2005 SUZUKI JIMNY electric
[x] Cancel search: electricPage 15 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-10 GENERAL INFORMATION
Precautions For Catalytic Converter
For vehicles equipped with a catalytic converter, use only unleaded gasoline and be careful not to let a
large amount of unburned gasoline enter the converter or it can be damaged.
Conduct a spark jump test only when necessary, make it as short as possible, and do not open the
throttle.
Conduct engine compression checks within the shortest possible time.
Avoid situations which can result in engine misfire (e.g. starting the engine when the fuel tank is
nearly empty.)
Precautions For Electrical Circuit Service
When replacing a fuse, make sure to use a fuse of the
specified capacity. Use of a fuse with a larger capacity
will cause a damage to the electrical parts and a fire.
When disconnecting and connecting coupler, make sure
to turn ignition switch OFF, or electronic parts may get
damaged.
When disconnecting connectors, never pull the wiring
harnesses. Unlock the connector lock first and then pull
them apart by holding connectors themselves.
Page 16 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-11
When connecting connectors, also hold connectors and
push them together until they lock securely (a click is
heard).
When installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps so
that no slack is left.
When installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the wir-
ing harness is not interfered with or caught by any other
part.
To avoid damage to the harness, protect its part which
may contact against a part forming a sharp angle by
winding tape or the like around it.
Be careful not to touch the electrical terminals of parts
which use microcomputers (e.g. electronic control unit
like as ECM, PCM, P/S controller, etc.). The static elec-
tricity from your body can damage these parts.
Page 17 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-12 GENERAL INFORMATION
Never connect any tester (voltmeter, ohmmeter, or what-
ever) to electronic control unit when its coupler is dis-
connected. Attempt to do it may cause damage to it.
Never connect an ohmmeter to electronic control unit
with its coupler connected to it. Attempt to do it may
cause damage to electronic control unit and sensors.
Be sure to use a specified voltmeter / ohmmeter. Other-
wise, accurate measurements may not be obtained or
personal injury may result.
When taking measurements at electrical connectors
using a tester probe (2), be sure to insert the probe from
the wire harness side (backside) of the connector (1).
When connecting meter probe (2) from terminal side of
coupler (1) because it can’t be connected from harness
side, use extra care not to bend male terminal of coupler
of force its female terminal open for connection.
In case of such coupler as shown connect probe as
shown to avoid opening female terminal.
Never connect probe where male terminal is supposed
to fit.
When checking connection of terminals, check its male
half for bend and female half for excessive opening and
both for locking (looseness), corrosion, dust, etc.
Before measuring voltage to check for electrical system,
check to make sure that battery voltage is 11V or higher.
Such terminal voltage check at low battery voltage will
lead to erroneous diagnosis.
Page 18 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-13
Electrical Circuit Inspection Procedure
While there are various electrical circuit inspection methods,
described here is a general method to check its open and short
circuit by using an ohmmeter and a voltmeter.
Open circuit check
Possible causes for the open circuit are as follows. As the cause
is in the connector or terminal in many cases, they need to be
checked particularly carefully.
Loose connection of connector
Poor contact of terminal (due to dirt, corrosion or rust on it,
poor contact tension, entry of foreign object etc.)
Wire harness being open
When checking system circuits including an electronic control unit
such as ECM, TCM, ABS control module, etc., it is important to
perform careful check, starting with items which are easier to
check.
1) Disconnect negative cable from battery
2) Check each connector at both ends of the circuit being
checked for loose connection. Also check lock condition of
connector if equipped with connector lock.
3) Using a test male terminal, check both terminals of the circuit
being checked for contact tension of its female terminal.
Check each terminal visually for poor contact (possibly
caused by dirt, corrosion, rust entry of foreign object, etc.).
At the same time, check to make sure that each terminal is
locked in the connector fully.
