2005 SUZUKI JIMNY air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 339 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5E-22 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Disconnect the applicable sensor connector with ignition
switch OFF.
2) Measure resistance between sensor terminals.
Resistance of wheel speed sensor: 1.4 – 1.8 kΩ (at
20°C, 68°F)
3) Measure resistance between each terminal and body
ground.
Insulation resistance: 1MΩ or higher
Were measured resistance values in step 2) and 3) as spec-
ified? (See [A])Go to step 2. Replace sensor.
2 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect connector from ABS hydraulic unit / control
module assembly. (See [B])
3) Check for proper connection to ABS hydraulic unit / con-
trol module assembly at each sensor terminal.
4) If OK, then turn ignition switch ON and measure voltage
between sensor positive terminal of module connector
and body ground.
Is it 0V?Go to step 3. Sensor positive cir-
cuit shorted to
power.
3 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Connect connector to sensor.
3) Measure resistance between sensor terminals at mod-
ule connector.
4) Measure resistance between sensor positive terminal
and negative terminal of module connector, between
positive terminal and body ground.
Are measured resistance values within each specified range
described in above step 1?Go to step 4. Circuit open or
shorted to ground.
4 1) Remove wheel speed sensor.
2) Check sensor for damage or foreign material being
attached.
Is it in good condition? (See [C])Go to step 5. Clean or replace
sensor.
5 Check visually through wheel speed sensor installation hole
for following.
Ring serration (teeth) neither missing or damaged.
No foreign material being attached.
Ring not being eccentric.
Wheel bearing free from excessive play.
Are they in good condition? (See [D])Go to step 6. Clean, repair or
replace.
6 1) Install sensor to knuckle or axle housing.
2) Tighten sensor bolt to specified torque and check that
there is not any clearance between sensor and knuckle
or axle housing. (See [E])
Replace sensor if any.
Referring to “Front Wheel Speed Sensor” in this section,
check output voltage or waveform of sensor. Is proper out-
put voltage or waveform obtained?Substitute a known-
good ABS hydraulic
unit / control module
assembly and
recheck.Replace sensor and
recheck.
Page 342 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-25
DTC C1057 (DTC 57) – Power Source Circuit
DESCRIPTION
The ABS control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “A18”. When the power source voltage
becomes extremely low, this DTC will be set. As soon as the voltage rises to the specified level, the set DTC will
be cleared.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 3. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly 5. ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector
2. Main fuse 4. Circuit fuse
Step Action Yes No
1 Check battery voltage. Is it about 11 V or
higher?Go to step 2. Check charging system
referring to “Under-
charged Battery” in Sec-
tion 6H.
2 Check ABS main fuse, circuit fuse and connec-
tion. Is it in good condition?Go to step 3. Repair and/or replace
fuse.
3 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit / control
module connector.
3) Check proper connection to ABS hydraulic
unit / control module connector at terminal
“A18”.
4) If OK, then measure voltage between con-
nector terminal “A18” and body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit / con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“B/W” circuit open.
Page 344 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-27
DTC C1063 (DTC 63) – ABS Fail Safe Circuit
DESCRIPTION
The ABS control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of the solenoid circuit constantly with the ignition
switch turned ON. Also, immediately after the ignition switch is turned “ON”, perform an initial check as follows.
Switch the fail safe transistor in the order of ON → OFF → ON and check if the voltage at 6 solenoid circuit ter-
minals changes to High → Low → High. If anything faulty is found in the initial check and when the voltage at all
solenoid circuit terminals is low with the ignition switch turned ON and ABS not operated, this DTC will be set.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 3-1. Lock position
2. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly 3-2. Unlock position
3. ABS hydraulic unit / control module connector of harness
Step Action Yes No
1 Check battery voltage. Is it about 11 V or
higher?Go to step 2. Check charging system
referring to “Under-
charged Battery” in Sec-
tion 6H.
2 Check ABS main fuse and connection.
Is it in good condition?Go to step 3. Repair and / or replace
fuse.
3 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit / control
module connector.
3) Check proper connection to ABS hydraulic
unit / control module at terminal “A25”.
4) If OK, then measure voltage between con-
nector terminal “A25” and body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit / con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“W/Bl” circuit open or
short to ground.
Page 345 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5E-28 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
DTC C1071 (DTC 71) – ABS Control Module
DESCRIPTION
This DTC will be set when an internal fault is detected in the ABS control module.
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect connectors from ABS control
module.
3) Check for proper connection to ABS control
module at all terminals.
Are they in good condition?Substitute a known-good
ABS control module and
recheck.Repair or replace.
