2007 ISUZU KB P190 air conditioning
[x] Cancel search: air conditioningPage 3605 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-18
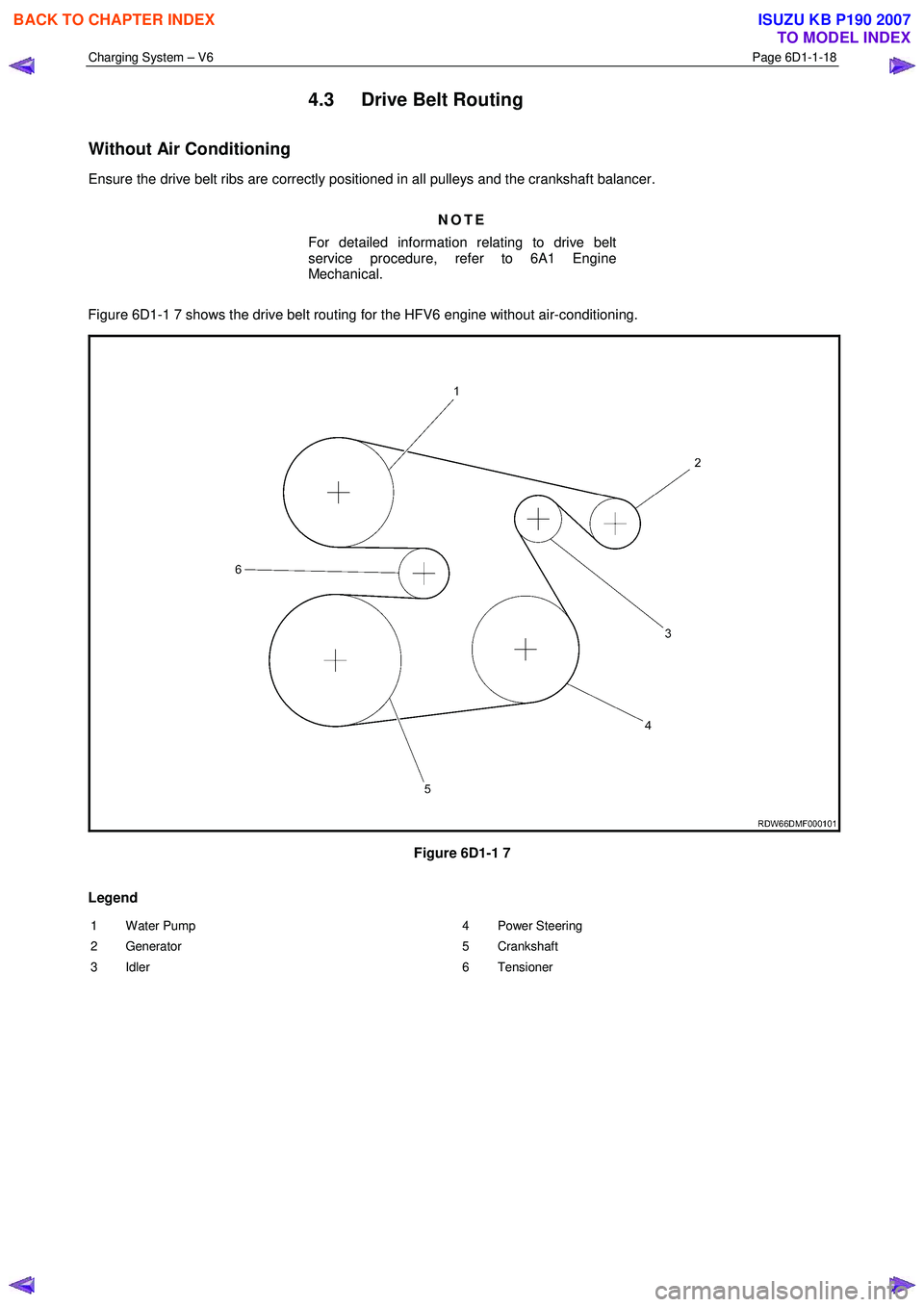
4.3 Drive Belt Routing
Without Air Conditioning
Ensure the drive belt ribs are correctly positioned in all pulleys and the crankshaft balancer.
NOTE
For detailed information relating to drive belt
service procedure, refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical.
Figure 6D1-1 7 shows the drive belt routing for the HFV6 engine without air-conditioning.
