Page 86 of 322
375
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Knowing your vehicle
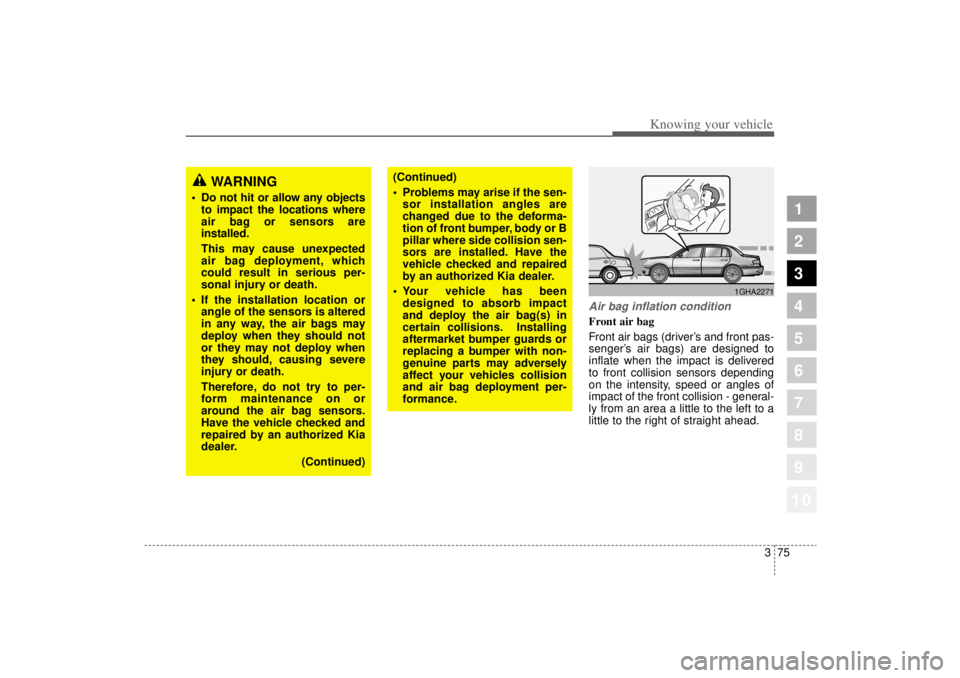
Air bag inflation conditionFront air bag
Front air bags (driver’s and front pas-
senger’ s air bags) are designed to
inflate when the impact is delivered
to front collision sensors depending
on the intensity, speed or angles of
impact of the front collision - general-
ly from an area a little to the left to a
little to the right of straight ahead.
WARNING
Do not hit or allow any objects
to impact the locations where
air bag or sensors are
installed.
This may cause unexpected
air bag deployment, which
could result in serious per-
sonal injury or death.
If the installation location or
angle of the sensors is altered
in any way, the air bags may
deploy when they should not
or they may not deploy when
they should, causing severe
injury or death.
Therefore, do not try to per-
form maintenance on or
around the air bag sensors.
Have the vehicle checked and
repaired by an authorized Kia
dealer.
(Continued)
(Continued)
Problems may arise if the sen-
sor installation angles are
changed due to the deforma-
tion of front bumper, body or B
pillar where side collision sen-
sors are installed. Have the
vehicle checked and repaired
by an authorized Kia dealer.
Your vehicle has been
designed to absorb impact
and deploy the air bag(s) in
certain collisions. Installing
aftermarket bumper guards or
replacing a bumper with non-
genuine parts may adversely
affect your vehicles collision
and air bag deployment per-
formance.
