2006 CHEVROLET HHR fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 273 of 394

A. Windshield Washer Fluid Reservoir. See “Adding
Washer Fluid” underWindshield Washer Fluid
on page 5-29.
B. Pressure Cap. SeePressure Cap on page 5-23.
C. Coolant Recovery Tank. See “Checking Coolant”
underEngine Coolant on page 5-20.
D. Engine Air Cleaner/Filter. SeeEngine Air
Cleaner/Filter on page 5-18.
E. Engine Oil Fill Cap. See “When to Add Engine Oil”
underEngine Oil on page 5-13.
F. Engine Oil Dipstick (Out of View). See “Checking
Engine Oil” underEngine Oil on page 5-13.
G. Brake Master Cylinder Reservoir. SeeBrakes on
page 5-30andHydraulic Clutch on page 5-20.
H. Remote Positive (+) Terminal. SeeJump Starting
on page 5-33.
I. Engine Compartment Fuse Block. SeeEngine
Compartment Fuse Block on page 5-85.Engine Oil
Checking Engine Oil
It is a good idea to check your engine oil every time you
get fuel. In order to get an accurate reading, the oil
must be warm and the vehicle must be on level ground.
The engine oil dipstick handle is a yellow loop. See
Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12for
the location of the engine oil dipstick.
1. Turn off the engine and give the oil several minutes
to drain back into the oil pan. If you do not do this,
the oil dipstick might not show the actual level.
2. Pull the dipstick and clean it with a paper towel or
cloth, then push it back in all the way. Remove it
again, keeping the tip down and check the level.
5-13
Page 310 of 394

Belt:A rubber coated layer of cords that is located
between the plies and the tread. Cords may be made
from steel or other reinforcing materials.
Bead:The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped by
steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire:A pneumatic tire in which the plies are
laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread.
Cold In�ation Pressure:The amount of air pressure
in a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi)
or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built up heat from
driving. SeeInflation - Tire Pressure on page 5-52.
Curb Weight:This means the weight of a motor vehicle
with standard and optional equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil, and coolant, but without
passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings:A code molded into the sidewall of
a tire signifying that the tire is in compliance with
the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) motor
vehicle safety standards. The DOT code includes
the Tire Identi�cation Number (TIN), an alphanumeric
designator which can also identify the tire manufacturer,
production plant, brand, and date of production.
GVWR:Gross Vehicle Weight Rating, seeLoading
Your Vehicle on page 4-32.GAWR FRT:Gross Axle Weight Rating for the front
axle, seeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-32.
GAWR RR:Gross Axle Weight Rating for the rear axle,
seeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-32.
Intended Outboard Sidewall:The side of an
asymmetrical tire, that must always face outward when
mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa):The metric unit for air pressure.
Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire:A tire used on light duty
trucks and some multipurpose passenger vehicles.
Load Index:An assigned number ranging from 1 to 279
that corresponds to the load carrying capacity of a tire.
Maximum In�ation Pressure:The maximum air
pressure to which a cold tire may be in�ated. The
maximum air pressure is molded onto the sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating:The load rating for a tire at the
maximum permissible in�ation pressure for that tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight:The sum of curb
weight; accessory weight; vehicle capacity weight;
and production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight:The number of occupants a
vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 150 lbs (68 kg).
SeeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-32.
Occupant Distribution:Designated seating positions.
5-50
Page 312 of 394

In�ation - Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell you that
under-in�ation or over-in�ation is all right. It is not.
If your tires do not have enough air (under-in�ation),
you can get the following:
Too much �exing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Premature or irregular wear
Poor handling
Reduced fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (over-in�ation), you
can get the following:
Unusual wear
Poor handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazardsA Tire and Loading Information label is attached to the
vehicle’s center pillar (B-pillar), below the driver’s
door latch. This label shows your vehicle’s original
equipment tires and the correct in�ation pressures for
your tires when they are cold. The recommended
cold tire in�ation pressure, shown on the label, is the
minimum amount of air pressure needed to support your
vehicle’s maximum load carrying capacity.
For additional information regarding how much weight
your vehicle can carry, and an example of the tire
and loading information label, seeLoading Your Vehicle
on page 4-32. How you load your vehicle affects
vehicle handling and ride comfort, never load your
vehicle with more weight than it was designed to carry.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more. Do not forget
to check the compact spare tire, it should be at
60 psi (420 kPa). For additional information regarding
the compact spare tire, seeCompact Spare Tire
on page 5-73.
5-52
Page 348 of 394
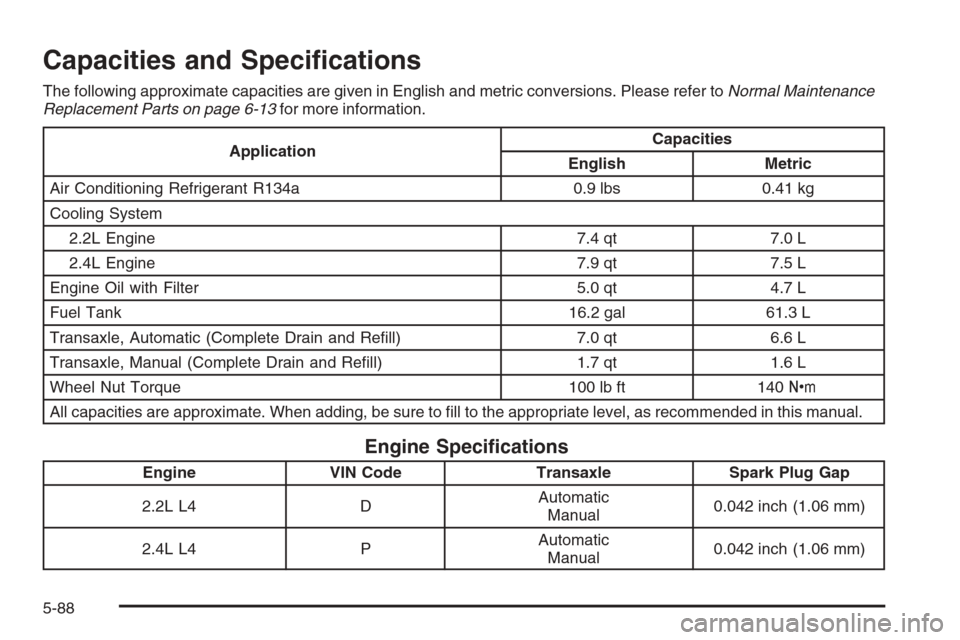
Capacities and Speci�cations
The following approximate capacities are given in English and metric conversions. Please refer toNormal Maintenance
Replacement Parts on page 6-13for more information.
ApplicationCapacities
English Metric
Air Conditioning Refrigerant R134a 0.9 lbs 0.41 kg
Cooling System
2.2L Engine 7.4 qt 7.0 L
2.4L Engine 7.9 qt 7.5 L
Engine Oil with Filter 5.0 qt 4.7 L
Fuel Tank 16.2 gal 61.3 L
Transaxle, Automatic (Complete Drain and Re�ll) 7.0 qt 6.6 L
Transaxle, Manual (Complete Drain and Re�ll) 1.7 qt 1.6 L
Wheel Nut Torque 100 lb ft 140Y
All capacities are approximate. When adding, be sure to �ll to the appropriate level, as recommended in this manual.
Engine Speci�cations
Engine VIN Code Transaxle Spark Plug Gap
2.2L L4 DAutomatic
Manual0.042 inch (1.06 mm)
2.4L L4 PAutomatic
Manual0.042 inch (1.06 mm)
5-88
Page 356 of 394