Figure 6D1-1 7
Legend
1 Water Pump
2 Generator
3 Idler 4 Power Steering
5 Crankshaft
6 Tensioner
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3774 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–14
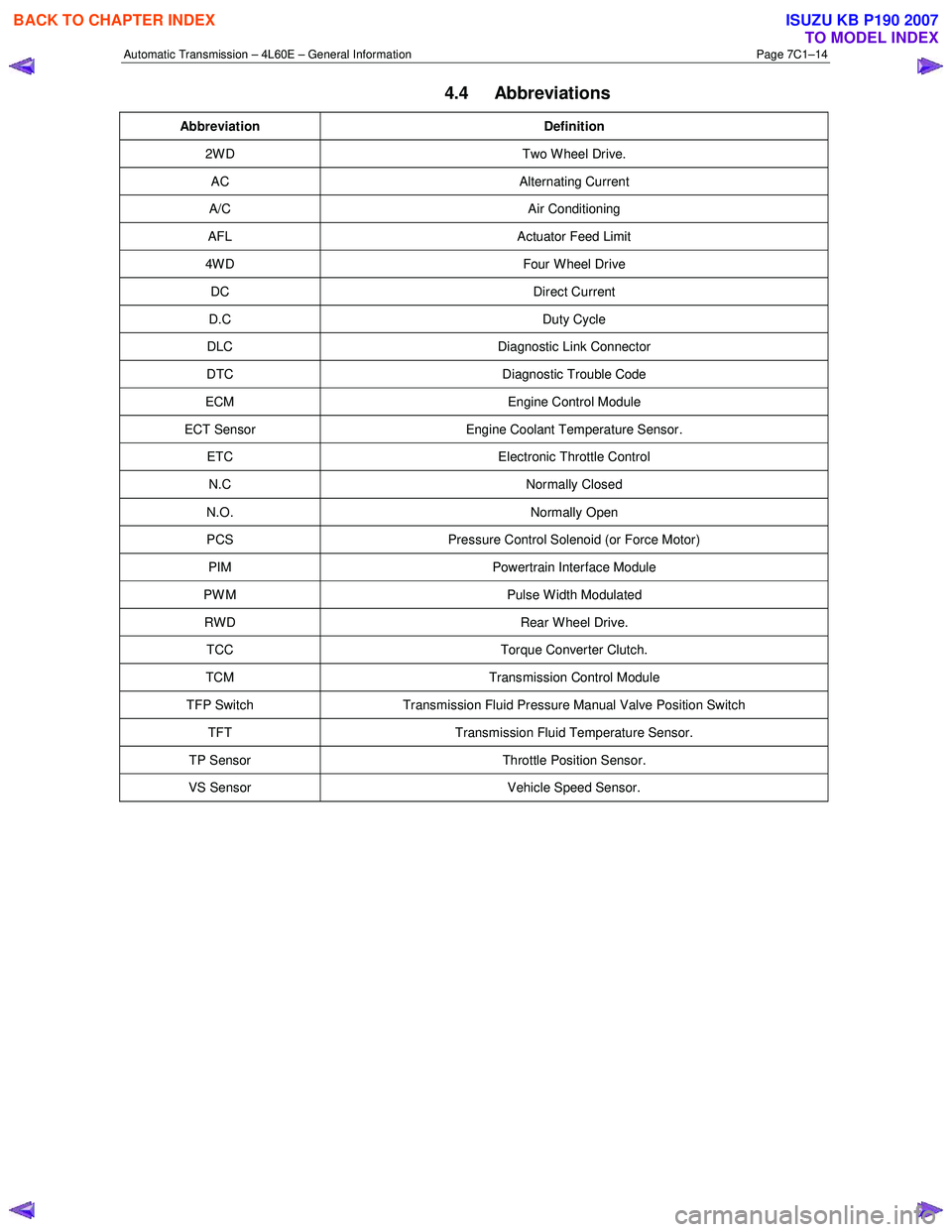
4.4 Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition
2W D Two W heel Drive.
AC Alternating Current
A/C Air Conditioning
AFL Actuator Feed Limit
4W D Four W heel Drive
DC Direct Current
D.C Duty Cycle
DLC Diagnostic Link Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code
ECM Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.
ETC Electronic Throttle Control
N.C Normally Closed
N.O. Normally Open
PCS Pressure Control Solenoid (or Force Motor)
PIM Powertrain Interface Module
PW M Pulse W idth Modulated
RWD Rear Wheel Drive.
TCC Torque Converter Clutch.
TCM Transmission Control Module
TFP Switch Transmission Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch
TFT Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor.
