2005 SUZUKI JIMNY Lines
[x] Cancel search: LinesPage 255 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-2 PROPELLER SHAFTS
General Description
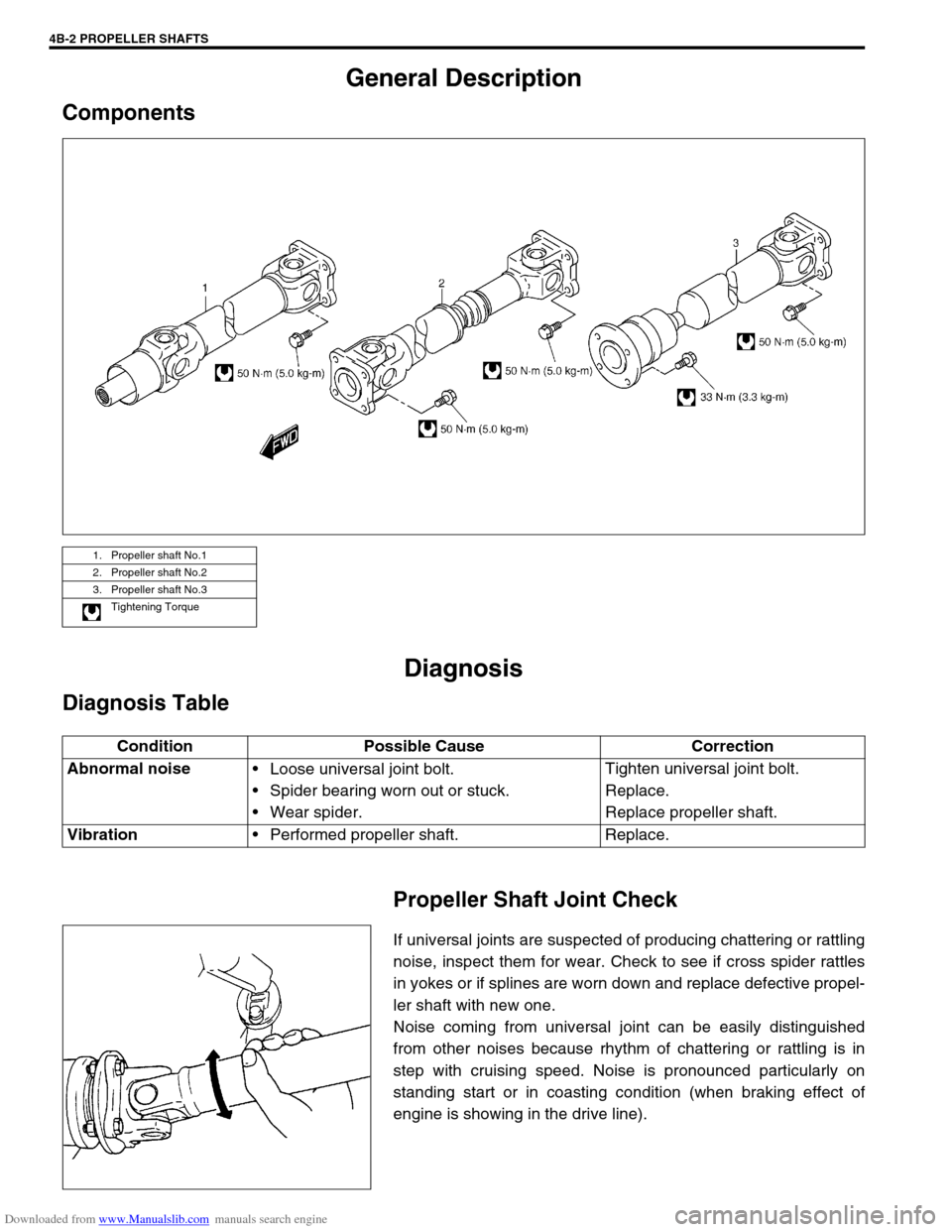
Components
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
Propeller Shaft Joint Check
If universal joints are suspected of producing chattering or rattling
noise, inspect them for wear. Check to see if cross spider rattles
in yokes or if splines are worn down and replace defective propel-
ler shaft with new one.
