2006 SUZUKI SWIFT High voltage
[x] Cancel search: High voltagePage 393 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-1
Engine
Ignition System
General Description
Ignition System ConstructionS7RS0B1801001
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below.
• ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the si gnals from the sensors, determines the most suitable
ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primar y coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power unit) in the
ignition coil assembly.
• Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built -in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is induced
in the secondary coil.
• High-tension cords and spark plugs
• CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression stroke,
detects the crank angle and adjusts in itial ignition timing automatically.
• TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, IAT sensor, knock sensor and other sensors / switches
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and No.4
spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). W hen an ignition signal is sent from ECM to the ignitor in
the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that
passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simultaneously. Likewise,
when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the ot her ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3 spark plugs spark
simultaneously.
Page 411 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-1
Engine
Charging System
General Description
Battery DescriptionS7RS0B1A01001
The battery has three major functions in the electrical
system.
• It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
• It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
• It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
Carrier and Hold-Down
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it
will support the battery securely and keep it level. Before
installing the battery, the ba ttery carrier and hold-down
clamp should be clean and free from corrosion and
make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the
hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-
tightened.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific
gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully
charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it
should not be charged until it is warmed.
Sulfation
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in
discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes
converted into a hard, cryst alline substance, which will
not easily turn back to the active material again during
the subsequent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result
as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery
can be revived by very slow charging and may be
restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than
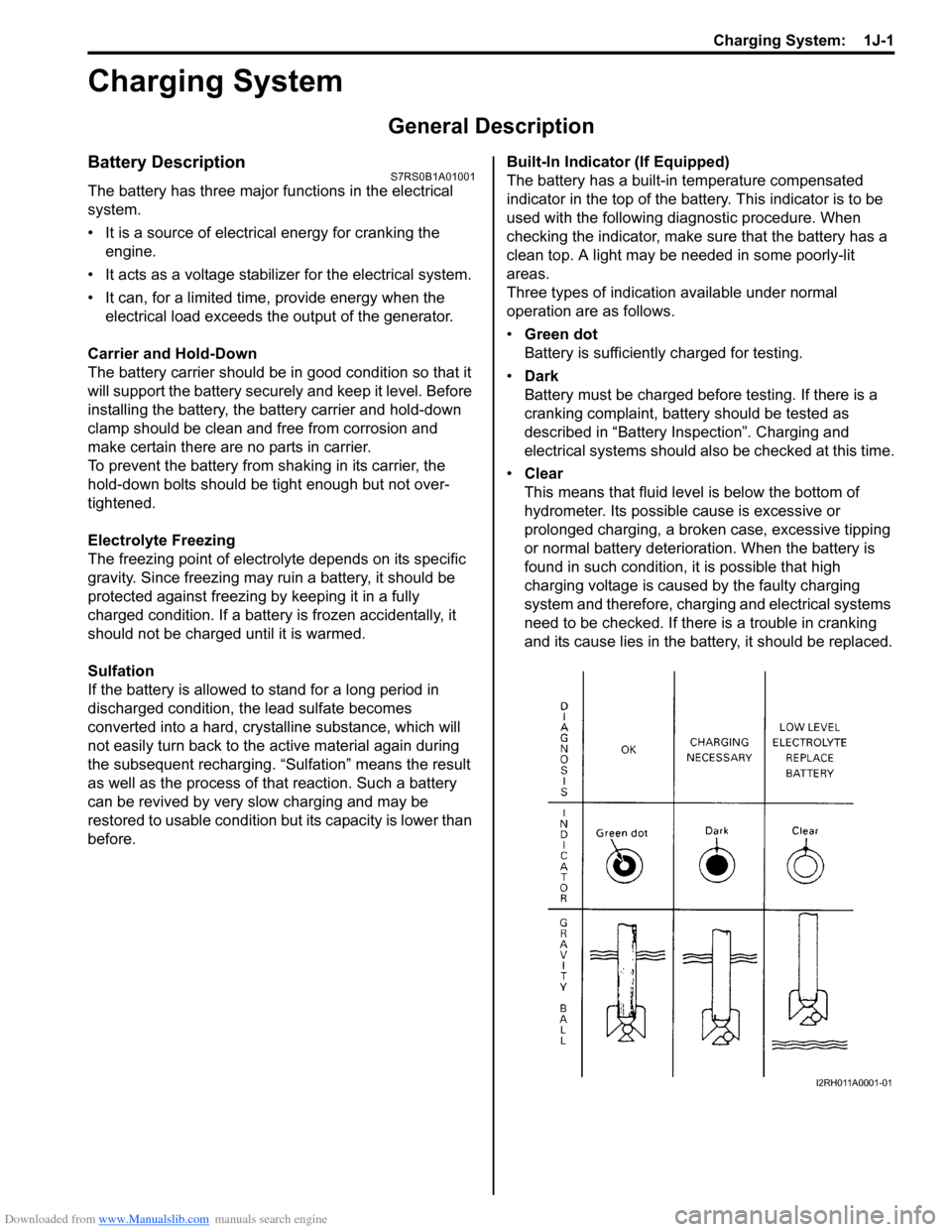
before. Built-In Indicator (If Equipped)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated
indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When
checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Three types of indication available under normal
operation are as follows.
