2006 SKODA ROOMSTER fuel consumption
[x] Cancel search: fuel consumptionPage 191 of 274
Driving and the Environment
190
Avoid driving short distances
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel
consumption.
– Avoid driving a distance of no more than 4 km if the engine is
cold.
The engine and catalytic converter must first have reached their optimal
operating temperature in order to effectively reduce fuel consumption
and pollutant emissions.
The cold engine vehicle consumes approx. 15 - 20 litres/100 km of fuel
immediately after starting. Fuel consumption drops to 10 litres/100 km
after just 1 kilometre. The engine reaches its operating temperature
(outside temperature and engine dependent) only after about 4 to 10 kilo-
metres and the fuel consumption then stabilizes. You should therefore
avoid driving short distances whenever possible. An important factor in this connection is also the
ambient temperature.
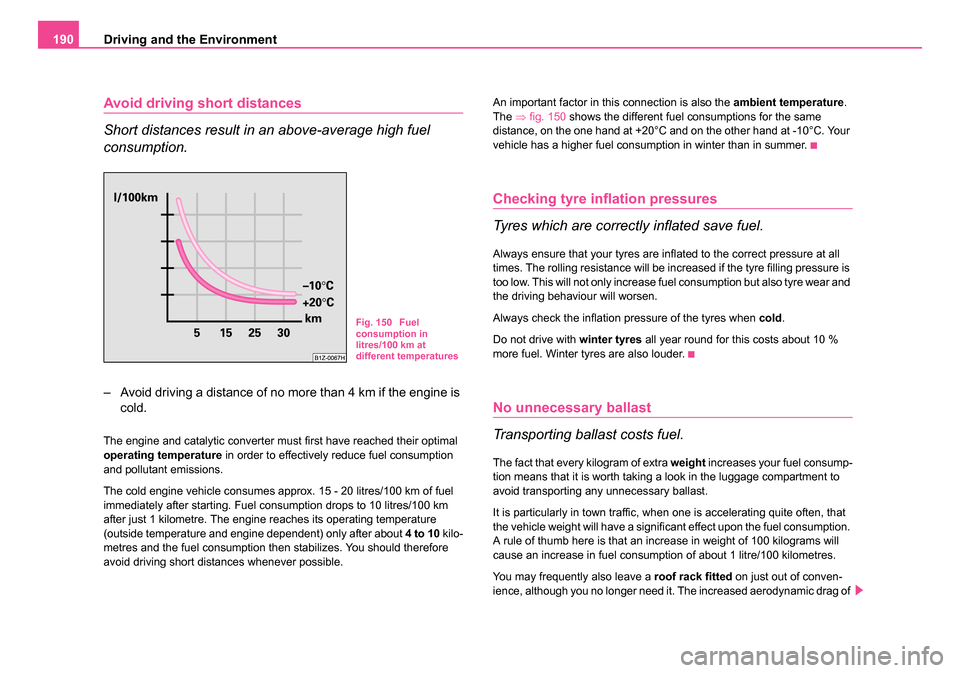
The ⇒fig. 150 shows the different fuel consumptions for the same
distance, on the one hand at +20°C and on the other hand at -10°C. Your
vehicle has a higher fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressures
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure that your tyres are inflated to the correct pressure at all
times. The rolling resistance will be increased if the tyre filling pressure is
too low. This will not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and
the driving behaviour will worsen.
Always check the inflation pressure of the tyres when cold.
Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 %
more fuel. Winter tyres are also louder.
No unnecessary ballast
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consump-
tion means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to
avoid transporting any unnecessary ballast.
It is particularly in town traffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that
the vehicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption.
A rule of thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will
cause an increase in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted on just out of conven-
ience, although you no longer need it. The increased aerodynamic drag of
Fig. 150 Fuel
consumption in
litres/100 km at
different temperatures
NKO 20 A05.book Page 190 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 192 of 274

Driving and the Environment191
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
your vehicle causes it to use about 1 l more fuel than normal at a speed
of 100 - 120 km/h, even when you are not carrying a load on the roof.
Saving electricity
Generating electricity costs fuel.
– Switch off electrical components as soon as you no longer
need them.
When the engine is running, the alternator generates and supplies elec-
trical power. The greater the load on the alternator as a result of having a
large number of electrical components switched on, the more fuel will be
consumed for operating the alternator.
Keeping a log of your fuel consumption
If you really wish to keep a close check on your fuel consumption, it is
best to enter the figures in a logbook. This does not take much time but is
a very worthwhile exercise. It enables you to detect any change (positive
and negative) at an early stage and to take any appropriate action.