Noise coming from universal joint can be easily distinguished
from other noises because rhythm of chattering or rattling is in
step with cruising speed. Noise is pronounced particularly on
standing start or in coasting condition (when braking effect of
engine is showing in the drive line).
1. Propeller shaft No.1
2. Propeller shaft No.2
3. Propeller shaft No.3
Tightening Torque
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Abnormal noise
Loose universal joint bolt.
Spider bearing worn out or stuck.
Wear spider.Tighten universal joint bolt.
Replace.
Replace propeller shaft.
Vibration
Performed propeller shaft. Replace.
Page 257 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-4 PROPELLER SHAFTS
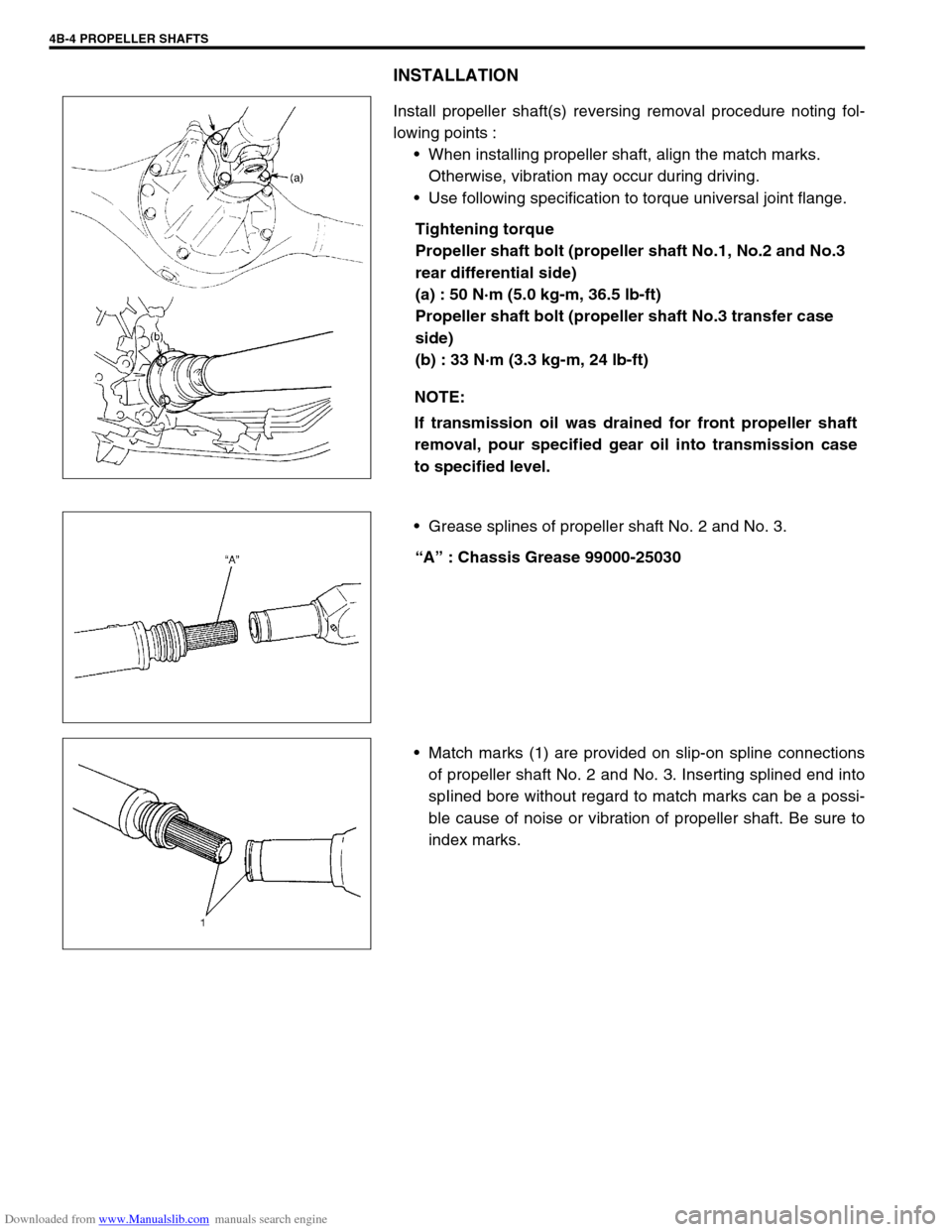
INSTALLATION
Install propeller shaft(s) reversing removal procedure noting fol-
lowing points :
When installing propeller shaft, align the match marks.