•
Green dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
• Dark
Battery must be charged before testing. If there is a
cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in “Battery Inspection”. Charging and
electrical systems should also be checked at this time.
• Clear
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of
hydrometer. Its possible cause is excessive or
prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive tipping
or normal battery deteriorat ion. When the battery is
found in such condition, it is possible that high
charging voltage is caused by the faulty charging
system and therefore, charging and electrical systems
need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
I2RH011A0001-01
Page 414 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 415 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-5
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04003
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator clear with dark or light yellow dot can be
caused by one or more of the following conditions even
though indicator lamp may be operating normal.
The following procedure also applies to cars with
voltmeter and ammeter.1) Make sure that undercharged condition has not been caused by accessories left on for extended period of
time.
2) Check drive belt for proper tension.
3) If battery defect is suspected, refer to “Battery Description”.
4) Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for tightness and cleanliness, battery cable connections
at battery, starting motor, ignition ground cable and
no “C” terminal circuit at ground.
5) Connect switch (6), load (5), battery (4), voltmeter (3) and ammeter (2) to generator (1) as shown in
figure.
Voltmeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and ground.
Ammeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and battery (+) terminal.
NOTE
Use fully charged battery.
6) Measure current and voltage.
No-Load Check 1) Run engine from idling up to 2000 rpm and read meters.
NOTE
Turn off switches of all accessories (wiper,
heater etc.).
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load
check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
NOTE
Consideration should be taken that voltage
will differ somewhat with regulator case
temperature as shown in figure.
2) Using service wire, ground “C” terminal (1) of
generator.
3) Measure voltage between “B” terminal of generator and body ground.
Voltage: 12.5 – 13.1 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
• If voltage is higher than standard value
If voltage is higher than standard value, check ground
of brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to the
following check.
Load Check 1) Run engine at 2000 rpm and turn on head light and blower motor.
2) Measure current. If measure current is less than 30 A, repair or
replace generator.
IYSQ011A0007-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heat sink temperature ( °C)
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 20
[A]
[B]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0B1A1002-01
I5JB0A1A0011-01
Page 416 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-6 Charging System:
Generator Test (Overcharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04004
1) To determine battery condition, refer to “Battery Description”.
2) If obvious overcharge condition exists as evidenced by excessive spewing of electrolyte, measure
generator “B” terminal voltage at engine 2000 rpm. 3) If measured voltage is higher than upper limit value,
proceed to disassemble generator.
4) Check ground of brushes. If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator. Then check field coil
for grounds and shorts, referring to “Generator
Inspection”.
Repair Instructions
Jump Starting in Case of EmergencyS7RS0B1A06001
CAUTION!
If vehicle is manual transaxle model and has
a catalytic converter, do not push or tow it to
start. Damage to its emission system and/or
to other parts may result.
Both booster and discharged battery should be treated
carefully when using ju mper cables. Follow the
procedure outlined as follows, being careful not to cause
sparks.
WARNING!
• Departure from these conditions or procedure described as follows could
result in:
– Serious personal injury (particularly to eyes) or property damage from such
causes as battery explosion, battery
acid, or electrical burns.
– Damage to electronic components of either vehicle.
• Remove rings, watches, and other jewelry. Wear approved eye protection.
• Be careful so that metal tools or jumper cables do not contact positive battery
terminal (or metal in contact with it) and
any other metal on vehicle, because a
short circuit could occur. • Never expose battery to open flame or
electric spark. Batteries generate gas
which is flammable and explosive.
• Do not allow battery fluid to contact eyes, skin, fabrics, or painted surface as fluid is
a corrosive acid. Flush any contacted area
with water immediately and thoroughly.
• Batteries should always be kept out of reach of children.
• Do not connect negative cable directly to negative terminal of dead battery.
1) Set parking brake and place automatic transaxle in PARK (NEUTRAL on manual transaxle). Turn off
ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line, add distilled water.
3) Attach end of one jumper cable to positive terminal of booster battery and the other end of the same
cable to positive terminal of discharged battery. (Use
12-volt battery only to jump start engine).
4) Attach one end of the remaining negative cable to negative terminal of booster battery, and the other
end to a solid engine ground (such as exhaust
manifold) at least 45 cm (18 in.) away from battery of
vehicle being started.
