2006 SUZUKI SWIFT APP SENSOR
[x] Cancel search: APP SENSORPage 549 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-10
Problem symptom confirmation
Check if what the customer claimed in “Customer
Questionnaire” is actually found in the vehicle and if that
symptom is found, whether it is identified as a failure.
(This step should be shared with the customer if
possible.) Check warning lights related to brake system
referring to “EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light)
Check” and “ABS Warning Light Check”.
DTC check, record and clearance
Perform “DTC Check” proced ure, record it and then
clear it referring to “DTC Clearance”.
Recheck DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
When DTC which is recorded at DTC check procedure is
detected again after performi ng DTC clearance, go to
“Step 4: ABS Check: ” to proceed the diagnosis.
When DTC which is recorded at DTC check procedure is
not indicated anymore after performing DTC clearance,
ABS control module does not perform the system
diagnosis, or temporary abnormality may occur,
therefore go to “Step 2: Driving Test: ” to proceed the
diagnosis.
Step 2: Driving Test
Test drive the vehicle at 40 km/h for more than a minute
and check if any trouble symptom (such as abnormal
lighting of ABS warn ing light) exists.
If the malfunction DTC is co nfirmed again at ignition
switch ON, driving test as described is not necessary.
Proceed to Step 3.
Step 3: DTC Check
Recheck DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Step 4: ABS Check
According to ABS Check for the DTC confirmation in
Step 3, locate the cause of the trouble, namely in a
sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator
assembly or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 5: Brakes Diagnosis
Check the parts or system suspected as a possible
cause referring to “Brakes Symptom Diagnosis in
Section 4A” and based on symptoms appearing on the
vehicle (symptom obtained through Steps 1 and 2 and
repair or replace faulty parts, if any).
Step 6: Check for Intermittent Problem
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, con nector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of trouble code recorded in Step 1
to 3.
Step 7: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
ABS is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is related to the malfunction DTC, clear
the DTC once referring to “DTC Clearance” and perform
test driving and confirm that no DTC is indicated.ABS Warning Light CheckS7RS0B4504002
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check that ABS warning light (1) comes ON for
about 2 seconds and then goes off.
If any faulty condition is found, advance to “ABS
Warning Light Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch
ON” or “ABS Warning Light Comes ON Steady”.
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light)
Check
S7RS0B4504003
NOTE
Perform this check on a level place.
1) Turn ignition switch ON with parking brake applied.
2) Check that EBD warning lig ht (brake warning light)
(1) is turned ON.
3) Release parking brake with ignition switch ON and check that EBD warning lig ht (brake warning light)
goes off.
If it doesn’t go off, go to “EBD Warning Light (Brake
Warning Light) Comes ON Steady”.
11
I4RS0A450007-01
BRAKE
1
I4RS0A450008-01
Page 551 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-12
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B4504006
WARNING!
When performing a driving test, select a safe
place where there is neither any traffic nor
any traffic accident possibility and be very
careful during testing to avoid occurrence of
an accident.
After repair or replace malfunction part(s), clear all DTCs
by performing the following procedure or using SUZUKI
scan tool.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector in the same manner as when making this connection
for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Erase DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan tool operator’s manual for
further derails.
NOTE
For DTC C 1021, C1022, C1025, C1026, C1031,
C1032, C1035, C1036 and C1061, confirm that
ABS warning light turns off after performing
Step 2 of “Test Driving” under “ABS Check”,
and then clear the DTCs.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
5) Perform “Driving Test” (S tep 2 of “ABS Check”) and
“DTC Check” and confirm that NO DTC is displayed
on scan tool.
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B4504007
The parameter data below are values measured with the
scan tool when the normally operating vehicle is under
the following conditions. When taking measurements for
comparison by using the scan tool, be sure to check that
the vehicle is under the following conditions.
• Apply parking brake and block wheels.
• Ignition switch ON.
• Turn OFF air conditioner (if equipped).
• Apply no load to power steering (if equipped). (Don’t turn it)
• Turn OFF all electric loads (except ignition).