4) Using the following continuity check or voltage check proce-
dure, check the wire harness for open circuit and poor con-
nection with its terminals. Locate abnormality, if any.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just for once
1. Looseness of crimping
2. Open
3. Thin wire (single strand of wire)
Page 20 of 687
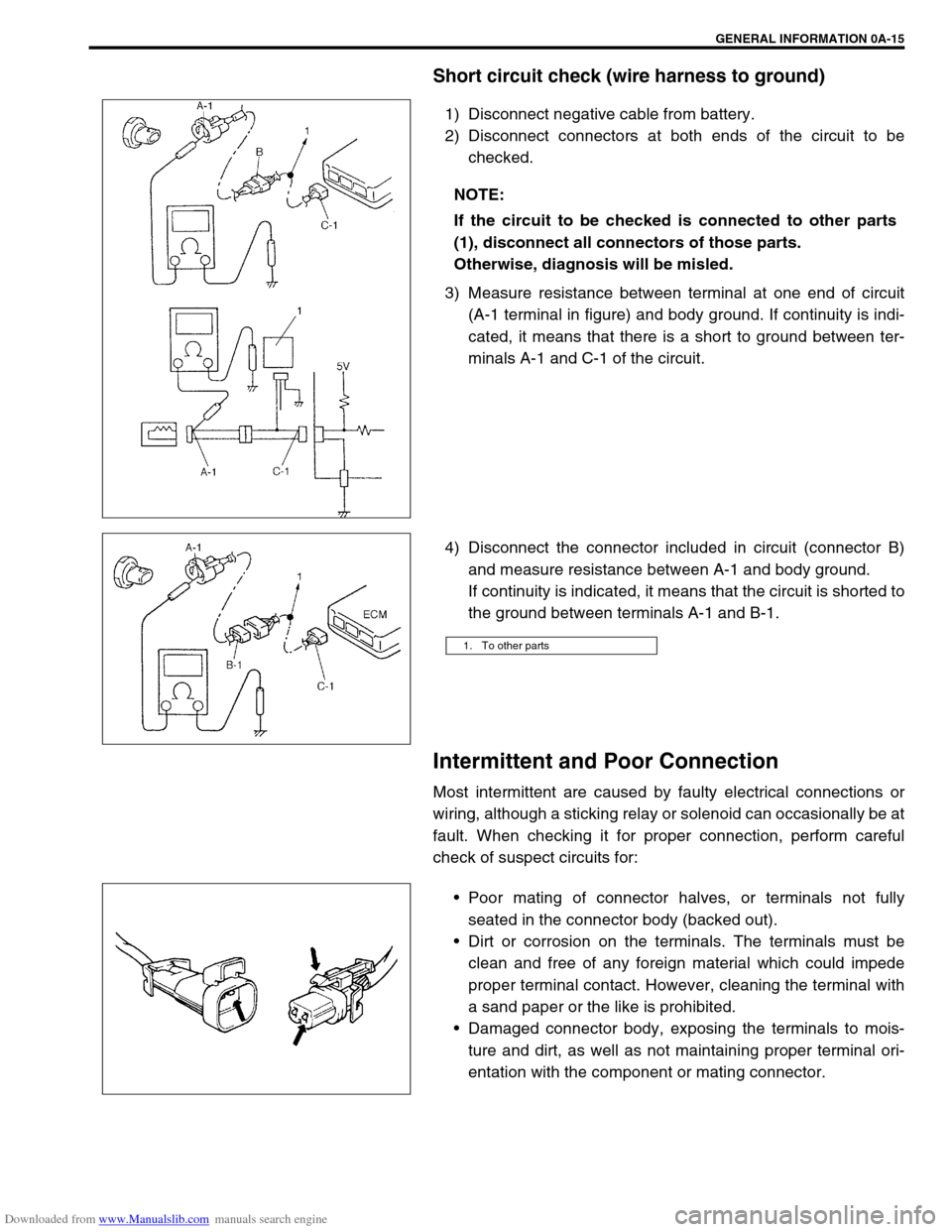
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-15
Short circuit check (wire harness to ground)
1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
2) Disconnect connectors at both ends of the circuit to be
checked.
