2005 SUZUKI SWIFT turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 262 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-212 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
WARNING!
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cooling fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan
is electric and can come on whether or not the engi ne is running. The fan can start automatically in
response to the ECT sensor with the ig nition switch at the “ON” position.
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
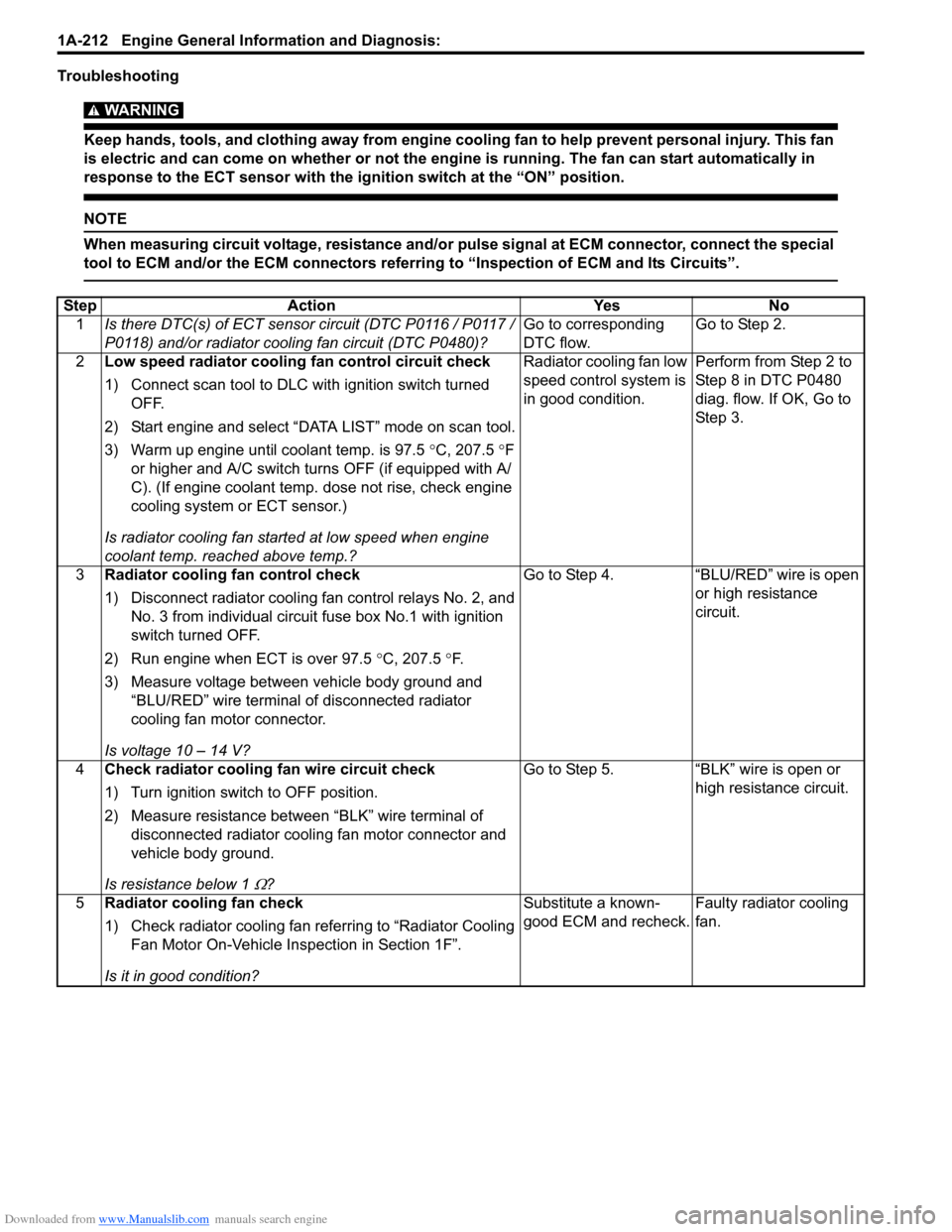
StepAction YesNo
1 Is there DTC(s) of ECT sensor circuit (DTC P0116 / P0117 /
P0118) and/or radiator cooling fan circuit (DTC P0480)? Go to corresponding
DTC flow.Go to Step 2.
