2006 SUZUKI SX4 Suspension
[x] Cancel search: SuspensionPage 435 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Suspension General Diagnosis: 2A-1
Suspension
Suspension General Diagnosis
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Suspension, Wheels and Tires Symptom DiagnosisS6RW0D2104001
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Vehicle pulls (Leads)Mismatched or uneven tiresReplace tires.
Tires not adequately inflatedAdjust tire pressure.
Broken or sagging coil springsReplace coil springs.
Radial tire lateral forceReplace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignmentCheck and adjust wheel alignment.
Brake dragging in one road wheelRepair brake.
Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension partsTighten or replace related suspension parts.
Abnormal or excessive
tire wearSagging or broken coil springReplace coil spring.
Tire out of balanceAdjust balance or replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignmentCheck and adjust wheel alignment.
Faulty strut (shock absorber)Replace strut (shock absorber).
Hard drivingReplace tires.
Overloaded vehicleReplace tires.
Not rotated tiresReplace or rotate tires.
Worn or loose wheel bearingReplace wheel bearing.
Wobbly wheel or tireReplace wheel or tire.
Tires not adequately inflatedAdjust tire pressure.
Front suspension frame and/or
suspension control arm are transformedCheck and replace.
Wheel trampBlister or bump on tireReplace tire.
Improper strut (shock absorber) actionReplace strut (shock absorber).
Shimmy, shake or
vibrationTire or wheel out of balanceBalance wheel or replace tire and/or wheel.
Loosen wheel bearingsReplace wheel bearings.
Worn tie-rod endsReplace tie-rod ends.
Worn lower ball jointsReplace suspension control arm.
Excessive wheel runoutRepair or replace wheel and/or tire.
Blister or bump on tireReplace tire.
Excessively loaded radial runout of tire /
wheel assemblyReplace tire or wheel.
Disturbed wheel alignmentCheck and adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or worn steering linkageTighten or replace steering linkage.
Abnormal noise, front endWorn, sticky or loose tie-rod ends, lower
ball joints, tie-rod inside ball joints or
drive shaft jointsReplace tie-rod end, suspension arm, tie-rod
or drive shaft joint.
Damaged struts or mountingsRepair or replace struts or mountings.
Worn suspension arm bushingsReplace suspension arm bushings.
Loose stabilizer barTighten bolts or nuts and/or replace bushes.
Loose wheel boltsTighten wheel bolts.
Loose suspension bolts or nutsTighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or damaged wheel bearingsReplace wheel bearings.
Broken suspension springsReplace suspension springs.
Worn strut bearingsReplace strut bearing.
Malfunction of Power Steering SystemCheck and correct malfunction.
Low or uneven trim height
NOTE
See NOTE *1.
Broken or sagging coil springsReplace coil springs.
Over loadedCheck loading.
Incorrect coil springsReplace coil spring.
Tires not adequately inflatedAdjust tire pressure.
Ride too softFaulty strut (shock absorber)Replace strut (shock absorber).
Suspension bottomsOverloadedCheck loading.
Faulty strut (shock absorber)Replace strut (shock absorber).
Incorrect, broken or sagging coil springsReplace coil spring.
Page 436 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2A-2 Suspension General Diagnosis:
NOTE
*1: Right-to-left trim height (“H”) difference should be within 15 mm (0.6 in.) with curb weight. (same
with rear side.)
Body leans or sways in
cornersLoose stabilizer barTighten stabilizer bar bolts or nuts, or replace
bushes.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) or
mountingReplace strut (shock absorber) or tighten
mounting.
Broken or sagging coil springsReplace coil springs.
OverloadedCheck loading.
Cupped tiresFront struts defectiveReplace struts.
Worn wheel bearingsReplace wheel bearings.
Excessive tire or wheel run-outReplace tire and/or wheel.
Worn ball jointsReplace suspension control arm.
Tire out of balanceAdjust tire balance. Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
“H”
I2RH01210001-01
Page 437 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Suspension General Diagnosis: 2A-3
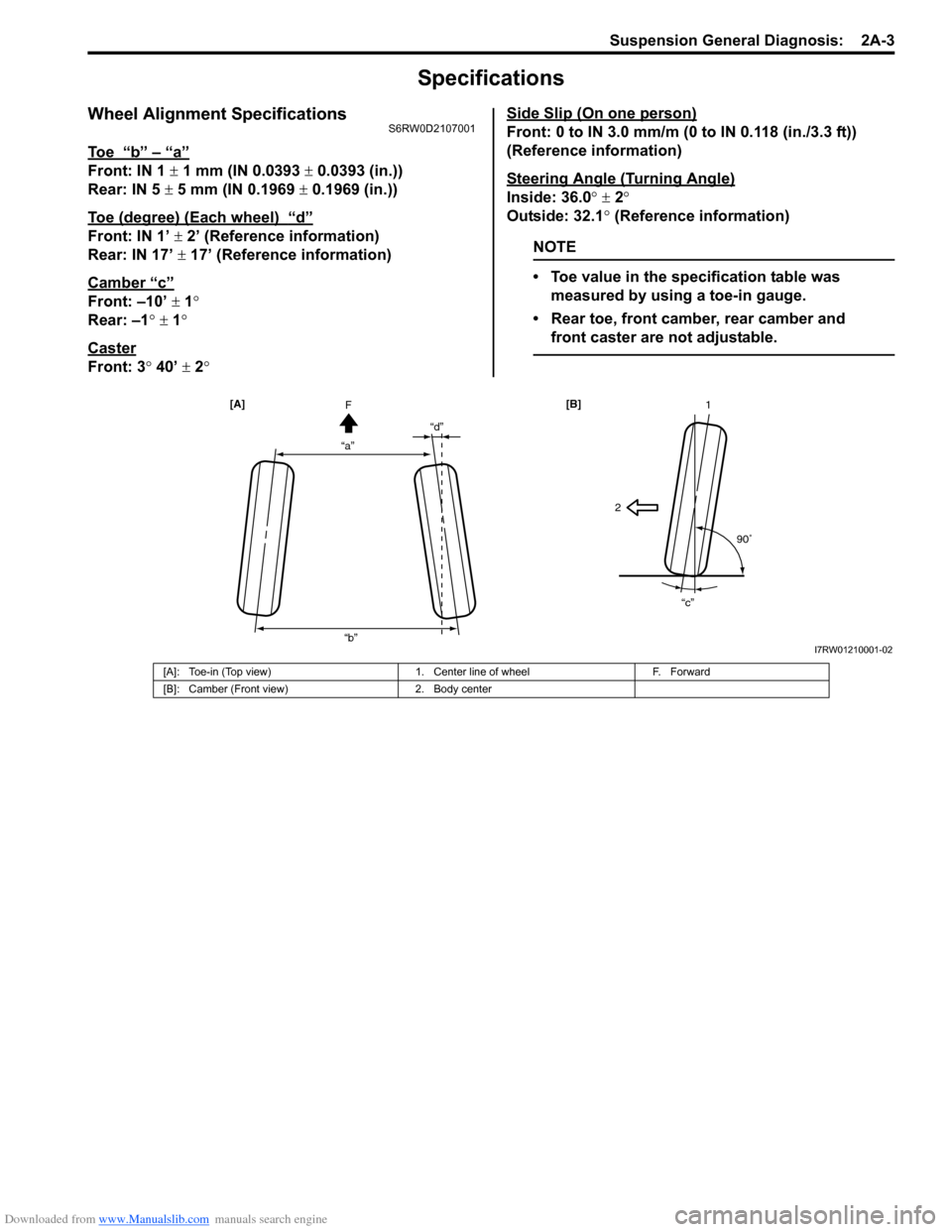
Specifications
Wheel Alignment SpecificationsS6RW0D2107001
To e “b” – “a”
Front: IN 1 ± 1 mm (IN 0.0393 ± 0.0393 (in.))
Rear: IN 5 ± 5 mm (IN 0.1969 ± 0.1969 (in.))
Toe (degree) (Each wheel)
“d”
Front: IN 1’ ± 2’ (Reference information)
Rear: IN 17’ ± 17’ (Reference information)
Camber
“c”
Front: –10’ ± 1°
Rear: –1° ± 1°
Caster
Front: 3° 40’ ± 2°Side Slip (On one person)
Front: 0 to IN 3.0 mm/m (0 to IN 0.118 (in./3.3 ft))
(Reference information)
Steering Angle (Turning Angle)
Inside: 36.0° ± 2°
Outside: 32.1° (Reference information)
NOTE
• Toe value in the specification table was
measured by using a toe-in gauge.
• Rear toe, front camber, rear camber and
front caster are not adjustable.
“a”“d”
“b”F [A]
21
90�
“c” [B]
I7RW01210001-02
[A]: Toe-in (Top view) 1. Center line of wheel F. Forward
[B]: Camber (Front view) 2. Body center
Page 438 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-1 Front Suspension:
Suspension
Front Suspension
General Description
Front Suspension ConstructionS6RW0D2201001
1
4 3
2
7
6
8
))
5
9(a)
(b)
(b)
(b)
(b)
(c)
(c)
(d)
(d)
(e)(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
(h)
F
I7RW01220002-03
1. Front strut assembly 8. Front suspension frame : 200 N⋅m (20.0 kgf-m, 145.0 lb-ft)
2. Front drive shaft 9. Suspension control arm : 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
3. Steering knuckle : 140 N⋅m (14.0 kgf-m, 101.5 lb-ft) : 95 N⋅m (9.5 kgf-m, 69.0 lb-ft)
4. Front wheel hub : 150 N⋅m (15.0 kgf-m, 108.5 lb-ft) : 55 N⋅m (5.5 kgf-m, 40.0 lb-ft)
5. Stabilizer joint : 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) : Do not reuse.
6. Stabilizer bar : 45 N⋅m (4.5 kgf-m, 32.5 lb-ft) F: Forward
7. Tie-rod : 60 N⋅m (6.0 kgf-m, 43.5 lb-ft)
Page 439 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-2
Front Wheel Alignment ConstructionS6RW0D2201002
Among factors for front wheel alignment, only toe setting
can be adjusted. Camber and caster are not adjustable.
Therefore, should camber or caster be out of
specification due to the damage caused by hazardous
road conditions or collision, whether the damage is in
body or in suspension should be determined and
damaged body should be repaired or damaged
suspension should be replaced.
Preliminary Checks Prior to Adjustment Front Wheel
Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the
result of improper wheel alignment. An additional item to
be checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or
improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the vehicle
deviation from a straight path on a level road without
hand pressure on the steering wheel. Refer to “Radial
Tire Lead / Pull Description in Section 2D” in order to
determine if the vehicle has a tire lead problem. Before
making any adjustment affecting wheel alignment, the
following checks and inspections should be made to
ensure correctness of alignment readings and alignment
adjustments:• Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and
approximately the same tread wear.
• Check for loose of ball joints. Check tie-rod ends; if
excessive looseness is noted, it must be corrected
before adjusting.
• Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
• Check vehicle trim heights; if it is out of limit and a
correction is needed, it must be done before adjusting
toe.
• Check for loose of suspension control arms.
• Check for loose or missing stabilizer bar attachments.
• Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as
tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment
checks.
• Consider condition of equipment being used to check
alignment and follow manufacturer’s instructions.
• Regardless of equipment used to check alignment,
vehicle must be placed on a level surface.
NOTE
To prevent possible incorrect reading of toe,
camber or caster, vehicle front and rear end
must be moved up and down a few times
before inspection.