3) Measure resistance between terminal at one end of circuit
(A-1 terminal in figure) and body ground. If continuity is indi-
cated, it means that there is a short to ground between ter-
minals A-1 and C-1 of the circuit.
4) Disconnect the connector included in circuit (connector B)
and measure resistance between A-1 and body ground.
If continuity is indicated, it means that the circuit is shorted to
the ground between terminals A-1 and B-1.
Intermittent and Poor Connection
Most intermittent are caused by faulty electrical connections or
wiring, although a sticking relay or solenoid can occasionally be at
fault. When checking it for proper connection, perform careful
check of suspect circuits for:
Poor mating of connector halves, or terminals not fully
seated in the connector body (backed out).
Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. The terminals must be
clean and free of any foreign material which could impede
proper terminal contact. However, cleaning the terminal with
a sand paper or the like is prohibited.
Damaged connector body, exposing the terminals to mois-
ture and dirt, as well as not maintaining proper terminal ori-
entation with the component or mating connector. NOTE:
If the circuit to be checked is connected to other parts
(1), disconnect all connectors of those parts.
Otherwise, diagnosis will be misled.
1. To other parts
Page 181 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3D-8 FRONT SUSPENSION
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
For description not found in the table below, refer to “Diagnosis Table” in Section 3.
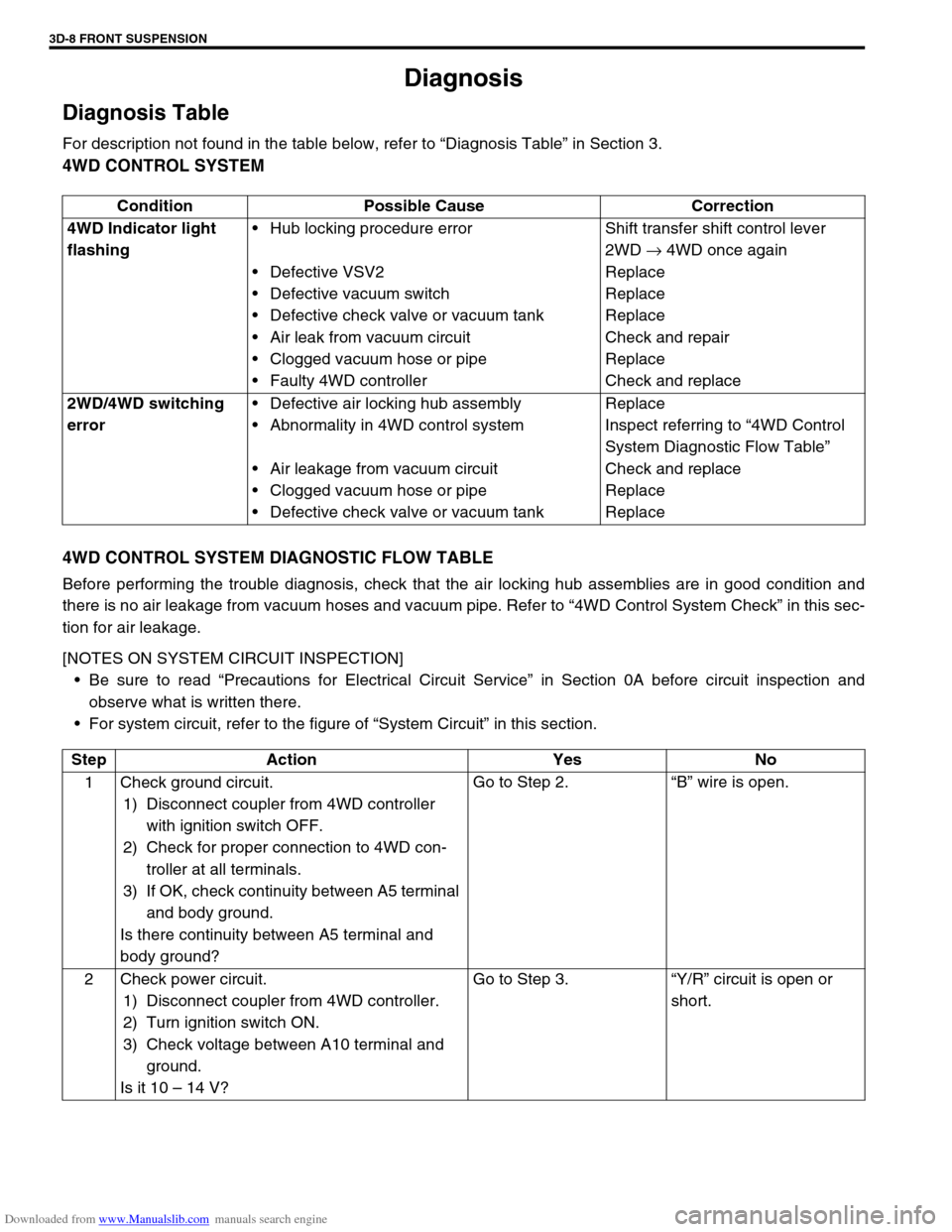
4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
4WD CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE
Before performing the trouble diagnosis, check that the air locking hub assemblies are in good condition and
there is no air leakage from vacuum hoses and vacuum pipe. Refer to “4WD Control System Check” in this sec-
tion for air leakage.
[NOTES ON SYSTEM CIRCUIT INSPECTION]
Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service” in Section 0A before circuit inspection and
observe what is written there.
For system circuit, refer to the figure of “System Circuit” in this section. Condition Possible Cause Correction
4WD Indicator light
flashingHub locking procedure error
Defective VSV2
Defective vacuum switch
Defective check valve or vacuum tank
Air leak from vacuum circuit
Clogged vacuum hose or pipe
Faulty 4WD controllerShift transfer shift control lever