• No DTC.
• ABS is not operated. (N ormal braking operation)
Scan Tool Data Definition
Battery Volt (V): Battery Voltage is an analog input
signal read by the ABS control module. Certain ABS
control module function s will be modified if the
battery voltage falls below or rises above
programmed thresholds.
Pump Motor Driver (V): This parameter indicates the
operational condition of the pump motor driver
(transistor).
RF Wheel Speed, LF Wheel Speed, RR Wheel Speed and LF Wheel Speed (km/h, MPH): Wheel speed
is an ABS control module inte rnal parameter. It is
computed by reference pulses from the wheel speed
sensor.
Brake Switch (ON, OFF): This switch signal informs
the ABS control modu le whether the brake is active
or not.
Scan Tool
Data Standards Condition
Battery
Voltage 10.0 – 18.0 V —
Pump Motor
Driver 0.0 V —
RF Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
LF Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
RR Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
LR Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
Brake Switch ONBrake pedal
depressed
OFF Brake pedal released
Page 557 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-18
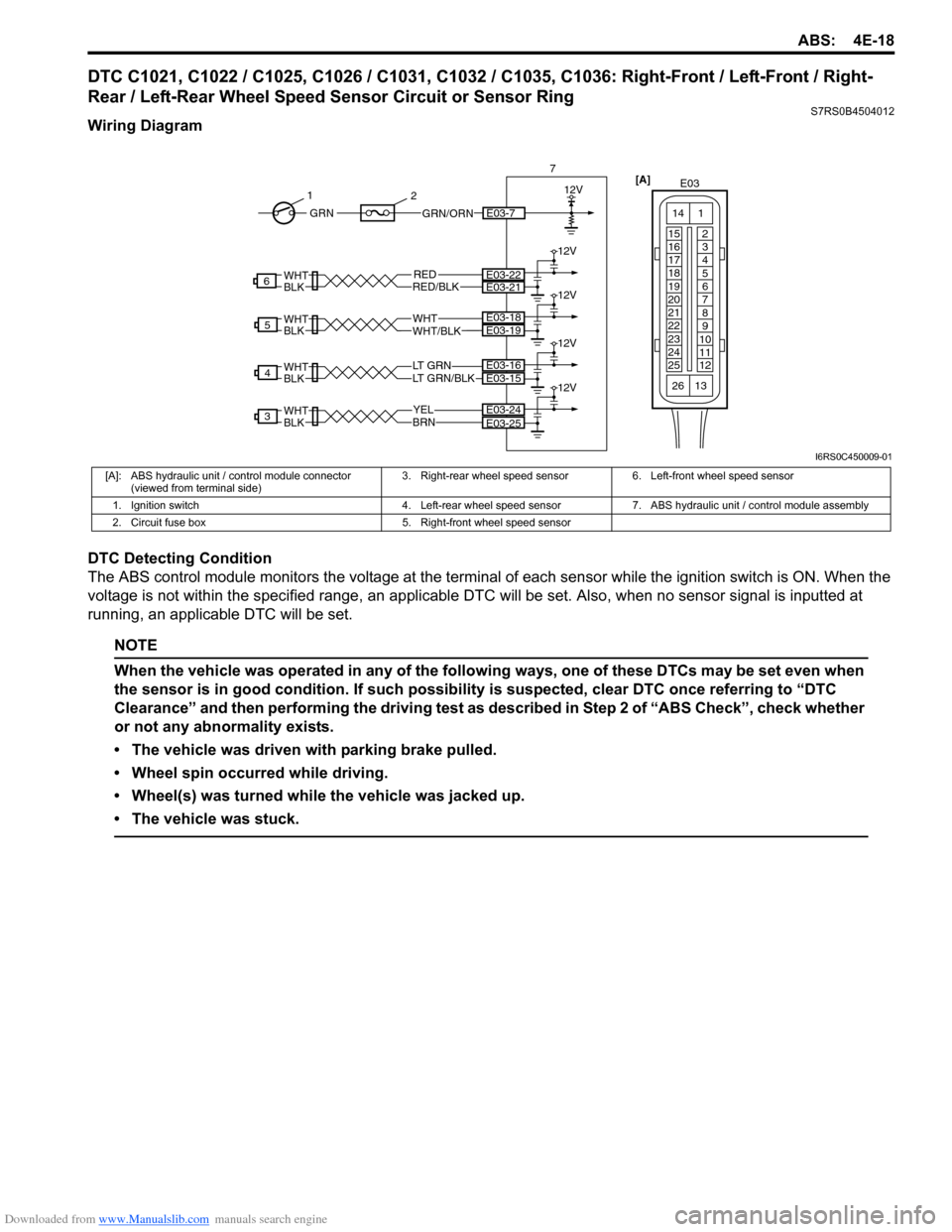
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Right-Front / Left-Front / Right-
Rear / Left-Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit or Sensor Ring
S7RS0B4504012
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition
The ABS control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of each sensor while the ignition swit ch is ON. When the
voltage is not within the specified range, an applicable DTC will be set. Also, when no sensor signal is inputted at
running, an applicable DTC will be set.
NOTE
When the vehicle was operated in any of the following ways, one of these DTCs may be set even when
the sensor is in good condition. If such possibility is suspected, clear DTC once referring to “DTC
Clearance” and then performing the driving test as described in Step 2 of “ABS Check”, check whether
or not any abnormality exists.
• The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
• Wheel spin occurred while driving.
• Wheel(s) was turned while the vehicle was jacked up.
• The vehicle was stuck.
YELBRN
3E03-24
LT GRN/BLKLT GRN
4
WHTWHT/BLK
5
RED
WHTBLK
WHTBLK
WHTBLK
WHTBLKRED/BLK
6
E03-25
E03-15E03-16
E03-19E03-18
E03-22E03-21
12V
12V
12V
12V
12V
7
GRN/ORNE03-7GRN
1
2
[A]
E03
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
13
14
26
I6RS0C450009-01
[A]: ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector
(viewed from terminal side) 3. Right-rear wheel speed sensor 6. Left-front wheel speed sensor
1. Ignition switch 4. Left-rear wheel speed sensor 7. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly
2. Circuit fuse box 5. Right-front wheel speed sensor
Page 558 of 1496
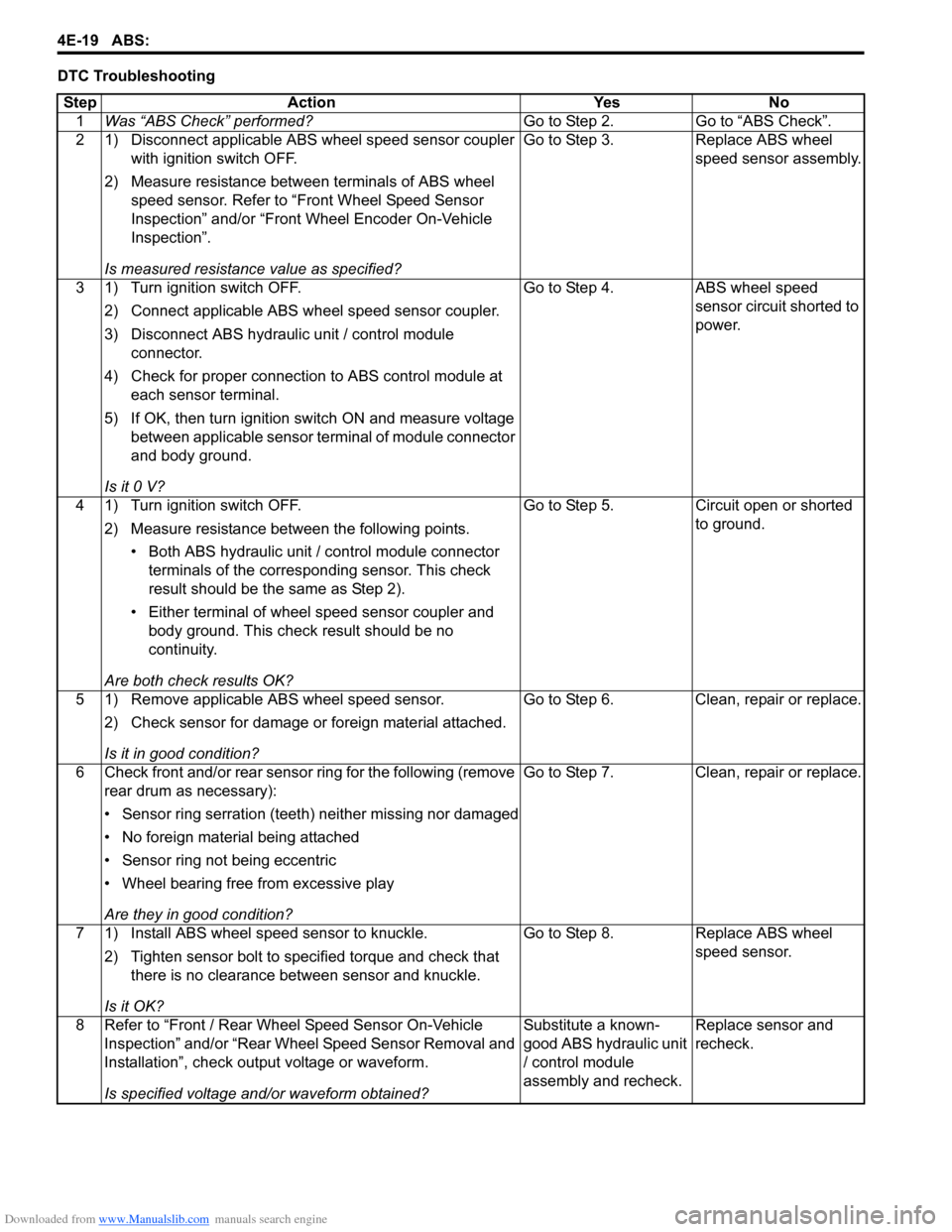
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4E-19 ABS:
DTC TroubleshootingStep Action Yes No 1 Was “ABS Check” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ABS Check”.
2 1) Disconnect applicable ABS wheel speed sensor coupler with ignition switch OFF.
2) Measure resistance betw een terminals of ABS wheel
speed sensor. Refer to “Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Inspection” and/or “Front Wheel Encoder On-Vehicle
Inspection”.
Is measured resistance value as specified? Go to Step 3. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor assembly.
3 1) Turn ignition switch OFF. 2) Connect applicable ABS wh eel speed sensor coupler.
3) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector.
4) Check for proper connection to ABS control module at each sensor terminal.
5) If OK, then turn ignition switch ON and measure voltage between applicable sensor terminal of module connector
and body ground.
Is it 0 V? Go to Step 4. ABS wheel speed
sensor circuit shorted to
power.
4 1) Turn ignition switch OFF. 2) Measure resistance between the following points.• Both ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector terminals of the correspo nding sensor. This check
result should be the same as Step 2).
• Either terminal of wheel speed sensor coupler and body ground. This check result should be no
continuity.
Are both check results OK? Go to Step 5. Circuit open or shorted
to ground.
5 1) Remove applicable ABS wheel speed sensor. 2) Check sensor for damage or foreign material attached.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 6. Clean, repair or replace.
6 Check front and/or rear sensor ring for the following (remove rear drum as necessary):
• Sensor ring serration (teeth) neither missing nor damaged
• No foreign material being attached
• Sensor ring not being eccentric
• Wheel bearing free from excessive play
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 7. Clean, repair or replace.
7 1) Install ABS wheel speed sensor to knuckle. 2) Tighten sensor bolt to specified torque and check that there is no clearance between sensor and knuckle.
Is it OK? Go to Step 8. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor.
8 Refer to “Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection” and/or “Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and
Installation”, check output voltage or waveform.
Is specified voltage and/or waveform obtained? Substitute a known-
good ABS hydraulic unit
/ control module
assembly and recheck.