TP Sensor Throttle Position Sensor.
VS Sensor Vehicle Speed Sensor.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3797 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–11
Figure 7C2 – 2
The TCM is an electronic control module receiving input or providing output to control the operation of the 4L60E
automatic transmission.
The TCM receives the following inputs from the engine control module (ECM):
• engine speed and torque values,
• engine intake air temperature (IAT), accelerator pedal position (APP) information,
• engine coolant temperature (ECT),
• driver selected shift mode, and
• air-conditioning (A/C) status.
The ECM provides this data to the TCM through the databus.
Other TCM inputs are:
• battery and ignition voltage,
• brake switch status,
• transmission fluid temperature (TFT), and
vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
The TCM provides the following outputs to control the automatic transmission:
• shift solenoids to control transmission shifting,
• torque converter clutch (TCC) pulse width modulated (PW M) solenoid operation to control the apply and release of
the torque converter clutch assembly, and
• pressure control (PC) solenoid to regulate the transmission line pressure.
Other TCM outputs provided to the ECM / PIM are:
• MIL illumination request,
• vehicle speed,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3808 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–22
negative number indicates that short shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been subtracted to
increase shift time.
A/C Clutch: This parameter displays the condition of the sirconditioning compressor as either On or Off .
AT Output Speed: This parameter displays the rotational speed of the transmission output shaft. Tech 2 displays output
shaft speed as revolutions per minute (RPM).
Commanded Gear: This parameter displays the current commanded state of the shift solenoid valves. Tech 2 displays 1,
2 , 3 or 4.
Current TAP Cell: This parameter displays the current transmission adaptive pressure (TAP) cell in use for transmission
line pressure adaptation. The cells are based on 17 Nm of engine torque. The higher the engine torque, the higher the
current TAP cell. The last cell used will remain displayed until the next adaptable upshift occurs.
Engine Coolant Temperature: This parameter displays the input signal from the engine coolant temperate (ECT)
sensor. ECT is high at 151°C when the signal voltage is low, 0 V. ECT is low at -40°C when the signal voltage is high,
5 V.
Engine Speed: This parameter displays the rotational speed of the engine expressed as revolutions per minute.
Engine Torque: This parameter displays the calculated value based on engine load, throttle position, mass air flow, and
other engine inputs. This parameter is accurate to within 20 Nm of actual measured engine torque.
Estimated Gear Ratio: This parameter displays the estimated turbine speed divided by the transmission output speed.
Estimated turbine speed is calculated from engine speed and engine torque.
Ignition Voltage: This parameter displays the
system voltage measured at the ignition feed.
Latest Shift: This parameter displays the actual time of the last upshift. This value is only accurate if the shift was
adaptable.
PCS Actual Current: This parameter displays the current flow through the pressure control solenoid circuit, which is
measured by the control module. High current flow results in low line pressure. Low current flow results in high line
pressure.
PCS Duty Cycle: This parameter displays the commanded state of the pressure control solenoid, expressed as a
percentage of energised on time. A reading of low percent indicates zero on time, non-energised, or no current flow. A
high percent at idle indicates maximum on time, energised, or high current flow.
PCS Desired Current: This parameter displays the commanded current of the pressure control solenoid circuit. High
current results in low line pressure. Low current results in high line pressure.
Shift Pattern: This parameter displays Normal, Power or Cruise depending on what mode the transmission is in.
Shift Solenoid A: This parameter displays the commanded state of the 1-2 shift solenoid valve. W hen the transmission
is in 1
st and 4th gear, the display should indicate On; current is flowing through the solenoid. When the transmission is in
2nd and 3rd gear, the display should indicate Off; current is not flowing through the solenoid.
Shift Solenoid A Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the 1-2 shift solenoid valve feedback signal. The 1-2 shift solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
Shift Solenoid B: This parameter displays the commanded state of the 2-3 shift solenoid valve. W hen the transmission
is in 1
st and 4th gear, the display should indicate On; current is flowing through the solenoid. When the transmission is in
2nd and 3rd gear, the display should indicate Off; current is not flowing through the solenoid.
Shift Solenoid B Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the 2-3 shift solenoid valve feedback signal. The 2-3 shift solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
Speed Ratio: This parameter displays the calculated speed ratio of the transmission.