1GHA2271
Page 87 of 322
Knowing your vehicle76
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
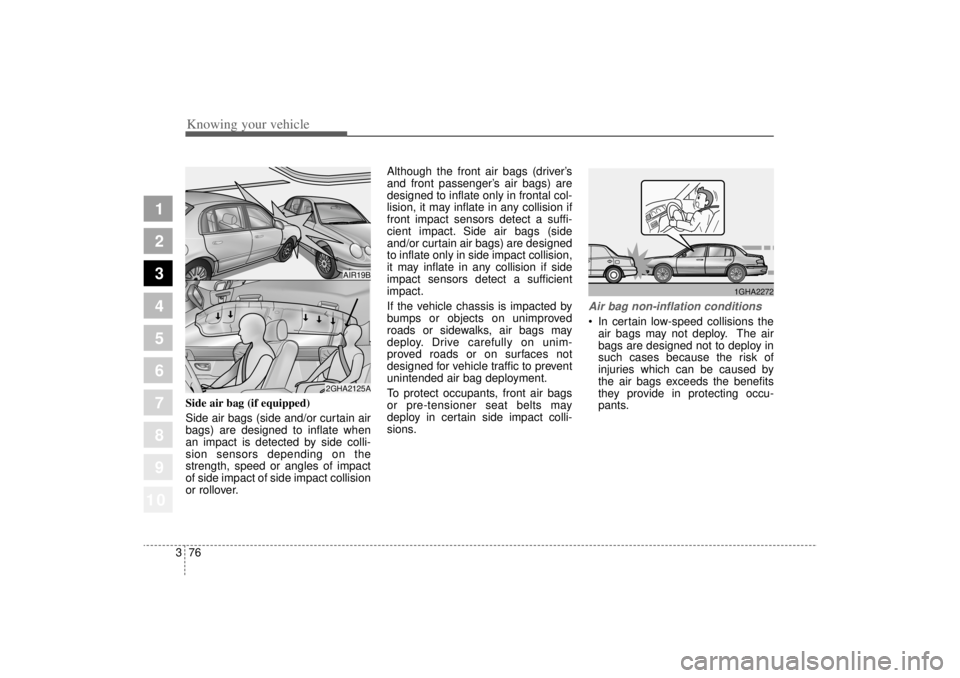
Side air bag (if equipped)
Side air bags (side and/or curtain air
bags) are designed to inflate when
an impact is detected by side colli-
sion sensors depending on the
strength, speed or angles of impact
of side impact of side impact collision
or rollover. Although the front air bags (driver’
s
and front passenger’ s air bags) are
designed to inflate only in frontal col-
lision, it may inflate in any collision if
front impact sensors detect a suffi-
cient impact. Side air bags (side
and/or curtain air bags) are designed
to inflate only in side impact collision,
it may inflate in any collision if side
impact sensors detect a sufficient
impact.
If the vehicle chassis is impacted by
bumps or objects on unimproved
roads or sidewalks, air bags may
deploy. Drive carefully on unim-
proved roads or on surfaces not
designed for vehicle traffic to prevent
unintended air bag deployment.
To protect occupants, front air bags
or pre-tensioner seat belts may
deploy in certain side impact colli-
sions.
Air bag non-inflation conditions In certain low-speed collisions the
air bags may not deploy. The air
bags are designed not to deploy in
such cases because the risk of
injuries which can be caused by
the air bags exceeds the benefits
they provide in protecting occu-
pants.
AIR19B
2GHA2125A
1GHA2272
Page 88 of 322
377
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Knowing your vehicle
Frontal air bags are not designed
to inflate in rear collisions, because
occupants are moved backward by
the force of the impact. In this
case, the air bags do not provide
proper protection.
Front air bags may not inflate in
side impact collision, because
occupants move to the direction of
the collision, and thus in side
impacts, frontal air bag deployment
does not provide occupant protec-
tion.
However, side or curtain air bags
may inflate depending on the inten-
sity, vehicle speed and angles of
impact.
In a slant or angled collision, the
force of impact may direct the
occupants in a direction between
the front and side air bags, and
thus the sensors may not deploy
any air bags.
1GHA2273
AIR19A
1GHA2270
Page 89 of 322
Knowing your vehicle78
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Just before impact, drivers often
brake heavily. Such heavy braking
lowers the front portion of the vehi-
cle causing it to “ride”under a vehi-
cle with a higher ground clearance.
Air bags may not inflate in this
"under-ride" situation because
deceleration forces that are detect-
ed by sensors may be significantly
altered by such “under-ride”colli-
sions.