If you find that your fuel consumption is too high, you should reflect on
how, where and in what conditions you have driven the vehicle since you
last refuelled.
Environmental compatibility
Environmental protection has played a major role in the design, selection
of materials and manufacture of your new Škoda. Particular emphasis has
been paid to a number of aspects, including:
Design measures
•joints designed to be easily detached
•simplified disassembly due to the modular structure system
•improved purity of different classes of materials
•identification of all plastic parts in accordance with VDA Recommen-
dation 260
•reduced fuel consumption and exhaust emission CO2
•minimum fuel leakage during accidents
•reduced noise
Choice of materials
•extensive use of recyclable material
•air conditioning filled with CFC-free refrigerant
•no cadmium
•no asbestos
•reduction in the “vaporisation” of plastics
Manufacture
•solvent-free cavity protection
•solvent-free protection of the vehicle for transportation from the
production plant to the customer
•the use of solvent-free adhesives
•no CFCs used in the production process
•without use of mercury
•use of water-soluble paints
NKO 20 A05.book Page 191 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 206 of 274

Fuel205
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Fuel
Petrol
Grades of petrol
There are various grades of petrol. Please read the brochure “Technical
Data” in order to know which grade of petrol your vehicle requires. You will
also find the same information affixed to the inside of the fuel filler flap of
your vehicle ⇒page 207, fig. 152 .
A distinction is made between unleaded and leaded petrol. All Škoda vehi-
cles with petrol engines are equipped with a catalytic converter and must
therefore be only driven with unleaded petrol. Unleaded petrol complies
with the standard DIN EN 228 .
The individual grades of petrol are distinguished by their octane number
(RON). Please adopt the following procedure if the grade of petrol which
you normally use is not be available in exceptional circumstances:
•Engines which need unleaded premium petrol 95 RON can also be
run on unleaded regular petrol 91 RON. This does, however, result in a
slight loss in performance.
•Engines which need unleaded premium plus petrol 98 RON can
also be run on unleaded regular petrol 95 RON. This does, however, result
in a slight loss in performance. You can in exceptional circumstances
also use unleaded regular petrol of 91 RON in the event that neither
unleaded premium petrol of 98 RON nor 95 RON is available. Refuel as
soon as possible with unleaded premium plus of 98 RON or unleaded
premium petrol of 95 RON.
If, in an emergency, the only fuel available is one which has a lower octane
number than that required by the engine then only drive at medium engine
speeds and lower engine loadings. You can make unlimited use of fuel which has a higher octane number
than that required by the engine. There will, however, be no advantages
gained by this in terms of engine performance and fuel consumption!
The handling, performance and life of your engine are determined to a
significant extent by the quality of the fuel. Do not use any petrol additives.
Use a fuel complying with the standard.
You can find further information on refuelling
⇒page 207.
Caution
•Filling the tank even only once with leaded petrol will result in the cata-
lytic converter being destroyed.
•Operating the engine with petrol of a low octane number than that
required can result in engine damage at high revolutions or severe engine
loading.
Diesel
Grades of diesel
Grades of diesel fuel
Your vehicle can be driven with the following grades of diesel fuel:
�„Diesel fuel with a cetane number of at least CN 49 (the cetane number
CN is a measure of the ignition performance of the diesel fuel). Diesel fuel
must comply with the DIN EN 590.
NKO 20 A05.book Page 205 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 207 of 274

Fuel
206
�„Biofuel (RME rape oil methyl ester fuel) must comply with the DIN
EN 14 214 . Please refer to the following guidelines ⇒page 206,
“Biofuel*”.
�„Diesel fuel mixture according to standard CSN 65 6508 from
02/2003 contains diesel fuel according to standard DINEN590 and a
concentration of biofuel (rape oil methyl ester) according to standard
DIN EN 14 214 in the following two concentrations:
�„5% share of biofuel RME according to the standard DIN EN 14 214
- Denomination SMN 5,
�„30% share of biofuel RME according to the standard
DIN EN 14 214 - Denomination SMN 30.
Fuel additives
You must not use fuel additives, so-called “flow improvers” (petrol and
similar products) in diesel fuel.
If the quality of the diesel fuel is poor, it is then necessary to drain the fuel
filter more often than stated in the Service schedule.
You can find information on refuelling ⇒page 207, “Refuelling”.
Caution
•Use a fuel complying with the standard. Filling the tank even only once,
which does not comply with the standard, can result in damage to the fuel
system.
•Water which has collected in the fuel filter can result in engine
problems.