2WD → 4WD once again
Replace
Replace
Replace
Check and repair
Replace
Check and replace
2WD/4WD switching
errorDefective air locking hub assembly
Abnormality in 4WD control system
Air leakage from vacuum circuit
Clogged vacuum hose or pipe
Defective check valve or vacuum tankReplace
Inspect referring to “4WD Control
System Diagnostic Flow Table”
Check and replace
Replace
Replace
Step Action Yes No
1 Check ground circuit.
1) Disconnect coupler from 4WD controller
with ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to 4WD con-
troller at all terminals.
3) If OK, check continuity between A5 terminal
and body ground.
Is there continuity between A5 terminal and
body ground?Go to Step 2.“B” wire is open.
2 Check power circuit.
1) Disconnect coupler from 4WD controller.
2) Turn ignition switch ON.
3) Check voltage between A10 terminal and
ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 3.“Y/R” circuit is open or
short.
Page 359 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) table ......... 6-16
Fail-safe table............................................ 6-19
Visual inspection ....................................... 6-20
Engine basic inspection ............................ 6-21
Engine diagnosis table .............................. 6-23
Scan Tool Data ............................................. 6-28
Scan tool data definitions .......................... 6-30
Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits ................ 6-33
Component Location ..................................... 6-42
Table A-1 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Lamp Does Not Come “ON” at Ignition
Switch ON (But Engine at Stop).................... 6-43
Table A-2 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Lamp Remains “ON” after Engine
Starts............................................................. 6-44
Table A-3 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Mil Flashes at Ignition Switch ON .... 6-45
Table A-4 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - MIL Does Not Flash, Just Remains
ON or Just Remains OFF Even with Grounding
Diagnosis Switch Terminal............................ 6-45
Table A-5 ECM Power and Ground Circuit
Check - MIL Doesn’t Light at Ignition Switch
ON and Engine Doesn’t Start Though It Is
Cranked Up ................................................... 6-46
DTC P0105 (DTC No.11) Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP) Circuit Malfunction .............. 6-48
DTC P0110 (DTC No.18) Intake Air Temp.