5) Start engine of vehicle with booster battery and turn off electrical accessories. Then start engine of the
vehicle with discharged battery.
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0 -30 0 20
[C]
[D]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0C1A0001-02
Page 553 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-14
ABS Warning Light Comes ON SteadyS7RS0B4504009
Wiring Diagram
Refer to “ABS Warning Light Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON”.
Circuit Description
Operation (ON/OFF) of ABS wa rning light is controlled by ABS contro l module through lamp driver module in
combination meter.
If the Antilock brake system is in good condition, ABS control module turns ABS warning lig ht ON at the ignition switch
ON, keeps it ON for 2 seconds and then turns it OFF. If an abnormality in the system is detected, ABS warning light is
turned ON continuously by ABS c ontrol module. Also, it is turned ON continuously by la mp driver module when the
connector of ABS control module is disconnected.
Troubleshooting 4 Check CAN communication circuit between combination
meter and ABS control module referring to “DTC U1073:
Control Module Communication Bus Off”.
Is CAN communication circuit in good condition? Go to Step 5.
Repair or replace.
5 1) Remove combination meter wit h ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to “RED/BLK” and “BLK/ ORN” wire of combinat ion meter connector.
3) If OK, turn ON ignition switch and measure voltage at “PPL/RED” wire of combi nation meter connector and
vehicle body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
Repair power supply
circuit for combination
meter.
6 1) Measure resistance between “BLK/ORN” wire of combination meter connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance less than 2
Ω? Replace combination
meter.
“BLK/ORN” circuit open
or high resistance.
Step Action Yes No
Step
Action YesNo
1 1) Perform diagnostic trouble code check.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 2.
2 Are main fuses for ABS pump motor and ABS solenoid in
good condition? Go to Step 3.
Replace fuse and check
circuit for short to
ground.
3 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS control module connector.
3) Check for proper connection to ABS control module connector at terminals “E03-7”, “E03-13” and “E03-26”.
4) If OK then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between terminal “E03-7” and vehicle
body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 4.
“GRN/ORN” circuit
open.
4 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position. 2) Check for proper connection to ABS control module connector at terminals “E03-1” and “E03-14”.
3) If OK then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between each terminal of “E03-1”,
“E03-14” and vehicle body ground.
Are they 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 5.
“WHT/RED” and/or
“WHT/BLU” circuit
open.
Page 556 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4E-17 ABS:
5 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.2) Check for proper connection to ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector at terminals “E03-13” and
“E03-26”.
3) If OK, measure resistance between each terminal of “E03-13”, “E03-26” and vehicle body ground.
Are resistance less than 2
Ω? Go to Step 6. Ground circuit for ABS
hydraulic unit / control
module open or high
resistance.
6 1) Check if communication is possible by trying communication with other controller (ECM, BCM or
SDM).
Is it possible to commun icate with other controller? Go to Step 7. Repair open in common
section of serial data
circuit (“PPL/WHT” wire
circuit) used by all
controllers or short to
ground or power circuit
which has occurred
somewhere in serial
data circuit (“PPL/WHT”
wire circuit).
7 1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
2) Measure voltage between terminal B of data link connector and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 12 V? Go to step 8. Terminal B circuit open
or shorted to ground.
8 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position. 2) Measure resistance between the following terminals;• Terminal G of data link connector and vehicle body ground.
• Terminal G1 of data link connector and vehicle body ground.
Is each resistance 1
Ω or less? Go to step 9. Terminal G and/or G1
circuit open or high
resistance.
9 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position. 2) Check proper connection at “E03-5” (“PPL/WHT” wire) terminal for serial data circuit.
3) If OK, then check resistance between “E03-5” (“PPL/ WHT” wire) terminal and “PPL/WHT” wire terminal (2) for
serial data circuit in DLC (1).
Is resistance 1
Ω or less? Substitute a known-
good ABS hydraulic unit
/ control module and
recheck.
Repair high resistance
or open in “PPL/WHT”
wire circuit for anti lock
brake system.
