Page 4826 of 5621

PARKING BRAKE SHOE
PB-7
C
D
E
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
PB
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
–Anti-rattle pin for excessive wear and corrosion.
–Return spring for sagging.
Make sure that adjuster moves smoothly.
Visually check the inside of drum for excessive wear, cracks, and damage. Check the inside of drum using
a pair of vernier calipers.
Replace with new part if the above part is malfunction.
INSTALLATION
Note the following, and install in the reverse order of removal.
Refer to PB-5, "Components" and apply PBC (Poly Butyl Cupry-
sil) grease or equivalent to the specified points during assembly.
Assemble adjusters so that threaded part is expanded when
rotating it in the direction shown by arrow.
Shorten adjuster by rotating it.
Check shoe sliding surface and drum inner surface for grease.
Wipe it off if it adhere on the surfaces.
Perform break-in operation as follows after replacing brake
shoes or disc rotors, or if brakes do not function well.
1. Adjust parking brake pedal stroke to the specified amount. Refer
to PB-2, "
ADJUSTMENT" .
2. Perform parking brake break-in (drag run) operation by driving vehicle under the following conditions:
3. Check parking brake pedal stroke of parking brake. Adjust again if it is outside the standard. Drive forward
Vehicle speed: Approx. 40 km/h (25 MPH) set (constant and forward)
Parking brake operating force: Approx. 400 N (40 kg, 88 lb) set constant
Time: Approx. 10 sec.
SFIA2426E
Page 4942 of 5621
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
PR-3
C
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
PR
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGPFP:00003
NVH Troubleshooting ChartNDS000E9
Use the chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
: Applicable Reference pageFront
PR-4—
—
—
—
PR-4PR-5
NVH in FFD and RFD section
NVH in FAX, RAX, FSU and RSU section
NVH in WT section
NVH in WT section
NVH in RAX section
NVH in BR section
NVH in PS section
RearPR-6PR-10—
PR-7—
PR-6PR-9
Possible cause and SUSPECTED PARTS
Uneven rotating torque
Center bearing improper installation
Excessive center bearing axial end play
Center bearing mounting (insulator) cracks, damage or deterioration
Excessive joint angle
Rotation imbalance
Excessive runout
DIFFERENTIAL
AXLE AND SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
DRIVE SHAFT
BRAKES
STEERING
SymptomNoiseShake
Vibration
Page 4960 of 5621

NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
PS-7
C
D
E
F
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
PS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGPFP:00003
NVH Trouble Shooting ChartNGS000D4
Use chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
: ApplicableReference page
PS-8PS-8PS-23PS-23PS-23PS-8PS-10PS-10
EM-15
,EM-174PS-10—
PS-22PS-16PS-13PS-20
NVH in PR section
NVH in RFD section
NVH in FAX, RAX, FSU, RSU section
NVH in WT section
NVH in WT section
NVH in FAX section
NVH in BR section
Possible cause and SUSPECTED PARTS
Fluid level
Air in hydraulic system
Outer socket ball joint swinging force
Outer socket ball joint rotating torque
Outer socket ball joint end play
Steering fluid leakage
Steering wheel play
Steering gear rack sliding force
Drive belt looseness
Improper steering wheel
Improper installation or looseness of tilt lock lever
Mounting rubber deterioration
Steering column deformation or damage
Improper installation or looseness of steering column
Steering linkage looseness
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
AXLE and SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
DRIVE SHAFT
BRAKES
Symptom SteeringNoise
Shake
Vibration
Shimmy
Judder
Page 5003 of 5621
RAX-4
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGPFP:00003
NVH Troubleshooting ChartNDS000FP
Use chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
: ApplicableReference page
—
RAX-10—
RAX-8—
NVH in PR section.
NVH in RFD section.
NVH in RAX and RSU sections.
Refer to REAR AXLE in this chart.
NVH in WT section.
NVH in WT section.
Refer to DRIVE SHAFT in this chart.
NVH in BR section.
NVH in PS section.