2 Low speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at low speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp.? Radiator cooling fan low
speed control system is
in good condition.
Perform from Step 2 to
Step 8 in DTC P0480
diag. flow. If OK, Go to
Ste p 3.
3 Radiator cooling fan control check
1) Disconnect radiator cooling fan control relays No. 2, and
No. 3 from individual circuit fuse box No.1 with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Run engine when ECT is over 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F.
3) Measure voltage between vehicle body ground and “BLU/RED” wire terminal of disconnected radiator
cooling fan motor connector.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 4.
“BLU/RED” wire is open
or high resistance
circuit.
4 Check radiator cooling fan wire circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Measure resistance between “BLK” wire terminal of
disconnected radiator coolin g fan motor connector and
vehicle body ground.
Is resistance below 1
Ω? Go to Step 5. “BLK” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.
5 Radiator cooling fan check
1) Check radiator cooling fan referring to “Radiator Cooling
Fan Motor On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1F”.
Is it in good condition? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Faulty radiator cooling
fan.
Page 264 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-214 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
WARNING!
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cooling fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan
is electric and can come on whether or not the engi ne is running. The fan can start automatically in
response to the ECT sensor with the ig nition switch at the “ON” position.
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
StepAction YesNo
1 Is there DTC(s) of ECT sensor circuit (DTC P0116 / P0117 /
P0118) and/or radiator cooling fan circuit (DTC P0480)? Go to corresponding
DTC flow.Go to Step 2.
2 Low speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at low speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp.? Go to Step 3.
Perform from Step 2 to
Step 5 in “Radiator
Cooling Fan Low Speed
Control System Check”.
3 High speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
2) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 102.5 °C, 216.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at high speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp? Radiator cooling fan
control system is in
good condition.
Perform from Step 9 to
Step 14 in DTC P0480
diag. flow.
If OK, Go to Step 4.
4 Radiator cooling fan control No. 2 and No. 3 check
1) Run engine when ECT is over 102.5 °C, 216.5 °F.
2) Measure voltage between vehicle body ground and “E23-48” terminal of ECM connector.
Is voltage lower than 1.5 V? Go to Step 5.
Faulty ECM.
5 Radiator cooling fan No. 2 wire circuit check
1) Remove radiator cooling fan control relay No.2 with
ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Measure voltage between “GRY” wire terminal of disconnected radiator cooling fan control relay No. 2
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
“GRY” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.
6 Radiator cooling fan No. 2 wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connector from radiator cooling fan motor
with ignition swit ch turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “BLU/BLK” wire terminal of disconnected radiator cooling fan control relay No. 2
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 7.
“BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit.
Page 283 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B1306018
NOTE
Before performed this inspection, be sure to
read the “Precautions of ECM Circuit
Inspection in Section 1A”.