(IAT) Circuit Malfunction ............................... 6-51
DTC P0115 (DTC No.19) Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) Circuit Malfunction ........ 6-53
DTC P0120 (DTC No.13) Throttle Position
Circuit Malfunction ........................................ 6-55
DTC P0121 Throttle Position Circuit Range /
Performance Problem ................................... 6-57
DTC P0130 (DTC No.14) Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Malfunction
(Sensor-1) ..................................................... 6-59
DTC P0133 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Circuit Slow Response (Sensor-1) ................ 6-61
DTC P0135 (DTC No.14) Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Sensor-1) ..................................................... 6-62
DTC P0136 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Circuit Malfunction (Sensor-2) ...................... 6-64
DTC P0141 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Heater Circuit Malfunction (Sensor-2)........... 6-66
DTC P0171 Fuel System Too Lean .............. 6-68
DTC P0172 Fuel System Too Rich ............... 6-68
DTC P0300 Random Misfire Detected
(Misfire Detected at 2 or More Cylinders) ..... 6-72DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0325 (DTC No.17) Knock Sensor Circuit
Malfunction .................................................... 6-77
DTC P0335 (DTC No.23) Crankshaft Position
(CKP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction .................. 6-79
DTC P0340 (DTC No.15) Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction ................. 6-82
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow
Malfunction .................................................... 6-85
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency below
Threshold ....................................................... 6-88
DTC P0443 Purge Control Valve Circuit
Malfunction .................................................... 6-91
DTC P0481 A/C Condenser Fan Control
Circuit Malfunction ......................................... 6-92
DTC P0500 (DTC No.16) Vehicle Speed
Sensor (VSS) Malfunction ............................. 6-94
DTC P0505 Idle Control System
Malfunction .................................................... 6-96
DTC P0601 Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error (DTC No.71) ...................... 6-98
DTC P1450 Barometric Pressure Sensor
Low / High Input ............................................. 6-99
DTC P1451 Barometric Pressure Sensor
Performance Problem .................................... 6-99
DTC P1500 Engine Starter Signal Circuit
Malfunction .................................................. 6-101
DTC P1510 ECM Back-up Power Supply
Malfunction .................................................. 6-103
DTC P1570 (DTC No.21) ABS Signal Circuit
Malfunction .................................................. 6-104
DTC P1600 Serial Communication Problem
Between ECM and TCM .............................. 6-105
DTC P1717 A/T Drive Range (Park / Neutral
Position) Signal Circuit Malfunction ............. 6-107
Table B-1 Fuel Injector Circuit Check ..........6-109
Table B-2 Fuel Pump and Its Circuit
Check........................................................... 6-110
Table B-3 Fuel Pressure Check................... 6-112
Table B-4 Idle Air Control System Check ....6-114
Table B-5 A/C Signal Circuits Check
(Vehicle with A/C) ........................................ 6-117
Table B-6 Electric Load Signal Circuit
Check........................................................... 6-119
TAble B-7 A/C Condenser Fan Control
System Check.............................................. 6-121
Special Tool ................................................... 6-123
Page 360 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-3
General Information
Statement on Cleanliness and Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances
that are measured in the thousands of an millimeter (ten thousands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
Throughout this section, it should be understood that proper cleaning and protection of machined surfaces and
friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically
stated.
A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate the
surfaces on initial operation.
Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft jour-
nal bearings are removed for service, they should be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in the same locations and with the same mating surfaces
as when removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness or other electrical parts.