Possible cause and SUSPECTED PARTS
Excessive joint angle
Joint sliding resistance
Imbalance
Improper installation, looseness
Parts interference
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
REAR AXLE AND REAR SUSPENSION
REAR AXLE
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
DRIVE SHAFT
BRAKES
STEERING
SymptomDRIVE
SHAFTNoise
Shake
REAR
AXLENoise
Shake
Vibration
Shimmy
Judder
Poor quality ride or handling
Page 5050 of 5621
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
RFD-7
C
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
RFD
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
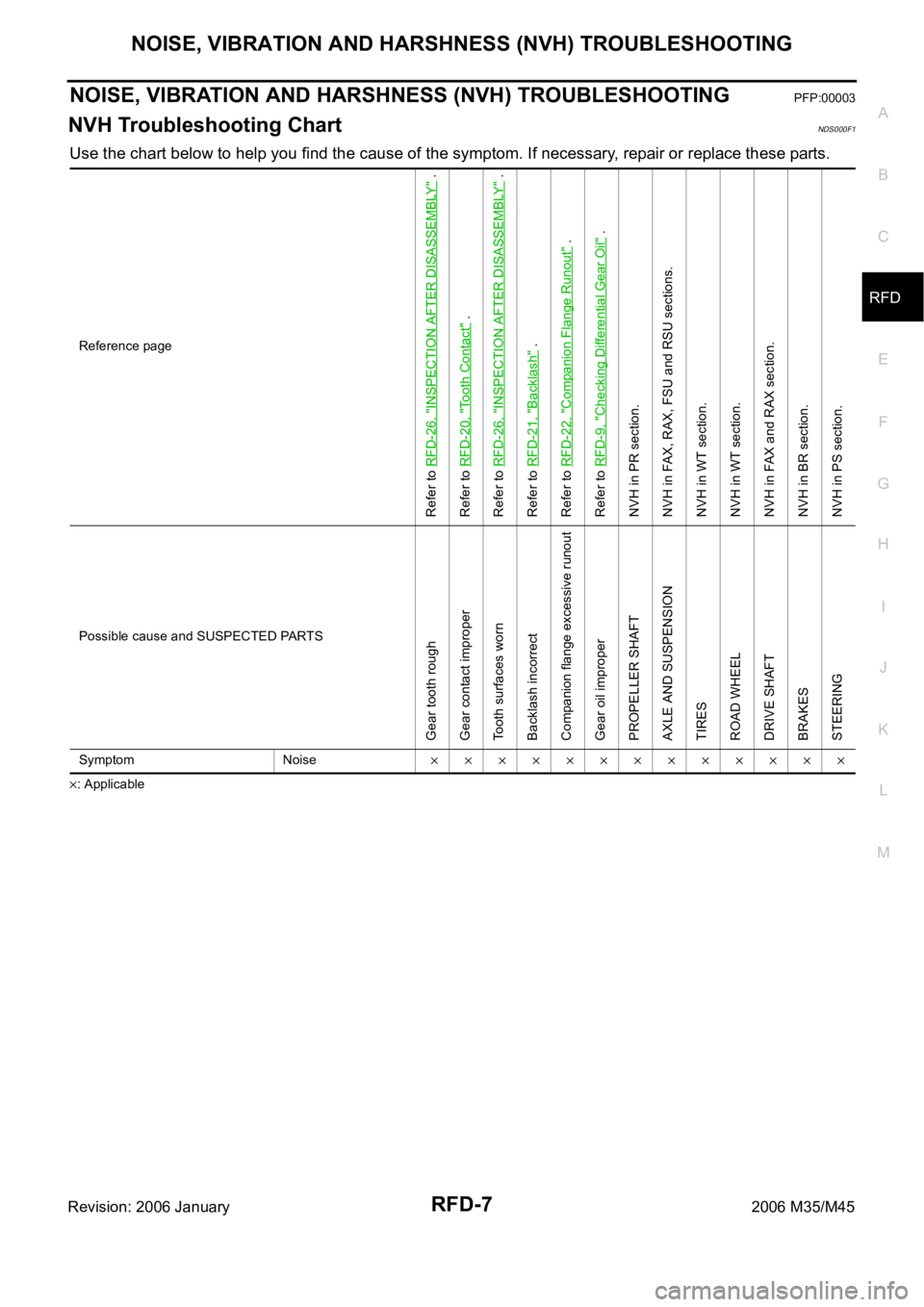
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGPFP:00003
NVH Troubleshooting ChartNDS000F1
Use the chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
: ApplicableReference page
Refer to RFD-26, "
INSPECTION AFTER DISASSEMBLY
" .
Refer to RFD-20, "
Tooth Contact
" .