Air bags may not inflate in rollover
accidents because air bag deploy-
ment would not provide proper pro-
tection to the occupants.
However, side air bags may inflate
when the vehicle is rolled over by a
side impact collision, if the vehicle
is equipped with side air bags and
curtain air bags.
Air bags may not inflate if the vehi-
cle collides with objects such as
utility poles or trees, where the
point of impact is concentrated to
one area and the full force of the
impact is not delivered to the sen-
sors.
1GHA2274
AIR21
1GHA2275
Page 90 of 322
379
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Knowing your vehicle
How does the air bag system
operate Air bag only operates when the
ignition switch is turned to the ON
or START positions.
Air bags inflate instantly in the
event of serious frontal or side col-
lision (if equipped with side air bag
or curtain air bag) in order to help
protect the occupants from serious
physical injury.
There is no single speed at which
the air bags will inflate.
Generally, air bags are designed to
inflate by the severity of a collision
and its direction. These two factors
determine whether the sensors
send out an electronic deploy-
ment/inflation signal.
Air bag deployment depends on a
number of factors including vehicle
speed, angles of impact and the
density and stiffness of the vehi-
cles or objects which your vehicle
hits in the collision. However, fac-
tors are not limited to those men-
tioned above.
The front air bags will completely
inflate and deflate in an instant.
It is virtually impossible for you to
see the air bags inflate during an
accident. It is much more likely that
you will simply see the deflated air
bags hanging out of their storage
compartments after the collision.
In order to help provide protection
in a severe collision, the air bags
must inflate rapidly. The speed of
air bag inflation is a consequence
of the extremely short time in which
a collision occurs and the need to
get the air bag between the occu-
pant and the vehicle structures
before the occupant impacts those
structures. This speed of inflation
reduces the risk of serious or life-
threatening injuries in a severe col-
lision and is thus a necessary part
of air bag design.
However, air bag inflation can also
cause injuries which normally can
include facial abrasions, bruises
and broken bones, and sometimes
more serious injuries because that
inflation speed also causes the air
bags to expand with a great deal
force.
There are even circumstances
under which contact with the
steering wheel air bag can cause
fatal injuries, especially if the
occupant is positioned exces-
sively close to the steering
wheel.
Page 106 of 322
395
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Knowing your vehicle
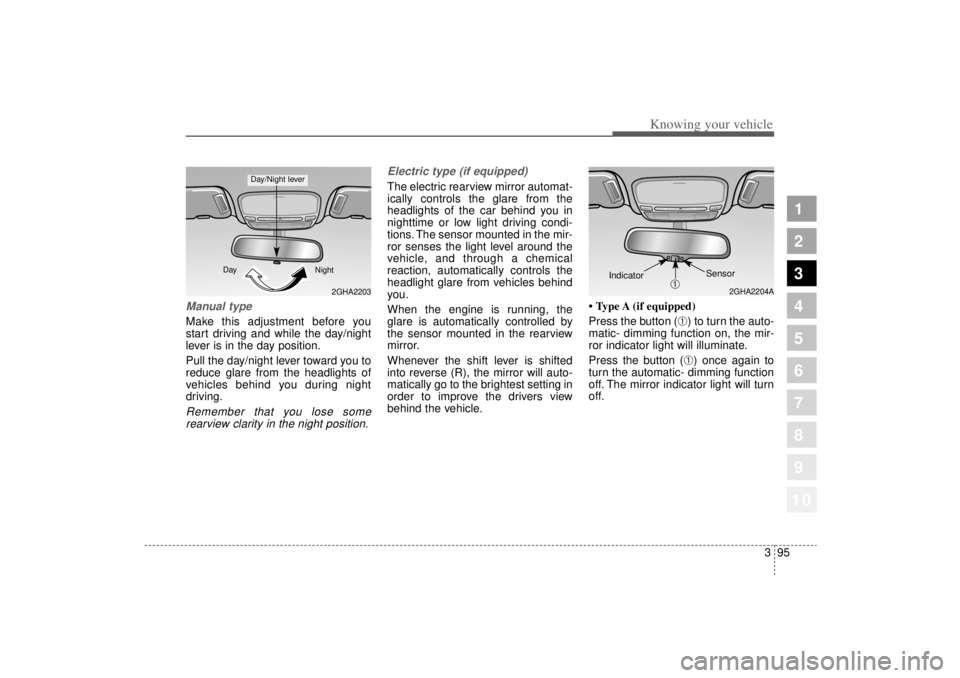
Manual type Make this adjustment before you
start driving and while the day/night
lever is in the day position.