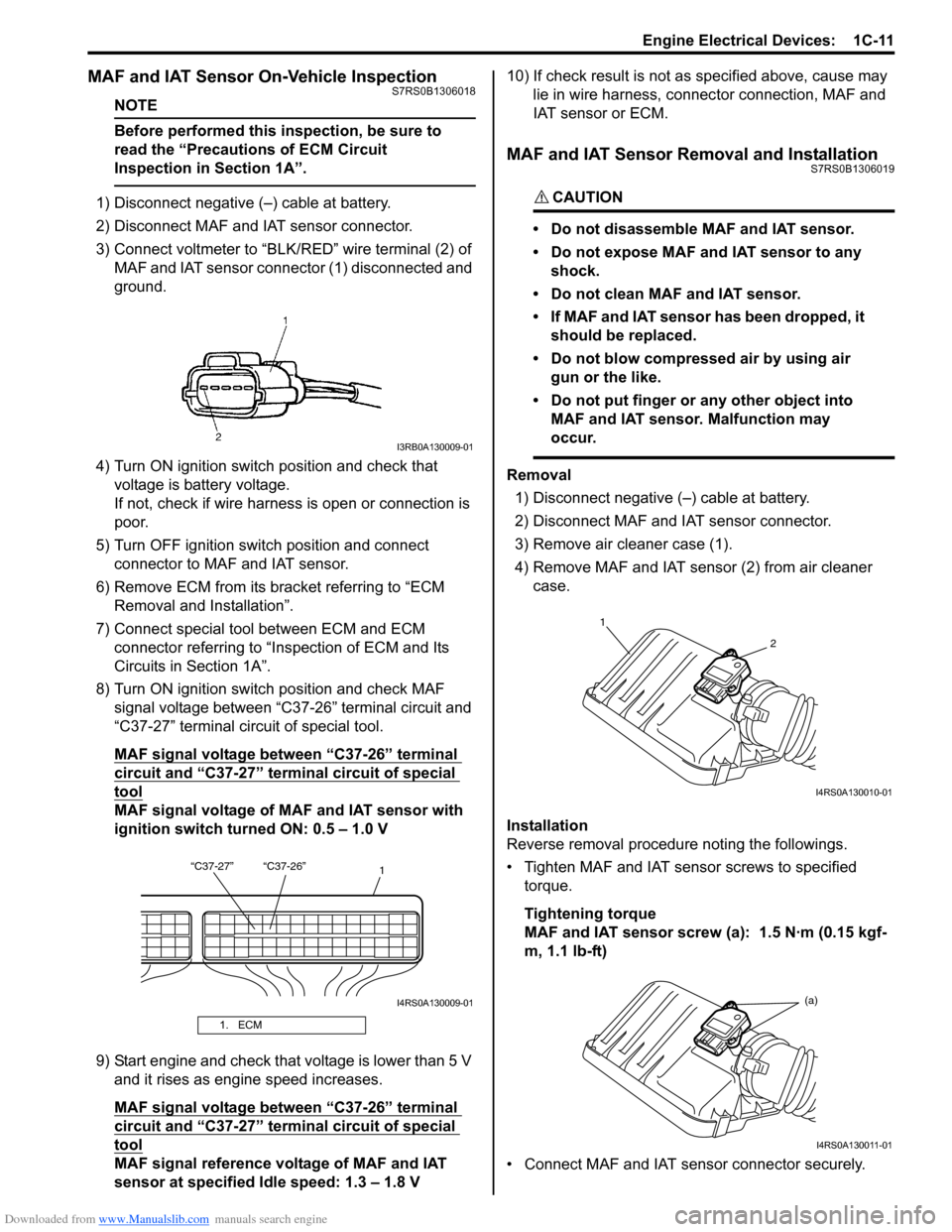
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect MAF and IAT sensor connector.
3) Connect voltmeter to “BLK/RED” wire terminal (2) of
MAF and IAT sensor connector (1) disconnected and
ground.
4) Turn ON ignition switch position and check that voltage is battery voltage.
If not, check if wire harness is open or connection is
poor.
5) Turn OFF ignition switch position and connect connector to MAF and IAT sensor.
6) Remove ECM from its bracket referring to “ECM Removal and Installation”.
7) Connect special tool between ECM and ECM connector referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its
Circuits in Section 1A”.
8) Turn ON ignition switch position and check MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal circuit and
“C37-27” terminal circuit of special tool.
MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal
circuit and “C37-27” termi nal circuit of special
tool
MAF signal voltage of MAF and IAT sensor with
ignition switch turned ON: 0.5 – 1.0 V
9) Start engine and check that voltage is lower than 5 V and it rises as engine speed increases.
MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal
circuit and “C37-27” termi nal circuit of special
tool
MAF signal reference voltage of MAF and IAT
sensor at specified Idle speed: 1.3 – 1.8 V 10) If check result is not as
specified above, cause may
lie in wire harness, connec tor connection, MAF and
IAT sensor or ECM.
MAF and IAT Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306019
CAUTION!
• Do not disassemble MAF and IAT sensor.
• Do not expose MAF and IAT sensor to any shock.
• Do not clean MAF and IAT sensor.
• If MAF and IAT sensor has been dropped, it should be replaced.
• Do not blow compressed air by using air gun or the like.
• Do not put finger or any other object into MAF and IAT sensor. Malfunction may
occur.
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect MAF and IAT sensor connector.
3) Remove air cleaner case (1).
4) Remove MAF and IAT sensor (2) from air cleaner case.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the followings.
• Tighten MAF and IAT sensor screws to specified torque.
Tightening torque
MAF and IAT sensor screw (a): 1.5 N·m (0.15 kgf-
m, 1.1 lb-ft)
• Connect MAF and IAT sensor connector securely.
1. ECM
I3RB0A130009-01
“C37-27” “C37-26” 1
I4RS0A130009-01
1
2
I4RS0A130010-01
(a)
I4RS0A130011-01
Page 287 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
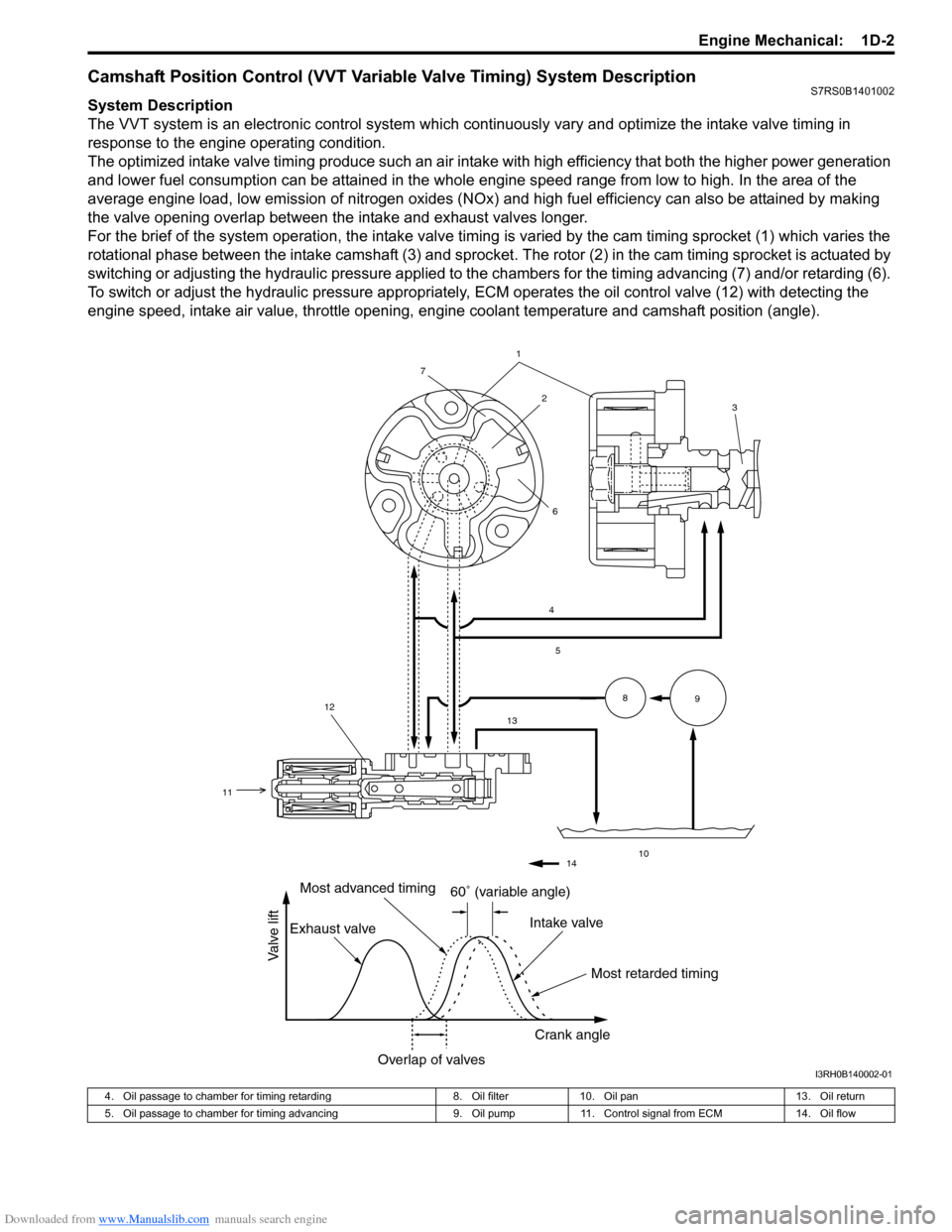
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 393 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-1
Engine
Ignition System
General Description
Ignition System ConstructionS7RS0B1801001
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below.
• ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the si gnals from the sensors, determines the most suitable
ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primar y coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power unit) in the
ignition coil assembly.
• Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built -in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is induced
in the secondary coil.
• High-tension cords and spark plugs
• CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression stroke,
detects the crank angle and adjusts in itial ignition timing automatically.
• TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, IAT sensor, knock sensor and other sensors / switches
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and No.4
spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). W hen an ignition signal is sent from ECM to the ignitor in
the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that
passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simultaneously. Likewise,
when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the ot her ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3 spark plugs spark
simultaneously.
Page 541 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-2
General Description
ABS DescriptionS7RS0B4501001