Replace sensor and
recheck.
Page 576 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-2 Electronic Stability Program:
Perform sensor calibration according to “Sensor Calibration”.
Precautions in Speedometer Test or Other TestsS7RS0B4600005
When performing speedometer or other tests using speedometer tester or chassis dynamometer, ESP® function must
be deactivated by ESP ® OFF switch or using SUZUKI scan to ol to complete the tests correctly.
When using SUZUKI scan tool, set to the “MISC. TEST” mode to stop the ESP ® function. Refer to SUZUKI scan tool
operator's manual for further details.
General Description
Electronic Stability Program DescriptionS7RS0B4601006
Electronic Stability Program (ESP ®) is an auxiliary function to enable the vehicle to av oid a danger safely while the
vehicle is running, stopping or turning.
Electronic Stability Program (ESP ®) consists of following functions.
ESP ® is a registered trademark of Daimler Chrysler AG.
Antilock Brake System (ABS)
This system prevents tire locking which may occur when br ake is applied suddenly or on slippery roads. With this
function, as the vehicle body is kept in the stable state an d tires unlocked, the driver can avoid any obstacle by turning
the steering wheel.
Electronic Brake force Distribution (EBD)
This function distributes braking force of front and rear wheels properly according to the vehicle load condition.
With this function, the braking force of the front and rear wheels is controlled for the optimum effect to secure the
maximum braking force regardless of the loadage.
Traction Control System (TCS)
This system controls the engine and brake to prevent the dr iving wheels from spinning at the time of starting and
accelerating. Particularly, this fu nction is helpful for safe driving on muddy or icy roads. When ESP ® control module
detects wheel spinning using information from the yaw rate sensor and wheel speed sensor, it lower the engine torque
by closing the electronic controlled thro ttle and controlling ignition. At the same time, brake is applied to the spinning
tire.
Stability Control
This function controls the vehicle body in the stable state by controlling the engine and braking so as to prevent the
vehicle from over-steering or under-steering while turning.
When under-steering occurs, this function lowers the engine torque and applies brake to the inner rear wheel in the
vehicle forward direction so as to pr event the vehicle from moving outward.
