Page 118 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT 3A-1
6F1
6F2
6G
6H
7A
3A
7B1
7C1
7D
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 3A
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
CONTENTS
General Description ........................................3A-2
Toe Setting .................................................... 3A-2
Camber ......................................................... 3A-2
Alignment Service Data (Reference) ............. 3A-2
Diagnosis .........................................................3A-3
Diagnosis Table ............................................ 3A-3
Preliminary Checks Prior To Adjusting Front
Wheel Alignment ........................................... 3A-3Toe Adjustment ............................................. 3A-3
Camber And Caster Check And
Adjustment .................................................... 3A-4
Steering Angle Check And Adjustment ......... 3A-4
Side Slip(Reference) ..................................... 3A-4
Page 119 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3A-2 FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
General Description
Front alignment refers to the angular relationship between the
front wheels, the front suspension attaching parts and the ground.
Generally, the only adjustment required for front wheel alignment
is toe setting.
Camber and caster can’t be adjusted. Therefore, should camber
or caster be out of specification due to the damage caused by
hazardous road conditions or collision, whether the damage is in
body or in suspension should be determined. If the body is dam-
aged, it should be repaired and if suspension is damaged, it
should be replaced.
Toe Setting
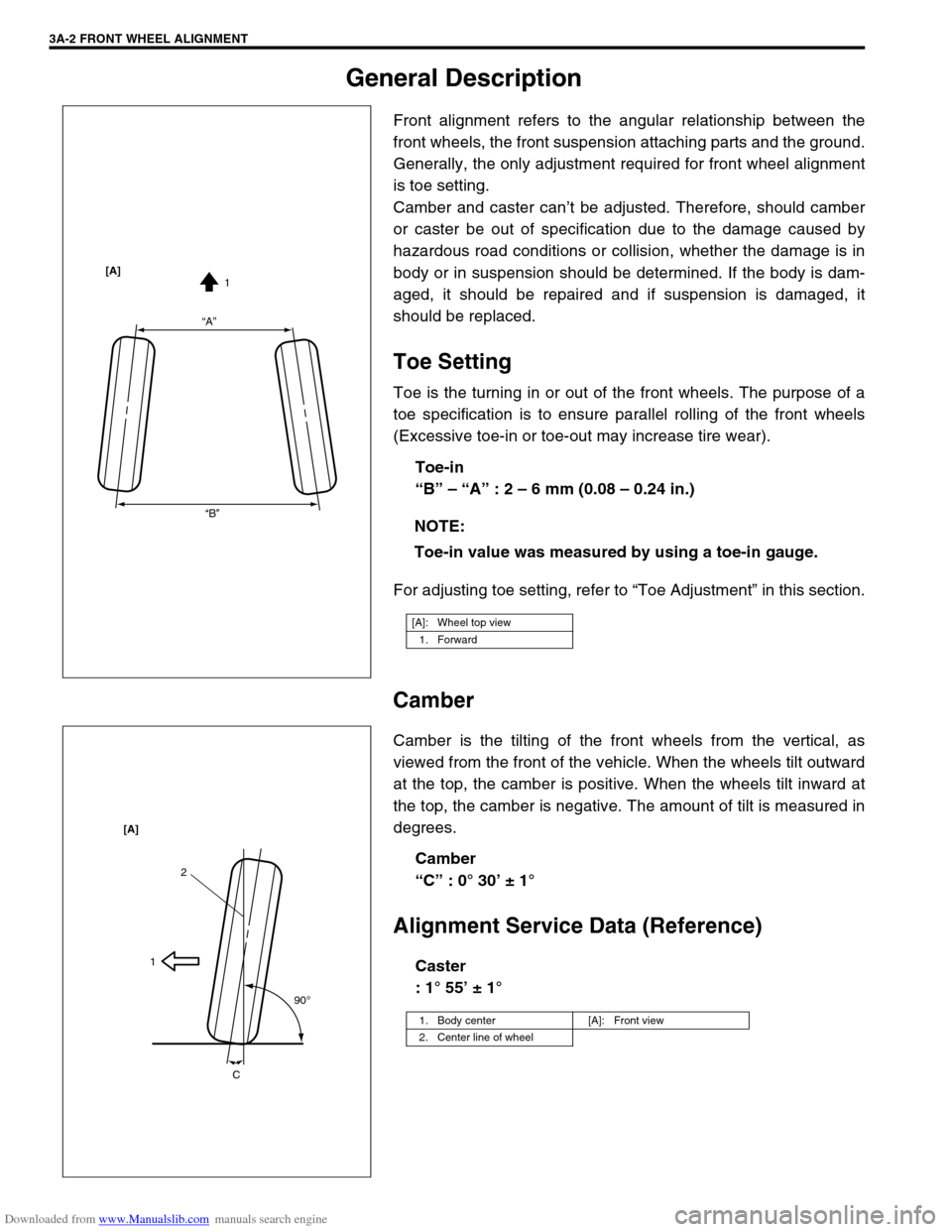
Toe is the turning in or out of the front wheels. The purpose of a
toe specification is to ensure parallel rolling of the front wheels
(Excessive toe-in or toe-out may increase tire wear).
Toe-in
“B” – “A” : 2 – 6 mm (0.08 – 0.24 in.)
For adjusting toe setting, refer to “Toe Adjustment” in this section.
Camber
Camber is the tilting of the front wheels from the vertical, as
viewed from the front of the vehicle. When the wheels tilt outward
at the top, the camber is positive. When the wheels tilt inward at
the top, the camber is negative. The amount of tilt is measured in
degrees.
Camber
“C” : 0° 30’ ± 1°
Alignment Service Data (Reference)
Caster
: 1° 55’ ± 1° NOTE:
Toe-in value was measured by using a toe-in gauge.
[A]: Wheel top view
1. Forward
“A”
“B”1 [A]
1. Body center [A]: Front view
2. Center line of wheel
2
1
90
o
C [A]
Page 120 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT 3A-3
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
For the details, refer to “Diagnosis Table” in Section 3.
Preliminary Checks Prior To Adjusting Front Wheel Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. An additional item to be
checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the deviation of the
vehicle from a straight path on a level road without hand pressure on the steering wheel. Section 3 of this man-
ual contains a procedure for determining the presence of a tire lead problem. Before making any adjustment
affecting toe setting, the following checks and inspections should be made to ensure correctness of alignment
readings and alignment adjustments:
1) Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and approximately the same tread wear.
2) Check for loose of king pin bearings. Check tie rod ends; if excessive looseness is noted, it must be cor-
rected before adjusting.
3) Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
4) Check vehicle trim heights; if out of limits and a correction is to be made, it must be made before adjusting
toe.
5) Check for loose of suspension arms.
6) Check for loose or missing stabilizer bar attachments.
7) Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment checks.
8) Consider condition of equipment being used to check alignment and follow manufacturer's instructions.
9) Regardless of equipment used to check alignment, vehicle must be on a level surface both fore and aft and
transversely.
Toe Adjustment
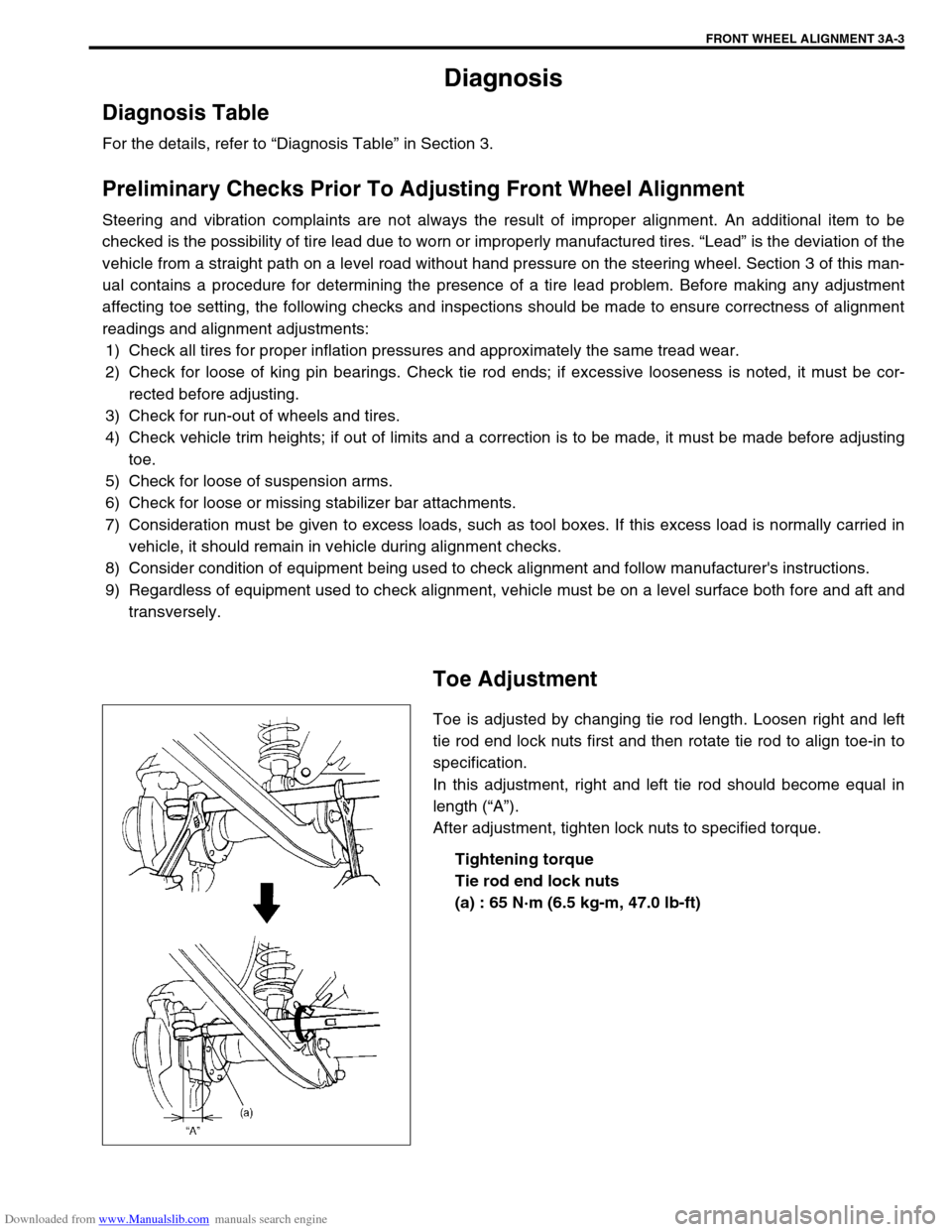
Toe is adjusted by changing tie rod length. Loosen right and left
tie rod end lock nuts first and then rotate tie rod to align toe-in to
specification.
In this adjustment, right and left tie rod should become equal in
length (“A”).
After adjustment, tighten lock nuts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Tie rod end lock nuts
(a) : 65 N·m (6.5 kg-m, 47.0 lb-ft)
Page 121 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3A-4 FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Camber And Caster Check And Adjustment
Should camber or caster be found out of specifications upon
inspection, locate its cause first. If it is in damaged, loose, bent,
dented or worn suspension parts and axle housing, they should
be replaced. If it is in vehicle body, repair it so as to attain specifi-
cations.
Steering Angle Check And Adjustment
When tie rod (2) or tie rod end (3) was replaced, check toe and
then also steering angle with turning radius gauge (1).
If steering angle is not correct, check if right and left tie rods are
equal in length “A”.
Steering angle
Inside : 35° ± 3°
Outside : 32° ± 3°
Side Slip(Reference)
For inspecting front wheel side slip with side slip tester:
If side slip exceeds limit, toe or front wheel alignment may out not
be correct.
Side slip limit
: Less than 3 mm/m (Less than 0.118 in/3 ft) NOTE:
To prevent possible incorrect reading of camber or
caster, vehicle front end must be moved up and down a
few times before inspection.
NOTE:
If tie rod lengths were changed to adjust steering angle,
reinspect toe-in.