The ABS (Antilock Brake System) controls the fluid
pressure applied to the wheel cylinder of each brake
from the master cylinder so that each wheel is not locked
even when hard braking is applied.
This ABS has also the following function.
While braking is applied, but before ABS control
becomes effective, braking force is distributed between
the front and rear so as to prevent the rear wheels from
being locked too early for better stability of the vehicle.
The main component parts of this ABS include the
following parts in addition to those of the conventional
brake system.
• Wheel speed sensor which senses revolution speed of each wheel and outputs its signal.
• ABS warning light which light s to inform abnormality
when system fails to operate properly.
• ABS hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly is
incorporated ABS co ntrol module, ABS hydraulic unit
(actuator assembly), solenoid valve power supply
driver (transistor), solenoid valve driver (transistor),
pump motor driver (transistor).
– ABS control module which sends operation signal to ABS hydraulic unit to control fluid pressure
applied to each wheel cylinder based on signal
from each wheel speed sensor so as to prevent
wheel from locking.
– ABS hydraulic unit which operates according to signal from ABS control module to control fluid
pressure applied to wheel cylinder of each 4
wheels.
– Solenoid valve power supp ly driver (transistor)
which supplies power to solenoid valve in ABS
hydraulic unit.
– Solenoid valve driver (transistor) which controls each solenoid valves in ABS hydraulic unit.
– Pump motor driver (transistor) which supplies power to pump motor in ABS hydraulic unit.
This ABS is equipped with Electronic Brake force
Distribution (EBD) system that controls a fluid pressure
of rear wheels to best condition, which is the same
function as that of proportion ing valve, by the signal from
wheel sensor independently of change of load due to
load capacity and so on. An d if the EBD system fails to
operate properly, the brake warning light lights to inform
abnormality.
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module Assembly
Description
S7RS0B4501002
ABS control module is a component of ABS hydraulic
unit / control module asse mbly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ABS control module diagnose s conditions of the system
component parts (whether or not there is any
abnormality) all the time and indicates the results
(warning of abnormality occurrence and DTC) through
the ABS warning light as described.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning light lights for 2 seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality has been detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning light turns OFF
after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in th e system is detected, ABS
warning light lights and the area where that
abnormality lies is stored in the memory of EEPROM
in ABS control module.