When over-steering occurs, this function applies brake to the outer front wheel in the vehicle forward direction so as to
prevent the vehicle from moving inward. Sensor Procedures required calibration
Steering angle sensor • Power is not su pplied to steering angle sensor. (battery, fuse and/or connector is
removed.)
• Steering angle sensor is replaced.
• Power is not supplied to ESP ® control module. (battery, fuse and/or connector is
removed.)
• ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is replaced.
Master cylinder pressure sensor • ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is removed or replaced.
Yaw rate / G sensor assembly • Yaw rate / G sensor assembly is removed or replaced.
• ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is replaced.
Page 578 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-4 Electronic Stability Program:
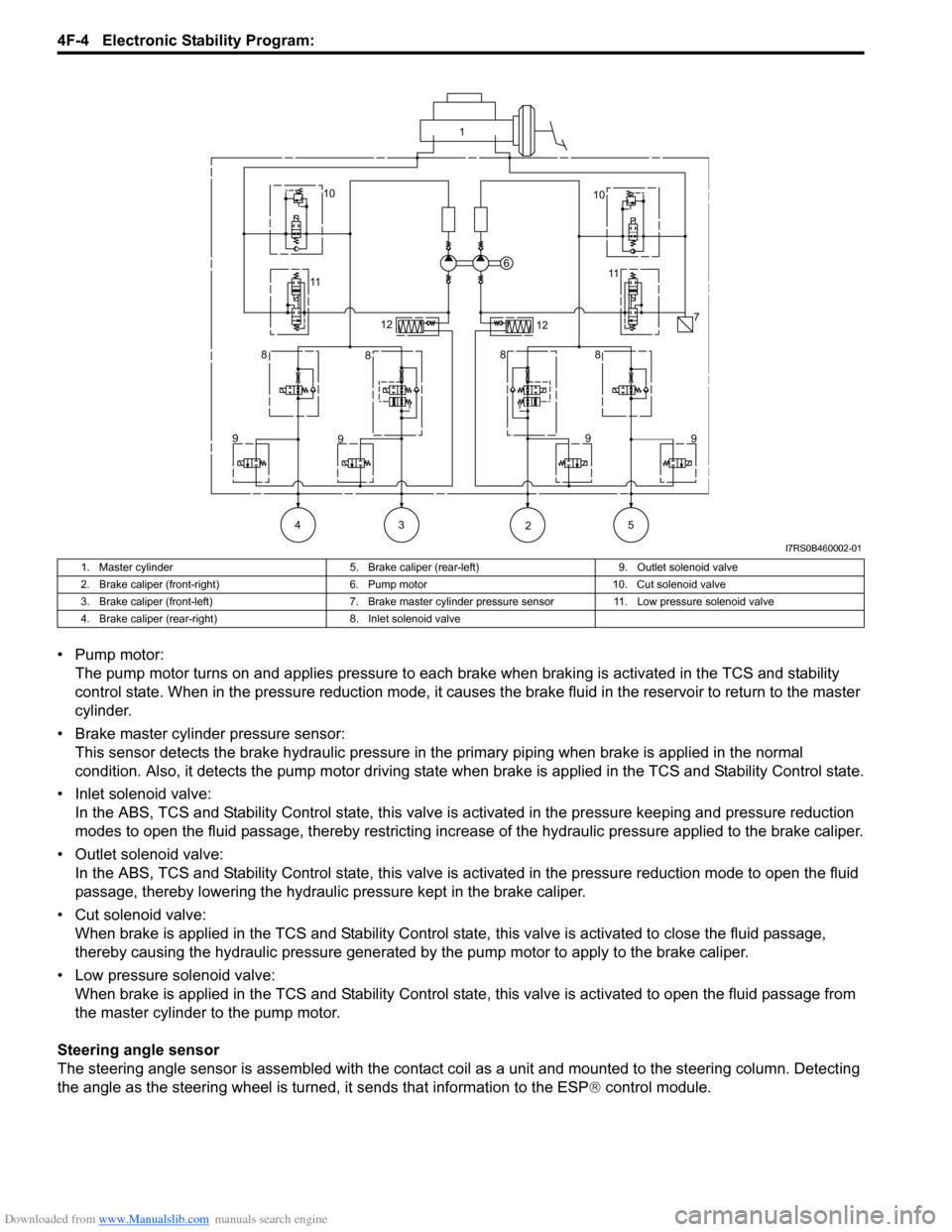
• Pump motor:The pump motor turns on and applies pressure to each brake when braking is activated in the TCS and stability
control state. When in the pressure reduction mode, it causes the brake fluid in the reservoir to return to the master
cylinder.
• Brake master cylinder pressure sensor: This sensor detects the brake hydraulic pressure in th e primary piping when brake is applied in the normal
condition. Also, it detects the pump motor driving state wh en brake is applied in the TCS and Stability Control state.
• Inlet solenoid valve: In the ABS, TCS and Stability Control stat e, this valve is activated in the pressure keeping and pressure reduction
modes to open the fluid passage, thereby restricting increase of the hydraulic pressure applied to the brake caliper.
• Outlet solenoid valve: In the ABS, TCS and Stability Control state, this valve is activated in the pressure reduction mode to open the fluid
passage, thereby lowering the hydraulic pressure kept in the brake caliper.
• Cut solenoid valve: When brake is applied in the TCS and Stability Control state, this valve is activated to close the fluid passage,
thereby causing the hydraulic pressure generated by the pump motor to apply to the brake caliper.
• Low pressure solenoid valve: When brake is applied in the TCS and Stab ility Control state, this valve is activated to open the fluid passage from
the master cylinder to the pump motor.
Steering angle sensor
The steering angle sensor is assembled with the contact co il as a unit and mounted to the steering column. Detecting
the angle as the steering wheel is turned, it sends that information to the ESP ® control module.