Otherwise, vibration may occur during driving.
Use following specification to torque universal joint flange.
Tightening torque
Propeller shaft bolt (propeller shaft No.1, No.2 and No.3
rear differential side)
(a) : 50 N·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
Propeller shaft bolt (propeller shaft No.3 transfer case
side)
(b) : 33 N·m (3.3 kg-m, 24 lb-ft)
Grease splines of propeller shaft No. 2 and No. 3.
“A” : Chassis Grease 99000-25030
Match marks (1) are provided on slip-on spline connections
of propeller shaft No. 2 and No. 3. Inserting splined end into
spIined bore without regard to match marks can be a possi-
ble cause of noise or vibration of propeller shaft. Be sure to
index marks. NOTE:
If transmission oil was drained for front propeller shaft
removal, pour specified gear oil into transmission case
to specified level.
Page 260 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine PROPELLER SHAFTS 4B-7
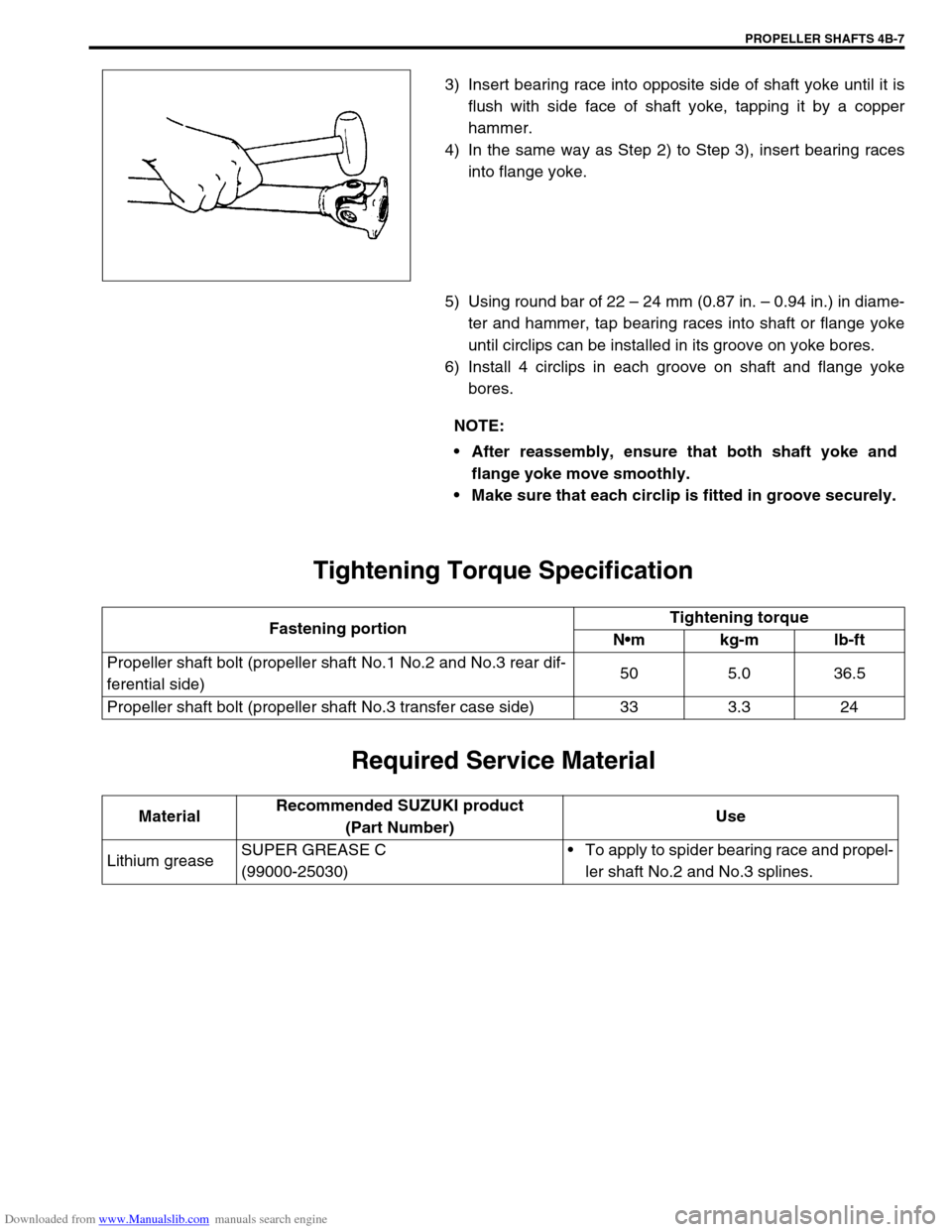
3) Insert bearing race into opposite side of shaft yoke until it is
flush with side face of shaft yoke, tapping it by a copper
hammer.
