2007 ISUZU KB P190 ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 3443 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–165
Step Action Yes
No
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0850 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.43 DTC P1648
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P1648 – W rong Security Code Entered.
Circuit Description
Tech 2 is used to program the engine control module (ECM). Before any programming, a security code must be entered
into Tech 2. The ECM will check if the code entered is correct before continuing. If the security code is incorrect, DTC
P1648 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
An incorrect security code is entered into Tech 2 when attempting to program the ECM.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
W hen the DTC sets, the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is not displayed.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The immobiliser security code is a Type ‘C’ DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type ‘C’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘C’ DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management –V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 – Service Operations for details on resetting the ECM.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3444 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–166
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 This step tests the ECM ground circuits and supply voltage.
DTC P1648 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
NOTE
Do not attempt to perform any Tech 2 function that
requires the ECM security code to be entered.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 Using Tech 2, attempt a programming function that requires the ECM
security code to be entered. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6
– Service Operations for details on resetting the ECM.
Has the programming function been successfully performed? System OK Go to Step 4
4 1 Test all ECM ground circuits for a high resistance or an open
circuit fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis
for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
2 Test the ECM ignition supply voltage circuit for a high resistance, open circuit or short to ground fault condition. Refer
to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical
fault diagnosis.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 – Service
Operations for details on replacing the ECM.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
7.44 DTC P1668, P2500 or P2501
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P1668 – Generator L Terminal Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P2500 – Generator L Terminal Low Voltage
• DTC P2501 – Generator L Terminal High Voltage
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3445 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–167
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) applies a signal voltage to the Generator L (GEN L) terminal circuit to control the load
of the generator on the engine. Refer to 6D1-1 Charging System for details of the charging system operation.
A GEN L terminal circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the Gen L circuit voltage is outside the specified range for a
predetermined set of parameters.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P1668
Runs continuously when one of the following conditions are met:
• Ignition on Test – The ignition is switched on with the engine not running for 5 seconds.
• Engine Run Test – The engine is running at speed less than 3,000 rpm
DTC P2500
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The engine is running.
• The generator is not commanded off.
DTC P2501
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The ignition is switched on with the engine not running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P1668
• Ignition on Test – the ECM detects a high signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
• Engine Run Test – the ECM detects a low signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
DTC P2500
The ECM detects a low signal voltage on the Gen L for 15 seconds.
DTC P2501
The ECM detects a high signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The Generator L-terminal circuit are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to 6D1-1 Charging System – V6 for details of the charging system operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3446 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–168
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P1668, P2500 or P2501 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P1668, P2500 or P2501 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Test the charging system for any fault condition that may cause
incorrect generator operation. Refer to 6D1-1 Charging System – V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4 Test the Gen L signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit, short
to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the Generator L terminal circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.45 DTC P1845
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction
Circuit Description
The ECM monitors and compares the engine torque output against the maximum allowable engine torque. Refer to
6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the engine torque limit management operation.
If the requested torque is higher than the maximum allowable torque, the ECM applies engine torque limitation and DTC
P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P1845 runs continuously when the engine is running at speeds greater than 40 rpm.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3447 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–169
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine torque output exceeds the maximum allowable torque output for 10 minutes.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction is a Type ‘C’ DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this
Section, for action taken when a Type ‘C’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘C’ DTC.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the Engine Torque Limit
Management operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 Fault conditions that apply excessive load on the engine may trigger this DTC.