1
I4RS0A450001-01
Page 551 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-12
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B4504006
WARNING!
When performing a driving test, select a safe
place where there is neither any traffic nor
any traffic accident possibility and be very
careful during testing to avoid occurrence of
an accident.
After repair or replace malfunction part(s), clear all DTCs
by performing the following procedure or using SUZUKI
scan tool.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector in the same manner as when making this connection
for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Erase DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan tool operator’s manual for
further derails.
NOTE
For DTC C 1021, C1022, C1025, C1026, C1031,
C1032, C1035, C1036 and C1061, confirm that
ABS warning light turns off after performing
Step 2 of “Test Driving” under “ABS Check”,
and then clear the DTCs.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
5) Perform “Driving Test” (S tep 2 of “ABS Check”) and
“DTC Check” and confirm that NO DTC is displayed
on scan tool.
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B4504007
The parameter data below are values measured with the
scan tool when the normally operating vehicle is under
the following conditions. When taking measurements for
comparison by using the scan tool, be sure to check that
the vehicle is under the following conditions.
• Apply parking brake and block wheels.
• Ignition switch ON.
• Turn OFF air conditioner (if equipped).
• Apply no load to power steering (if equipped). (Don’t turn it)
• Turn OFF all electric loads (except ignition).
• No DTC.
• ABS is not operated. (N ormal braking operation)
Scan Tool Data Definition
Battery Volt (V): Battery Voltage is an analog input
signal read by the ABS control module. Certain ABS
control module function s will be modified if the
battery voltage falls below or rises above
programmed thresholds.
Pump Motor Driver (V): This parameter indicates the
operational condition of the pump motor driver
(transistor).
RF Wheel Speed, LF Wheel Speed, RR Wheel Speed and LF Wheel Speed (km/h, MPH): Wheel speed
is an ABS control module inte rnal parameter. It is