4) In the same way as Step 2) to Step 3), insert bearing races
into flange yoke.
5) Using round bar of 22 – 24 mm (0.87 in. – 0.94 in.) in diame-
ter and hammer, tap bearing races into shaft or flange yoke
until circlips can be installed in its groove on yoke bores.
6) Install 4 circlips in each groove on shaft and flange yoke
bores.
Tightening Torque Specification
Required Service Material
NOTE:
After reassembly, ensure that both shaft yoke and
flange yoke move smoothly.
Make sure that each circlip is fitted in groove securely.
Fastening portionTightening torque
Nm kg-m lb-ft
Propeller shaft bolt (propeller shaft No.1 No.2 and No.3 rear dif-
ferential side)50 5.0 36.5
Propeller shaft bolt (propeller shaft No.3 transfer case side) 33 3.3 24
MaterialRecommended SUZUKI product
(Part Number)Use
Lithium greaseSUPER GREASE C
(99000-25030)To apply to spider bearing race and propel-
ler shaft No.2 and No.3 splines.
Page 266 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-5
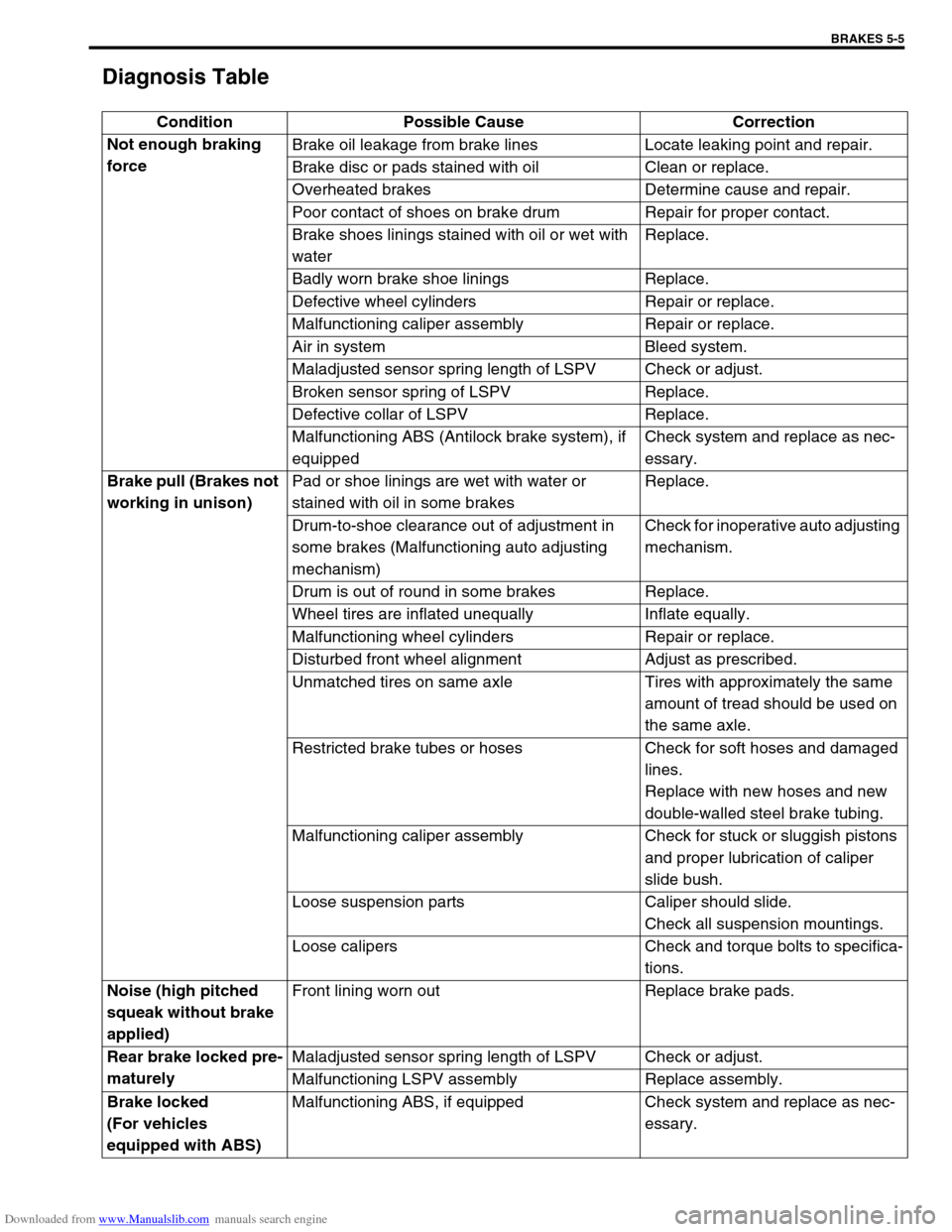
Diagnosis Table
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Not enough braking
forceBrake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or pads stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Poor contact of shoes on brake drum Repair for proper contact.
Brake shoes linings stained with oil or wet with
waterReplace.
Badly worn brake shoe linings Replace.
Defective wheel cylinders Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Air in system Bleed system.