Pull the day/night lever toward you to
reduce glare from the headlights of
vehicles behind you during night
driving.Remember that you lose somerearview clarity in the night position. Electric type (if equipped)
The electric rearview mirror automat-
ically controls the glare from the
headlights of the car behind you in
nighttime or low light driving condi-
tions. The sensor mounted in the mir-
ror senses the light level around the
vehicle, and through a chemical
reaction, automatically controls the
headlight glare from vehicles behind
you.
When the engine is running, the
glare is automatically controlled by
the sensor mounted in the rearview
mirror.
Whenever the shift lever is shifted
into reverse (R), the mirror will auto-
matically go to the brightest setting in
order to improve the drivers view
behind the vehicle.
• Type A (if equipped)
Press the button (
➀) to turn the auto-
matic- dimming function on, the mir-
ror indicator light will illuminate.
Press the button (➀) once again to
turn the automatic- dimming function
off. The mirror indicator light will turn
off.
2GHA2203
Day
Night
Day/Night lever
2GHA2204A
Sensor
➀
Indicator
Page 140 of 322
Driving your vehicle18
4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Power steeringPower Steering uses energy from the
engine to assist you in steering the
vehicle. If the engine is off or if the
power steering system becomes
inoperative, the vehicle may still be
steered, but it will require increased
steering effort.
Should you notice any change in the
effort required to steer during normal
vehicle operation, have the power
steering checked by an Authorized
Kia Dealer.
Electronic power steering The wheel speed sensor controls
steering power according to the vehi-
cle’s speed.
The steering wheel becomes heavier
as the vehicle’s speed increases and
becomes lighter as the vehicle’s
speed decreases for the better con-
trol of the steering wheel.
✽ ✽
NOTICE• Never hold the steering wheel
against a stop (extreme right or
left turn) for more than 5 seconds
with the engine running. Holding
the steering wheel for more than 5
seconds in either position may
cause damage to the power steer-
ing pump.
• If the power steering drive belt breaks or if the power steering
pump malfunctions, the steering
effort will greatly increase.
STEERING WHEEL
Page 151 of 322
429
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
Driving your vehicle
The Electronic Stability Program
(ESP) monitors information from var-
ious vehicle sensors and then com-
pares the driver's commands with
the actual behavior of the vehicle. If
an unstable condition occurs - a sud-
den evasive movement for example -
ESP intervenes within fractions of a
second via the engine computer and
brake system and attempts to stabi-
lize the vehicle.
ESP operationESP ON condition
When the ignition is turnedON, ESP and ESP OFF
indicator lights illuminate
for approximately 3 sec-
onds, then ESP is turned
on.
Press the ESP button to turn ESP off. (ESP OFF
indicator will illuminate). To
turn the ESP on, press the
ESP button (ESP OFF
indicator light will go off).
When starting the engine, you may hear a slight tick-
ing sound. This is the ESP
performing an automatic
system self-check and
does not indicate a prob-
lem.
When operating
When the ESP is in opera-
tion, ESP indicator light
blinks.
When the ElectronicStability Program is oper-
ating properly, you can feel
a slight pulsation in the
vehicle. This is only the
effect of brake control and
indicates nothing unusual.
When moving out of the mud or slippery road,
pressing the accelerator
pedal may not cause the
bv engine rpm (revolutions
per minute) to increase.
ELECTRONIC STABILITY PROGRAM (IF EQUIPPED)
-
ESP
ESP
2GHN2051D