2006 SUZUKI SX4 Water
[x] Cancel search: WaterPage 49 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1-v
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 1H-4
Ignition System Symptom Diagnosis................... 1H-4
Reference Waveform of Ignition System............. 1H-4
Ignition System Check ........................................ 1H-4
Ignition Spark Test .............................................. 1H-6
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1H-6
High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation...... 1H-6
High-Tension Cord Inspection ............................ 1H-7
Spark Plug Removal and Installation .................. 1H-7
Spark Plug Inspection ......................................... 1H-7
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
Removal and Installation................................... 1H-8
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
Inspection.......................................................... 1H-8
Ignition Timing Inspection ................................... 1H-8
Specifications..................................................... 1H-10
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 1H-10
Special Tools and Equipment ........................... 1H-10
Special Tool ...................................................... 1H-10
Starting System ......................................... 1I-1
Schematic and Routing Diagram ......................... 1I-1
Cranking System Circuit Diagram ........................ 1I-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............. 1I-1
Cranking System Symptom Diagnosis ................. 1I-1
Cranking System Test.......................................... 1I-3
Repair Instructions ............................................... 1I-4
Starting Motor Dismounting and Remounting ...... 1I-4
Starting Motor Components ................................. 1I-5
Starting Motor Inspection ..................................... 1I-6
Specifications........................................................ 1I-9
Cranking System Specifications........................... 1I-9
Tightening Torque Specifications ......................... 1I-9
Special Tools and Equipment.............................. 1I-9
Recommended Service Material .......................... 1I-9
Charging System ...................................... 1J-1
General Description ............................................. 1J-1
Battery Description .............................................. 1J-1
Generator Description ......................................... 1J-3
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 1J-4
Battery Inspection ............................................... 1J-4
Generator Symptom Diagnosis ........................... 1J-4
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery
Check) ............................................................... 1J-5
Generator Test (Overcharged Battery Check) .... 1J-6
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1J-6
Jump Starting in Case of Emergency.................. 1J-6
Battery Dismounting and Remounting ................ 1J-7
Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension
Inspection and Adjustment ................................ 1J-7
Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Removal
and Installation .................................................. 1J-8
Generator Dismounting and Remounting............ 1J-9
Generator Components..................................... 1J-10
Generator Inspection......................................... 1J-11
Specifications ..................................................... 1J-13
Charging System Specifications ....................... 1J-13
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 1J-13
Exhaust System ....................................... 1K-1
General Description .............................................1K-1
Exhaust System Description ............................... 1K-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............1K-1
Exhaust System Check ....................................... 1K-1
Repair Instructions ..............................................1K-2
Exhaust System Components ............................. 1K-2
Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation ........ 1K-3
Exhaust Pipe and Muffler Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1K-4
Specifications .......................................................1K-5
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................ 1K-5
Page 52 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– CAN communication OBD generic scan tool
displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM
(for A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instruction in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel
system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too
rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304
(Misfire detected)
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit
Service in Section 00” before inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement:
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as
specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if
equipped with A/C), accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor and TP sensor are in good condition
and none of power circuits of these sensors is
shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, combination meter,
keyless start control module (if equipped with keyless
start control system), 4WD control module (if
equipped), TCM (for A/T model) and ABS control
module, is established by CAN (Controller Area
Network). (For more detail of CAN communication for
ECM, refer to “CAN Communication System
Description”). Therefore, handle CAN communication
line with care referring to “Precaution for CAN
Communication System in Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM (Immobilizer model)
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions for DTC TroubleshootingS6RW0D1100003
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read
the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or
pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to
“Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work,
perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm
that the trouble has been corrected.
Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS6RW0D1100004
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of
the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring circuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into the sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are
different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S6RW0D1100005
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of
battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2119 and/or P2135
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal
position (APP) sensor assembly
Page 93 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-43
THROTTLE MOTOR RELAY (ON/OFF)
ON: Throttle actuator (motor) control activated by ECM.
OF: Throttle actuator (motor) control stopped by ECM.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, mph)
It is computed based on pulse signals from front wheel
speed sensor (RH, LH) (for M/T model) or output shaft
speed sensor (VSS) (for A/T model).INJ PULSE WIDTH (FUEL INJECTION PULSE WIDTH,
msec.)
This parameter indicates time of the injector drive (valve
opening) pulse which is output from ECM (but injector
drive time of NO.1 cylinder for multiport fuel injection).
Visual InspectionS6RW0D1104008
Visually check the following parts and systems.
Engine Basic InspectionS6RW0D1104009
This check is very important for troubleshooting when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been found
in “Visual Inspection”.
Follow the flow carefully.Inspection item Reference section
• Engine oil – level, leakage “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
• Engine coolant – level, leakage “Coolant Level Check in Section 1F”
• Fuel – level, leakage“Fuel Lines and Connections Inspection in
Section 0B”
• Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging “Air Cleaner Filter Inspection in Section 0B”
• Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal“Battery Dismounting and Remounting in
Section 1J”
• Water pump belt – tension damage“Accessory Drive Belt Inspection in Section
0B”
• Throttle valve – operating sound“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
• Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend“Vacuum Hose Inspection in Section 1B”
• Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
• Fuses – burning
• Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
• Parts – deformation
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Also check the following items at engine start, if possible
• Malfunction indicator lamp – Operation “Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check”
• Charge warning lamp – Operation “Generator Symptom Diagnosis in Section 1J”
• Engine oil pressure warning lamp – Operation “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
• Engine coolant temp. meter – Operation“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”
• Fuel level meter – Operation “Fuel Level Sensor Inspection in Section 9C”
• Tachometer – Operation
• Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
• Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed?Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2Check battery voltage
Is it 11 V or more?Go to Step 3. Charge or replace
battery.
3Is vehicle equipped with keyless start control system?Go to Step 4. Go to Step 5.
Page 97 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-47
Engine overheatingInoperative thermostat“Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance“Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator“Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade“Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer“Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance“Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system“Radiator Cooling Fan Control System Check”
Dragging brakesCondition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch (for M/T model)Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C” for M/T
model
Blown cylinder head gasket“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Poor gasoline mileageLeaks or loose connection of high-
tension cord“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.)“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Malfunctioning EGR valve“EGR Valve Inspection (If Equipped) in Section
1B”
High idle speedCondition “Improper engine idling or engine
fails to idle”
Poor performance of ECT sensor, MAF
sensor“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”, or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s)“Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Low compression“Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor valve seating“Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Dragging brakesCondition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch (for M/T model)Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C” for M/T
model
Thermostat out of order“Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Improper tire pressure“Tires Description in Section 2D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
leakageBlown cylinder head gasket“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Leaky camshaft oil seals“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D” Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 177 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-127
DTC Troubleshooting
WARNING!
In order to reduce risk of fire and personal injury, this work must be performed in a well ventilated area
and away from any open flames such as gas water heater.
NOTE
Before this troubleshooting is performed, read the precautions for DTC troubleshooting referring to
“Precautions for DTC Troubleshooting”.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed?Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2EVAP canister purge power supply circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch and disconnect connector from
EVAP canister purge valve.
2) Measure voltage between engine ground and “BLK/
RED” wire terminal of EVAP canister purge valve
connector with ignition switch turned ON.
Is it voltage 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 3. “BLK/RED” wire is open
circuit.
3Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “C01-29” terminal of ECM
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity?Go to Step 4. “BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit.
4Wire circuit check
1) Measure voltage between “C01-29” terminal of ECM
connector and vehicle body ground with ignition switch
turned ON.
Is voltage 0 V?Go to Step 5. “BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to other circuit.
5Wire circuit check
1) Connect connector to purge control valve with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and measure voltage between
“C01-29” terminal of ECM connector and vehicle body
ground.
Is it voltage 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 6. “BLU/BLK” wire is open
circuit.
6EVAP canister purge control valve check
1) Check EVAP canister purge control valve referring to
“EVAP Canister Purge Valve Inspection in Section 1B”.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 7. Faulty EVAP canister
purge control valve.
7EVAP canister purge control circuit check
1) With ignition switch turn OFF, measure resistance
between “E01-1/16” terminal and “C01-29” terminal of
ECM connector.