DTC P1845 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC or road test the vehicle under various driving condition.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P1845 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Are there any other ECM or TCM DTCs set? Refer to the
appropriate DTC table. Go to Step 4
4 Inspect for fault conditions in the engine or transmission that applies
excessive load on the engine.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P1845 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3448 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–170
Step Action Yes
No
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.46 DTC P2096 or P2098
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2096 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 1)
• DTC P2098 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor 1 measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and provides more
information than the switching style HO2S2. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen
pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the
pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to
the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the
oxygen pumping cell, maintaining a constant voltage in the oxygen sensing cell. The ECM monitors the voltage variation
in the sensing cell and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow, or
oxygen ion flow, to the pumping cell. By measuring the amount of current required to maintain the voltage in the sensing
cell, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. The HO2S voltage is displayed as a lambda
value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the
lambda value will remain around 1. W hen the fuel system is lean, the oxygen level will be high and the lambda signal
will be high or more than 1. W hen the fuel system is rich, the oxygen level will be low, and the lambda signal will be low
or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the correct air / fuel ratio.
Fuel trim biasing is used by the ECM to keep the post catalyst HO2S voltage within a range of 580 – 665 mV as
possible. This allows optimal catalyst efficiency under light load conditions, such as at idle or a steady cruise. The ECM
constantly monitors how lean or rich the fuel trim bias is commanded. If the ECM detects that the fuel trim bias is
commanded lean for more than a calibrated amount, DTC P2096 or P2098 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2096 or P2098 failed, DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0041, P0050, P0051,
P0052, P0101, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0151, P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2231, P2234, P2237, P2240, P2243, P2247, P2251, P2254, P2270, P2271, P2273, P2626, and
P2629 must run and pass.
• The engine is operating for more than 2 seconds.
• The post catalyst fuel trim control is enabled.
• The front and rear HO2S are in Closed Loop.
• DTCs P2096and P2098 run continuously once the above conditions are met for more than 40 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The post catalyst fuel trim correction factor is biased lean by more than 3 percent of the HO2S lambda value for more
than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM activates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the
diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the
control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second
consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The
control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3449 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–171
