2006 SUZUKI SX4 check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 330 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-48 Engine Mechanical:
Valve Spring InspectionS6RW0D1406030
Valve Spring Free Length and Preload
Referring to data, check to be sure that each spring is in
sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or
weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can
cause chatter, not to mention possibility of reducing
power output due to gas leakage caused by decreased
seating pressure.
Valve spring free length
Standard: 36.83 mm (1.450 in.)
Limit: 35.83 mm (1.411 in.)
Valve spring preload
Standard: 107 – 125 N (10.7 – 12.5 kgf) for 31.50 mm
(23.6 – 27.6 lb/1.240 in.)
Limit: 102 N (10.2 kgf) for 31.50 mm (22.5 lb/1.240 in.)Spring Squareness
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for
squareness in terms of clearance between end of valve
spring and square. Valve springs found to exhibit a
larger clearance than limit must be replaced.
Valve spring squareness
Limit: 1.6 mm (0.063 in.)
I2RH01140143-01
I2RH01140144-01
Page 332 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-50 Engine Mechanical:
Installation
1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls,
connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
2) Install guide hoses (1) over connecting rod bolts.
These guide hoses protect crank pin and threads of
rod bolt from damage during installation of
connecting rod and piston assembly.
3) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly
into cylinder bore, point front mark (1) on piston head
to crankshaft pulley side.4) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
5) Install bearing cap (1):
Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to rod bolts and tighten cap
nuts (3) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all cap nuts to 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-
ft).
b) Retighten them to 45°.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for connecting rod bolt
deformation. Refer to “Piston Pins and
Connecting Rods Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap nut (a): Tighten
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft), 45° and 45° by
the specified procedure
6) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder
Head Removal and Installation”.A: Crankshaft pulley side B: Flywheel side
I2RH01140147-01
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I2RH0B140112-01
Page 335 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-53