Repair Instructions
Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and
Adjustment
S6RW0D2206001
Toe Inspection and Adjustment
Preparation for toe inspection and adjustment.
• Place vehicle in unloaded state on level surface.
• Set steering wheel in straight state.
• Check that inflation pressure of each tire is adjusted
properly and wheel is free from deflection.
• Check that each suspension part is free from bend,
dent, wear or damage in any other form.
• Check that ground clearance at the right and left is
just about the same.Inspection
Measure toe with toe-in gauge (1).
Toe should be within following specifications.
If toe is out of the specification, adjust toe properly.
To e
IN 1.0 ± 1.0 mm (0.0394 ± 0.0394 in.)
I2RH01220062-01
Page 440 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-3 Front Suspension:
Adjustment
1) Loosen right and left tie-rod end lock nuts (1) first.
2) Rotate right and left tie-rods (2) by the same amount
to align toe to specification. In this adjustment, the
lengths “A” of both right and left tie-rod should be
equal.
NOTE
Before rotating tie-rods (2), apply grease
between tie-rods and rack boots so that
boots won’t be twisted.
3) After adjustment, tighten lock nuts (1) to specified
torque.
Tightening torque
Tie-rod end lock nut (a): 45 N·m (4.5 kgf-m, 32.5
lb-ft)
NOTE
Make sure that rack boots are not twisted.
Steering Angle Check and Adjustment
When tie-rod or tie-rod end was replaced, check toe and
then also steering angle with turning radius gauge (1).
If steering angle is not correct, check whether right and
left tie-rods length “A” are equal.
NOTE
If tie-rod lengths were changed to adjust
steering angle, reinspect toe-in.
Steering angle
Inside: 36.0° ± 2°
Outside: 32.1° (Reference)
Reference Information
Side slip
When checked with side slip tester, side slip should
satisfy following specification.
Side slip
0 to IN 3.0 mm/m (0 to IN 0.118 in/3.3 ft)
If side slip is greatly difference, toe or front wheel
alignment may not be correct.
I3RH0A220002-01
I3RH0A220003-01
Page 441 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-4
Front Strut Assembly ComponentsS6RW0D2206002
1
2 3 4 5 7
6 8 910 11
121314
15
(a)
(b)
(c)
(a)
I7RW01220003-03
1. Front strut 6. Coil spring upper seat 11. Strut nut : 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
2. Coil spring 7. Strut bearing 12. Strut bracket bolt
: Insert from vehicle front side.:55 N⋅m (5.5 kgf-m, 40.0 lb-ft)
3. Bump stopper 8. Strut support 13. Strut bracket nut : 140 N⋅m (14.0 kgf-m, 101.5 lb-ft)
4. Strut dust cover 9. Strut support lower nut 14. Stabilizer joint nut : Do not reuse.
5. Coil spring seat 10. Rebound stopper 15. Stabilizer joint
Page 442 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-5 Front Suspension:
Front Strut Assembly Removal and InstallationS6RW0D2206003
CAUTION!
When rebound stopper and strut assembly
were removed, check strut support lower nut
for specified torque before installing strut
assembly.