Page 352 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-35
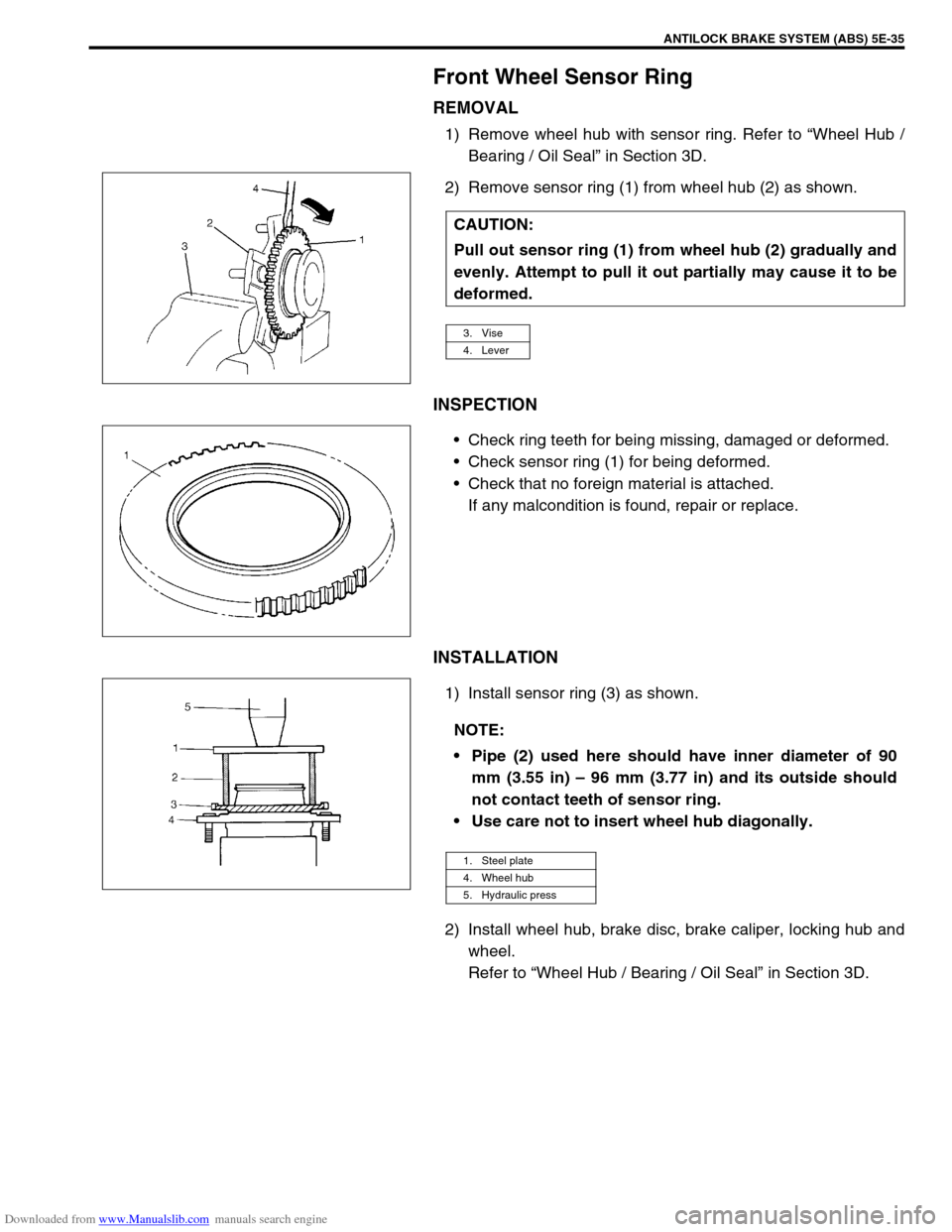
Front Wheel Sensor Ring
REMOVAL
1) Remove wheel hub with sensor ring. Refer to “Wheel Hub /
Bearing / Oil Seal” in Section 3D.
2) Remove sensor ring (1) from wheel hub (2) as shown.
INSPECTION
Check ring teeth for being missing, damaged or deformed.
Check sensor ring (1) for being deformed.
Check that no foreign material is attached.
If any malcondition is found, repair or replace.
INSTALLATION
1) Install sensor ring (3) as shown.
2) Install wheel hub, brake disc, brake caliper, locking hub and
wheel.
Refer to “Wheel Hub / Bearing / Oil Seal” in Section 3D. CAUTION:
Pull out sensor ring (1) from wheel hub (2) gradually and
evenly. Attempt to pull it out partially may cause it to be
deformed.
3. Vise
4. Lever
NOTE:
Pipe (2) used here should have inner diameter of 90
mm (3.55 in) – 96 mm (3.77 in) and its outside should
not contact teeth of sensor ring.