Piston clearance
Measure cylinder bore diameter and piston diameter to
find their difference which is piston clearance. Piston
clearance should be within specification as follows. If it is
out of specification, rebore cylinder and use oversize
piston.
NOTE
Cylinder bore diameters used here are
measured in thrust direction at two positions.
Piston clearance
Standard (used piston): 0.032 – 0.061 mm (0.0013 –
0.0024 in.)
Standard (new piston with coating): 0.010 – 0.051
mm (0.0004 – 0.0020 in.)
Limit: 0.161 mm (0.0065 in.)
Ring groove clearance
Before checking, piston grooves must be clean, dry and
free of carbon deposits.
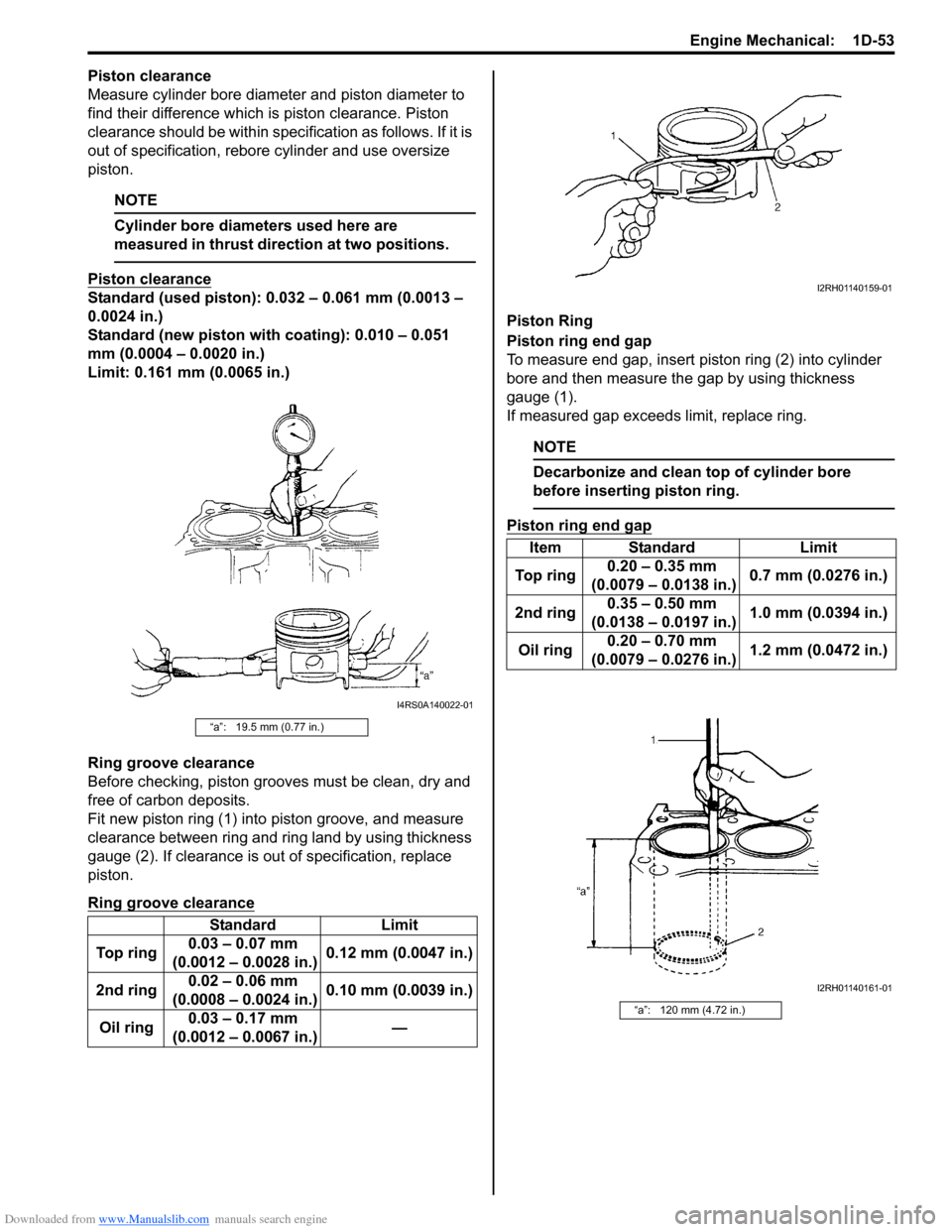
Fit new piston ring (1) into piston groove, and measure
clearance between ring and ring land by using thickness
gauge (2). If clearance is out of specification, replace
piston.
Ring groove clearance
Piston Ring
Piston ring end gap
To measure end gap, insert piston ring (2) into cylinder
bore and then measure the gap by using thickness
gauge (1).
If measured gap exceeds limit, replace ring.
NOTE
Decarbonize and clean top of cylinder bore
before inserting piston ring.
Piston ring end gap
“a”: 19.5 mm (0.77 in.)
Standard Limit
To p r i n g0.03 – 0.07 mm
(0.0012 – 0.0028 in.)0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
2nd ring0.02 – 0.06 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0024 in.)0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Oil ring0.03 – 0.17 mm
(0.0012 – 0.0067 in.)—
I4RS0A140022-01
Item Standard Limit
To p r i n g0.20 – 0.35 mm
(0.0079 – 0.0138 in.)0.7 mm (0.0276 in.)
2nd ring0.35 – 0.50 mm
(0.0138 – 0.0197 in.)1.0 mm (0.0394 in.)
Oil ring0.20 – 0.70 mm
(0.0079 – 0.0276 in.)1.2 mm (0.0472 in.)
“a”: 120 mm (4.72 in.)
I2RH01140159-01
I2RH01140161-01
Page 336 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-54 Engine Mechanical:
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods InspectionS6RW0D1406035
Piston Pin
Visual inspection
Check piston pin, connecting rod small end bore and
piston bore for wear or damage, paying particular
attention to condition of small end bore bush. If pin,
connecting rod small end bore or piston bore is badly
worn or damaged, replace pin, connecting rod and/or
piston.
Piston pin clearance
Check piston pin clearance in small end and piston.
Replace connecting rod and/or piston if its small end is
badly worn or damaged or if measured clearance
exceeds limit.
Piston pin clearance in connecting rod small end
Standard: 0.003 – 0.014 mm (0.0001 – 0.0006 in.)