computed by reference pulses from the wheel speed
sensor.
Brake Switch (ON, OFF): This switch signal informs
the ABS control modu le whether the brake is active
or not.
Scan Tool
Data Standards Condition
Battery
Voltage 10.0 – 18.0 V —
Pump Motor
Driver 0.0 V —
RF Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
LF Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
RR Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
LR Wheel
Sp ee d 0 km/h, 0.0 MPH Vehicle stop
Brake Switch ONBrake pedal
depressed
OFF Brake pedal released
Page 557 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-18
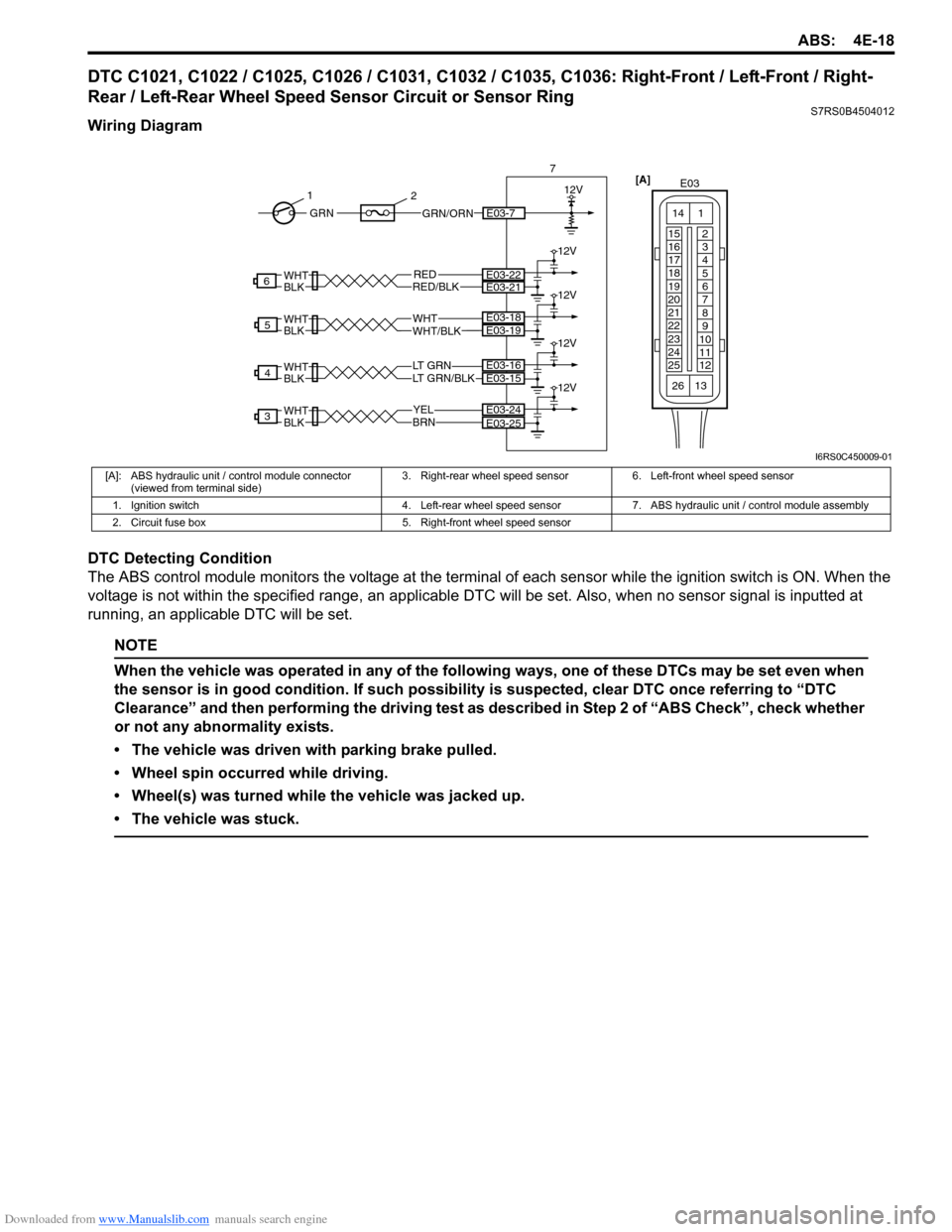
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Right-Front / Left-Front / Right-
Rear / Left-Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit or Sensor Ring
S7RS0B4504012
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition
The ABS control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of each sensor while the ignition swit ch is ON. When the
voltage is not within the specified range, an applicable DTC will be set. Also, when no sensor signal is inputted at
running, an applicable DTC will be set.
NOTE
When the vehicle was operated in any of the following ways, one of these DTCs may be set even when
the sensor is in good condition. If such possibility is suspected, clear DTC once referring to “DTC
Clearance” and then performing the driving test as described in Step 2 of “ABS Check”, check whether
or not any abnormality exists.
• The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
• Wheel spin occurred while driving.
• Wheel(s) was turned while the vehicle was jacked up.
• The vehicle was stuck.
YELBRN
3E03-24
LT GRN/BLKLT GRN
4
WHTWHT/BLK
5
RED
WHTBLK
WHTBLK
WHTBLK
WHTBLKRED/BLK
6
E03-25
E03-15E03-16
E03-19E03-18
E03-22E03-21
12V
12V
12V
12V
12V
7
GRN/ORNE03-7GRN
1
2
[A]
E03
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
13
14
26
I6RS0C450009-01
[A]: ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector
(viewed from terminal side) 3. Right-rear wheel speed sensor 6. Left-front wheel speed sensor
1. Ignition switch 4. Left-rear wheel speed sensor 7. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly
2. Circuit fuse box 5. Right-front wheel speed sensor