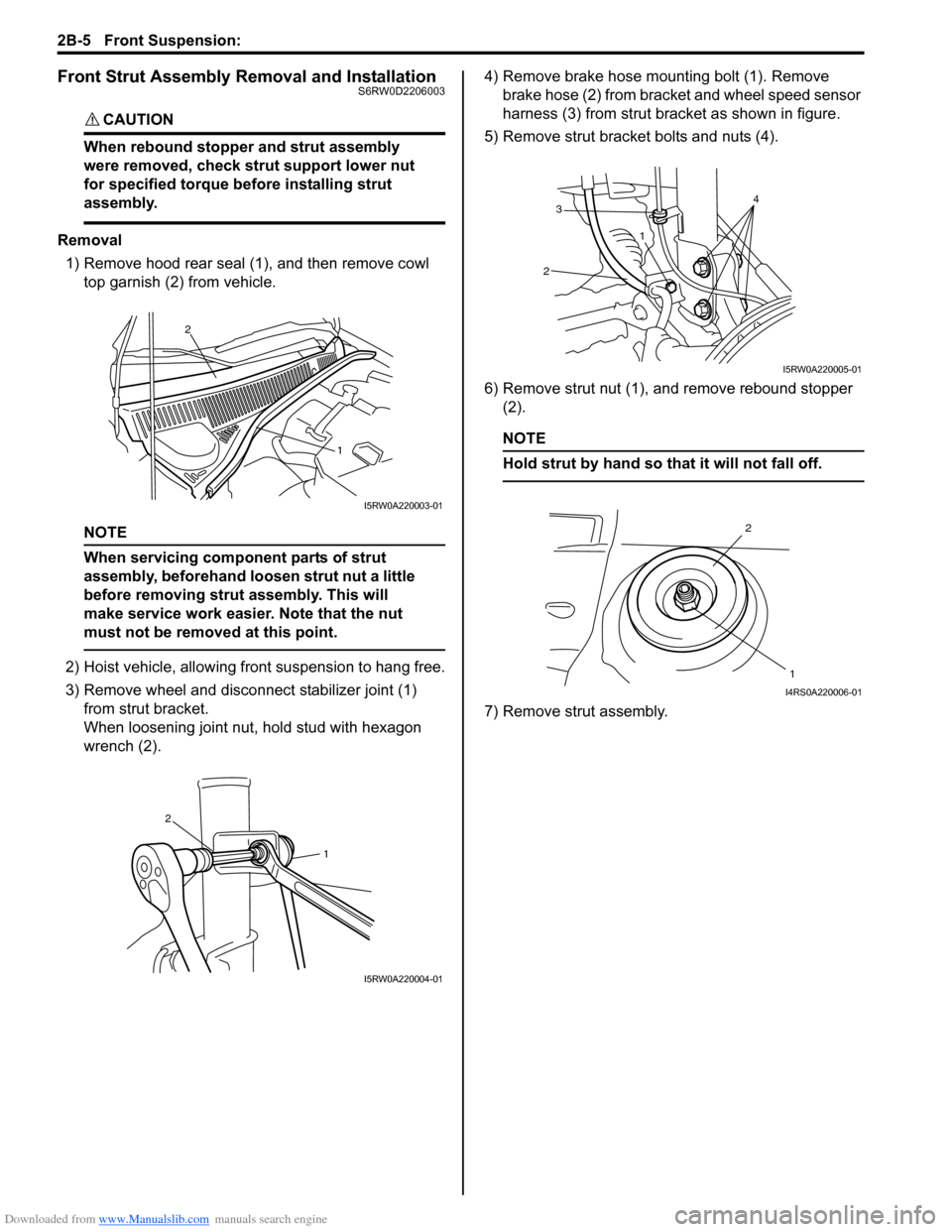
Removal
1) Remove hood rear seal (1), and then remove cowl
top garnish (2) from vehicle.
NOTE
When servicing component parts of strut
assembly, beforehand loosen strut nut a little
before removing strut assembly. This will
make service work easier. Note that the nut
must not be removed at this point.
2) Hoist vehicle, allowing front suspension to hang free.
3) Remove wheel and disconnect stabilizer joint (1)
from strut bracket.
When loosening joint nut, hold stud with hexagon
wrench (2).4) Remove brake hose mounting bolt (1). Remove
brake hose (2) from bracket and wheel speed sensor
harness (3) from strut bracket as shown in figure.
5) Remove strut bracket bolts and nuts (4).
6) Remove strut nut (1), and remove rebound stopper
(2).
NOTE
Hold strut by hand so that it will not fall off.
7) Remove strut assembly.
2
1
I5RW0A220003-01
1
2
I5RW0A220004-01
3
214
I5RW0A220005-01
2
1
I4RS0A220006-01