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
These post catalyst fuel trim system DTCs are Type ‘B’ DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section,
for action taken when a Type ‘C’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘B’ DTCs.
Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the post catalyst oxygen sensor
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this
diagnostic procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
• The lower connector of the ECM is connector X1 and the upper connector of the ECM is connector X2. Refer to
3.2 ECM Connector End Views in this Section, for pin and circuit identification.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines if a condition exists.
4 This step is testing for a rear HO2S sensor circuit condition. A circuit condition sets this DTC.
7 This step inspects for the rear sensors being connected to the correct bank of the engine. This condition causes this DTC to set.
8 This step is testing for an intermittent circuit condition. Thoroughly inspect the HO2S circuits for an intermittent circuit condition.
9 This step is testing for an intermittent circuit condition. Thoroughly inspect the HO2S circuits for an intermittent circuit condition.
DTC P2096 or P2098 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? —
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 Refer to Road-testing, in 1.5 Warning
Caution and Notes in this Section.
1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
NOTE
The rear heated oxygen sensors (HO2S)
must be in Closed Loop for this diagnostic
to run. A road load condition is necessary
to obtain Closed Loop.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2096 or P2098 fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3450 of 6020
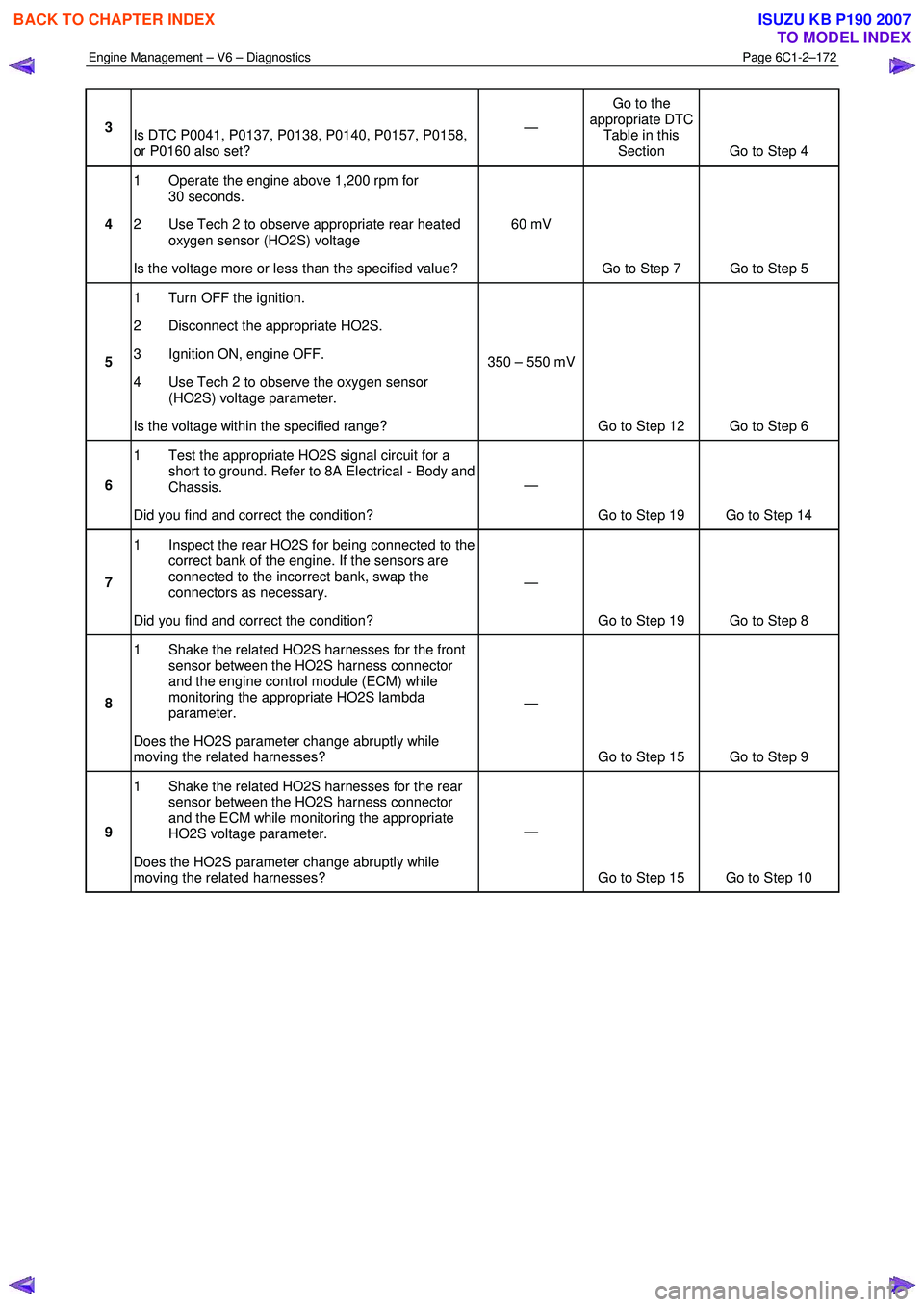
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–172
3
Is DTC P0041, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0157, P0158,
or P0160 also set? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section Go to Step 4
4 1 Operate the engine above 1,200 rpm for
30 seconds.
2 Use Tech 2 to observe appropriate rear heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage
Is the voltage more or less than the specified value? 60 mV
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Turn OFF the ignition.
2 Disconnect the appropriate HO2S.
3 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
4 Use Tech 2 to observe the oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage parameter.
Is the voltage within the specified range? 350 – 550 mV
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 6
6 1 Test the appropriate HO2S signal circuit for a
short to ground. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 14
7 1 Inspect the rear HO2S for being connected to the
correct bank of the engine. If the sensors are
connected to the incorrect bank, swap the
connectors as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 8
8 1 Shake the related HO2S harnesses for the front
sensor between the HO2S harness connector
and the engine control module (ECM) while
monitoring the appropriate HO2S lambda
parameter.
Does the HO2S parameter change abruptly while
moving the related harnesses? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 9
9 1 Shake the related HO2S harnesses for the rear
sensor between the HO2S harness connector
and the ECM while monitoring the appropriate
HO2S voltage parameter.
Does the HO2S parameter change abruptly while
moving the related harnesses? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007