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.00020 in.)
Piston pin clearance in piston
Standard: 0.006 – 0.017 mm (0.00024 – 0.00067 in.)
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Small-end bore
20.003 – 20.011 mm (0.7875 – 0.7878 in.)
Piston pin dia.
19.997 – 20.000 mm (0.7873 – 0.7874 in.)
Piston bore
20.006 – 20.014 mm (0.7876 – 0.7880 in.)Connecting Rod
Big-end side clearance
Check big-end of connecting rod for side clearance, with
rod fitted and connected to its crank pin in the normal
manner. If measured clearance is found to exceed its
limit, replace connecting rod.
Big-end side clearance
Standard: 0.25 – 0.40 mm (0.0098 – 0.0157 in.)
Limit: 0.55 mm (0.0217 in.)
Connecting rod alignment
Mount connecting rod on aligner to check it for bow and
twist. If measured value exceeds the limit, replace it.
Connecting rod alignment
Limit on bow: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Limit on twist: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
I4RS0A140023-01
I2RH0B140148-01
I4RH01140053-01
Page 338 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-56 Engine Mechanical:
Connecting Rod Bearing General Information
Service connecting rod bearings are available in
standard size and 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) undersize
bearing, and standard size bearing has 5 kinds of
bearings differing in tolerance.
For identification of undersize bearing, it is painted red at
the position as indicated in figure, undersize bearing
thickness is 1.605 – 1.615 mm (0.0632 – 0.0635 in.) at
the center of it.
Connecting Rod Bearing Visual Inspection
Inspect bearing shells for signs of fusion, pitting, burn or
flaking and observe contact pattern. Bearing shells
found in defective condition must be replaced.
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
1) Before checking bearing clearance, clean bearing
and crank pin.
2) Install bearing in connecting rod and bearing cap.
3) Place a piece of gauging plastic (1) to full width of
crank pin as contacted by bearing (parallel to
crankshaft), avoiding oil hole.4) Install rod bearing cap (1) to connecting rod.
When installing cap, be sure to point arrow mark (2)
on cap to crankshaft pulley side, as shown in figure.
After applying engine oil to rod bolts, tighten cap nuts
(3) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all cap nuts to 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-
ft)
b) Retighten them to 45°
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap nut (a): Tighten
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) 45° and 45° by
the specified procedure
5) Remove cap and using a scale (1) on gauging
plastic envelope (2), measure gauging plastic (2)
width at the widest point (clearance).
If clearance exceed its limit, use a new standard size
bearing referring to “Selection of Connecting Rod
Bearings: ”.
After selecting new bearing, recheck clearance.
Connecting rod bearing clearance
Standard: 0.029 – 0.047 mm (0.0011 – 0.0018 in.)
Limit: 0.065 mm (0.0026 in.)
6) If clearance can not be brought to its limit even by
using a new standard size bearing, use next thicker
bearing and recheck clearance or regrind crank pin
to undersize and use 0.25 mm undersize bearing.
1. Red paint
I2RH01140164-01
I2RH0B140121-01
I2RH0B140122-01
I2RH0B140123-01
Page 339 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-57
Selection of Connecting Rod Bearings
NOTE
• If bearing is in malcondition, or bearing
clearance is out of specification, select a
new standard bearing according to the
following procedure and install it.
• When replacing crankshaft or connecting
rod and its bearing due to any reason,
select new standard bearings to be
installed by referring to numbers stamped
on connecting rod and its cap and/or
alphabets stamped on crank web of No.3
cylinder.
1) Check stamped numbers on connecting rod and its
cap as shown.
Three kinds of numbers (“1”, “2” and “3”) represent
the following connecting rod big end inside
diameters.
For example, stamped number “1” indicates that
corresponding connecting rod big end inside
diameter is 45.000 – 45.006 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718
in.).
Connecting rod big end inside diameter
2) Next, check crankshaft pin diameter. On crank web
No.3, four alphabets are stamped as shown in figure.
Three kinds of alphabet (“A”, “B” and “C”) represent
the following crankshaft pin diameter respectively.