Biofuel*
Biofuel (methyl ester from rape oil) is manufactured from vegetable oil by
means of a chemical process. Biofuel does not contain sulphur. This means that no sulphur dioxide
(SO
2) is produced when it is burnt.
The exhaust gases contain less
•carbon monoxide (CO),
•hydrocarbons (HC),
•particles (soot)
than when operating with conventional diesel fuel.
The Biofuel is more biodegradable.
When using biofuel pay attention to the following points:
•The Performance may be reduced slightly if you switch to driving with
biofuel.
•The fuel consumption may increase slightly if you switch to driving
with biofuel.
Biodiesel conforming to the standard E 14.214 can be mixed in any
desired ratio with diesel fuel conforming to the standard EN 590.
We recommend refuelling with diesel fuel at temperatures below -10°C.
Caution
•Filling the tank even only once with biofuel, which does not comply with
the standard DIN EN 14 214 , can result in damage to the fuel system.
•It is prohibited to use biofuel (RME) and diesel fuel mixture for diesel
engines with the exhaust standard EU4.
NKO 20 A05.book Page 206 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 215 of 274

Inspecting and Replenishing
214
Oil level within range
– You may top up the oil. It is possible that the oil level may then
be within range after doing this.
Oil level within range
– You must top up the oil. It is sufficient, once this is done, to
keep the oil level is within range .
It is normal for the engine to consume oil. The oil consumption may be as
much as 0.5 l/1 000 km depending on your style of driving and the condi-
tions under which you operate your vehicle. The oil consumption may be
slightly higher than this during the first 5 000 kilometres.
One should therefore check the oil level at regular intervals, preferably
every time after the fuel tank is filled or after driving for long stretches.
We recommend maintaining the oil level within the range if the engine
has been operating at high loads, for example during a lengthy motorway
trip during the summer months, towing a trailer or negotiating a high
mountain pass, but not above this .
The warning light in the instrument cluster* will indicate ⇒page 32
whether the oil level is too low. In this case, check the oil level as soon as
possible. Top up with an appropriate quantity of oil.
WARNING
Read and observe the warning notes ⇒page 210, “Working in the
engine compartment” before working in the engine compartment.
Caution
•Always check the oil level on vehicles with engine 1.2 l/47 kW when
the engine is warm. Otherwise the measuring result is incorrect und oil
could be incorrectly replenished - risk of engine damage!
•The oil level must on no account extend beyond the range . Danger
of damaging the catalytic converter.
•Do not continue your journey if for some reason it is not possible
under the conditions prevailing to top up with oil. Switch the engine off
and obtain professional assistance from a specialist garage, otherwise it
could lead to severe engine damage.
Replenishing engine oil
– Inspect the oil level ⇒page 213.
– Unscrew the cap of the engine oil filler opening.
– Pour in a suitable grade of oil in portions of 0.5 litres ⇒page 212, “Engine oil specifications”.
– Inspect the oil level ⇒page 213.
– Carefully screw on the cap of the filler opening and push the dipstick in fully.
WARNING
•Avoid dripping oil onto hot parts of the engine when topping up
will oil - a risk of fire!
•Read and observe the warning notes ⇒page 210, “Working in
the engine compartment” before working in the engine compart-
ment.
Ab
Aa
Ac
Ab
Ab
Aa
NKO 20 A05.book Page 214 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 227 of 274
Wheels and Tyres
226
Tyre life
The life of your tyres very much depends on the following points:
Tyre pressure
The working life of tyres will be shortened considerably if the tyres are
insufficiently or over-inflated and this will have an adverse effect on the
handling of your vehicle.
Correctly inflated tyres are of particular importance when travelling at high
speeds . It is therefore good to check the pressure at least once a month
and also before setting off on a long trip. Please do not forget the spare
wheel when checking the tyres.
The tyre inflation pressures for summer tyres are indicated on the inside
of the fuel filler flap ⇒fig. 163 . The inflation pressures for winter tyres are
20 kPa (0.2 bar) higher than those for summer tyres ⇒page 229.
The tyre pressure should be at the highest pressure specified for your
vehicle at all times. Always check the inflation pressure of tyres when cold. Do not reduce the
higher pressure of warm tyres. Adapt the inflation pressure of the tyres
accordingly if your vehicle is carrying a significantly higher payload.
Driving style
Fast cornering, sharp acceleration and braking (squealing tyres) increase
wear-and-tear on your tyres.
Balancing wheels
The wheels of a new vehicle are balanced. There are a wide range of influ-
ences when driving which may result in an imbalance and which makes
themselves felt through vibration in the steering.