Is resistance below 34
Ω at 20 °C, 68 °F?Faulty ECM. Substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.“BLK/RED” and/or
“BLU/BLK” wire are high
resistance circuit.
Page 273 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-5
Electric Throttle Body System CalibrationS6RW0D1306004
NOTE
If the service described under the
“Precautions of Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1A” is
performed, calibrate electric throttle body
system as follows.
1) If electric throttle body assembly and/or accelerator
pedal position (APP) sensor assembly are replaced,
perform following steps.
a) Disconnect negative cable at battery for 20
seconds or more for the purpose of clearing
calibration data of closed throttle position from
memory in ECM.
b) Connect negative cable to battery.
2) Keep ignition switch at ON position for 5 seconds or
more without running engine.
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection
S6RW0D1306005
1) Check that APP sensor assembly has been mounted
to vehicle body properly (no pinched floor carpet,
etc.).
If mounting is not properly, reinstall APP sensor
assembly properly referring to “Accelerator Pedal
Position (APP) Sensor Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
2) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
3) Turn ON ignition switch and select “Data List” mode
on scan tool.4) Check that accelerator pedal position sensor voltage
varies as the following graph.
If sensor voltage is out of specified value or does not
vary linearly as the following graph, check APP
sensor assembly referring to “Accelerator Pedal
Position (APP) Sensor Assembly Inspection”.
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Removal and Installation
S6RW0D1306006
CAUTION!
• Do not expose APP sensor assembly to
excessive shock like a dropping it. If APP
sensor assembly has been exposed to
excessive shock, it should be replaced.
• Be careful not to expose sensor section of
APP sensor assembly to water.
NOTE
After replacing APP sensor assembly,
perform calibration of throttle valve referring
to “Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration”.
[A]: APP sensor (main) voltage
[B]: APP sensor (sub) voltage
[C]: Voltage
[D]: Idle position of accelerator pedal
[E]: Full depressed position of accelerator pedal
[C]
[D] [E]
3.50 - 4.27 V
1.74 - 2.17 V
0.65 - 0.82 V
0.30 - 0.44 V
[A]
[B]
I7RW01130020-01
Page 275 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-7
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Removal and Installation
S6RW0D1306008
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining
in Section 1F”.
WARNING!
To avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot.
Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure if cap is taken off too soon.
3) Remove air intake pipe.
4) Disconnect connector from ECT sensor (1).
5) Remove ECT sensor from water outlet.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surfaces of ECT sensor and water
outlet.
• Check O-ring for damage and replace, if necessary.
• Tighten ECT sensor (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
ECT sensor (a): 15 N·m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
• Connect connector to ECT sensor securely.
• Refill coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and
Refill in Section 1F”.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection
S6RW0D1306009
Immerse temperature sensing part of ECT sensor (1) in
water (or ice) and measure resistance between sensor
terminals while heating water gradually.
If measured resistance doesn’t show such characteristic
as shown, replace ECT sensor.
1
I2RH0B130008-01
1,(a)
I2RH0B130009-01
I5RW0A130007-01
Page 278 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-10 Engine Electrical Devices:
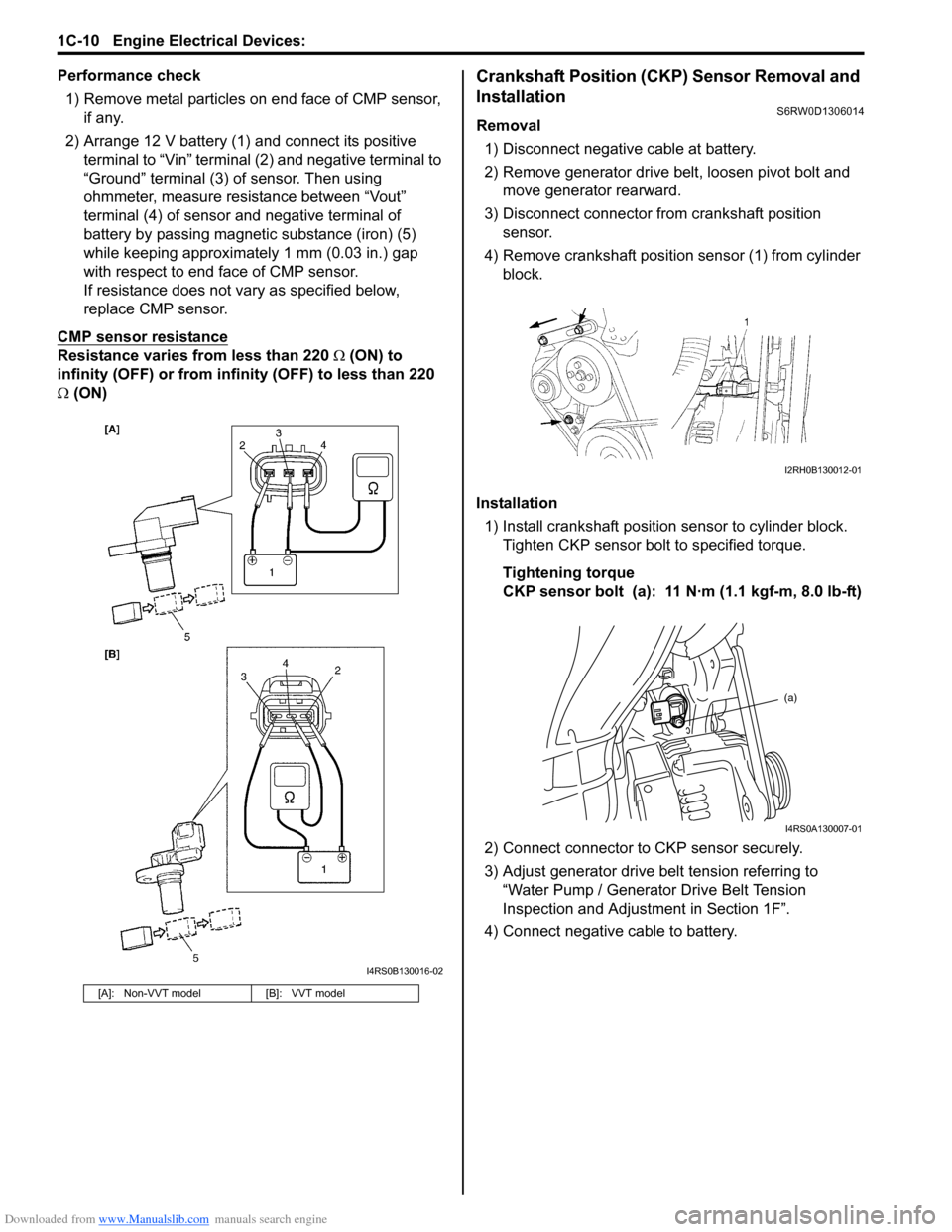
Performance check
1) Remove metal particles on end face of CMP sensor,
if any.
2) Arrange 12 V battery (1) and connect its positive
terminal to “Vin” terminal (2) and negative terminal to
“Ground” terminal (3) of sensor. Then using
ohmmeter, measure resistance between “Vout”
terminal (4) of sensor and negative terminal of
battery by passing magnetic substance (iron) (5)
while keeping approximately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap
with respect to end face of CMP sensor.
If resistance does not vary as specified below,
replace CMP sensor.
CMP sensor resistance
Resistance varies from less than 220 Ω (ON) to
infinity (OFF) or from infinity (OFF) to less than 220
Ω (ON)
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Removal and
Installation
S6RW0D1306014
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove generator drive belt, loosen pivot bolt and
move generator rearward.
3) Disconnect connector from crankshaft position
sensor.
4) Remove crankshaft position sensor (1) from cylinder
block.
Installation
1) Install crankshaft position sensor to cylinder block.
Tighten CKP sensor bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
CKP sensor bolt (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to CKP sensor securely.
3) Adjust generator drive belt tension referring to
“Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension
Inspection and Adjustment in Section 1F”.
4) Connect negative cable to battery.
[A]: Non-VVT model [B]: VVT model
I4RS0B130016-02
I2RH0B130012-01
(a)
I4RS0A130007-01