For example, stamped “A” indicates that
corresponding crankshaft pin diameter is 41.994 –
42.000 mm (1.6533 – 1.6534 in.).
Crankshaft pin outer diameter
Stamped
numbersConnecting rod big end inside diameter
1 45.0000 – 45.0060 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718 in.)
2 45.0061 – 45.0120 mm (1.7719 – 1.7721 in.)
3 45.0121 – 45.0180 mm (1.7722 – 1.7723 in.)
[A]: Connecting rod big end inside diameter number
[B]: Weight indication mark
I3RH0A140017-01
Stamped
alphabetCrankshaft pin diameter
A 41.9940 – 42.0000 mm (1.6533 – 1.6534 in.)
B 41.9880 – 41.9939 mm (1.6531 – 1.6532 in.)
C 41.9820 – 41.9879 mm (1.6529 – 1.6530 in.)
[A]: Crankshaft pin diameter for No.1 cylinder
[B]: Crankshaft pin diameter for No.2 cylinder
[C]: Crankshaft pin diameter for No.3 cylinder
[D]: Crankshaft pin diameter for No.4 cylinder
I3RH0A140018-01
Page 344 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-62 Engine Mechanical:
6) Install bearing cap to cylinder block, making sure to
point arrow mark (on each cap) to crankshaft pulley
side. Fit them sequentially in ascending order, 1, 2,
3, 4 and 5, starting from pulley side.
After applying engine oil to main bearing cap No.1
bolts ((1) – (10)) and main bearing cap No.2 bolts
((11) – (20)), tighten them gradually as follows.
a) Tighten bolts ((1) – (10)) to 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m,
22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as shown
by using a 12 corner socket wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them
to 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft).
c) In the same manner as in Step a), retighten them
to 60°.
d) Tighten bolts ((11) – (20)) to 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m,
18.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as
shown.
Tightening torque
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt ((1) – (10)):
Tighten 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N⋅m
(5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and 60° by the specified
procedure
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt ((11) – (20)):
Tighten 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) by the
specified procedure
CAUTION!
After tightening cap bolts, check to be sure
that crankshaft rotates smoothly when
turning it by 12 N⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 9.0 lb-ft)
torque or below.
7) If necessary, press-fit rear oil seal (1) to oil seal
housing (2) by using special tool as shown in figure.
Special tool
(A): 09911–97821
Crank rear oil seal installing position