TCC Duty Cycle Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the TCC PW M solenoid valve feedback signal. The TCC PW M solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
TCC Solenoid: This parameter displays the commanded sate of the TCC solenoid. On indicates a commanded
energised state; current is flowing through the solenoid. Off indicates a commanded non-energised state; current is not
flowing through the solenoid. This commanded state occurs at various vehicle speeds between applications.
TCC Slip Speed: This parameter displays the difference between transmission output speed and engine speed. A
negative value indicates the engine speed is less than the output speed, deceleration. A positive value indicates the
engine speed is greater than the output speed, acceleration. A value of zero indicates the engine speed is equal to the
output speed, TCC applied.
TCC PWM Solenoid: This parameter displays the commanded percentage of on time for the TCC PWM solenoid. A high
percentage represents an on, energised, commanded state.0 percent represents an off, non-energised, commanded
state.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4424 of 6020

7A2-140 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
• Electrically Erasable Programmable Read OnlyMemory (EEPROM)
This type of memory allows selected portions of
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM,
such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/ calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory
Flash memory has increased memory storage capacity.
During programming, all information within this type of
memory is erased, and then replaced with entirely new
information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming a TCM are listed
below:
• Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming a TCM using one of
the methods listed above, refer to Service
Programming System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru
Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important: DO NOT program an existing TCM with the
identical software/ calibration package. This procedure
is not a short cut to correct the driveability condition.
This is an ineffective repair. An TCM should only be
programmed when the following occurs:
• When a service procedure instructs you to replace the TCM.
• An updated software/ calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming a TCM:
• The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
• The hardware key is plugged into the computer port.
• Vehicle system voltage:
- There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the TCM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the TCM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or TCM damage. - Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a
load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure:
- The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
TCM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the TCM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the TCM.