Maladjusted sensor spring length of LSPV Check or adjust.
Broken sensor spring of LSPV Replace.
Defective collar of LSPV Replace.
Malfunctioning ABS (Antilock brake system), if
equippedCheck system and replace as nec-
essary.
Brake pull (Brakes not
working in unison)Pad or shoe linings are wet with water or
stained with oil in some brakesReplace.
Drum-to-shoe clearance out of adjustment in
some brakes (Malfunctioning auto adjusting
mechanism)Check for inoperative auto adjusting
mechanism.
Drum is out of round in some brakes Replace.
Wheel tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Malfunctioning wheel cylinders Repair or replace.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same
amount of tread should be used on
the same axle.
Restricted brake tubes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged
lines.
Replace with new hoses and new
double-walled steel brake tubing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Check for stuck or sluggish pistons
and proper lubrication of caliper
slide bush.
Loose suspension parts Caliper should slide.
Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifica-
tions.
Noise (high pitched
squeak without brake
applied)Front lining worn out Replace brake pads.
Rear brake locked pre-
maturelyMaladjusted sensor spring length of LSPV Check or adjust.
Malfunctioning LSPV assembly Replace assembly.
Brake locked
(For vehicles
equipped with ABS)Malfunctioning ABS, if equipped Check system and replace as nec-
essary.