You should have the wheels rebalanced since any imbalance increases
wear-and-tear on the steering, the suspension and tyres. A wheel must
also be rebalanced when a new tyre is fitted and each time a tyre is
repaired.
Wheel alignment errors
Incorrect wheel alignment at the front and rear will not only increase wear-
and-tear on the tyres but will also has an adverse effect on vehicle safety.
Contact your specialist garage if you notice any unusual tyre wear.
WARNING
•If the inflation pressu
re is too low, the tyre must perform a
greater flexing work. At higher sp eeds the tyre will warm up as a
result of this. This can result in tread separation and even a tyre
blowout.
•Immediately replace the damaged rims or tyres.
For the sake of the environment
Tyres which are insufficiently inflated increase your fuel consumption.
Fig. 163 An opened
fuel filler flap with the
tyre inflation pressure
table
NKO 20 A05.book Page 226 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 231 of 274

Wheels and Tyres
230
Please remember that the tyres should be inflated to 20 kPa (0.2 bar)
more than is the case for summer tyres ⇒page 226.
Winter tyres no longer offer the same winter performance once the tyre
tread has worn down to a depth of about 4 mm.
Ageing also causes winter tyres to lose most of their winter performance
properties - even in cases where the remaining tread depth is still clearly
more than 4 mm.
Speed restrictions apply to winter tyres as well as to summer tyres
⇒ page 227, ⇒.
You can fit winter tyres of a lower speed category to your vehicle provided
that you also do not drive faster than the permissible maximum speed for
such tyres, even if the possible maximum speed of your vehicle is higher.
The corresponding tyre category can damage the tyres when exceeding
the permissible maximum speed.
Please pay attention to the notes if you decide to fit winter tyres
⇒ page 225.
You can also fit so-called “all-year tyres” instead of winter tyres.
Please contact your specialist garage if there are any points which are not
clear who will be able to provide you with information regarding the
maximum speed for your tyres.
WARNING
You must on no account drive your car at more than the permis-
sible maximum speed for your winter tyres - risk of an accident
resulting from tyre damage and loss of control over your car.
For the sake of the environment
Fit your summer tyres on again in good time since summer tyres offer you
better grip and handling on roads which are free of snow and ice as well as ar temperatures below 7 °C - the braking distance is shorter, there is
less tyre noise, tyre wear is reduced and fuel consumption is reduced.
Note
Please observe the various differing legal requirements regarding tyres.
Unidirectional tyres*
The direction of rotation of the tyres is marked by
arrows on the wall of
the tyre . This indicates the direction of rotation of the tyre, and it is essen-
tial that the tyres are fitted on to run in this direction. Only then are the
tyres able to provide the optimal properties in terms of grip, low noise,
wear-and-tear and aquaplaning.
Should it be necessary to fit on a spare wheel in exceptional cases with a
tyre not dedicated to the running direction or in opposite running direction,
please adopt a cautious style of driving as the tyre is no longer able to
provide optimal grip and handling in such a situation. This particularly
important on wet roads. Please refer to the notes ⇒page 237, “Spare
wheel*”.
You should have the defective tyre replaced as soon as possible and
restore the correct direction of rotation on all tyres
Snow chains
Snow chains must only be mounted on the front wheels.
When driving on wintry roads, snow chains improve not only traction, but
also the braking performance.
NKO 20 A05.book Page 230 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 268 of 274

Index267
Environmental compatibility . . . . . . . . . 187, 191
ESP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Exhaust gas Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Exhaust gas inspection Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Explanations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Exterior mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Exterior mirror heater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
F
Fastening elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
First-aid box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Fixing net . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Fog lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57, 257 Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Fog lights with integrated turning light . . . . . . 57
Folding seats forwards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Force limiter of the power windows . . . . . . . . 53
Front airbag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Front armrest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Front headlight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205 Diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Fuel gauge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Petrol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fuel consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20, 187 Saving energy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187 Fuel gauge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Fuel reserve
Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Full wheel trim . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Fuse Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
G
Gauges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Gearbox mechanical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
General view Cockpit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Glow plug system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112 Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
H
Handbrake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Hazard warning light system . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Head airbag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Head restraint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Headlight cleaning system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Headlight flasher . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Headlights Fog lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Headlight cleaning system . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Heated windscreen washer nozzles . . . . . . . 63 Heating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Heating the front seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Horn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
I
Ignition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Ignition lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Immobiliser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Warning light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Information display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Instrument cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Interior light Luggage compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Interior lighting front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Interior monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Intermittent wiping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
ISOFIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
ISOFIX system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
J
Jacking points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Jump-starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243, 244
K
Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
NKO 20 A05.book Page 267 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM