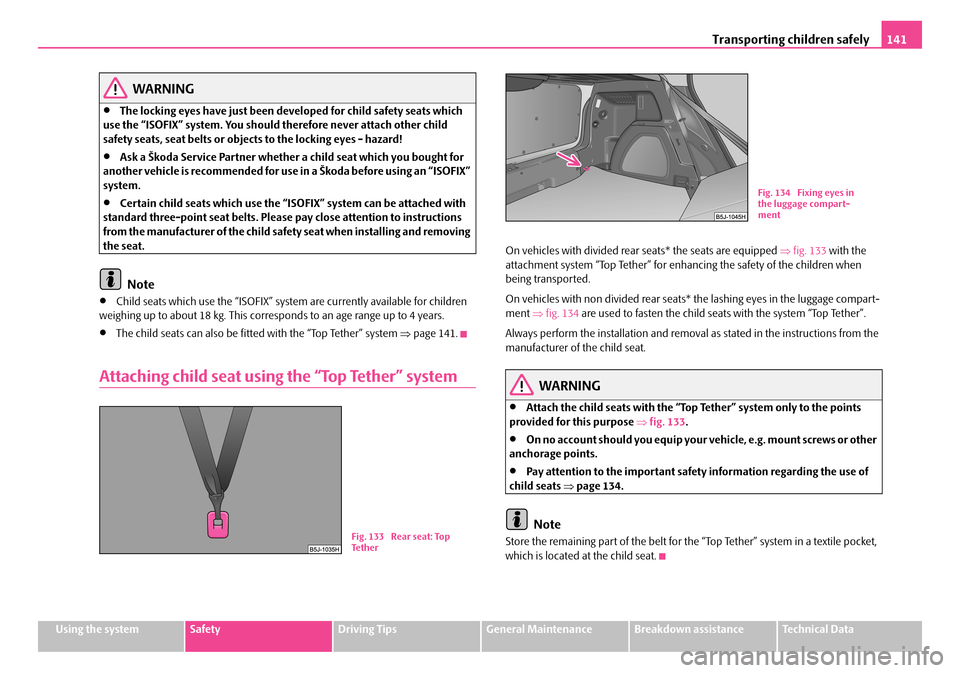
On vehicles with divided rear seats* the seats are equipped ⇒fig. 133 with the attachment system “Top Tether” for enhancing the safety of the children when being transported.
On vehicles with non divide d rear seats* the lashing eyes in the luggage compart- ment ⇒fig. 134 are used to fasten the child seats with the system “Top Tether”.
Always perform the installation and removal as stated in the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat.
WARNING
•Attach the child seats with the “Top Tether” system only to the points provided for this purpose ⇒fig. 133.
•On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other anchorage points.
•Pay attention to the important safety information regarding the use of child seats ⇒page 134.
Note
Store the remaining part of the belt for the “Top Tether” system in a textile pocket, which is located at the child seat.
Fig. 133 Rear seat: Top Te t h e r
Fig. 134 Fixing eyes in the luggage compart-ment
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 141 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 144 of 242

Intelligent Technology143
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology
Electronic stability programme (ESP)*
General
General
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in borderline driving situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk of skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on the conditions of the road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
•electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•traction control system (TCS),
•antilock brake system (ABS),
•brake Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehi cle about its vertical axis, the lateral accel- eration of the vehicle, the brakin g pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to ta ke is determined based on the steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exis t, such as the car beginning to skid, the ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break away) while occurs this is on the inner re ar wheel of a vehicle which tends to under- steer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 147, “Antilock brake system (ABS)*”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light ⇒page 27 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the button ⇒ fig. 135. The ESP warning light ⇒page 27 lights up in the instrument cluster when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the system.
Examples:
Fig. 135 ESP switch
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 143 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 145 of 242

Intelligent Technology144
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
Then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your style of driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation. This particularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than other- wise - risk of an accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign- ment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒page 192, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spinning
when accelerating.
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when th e engine is started and then conducts a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sensors. If the wheels ar e spinning, the force transmitted to the road surface is automatically adapted by reducing the engi ne speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 147, “Antilock brake system (ABS)*”. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS system.
The TCS warning light ⇒page 26 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the TCS.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the button ⇒ fig. 136. The TCS warning light ⇒page 26 lights up in the instrument cluster when the TCS is switched off.
Fig. 136 TCS switch
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 144 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 146 of 242