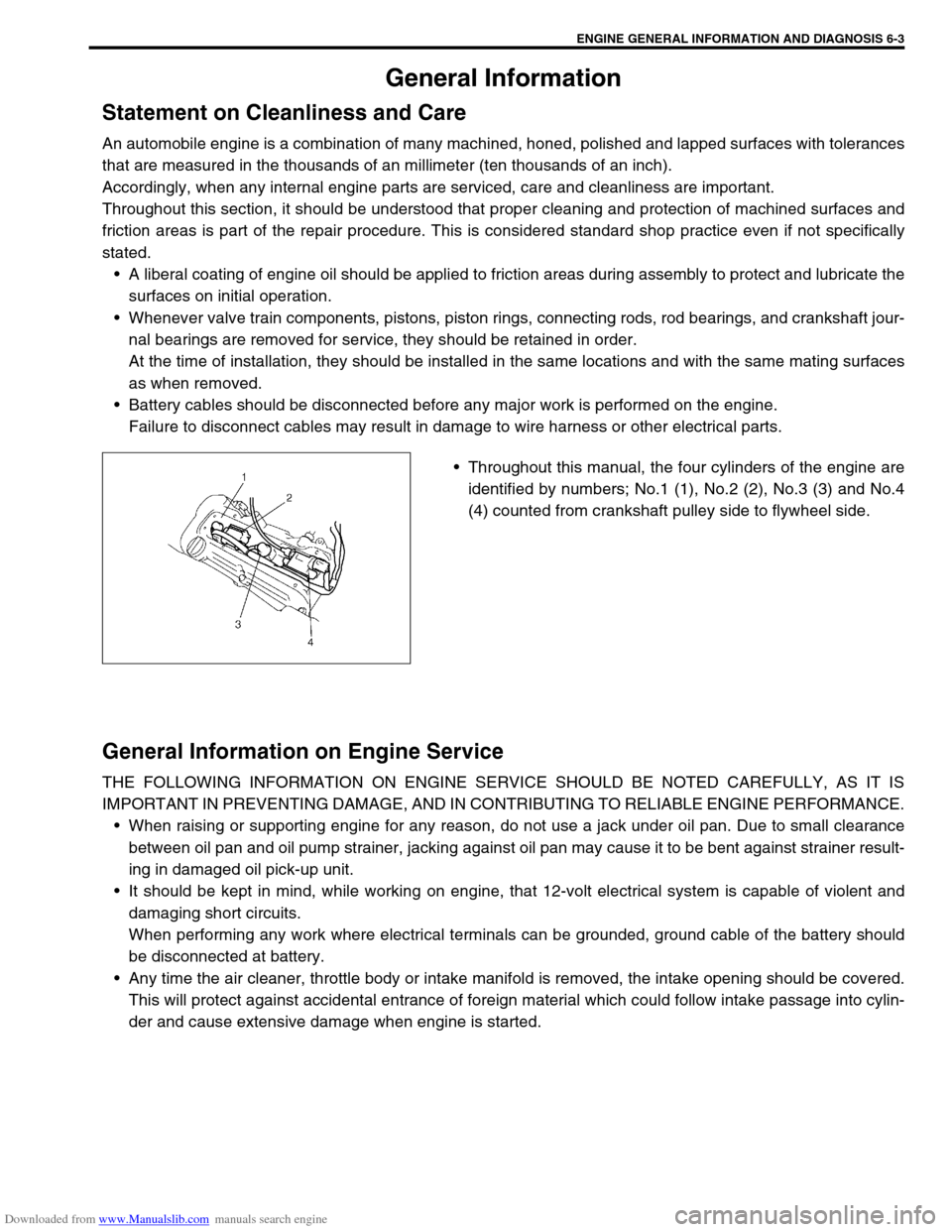
Throughout this manual, the four cylinders of the engine are
identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2), No.3 (3) and No.4
(4) counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
General Information on Engine Service
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION ON ENGINE SERVICE SHOULD BE NOTED CAREFULLY, AS IT IS
IMPORTANT IN PREVENTING DAMAGE, AND IN CONTRIBUTING TO RELIABLE ENGINE PERFORMANCE.
When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer result-
ing in damaged oil pick-up unit.
It should be kept in mind, while working on engine, that 12-volt electrical system is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be covered.
This will protect against accidental entrance of foreign material which could follow intake passage into cylin-
der and cause extensive damage when engine is started.