Step Action Yes No
I4RS0A450013-02
Page 560 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4E-21 ABS:
DTC C1057: Power Source CircuitS7RS0B4504014
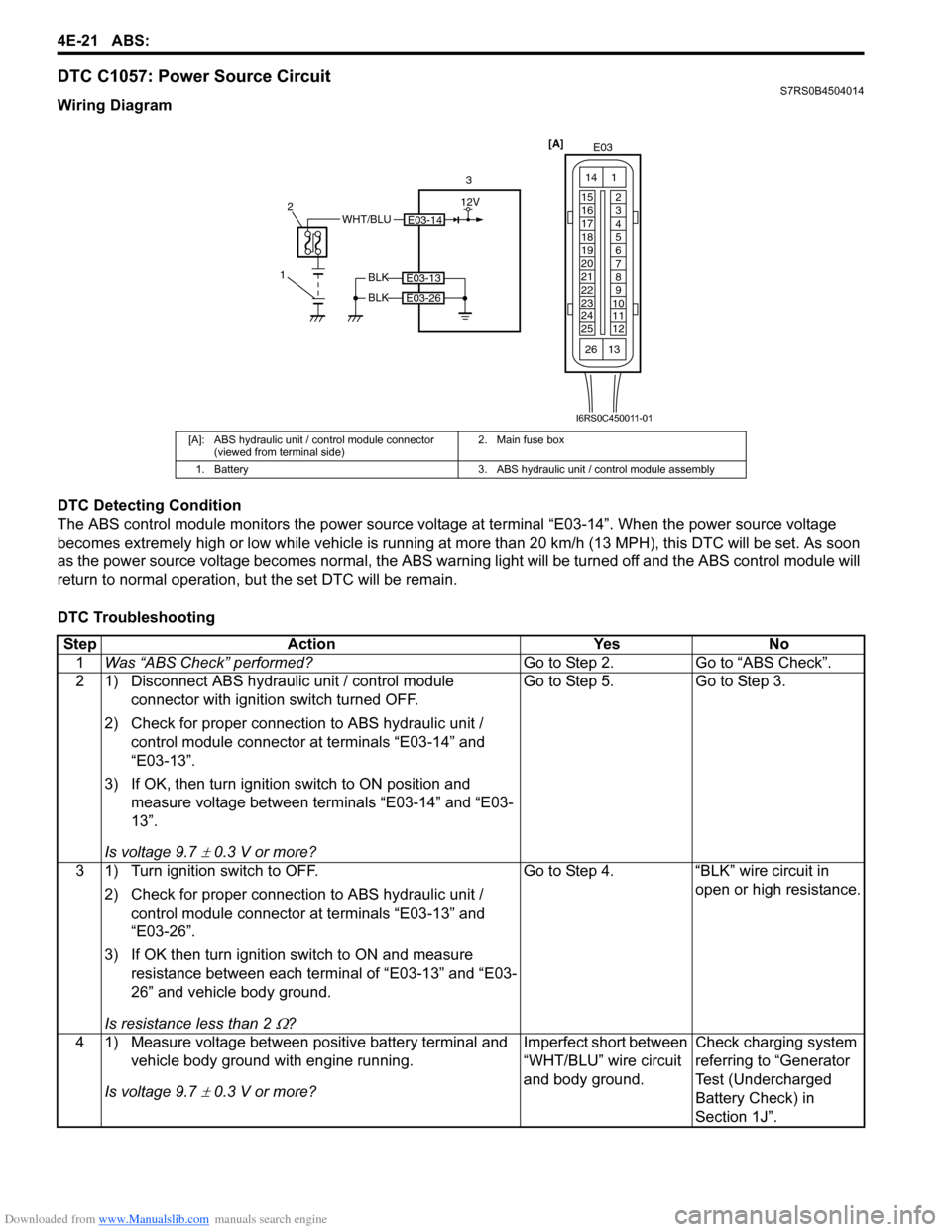
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition
The ABS control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “E03-14”. When the power source voltage
becomes extremely high or low while vehicle is running at more than 20 km/h (13 MPH), this DTC will be set. As soon
as the power source volta ge becomes normal, the ABS warning light will be turned off and the ABS control module will
return to normal operation, bu t the set DTC will be remain.
DTC Troubleshooting
[A]: ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector (viewed from terminal side) 2. Main fuse box
1. Battery 3. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly
E03-14WHT/BLU
1 2
3
BLK
BLK
E03-13
E03-26
[A]
E03
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
13
14
26
12V
I6RS0C450011-01
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “ABS Check” performed? Go to Step 2.Go to “ABS Check”.
2 1) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector at terminals “E03-14” and
“E03-13”.
3) If OK, then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between terminals “E03-14” and “E03-
13”.
Is voltage 9.7
± 0.3 V or more? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 3.
3 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF. 2) Check for proper connection to ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector at terminals “E03-13” and
“E03-26”.
3) If OK then turn ignition switch to ON and measure resistance between each terminal of “E03-13” and “E03-
26” and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance less than 2
Ω? Go to Step 4. “BLK” wire circuit in
open or high resistance.
4 1) Measure voltage between positive battery terminal and vehicle body ground with engine running.
Is voltage 9.7
± 0.3 V or more? Imperfect short between
“WHT/BLU” wire circuit
and body ground.
Check charging system
referring to “Generator
Test (Undercharged
Battery Check) in
Section 1J”.