1
10 10
11 11
6
7
12 12
8 8 88
9 9 9
9
43 5 2
I7RS0B460002-01
1. Master cylinder 5. Brake caliper (rear-left)9. Outlet solenoid valve
2. Brake caliper (front-right) 6. Pump motor10. Cut solenoid valve
3. Brake caliper (front-left) 7. Brake master cylinder pressure sensor 11. Low pressure solenoid valve
4. Brake caliper (rear-right) 8. Inlet solenoid valve
Page 588 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-14 Electronic Stability Program:
Step 2: Driving Test
Test the vehicle at 40 km/h for more than a minute including left and right turns and check if any trouble symptom
(such as ESP ® warning lamp and/or ABS warning lamp) exists.
If the malfunction DTC is confirmed at ignition switch ON, proceed to Step 3.
If the malfunction DTC is not confirmed at ignition switch ON, proceed to Step 6.
Step 3: DTC Check
Recheck DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Step 4: ESP ® Check
According to ESP ® Check for the DTC confirmation in Step 3, locate the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor,
switch, wire harness, connector, actuator assembly or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 5: Brakes Diagnosis
Check the parts or system suspected as a possible cause referring to “Brakes Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A” and
based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptom obtain ed through Steps 1 and 2 and repair or replace faulty
parts, if any).
Step 6: Intermittent Problem Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section 00” and related circuit of trouble code recorded in Step 1 to 3.
Step 7: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the ESP ® is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has been
repaired is related to the malfunction DTC, clear the DTC once referrin g to “DTC Clearance” and perform test driving
and confirm that no DTC is indicated.
ESP ® Warning lamp CheckS7RS0B4604022
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check that ESP ® warning lamp (1) comes ON for
about 2 seconds and then goes off.
If any faulty condition is found, advance to “ESP ®
Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch
ON” or “ESP ® Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady”.
ABS Warning Lamp CheckS7RS0B4604046
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check that ABS warning lamp (1) comes ON for
about 2 seconds and then goes off.
If any faulty condition is found, advance to “ABS
Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch
ON” or “ABS Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady”.
1
I6RS0B460009-01
11
I4RS0A450007-01
Page 589 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-15
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp)
Check
S7RS0B4604047
NOTE
Perform this check on a level place.
1) Turn ignition switch ON with parking brake applied.
2) Check that EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
(1) is turned ON.
3) Release parking brake with ignition switch ON and check that EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
goes off.
If it doesn't go off, go to “EBD Warning Lamp (Brake
Warning Lamp) Comes ON Steady”.
DTC CheckS7RS0B4604004
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (1).
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Read DTC according to instructions displayed on
SUZUKI scan tool and print it or write it down. Refer
to SUZUKI scan tool operator’s manual for further
details.
NOTE
If SUZUKI scan tool can not communicate
ESP® control module, perform “Serial Data
Link Circuit Check”.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from DLC.
DTC TableS7RS0B4604005
CAUTION!
Be sure to perform “Electronic Stability Program System Check” before starting diagnosis.
BRAKE
1
I4RS0A450008-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
DTC (displayed
on SUZUKI scan tool) Diagnostic Items
Detecting condition (DTC will
beset when detecting) ABS
warning lamp EBD
warning lamp ESP
®
warning lamp
NO DTC Normal — — — —
�) C1016 Stop lamp switch failure Vehicle behavior and stop lamp
switch signal is disagreed for
specified time.———
�) C1017 Lateral G sensor range /
performance Lateral G sensor signal is out of
specified range.
——
�{
�) C1018 Brake fluid level switch
failure • Brake fluid level is too low.
• Input signal of brake fluid level
switch to BCM is low level. ——
�{
�) C1020 Master cylinder pressure
sensor power supply failure Power supply volt
age to master
cylinder pressure sensor in ESP ®
hydraulic unit / control module
assembly is out of specification. ——
�{
�) C1021 Right-front wheel speed
sensor circuit failure Wheel sensor signal is out of
specified range.
�{
*1 �{