(dimension)
“a”: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
8) Apply sealant to mating surface of rear oil seal
housing (1).
“A”: Water tight sealant 99000–31250 (SUZUKI
Bond No.1207F)
Sealant amount for rear oil seal housing
Width: “a”: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Height “b”: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
I2RH0B140131-01
I5RW0C140027-01
I4RS0A140018-01
Page 346 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-64 Engine Mechanical:
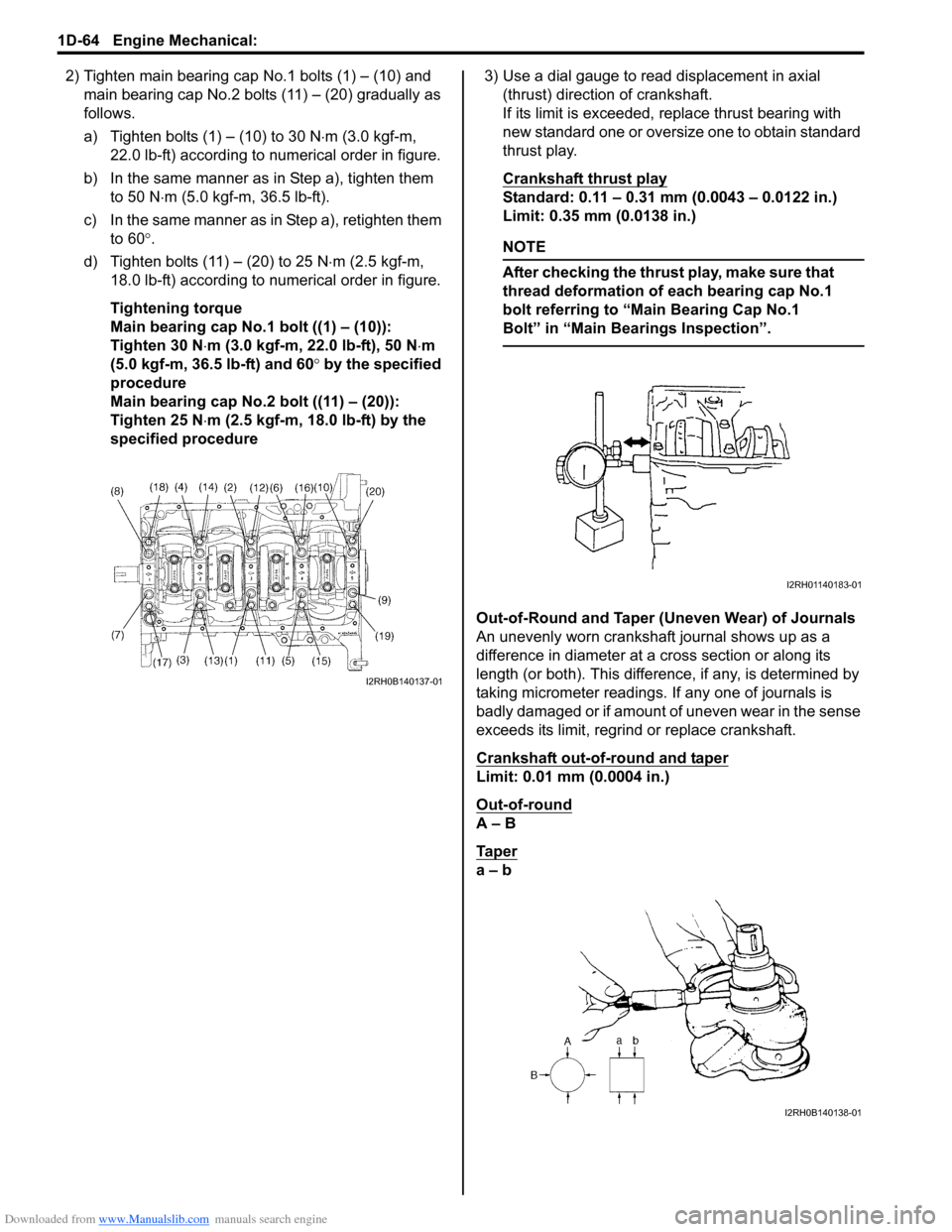
2) Tighten main bearing cap No.1 bolts (1) – (10) and
main bearing cap No.2 bolts (11) – (20) gradually as
follows.
a) Tighten bolts (1) – (10) to 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m,
22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order in figure.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them
to 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft).
c) In the same manner as in Step a), retighten them
to 60°.
d) Tighten bolts (11) – (20) to 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m,
18.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order in figure.
Tightening torque
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt ((1) – (10)):
Tighten 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N⋅m
(5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and 60° by the specified
procedure
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt ((11) – (20)):
Tighten 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) by the
specified procedure3) Use a dial gauge to read displacement in axial
(thrust) direction of crankshaft.
If its limit is exceeded, replace thrust bearing with
new standard one or oversize one to obtain standard
thrust play.
Crankshaft thrust play
Standard: 0.11 – 0.31 mm (0.0043 – 0.0122 in.)
Limit: 0.35 mm (0.0138 in.)
NOTE
After checking the thrust play, make sure that
thread deformation of each bearing cap No.1
bolt referring to “Main Bearing Cap No.1
Bolt” in “Main Bearings Inspection”.
Out-of-Round and Taper (Uneven Wear) of Journals
An unevenly worn crankshaft journal shows up as a
difference in diameter at a cross section or along its
length (or both). This difference, if any, is determined by
taking micrometer readings. If any one of journals is
badly damaged or if amount of uneven wear in the sense
exceeds its limit, regrind or replace crankshaft.
Crankshaft out-of-round and taper
Limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in.)
Out-of-round
A – B
Ta p e r
a – b
I2RH0B140137-01
I2RH01140183-01
I2RH0B140138-01