Page 270 of 687
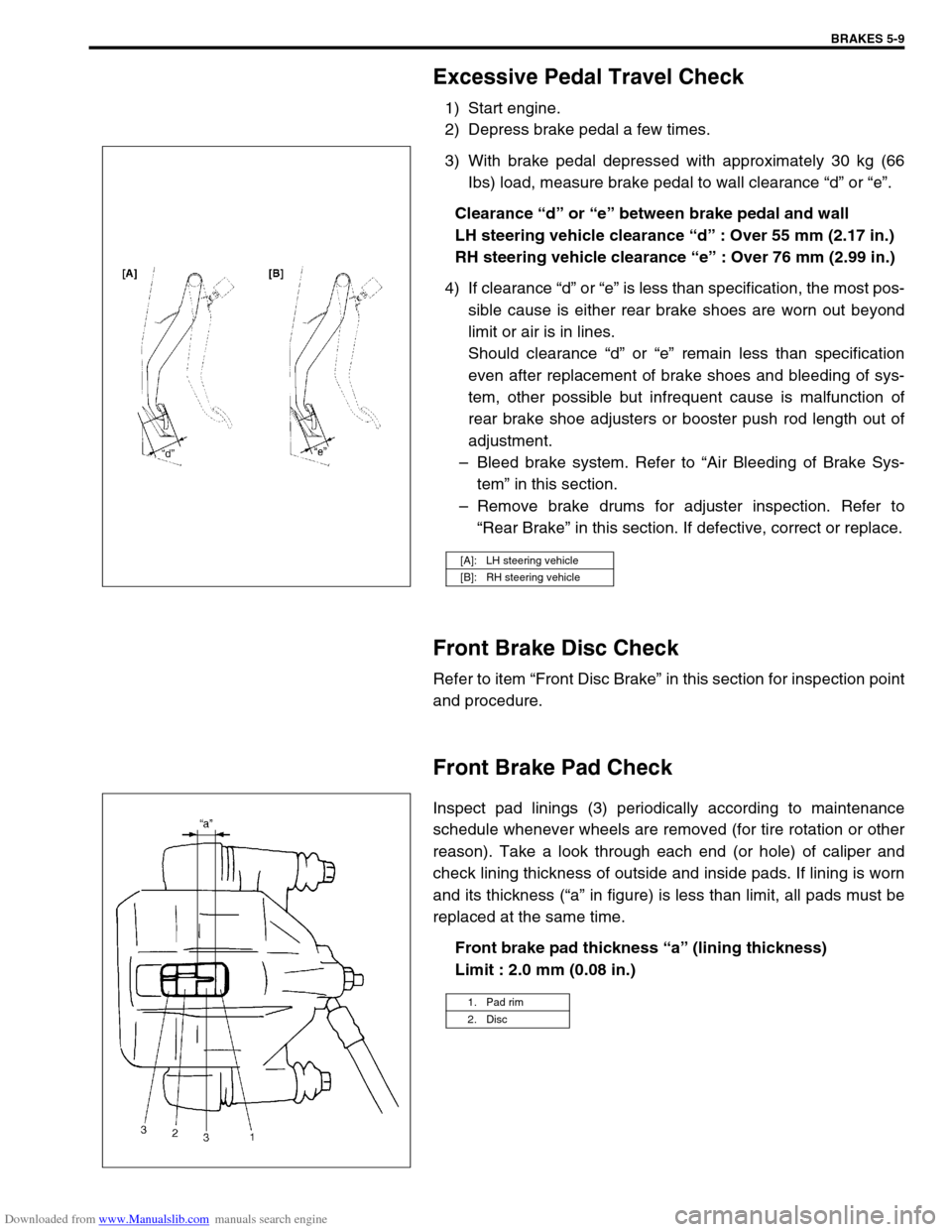
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-9
Excessive Pedal Travel Check
1) Start engine.
2) Depress brake pedal a few times.
3) With brake pedal depressed with approximately 30 kg (66
Ibs) load, measure brake pedal to wall clearance “d” or “e”.
Clearance “d” or “e” between brake pedal and wall
LH steering vehicle clearance “d” : Over 55 mm (2.17 in.)
RH steering vehicle clearance “e” : Over 76 mm (2.99 in.)
4) If clearance “d” or “e” is less than specification, the most pos-
sible cause is either rear brake shoes are worn out beyond
limit or air is in lines.
Should clearance “d” or “e” remain less than specification
even after replacement of brake shoes and bleeding of sys-
tem, other possible but infrequent cause is malfunction of
rear brake shoe adjusters or booster push rod length out of
adjustment.
–Bleed brake system. Refer to “Air Bleeding of Brake Sys-
tem” in this section.
–Remove brake drums for adjuster inspection. Refer to
“Rear Brake” in this section. If defective, correct or replace.
Front Brake Disc Check
Refer to item “Front Disc Brake” in this section for inspection point
and procedure.