Refer to RFD-26, "
INSPECTION AFTER DISASSEMBLY
" .
Refer to RFD-21, "
Backlash
" .
Refer to RFD-22, "
Companion Flange Runout
" .
Refer to RFD-9, "
Checking Differential Gear Oil
" .
NVH in PR section.
NVH in FAX, RAX, FSU and RSU sections.
NVH in WT section.
NVH in WT section.
NVH in FAX and RAX section.
NVH in BR section.
NVH in PS section.
Possible cause and SUSPECTED PARTS
Gear tooth rough
Gear contact improper
Tooth surfaces worn
Backlash incorrect
Companion flange excessive runout
Gear oil improper
PROPELLER SHAFT
AXLE AND SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
DRIVE SHAFT
BRAKES
STEERING
Symptom Noise
Page 5085 of 5621
RSU-4
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGPFP:00003
NVH Troubleshooting ChartNES000J5
Use chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
: ApplicableReference page
RSU-7RSU-10
—
—
—
RSU-7RSU-5RSU-17
NVH in PR section.
NVH in RFD section.
NVH in RAX and RSU sections.
NVH in WT section.
NVH in WT section.
NVH in RAX section.
NVH in BR section.
NVH in PS section.
Possible cause and SUSPECTED PARTS
Improper installation, looseness
Shock absorber deformation, damage or deflection
Bushing or mounting deterioration
Parts interference
Spring fatigue
Suspension looseness
Incorrect wheel alignment
Stabilizer bar fatigue
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
REAR AXLE AND REAR SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEELS
DRIVE SHAFT
BRAKES
STEERING
Symptom REAR SUSPENSIONNoise
Shake
Vibration
Shimmy
Judder
Poor quality ride or
handling
Page 5133 of 5621

SB-34
SEAT BELTS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
NOTE:
Apply the tape so that there is no looseness or wrinkling.
6. Remove the clip fixing the seat belt and check that the webbing returns smoothly.
6. Repeat steps above as necessary to check the other seat belts.
SEAT BELT RETRACTOR ON-VEHICLE CHECK
Emergency Locking Retractors (ELR) and Automatic Locking Retractors (ALR)
NOTE:
All seat belt retractors are of the Emergency Locking Retractors (ELR) type. In an emergency (sudden stop)
the retractor will lock and prevent the webbing from extending any further. All 3-point type seat belt retractors
except the driver's seat belt also have an Automatic Locking Retractors (ALR) mode. The ALR mode (also
called child restraint mode) is used when installing child seats. The ALR mode is activated when the seat belt
is fully extended. When the webbing is then retracted partially, the ALR mode automatically locks the seat belt
in a specific position so the webbing cannot be extended any further. To cancel the ALR mode, allow the seat
belt to fully wind back into the retractor.
Check the seat belt retractors using the following test(s) to determine if a retractor assembly is operating prop-
erly.
ELR Function Stationary Check
Grasp the shoulder webbing and pull forward quickly. The retractor should lock and prevent the belt from
extending further.
ALR Function Stationary Check
1. Pull out entire length of seat belt from retractor until a click is heard.
2. Retract the webbing partially. A clicking noise should be heard as the webbing retracts indicating that the
retractor is in the Automatic Locking Retractors (ALR) mode.
3. Grasp the seat belt and try to pull out the retractor. The webbing must lock and not extend any further. If
NG, replace the retractor assembly.
4. Allow the entire length of the webbing to retract to cancel the automatic locking mode.
ELR Function Moving Check
WAR NING :
Perform the following test in a safe, open area clear of other vehicles and obstructions (for example, a
large, empty parking lot). Road surface must be paved and dry. DO NOT perform the following test on
wet or gravel roads or on public streets and highways. This could result in an accident and serious
personal injury. The driver and passenger must be prepared to brace themselves in the event the
retractor does not lock.
1. Fasten driver's seat belt. Buckle a passenger into the seat for the belt that is to be tested.
2. Proceed to the designated safe area.
3. Drive the vehicle at approximately 16 km/h (10 MPH). Notify any passengers of a pending sudden stop
and the driver and passenger must be prepared to brace themselves in the event the retractor does not
lock, apply brakes firmly and make a very hard stop.
During stop, seat belts should lock and not be extended. If the seat belt retractor assembly does not lock, per-
form the retractor off-vehicle check.
Page:
< prev 1-8 9-16 17-24