Performing the Remote Procedure 1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the TCM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the TCM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4940 of 6020

8A-2 ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS
PAGE
Fuse Block Circuit (4JJ1-TC/4JK1-TC (RHD)) SOUTH AFRICA ...............................8A- 39
Fuse Block Circuit (4JJ1-TC/4JK1-TC (RHD)) EXCEPT SOUTH AFRICA ...............8A- 41
Fuse Block Circuit (4JJ1-TC/4JK1-TC) - (LHD) G.EXP .............................................8A- 43
Fuse Block Circuit (4JH1-TC) - (LHD) ........................................................................8A- 45
Fuse Block Circuit (4JA1T (L)) ...................................................................................8A- 47
Grounding Point ..............................................................................................................8 A- 49
Ground Point ...............................................................................................................8A- 49
Ground Point Location ...............................................................................................8A- 89
Cable Harness Routing ...................................................................................................8A- 91
Main Cable Harness (RHD)..........................................................................................8A- 91
Instrument Harness (RHD) ..........................................................................................8A- 92
Main Cable Harness (LHD) ..........................................................................................8A- 93
Instrument Harness (LHD) ..........................................................................................8A- 94
Engine Harness C24SE ...............................................................................................8A- 95
Engine Harness 4JJ1-TC/4JK1-TC ............................................................................8A- 96
Engine Harness 4JH1-TC/4JA1T (L) ...........................................................................8A- 97
Transmission Harness ...............................................................................................8A- 98
System Repair ................................................................................................................. .8A- 100
Start and Charging ......................................................................................................8A- 10 0
Engine Control Module (ECM) ...................................................................................8A- 111
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) & GLOW; 4JA1T (L) Only ...................................8A- 143
Lighting ...................................................................................................................... ..8A- 149
Front Fog Light ...........................................................................................................8A- 180