(i)Drain, flush, and refill cooling system. This service
can be complex; you should have your dealer perform
this service. See Engine Coolant on page 5-20 for
what to use. Inspect hoses. Clean radiator, condenser,
pressure cap, and filler neck. Pressure test the
cooling system and pressure cap.
(j)A fluid loss in any vehicle system could indicate a
problem. Have the system inspected and repaired and
the fluid level checked. Add fluid if needed.
(k)If you drive regularly under dusty conditions, inspect
the filter at each engine oil change.
(l)If you drive regularly under dusty conditions, the filter
may require replacement more often.
(m)Visually inspect belt for fraying, excessive cracks,
or obvious damage. Replace belt if necessary.
Owner Checks and Services
These owner checks and services should be performed
at the intervals speci�ed to help ensure the safety,
dependability, and emission control performance of your
vehicle. Your GM Goodwrench
®dealer can assist you
with these checks and services.
Be sure any necessary repairs are completed at once.
Whenever any �uids or lubricants are added to your
vehicle, make sure they are the proper ones, as shown
inRecommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-11.
At Each Fuel Fill
It is important to perform these underhood checks
at each fuel fill.
Engine Oil Level Check
Check the engine oil level and add the proper oil if
necessary. SeeEngine Oil on page 5-13for further
details.
Notice:It is important to check your oil regularly
and keep it at the proper level. Failure to keep your
engine oil at the proper level can cause damage
to your engine not covered by your warranty.
Engine Coolant Level Check
Check the engine coolant level and add
DEX-COOL®coolant mixture if necessary.
SeeEngine Coolant on page 5-20for further details.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level Check
Check the windshield washer �uid level in the windshield
washer �uid reservoir and add the proper �uid if
necessary.
6-8
Page 382 of 394

Automatic Door Lock.......................................2-11
Automatic Headlamp System............................3-15
Automatic Transaxle
Fluid..........................................................5-19
Operation...................................................2-27
B
Battery..........................................................5-32
Run-Down Protection...................................3-17
Before Leaving on a Long Trip.........................4-23
Brake
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)........................ 4-7
Emergencies................................................ 4-9
Parking......................................................2-32
System Warning Light..................................3-32
Brakes..........................................................5-30
Braking........................................................... 4-6
Braking in Emergencies..................................... 4-9
Break-In, New Vehicle.....................................2-21
Bulb Replacement...........................................5-41
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL)........5-43
Halogen Bulbs............................................5-41
Headlamp Aiming........................................5-38
Headlamps, Front Turn Signal, and
Parking Lamps.........................................5-42Bulb Replacement (cont.)
Replacement Bulbs......................................5-45
Taillamps, Turn Signal, Stoplamps and
Back-up Lamps........................................5-44
Buying New Tires...........................................5-55
C
Calibration.............................................2-38, 2-40
California Fuel.................................................. 5-6
California Proposition 65 Warning....................... 5-3
Canadian Owners................................................ ii
Capacities and Speci�cations............................5-88
Carbon Monoxide...................2-13, 2-36, 4-26, 4-39
Care of
Safety Belts................................................5-76
Your CD Player...........................................3-80
Your CDs ...................................................3-79
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL)...........5-43
Chains, Tire...................................................5-60
Charging System Light....................................3-31
Check
Engine Light...............................................3-35
Checking Things Under the Hood......................5-10
Chemical Paint Spotting...................................5-80
2