Use care not to insert wheel hub diagonally.
1. Steel plate
4. Wheel hub
5. Hydraulic press
Page 354 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-37
5) Remove rear wheel speed sensor (1) from rear axle housing.
SENSOR INSPECTION
Check sensor for damage.
Check sensor for resistance.
Resistance between terminals of sensor
: 1.4 – 1.8 k
Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
Resistance between sensor terminal and sensor body
: 1 M
Ω or more
If any malcondition is found, replace.
SENSOR RING INSPECTION
Check ring teeth for being missing, damaged or deformed.
Turn wheel and check if ring rotation is free from eccentricity
and looseness.
Check that no foreign material is attached.
If any faulty is found, repair or replace.
INSTALLATION
1) Check that no foreign material is attached to sensor and ring.
2) Install it by reversing removal procedure.
Tightening torque
Rear wheel speed sensor bolt and rear wheel speed sen-
sor harness clamp bolts
(a) : 10 N·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.2 lb-ft)
3) Check that there is no clearance between sensor and rear
axle housing. CAUTION:
Do not pull wire harness when removing rear wheel
speed sensor (1).
Do not cause damage to surface of rear wheel speed
sensor and do not allow dust, etc. to enter its installa-
tion hole.
2. Rear wheel sensor ring
CAUTION:
Do not pull wire harness or twist more than necessary
when installing rear wheel speed sensor.
1. Sensor bolt
2. Clamp bolt
Page 358 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-1
6F2
6G
6H
6K
7A
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8B
6
8D
8E
8B
9
10A
10B
SECTION 6
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND
DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL INFORMATION AND ENGINE DIAGNOSIS ..............................................................................
6-1
ENGINE MECHANICAL ...........................................................................................................................
6A1-1
ENGINE COOLING.....................................................................................................................................
6B-1
ENGINE FUEL ............................................................................................................................................
6C-1
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM ........................................................................................
6E-1
IGNITION SYSTEM ....................................................................................................................................
6F-1
CRANKING SYSTEM .................................................................................................................................
6G-1
CHARGING SYSTEM .................................................................................................................................
6H-1
EXHAUST SYSTEM ...................................................................................................................................
6K-1
CONTENTS
General Information .......................................... 6-3
Statement on Cleanliness and Care ............... 6-3
General Information on Engine Service .......... 6-3
Precaution on fuel system service............... 6-4
Fuel pressure relief procedure .................... 6-5
Fuel leakage check procedure .................... 6-5
Engine Diagnosis .............................................. 6-6
General Description ........................................ 6-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Immobilizer Indicator Lamp) ............................ 6-6On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Immobilizer Indicator Lamp)............................ 6-9
Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble ................. 6-10
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table ...................... 6-11
Customer problem inspection form
(example) .................................................. 6-13
Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) check..... 6-14
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) check ....... 6-14
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
clearance................................................... 6-15 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System :
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether the following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on vehicle
specifications. Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor(s) or CO adjusting resistor
Three-way catalytic converter (TWC) and warm up three-way catalytic converter (WU-TWC)
Page 364 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-7
DRIVING CYCLE
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup and engine shutoff.
2 DRIVING CYCLES DETECTION LOGIC
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is stored in
ECM memory (in the form of pending DTC and freeze frame data)
but the malfunction indicator lamp does not light at this time. It
lights up at the second detection of same malfunction also in the
next driving cycle.
PENDING DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored temporarily at 1
driving cycle of the DTC which is detected in the 2 driving cycle
detection logic.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the from of data
as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a mal-
function in its memory. This data is called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving conditions
(e.g., whether the engine was warm or not, where the vehicle was
running or stopped, where air / fuel mixture was lean or rich)
when a malfunction was detected by checking the freeze frame
data. Also, ECM has a function to store each freeze frame data
for three different malfunctions in the order as the malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the order of
malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is helpful when
rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
Priority of freeze frame data :
ECM has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stored.
The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the malfunction
which was detected first. However, the freeze frame data stored
in this frame is updated according to the priority described below.
(If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” below is
detected while the freeze frame data in the lower square “2” has
been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by the
freeze frame data “1”.)
[A] : An Example of Freeze Frame Data
[B] : 1st, 2nd or 3rd in parentheses here represents which position in the order
the malfunction is detected.
PRIORITY FREEZE FRAME DATA IN FRAME 1
1Freeze frame data at initial detection of mal-
function among misfire detected (P0300 –
P0304), fuel system too lean (P0171) and fuel
system too rich (P0172)
2Freeze frame data when a malfunction other
than those in “1” above is detected