Intelligent Technology145
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the system.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
Then you should switch on the TCS again.
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem- free operation of the TCS. Differing rollin g circumferences of the tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign- ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the TCS ⇒page 192, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock pr events an individual wheel from
slipping.
Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditio ns of the road surface are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part of the driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sensors. Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function brakes the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to the other driven wheel. This control proce ss is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unus ually severe stresses exist in order to avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
WARNING
•Depress the accelerator carefully when accelerating on uniformly slip- pery road surfaces, such as ice and sn ow. The driven wheels might still spin despite the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
•You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road surface and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL. The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•If the ABS or TCS or ESP warning light comes on, this may also indicate a fault in the EDL. Please have the car inspected as soon as possible by a specialist garage.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign- ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the EDL ⇒page 192, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 145 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM
Page 147 of 242

Intelligent Technology146
Brakes
What has a negative effect on braking efficiency?
Wear-and-tear
Wear-and-tear to the brake pads is greatly dependent on the operating conditions of the vehicle and your style of driving. Particularly if you drive a great deal in towns and over short distances or if you adopt a sporty style of driving, it may be neces- sary to have the thickness of the brake pads inspected at a specialist garage between the service inspections.
Wet roads or road salt
There may be a certain delay before the brakes take full effect under certain condi- tions such as when driving through water, during heavy rain showers or after the vehicle has been washed in an automatic vehicle wash, since the brake discs and brake pads may be moist or even have a coating of ice on them in winter. You should dry the brakes as soon as possib le (by applying and releasing the brakes several times, if the road conditions and the traffic situation allows it).
There also may be a certain delay before the full braking efficiency is available when driving on roads which have been treated wi th road salt if you have not used the brakes for some considerable time beforeha nd. The layer of salt on the brake discs and brake pads must first be rubb ed off when you apply the brakes.
Corrosion
Corrosion on the brake discs and dirt on th e bake pads occur if the vehicle has been parked for a long period and if you do not make much use of the braking system.
We recommend cleaning the brake discs by firmly applying the brakes at a fairly high speed if you do not make much use of the braking system or if surface corro- sion is present ⇒.
Faults in the brake surface
If you notice that the braking distance has suddenly become longer and that the brake pedal can be depressed further, it is possible that a brake circuit of the dual- circuit brake system has failed. Drive, in such cases, to the nearest specialist garage without delay in order to have the problem rectified. Drive at a reduced speed while on your way to the dealer and adapt your style of driving to the higher brake pedal pressure required.
Low brake fluid level
An insufficient level of brake fluid may result in problems in the brake system. The level of the brake fluid is monitored electronically ⇒page 28, “Brake system ”.
WARNING
•Only apply the brakes for the purpose of drying and cleaning the brake discs if the traffic conditions permit this. Do not place any other road users in jeopardy.
•When retrospectively mounting a front spoiler, solid wheel hubs etc. one must ensure that the air supply to the front wheel brakes is not reduced otherwise the braking sy stem could run too hot.
•Allow for the fact that new brake pads do not achieve their full braking efficiency until approximately 200 kilo metres. New brake pads must be first “run in” before they develop their optimal friction force. You can, however, compensate for this slightly reduced braking force by increasing the pres- sure on the brake pedal. This guidelin e also applies to any new brake pads installed at a future date.
Caution
•Never allow the brakes to ru b by applying slight pressure if you do not wish to brake the vehicle. This causes the brakes to overheat and can also result in a longer braking distance and excessive wear.
•Before negotiating a steep downhill section, please reduce your speed and shift down into the next lower gear (manual ge arbox) or select a lower driving stage (automatic gearbox). This enables you to make full use of the braking power of the vehicle and reduces the strain on the brakes . Any additional braking should be done intermittently, not continuously.
Brake booster
The brake booster boosts the pressure which you generate with the brake pedal. The necessary pressure is only gene rated when the engine is running.
NKO A05F 20 MR08.book Page 146 Thursday, April 19, 2007 11:34 AM