Rear Fog Light ............................................................................................................8A- 190
Headlight Leveling ......................................................................................................8A- 19 4
Illumination .................................................................................................................. 8A- 200
Hazard Warning Flasher, Turn Signal Light, Backup Light, Horn and Stoplight ....................................................................................................8A- 213
Dome Light, Spotlight, Map Light and Warning Buzzer ..........................................8A- 245
Windshield Wiper and Washer ..................................................................................8A- 264
Transmission Control Module (TCM) ........................................................................8A- 285
Manual Transmission Shift Assist .............................................................................8A- 298
Meter, Warning Light and Indicator Light .................................................................8A- 303
Heater and Air Conditioning ......................................................................................8A- 371
Power Door Lock ........................................................................................................8A- 386
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4950 of 6020
8A-12 ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS
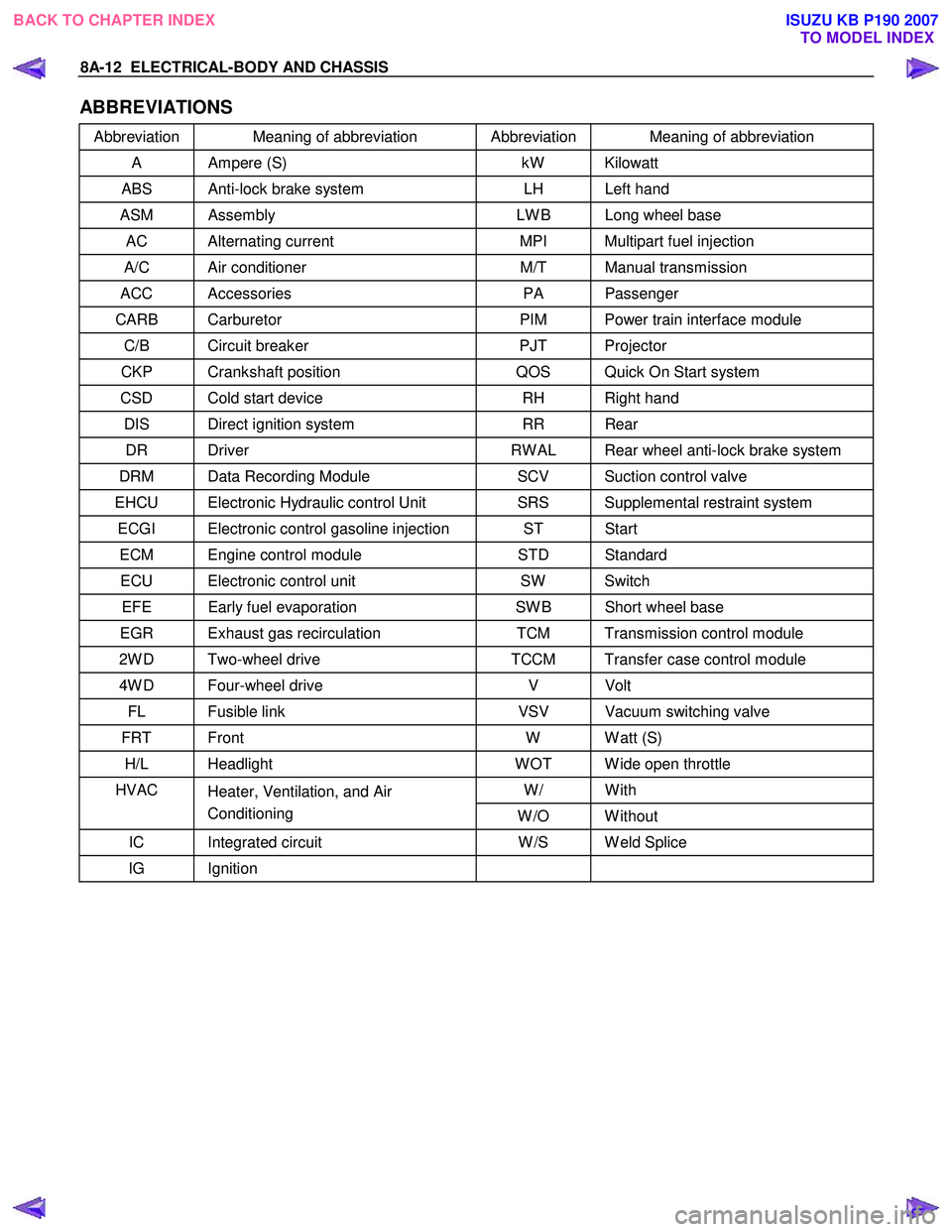
ABBREVIATIONS
Abbreviation Meaning of abbreviation Abbreviation Meaning of abbreviation
A Ampere (S) kW Kilowatt
ABS Anti-lock brake system LH Left hand
ASM Assembly LW B Long wheel base
AC Alternating current MPI Multipart fuel injection
A/C Air conditioner M/T Manual transmission
ACC Accessories PA Passenger
CARB Carburetor PIM Power train interface module
C/B Circuit breaker PJT Projector
CKP Crankshaft position QOS Quick On Start system
CSD Cold start device RH Right hand
DIS Direct ignition system RR Rear
DR Driver RW AL Rear wheel anti-lock brake system
DRM Data Recording Module SCV Suction control valve
EHCU Electronic Hydraulic control Unit SRS Supplemental restraint system
ECGI Electronic control gasoline injection ST Start
ECM Engine control module STD Standard
ECU Electronic control unit SW Switch
EFE Early fuel evaporation SW B Short wheel base
EGR Exhaust gas recirculation TCM Transmission control module
2W D Two-wheel drive TCCM Transfer case control module
4W D Four-wheel drive V Volt
FL Fusible link VSV Vacuum switching valve
FRT Front W W att (S)
H/L Headlight W OT W ide open throttle
W/ With HVAC
Heater, Ventilation, and Air
Conditioning W /O W ithout
IC Integrated circuit W /S W eld Splice
IG Ignition
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5309 of 6020
ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS 8A-371
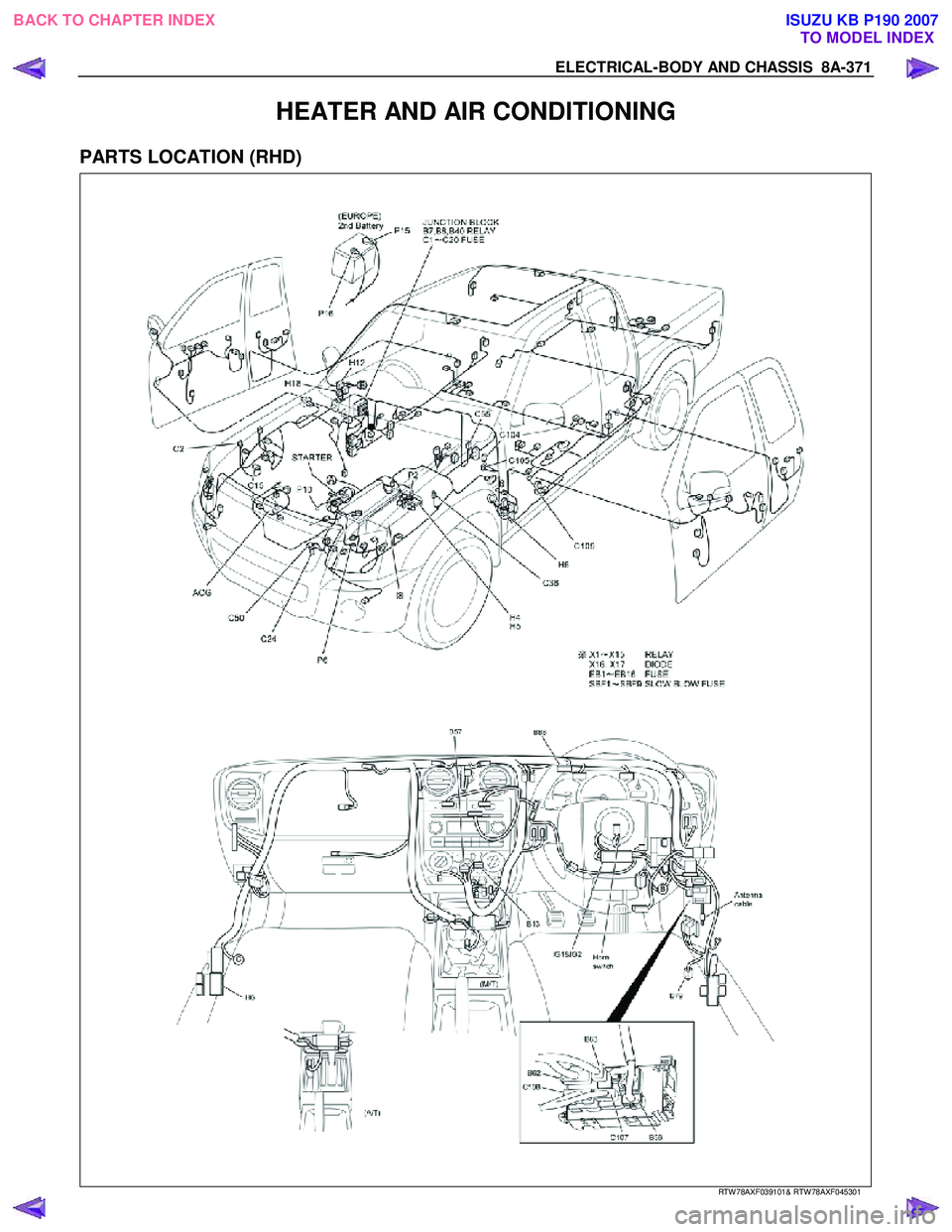
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING
PARTS LOCATION (RHD)
RTW 78AXF039101& RTW 78AXF045301
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007