Front Brake Pad Check
Inspect pad linings (3) periodically according to maintenance
schedule whenever wheels are removed (for tire rotation or other
reason). Take a look through each end (or hole) of caliper and
check lining thickness of outside and inside pads. If lining is worn
and its thickness (“a” in figure) is less than limit, all pads must be
replaced at the same time.
Front brake pad thickness “a” (lining thickness)
Limit : 2.0 mm (0.08 in.)
[A]: LH steering vehicle
[B]: RH steering vehicle
1. Pad rim
2. Disc
Page 272 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-11
Rear Drum Brake Shoe Adjustment
Rear brake has self-adjusting mechanism but it does require
adjustment for proper drum to shoe clearance when brake shoe
has been replaced or brake drum has been removed for some
other service.
Adjustment is automatically accomplished by depressing brake
pedal about 30 times with approximately 30 kg (66 Ibs) load after
all parts are installed.
Then check brake drum for dragging and brake system for proper
performance. After lowering vehicle from hoist, brake test should
be performed.
Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment
INSPECTION
Hold center of parking brake lever grip and pull it up with 20 kg
(44 Ibs) force.
With parking brake lever pulled up as above, count ratchet
notches.
There should be 6 to 8 notches.
Also, check if both right and left rear wheels are locked firmly. To
count number of notches easily, listen to click sounds that ratchet
makes while pulling parking brake lever without pressing its but-
ton.
One click sound corresponds to one notch.NOTE:
Be sure to use particular brake fluid either as indicated
on reservoir cap of that vehicle or recommended in
owner’s manual which comes along with that vehicle.
Use of any other fluid is strictly prohibited.
Fluid level should be between MIN and MAX lines marked
on reservoir.
When brake warning lamp lights sometimes during driv-
ing, replenish fluid to MAX level.
When fluid decreases quickly, inspect brake system for
leakage.
Correct leaky points and then refill to specified level.
CAUTION:
Do not use shock absorber fluid or any other fluid which
contains mineral oil. Do not use a container which has
been used for mineral oil or a container which is wet from
water. Mineral oil will cause swelling and distortion of
rubber parts in hydraulic brake system and water mixed
into brake fluid will lower fluid boiling point. Keep all fluid
containers capped to prevent contamination.
Page 274 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-13
CHECK AIR TIGHTNESS
1) Start engine.
2) Stop engine after running for 1 to 2 minutes.
3) Depress brake pedal several times with the same load as in
ordinary braking and observe pedal travel. If pedal goes
down deep the first time but its travel decreases as it is
depressed the second and more times, air tightness is
obtained.
4) If pedal travel doesn’t change, air tightness isn’t obtained.
CHECK OPERATION
1) With engine stopped, depress brake pedal several times with
the same load and make sure that pedal travel doesn’t
change.
2) Start engine while depressing brake pedal. If pedal travel
increases a little, operation is satisfactory. But no change in
pedal travel indicates malfunction.
1. 1st
2. 2nd
3. 3rd
NOTE:
If defective, inspect vacuum lines and sealing parts, and
replace any faulty part. When this has been done, repeat
the entire test.
1. 1st, 2nd, 3rd
Page 278 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-17
On-Vehicle Service
Air Bleeding of Brake System
Bleeding operation is necessary to remove air whenever it
entered hydraulic brake system.
Hydraulic lines of brake system consists of two separate lines,
one for front wheel brakes and the other for rear wheel brakes. Air
bleeding is necessary at right and left front wheel brakes, left rear
wheel brake and LSPV (if equipped), i.e. 3 (4 for vehicle with
LSPV) places in all.
Be sure to bleed air of brake system according to following proce-
dure when its oil hydraulic circuit has been disconnected.
1) Fill master cylinder reservoir with brake fluid and keep at
least one-half full of fluid during bleeding operation.
2) Remove bleeder plug cap (1).
Attach a vinyl tube (2) to bleeder plug, and insert the other
end into container (3).
3) Depress brake pedal several times, and then while holding it
depressed, loosen bleeder plug about one-third to one-half
turn. CAUTION:
Brake fluid is extremely damaging to paint. If fluid should
accidentally touch painted surface, immediately wipe
fluid from paint and clean painted surface.